Abstract
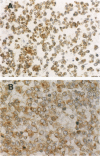
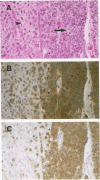
For determination of the cellular distribution of bcl-2 expression in lung cancer and clarification of its correlation with cell neuroendocrine differentiation, Bcl-2 immunostaining was carried out on a large series of formalin-fixed, paraffin-embedded lung cancer samples, and four general neuroendocrine marker and seven peptide hormone stainings were carried out on all Bcl-2-positive squamous cell carcinomas and adenocarcinomas of the lung as well as on 8 pulmonary neuroendocrine carcinomas histologically diagnosed. In addition, 3 small cell lung cancer cell lines were studied by Western blotting. Neuroendocrine differentiation in Bcl-2-negative squamous cell carcinomas and adenocarcinomas was examined with chromogranin A and alpha-subunit of Go protein stainings. Bcl-2 protein was detected in 104/111 small cell carcinomas, 8/8 neuroendocrine carcinomas, 0/6 typical (well differentiated) carcinoids, 23/64 squamous cell carcinomas, 4/65 adenocarcinomas, and all 3 small cell lung cancer cell lines. All 8 neuroendocrine carcinomas, 11 of the Bcl-2-positive squamous cell carcinomas, and all 4 Bcl-2 positive adenocarcinomas expressed multiple neuroendocrine markers. The distributions of Bcl-2 and neuroendocrine marker immunoreactivity closely paralleled each other on consecutive sections. In squamous cell carcinomas, Bcl-2-positive cells could be roughly subdivided into those with neuroendocrine differentiation features, usually demonstrating intense Bcl-2 staining, with basaloid tumor cells usually expressing weak to moderate Bcl-2 staining. The present study clearly shows Bcl-2 protein expression to be remarkably differentially regulated according to histological types of lung cancers and to appear to quite likely be closely associated with neuroendocrine differentiation of tumor cells, indicating that bcl-2 is importantly involved in cell development and differentiation, in addition to protecting cells from apoptosis. Bcl-2 might be usable as a neuroendocrine marker in lung cancers and possibly also in neural-crest-derived tumors.
Full text
PDF


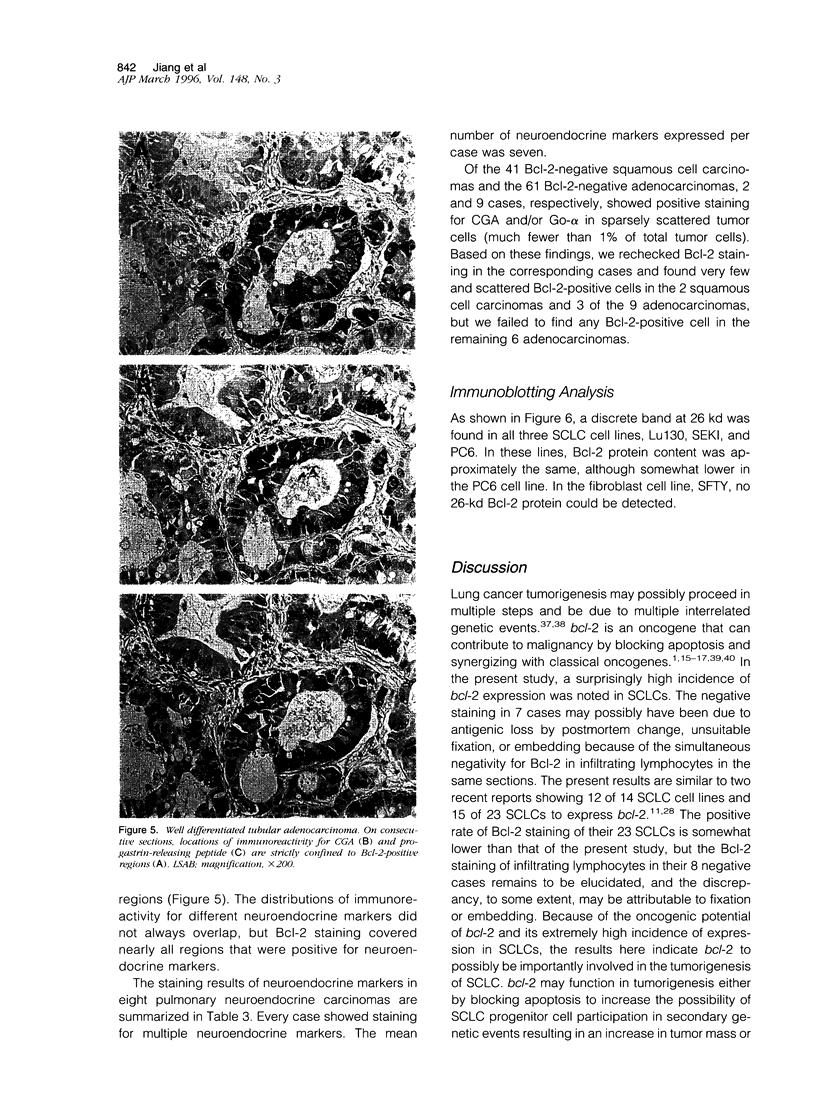
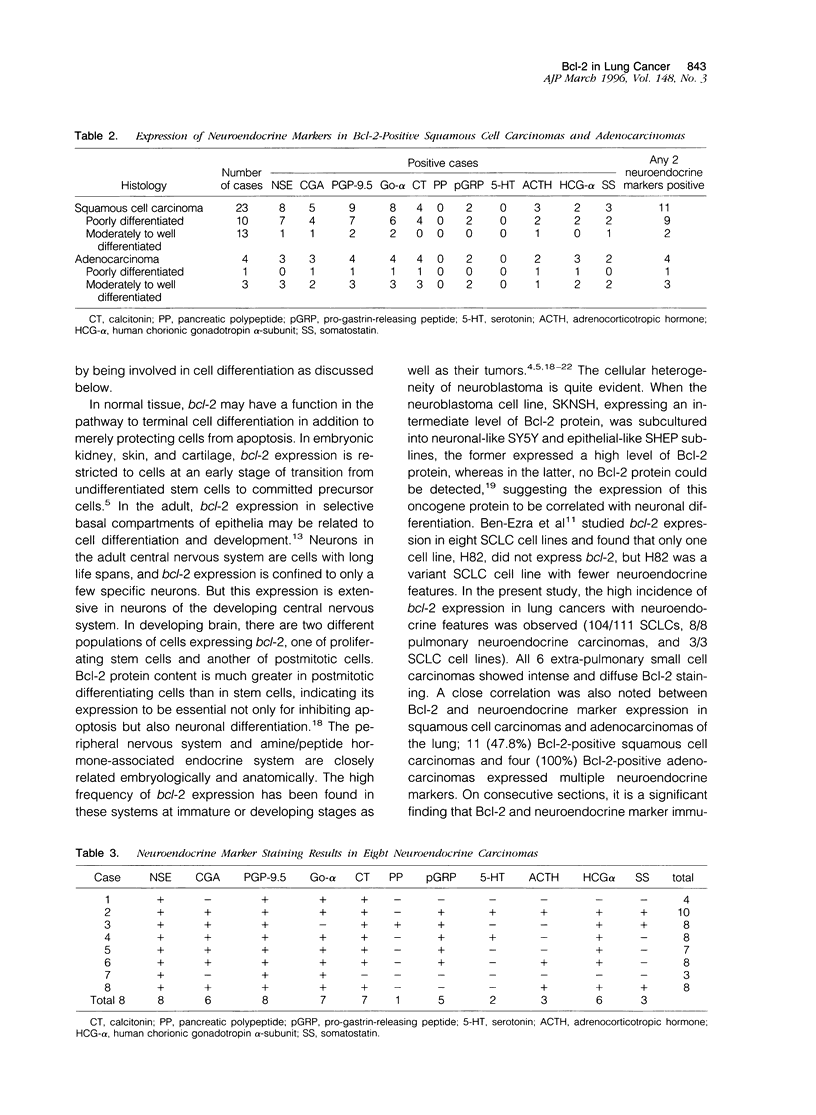



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Addis B. J., Hamid Q., Ibrahim N. B., Fahey M., Bloom S. R., Polak J. M. Immunohistochemical markers of small cell carcinoma and related neuroendocrine tumours of the lung. J Pathol. 1987 Oct;153(2):137–150. doi: 10.1002/path.1711530207. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ben-Ezra J. M., Kornstein M. J., Grimes M. M., Krystal G. Small cell carcinomas of the lung express the Bcl-2 protein. Am J Pathol. 1994 Nov;145(5):1036–1040. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bensch K. G., Corrin B., Pariente R., Spencer H. Oat-cell carcinoma of the lung. Its origin and relationship to bronchial carcinoid. Cancer. 1968 Dec;22(6):1163–1172. doi: 10.1002/1097-0142(196811)22:6<1163::aid-cncr2820220612>3.0.co;2-l. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bissonnette R. P., Echeverri F., Mahboubi A., Green D. R. Apoptotic cell death induced by c-myc is inhibited by bcl-2. Nature. 1992 Oct 8;359(6395):552–554. doi: 10.1038/359552a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carbone D. P., Minna J. D. The molecular genetics of lung cancer. Adv Intern Med. 1992;37:153–171. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Castle V. P., Heidelberger K. P., Bromberg J., Ou X., Dole M., Nuñez G. Expression of the apoptosis-suppressing protein bcl-2, in neuroblastoma is associated with unfavorable histology and N-myc amplification. Am J Pathol. 1993 Dec;143(6):1543–1550. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fanidi A., Harrington E. A., Evan G. I. Cooperative interaction between c-myc and bcl-2 proto-oncogenes. Nature. 1992 Oct 8;359(6395):554–556. doi: 10.1038/359554a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gazdar A. F. Advances in the biology of non-small cell lung cancer. Chest. 1986 Apr;89(4 Suppl):277S–283S. doi: 10.1378/chest.89.4.277s. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ikegaki N., Katsumata M., Minna J., Tsujimoto Y. Expression of bcl-2 in small cell lung carcinoma cells. Cancer Res. 1994 Jan 1;54(1):6–8. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jiang S. X., Sato Y., Kuwao S., Kameya T. Expression of bcl-2 oncogene protein is prevalent in small cell lung carcinomas. J Pathol. 1995 Oct;177(2):135–138. doi: 10.1002/path.1711770206. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kameya T., Shimosato Y., Kodama T., Tsumuraya M., Koide T., Yamaguchi K., Abe K. Peptide hormone production by adenocarcinomas of the lung; its morphologic basis and histogenetic considerations. Virchows Arch A Pathol Anat Histopathol. 1983;400(3):245–257. doi: 10.1007/BF00612186. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Korsmeyer S. J. Bcl-2 initiates a new category of oncogenes: regulators of cell death. Blood. 1992 Aug 15;80(4):879–886. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Krajewski S., Chatten J., Hanada M., Reed J. C. Immunohistochemical analysis of the Bcl-2 oncoprotein in human neuroblastomas. Comparisons with tumor cell differentiation and N-Myc protein. Lab Invest. 1995 Jan;72(1):42–54. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LeBrun D. P., Warnke R. A., Cleary M. L. Expression of bcl-2 in fetal tissues suggests a role in morphogenesis. Am J Pathol. 1993 Mar;142(3):743–753. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Linnoila R. I., Mulshine J. L., Steinberg S. M., Funa K., Matthews M. J., Cotelingam J. D., Gazdar A. F. Neuroendocrine differentiation in endocrine and nonendocrine lung carcinomas. Am J Clin Pathol. 1988 Dec;90(6):641–652. doi: 10.1093/ajcp/90.6.641. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lotem J., Sachs L. Regulation by bcl-2, c-myc, and p53 of susceptibility to induction of apoptosis by heat shock and cancer chemotherapy compounds in differentiation-competent and -defective myeloid leukemic cells. Cell Growth Differ. 1993 Jan;4(1):41–47. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lu Q. L., Elia G., Lucas S., Thomas J. A. Bcl-2 proto-oncogene expression in Epstein-Barr-virus-associated nasopharyngeal carcinoma. Int J Cancer. 1993 Jan 2;53(1):29–35. doi: 10.1002/ijc.2910530107. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lu Q. L., Poulsom R., Wong L., Hanby A. M. Bcl-2 expression in adult and embryonic non-haematopoietic tissues. J Pathol. 1993 Apr;169(4):431–437. doi: 10.1002/path.1711690408. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McDonnell T. J., Deane N., Platt F. M., Nunez G., Jaeger U., McKearn J. P., Korsmeyer S. J. bcl-2-immunoglobulin transgenic mice demonstrate extended B cell survival and follicular lymphoproliferation. Cell. 1989 Apr 7;57(1):79–88. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90174-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McDonnell T. J., Korsmeyer S. J. Progression from lymphoid hyperplasia to high-grade malignant lymphoma in mice transgenic for the t(14; 18). Nature. 1991 Jan 17;349(6306):254–256. doi: 10.1038/349254a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Merry D. E., Veis D. J., Hickey W. F., Korsmeyer S. J. bcl-2 protein expression is widespread in the developing nervous system and retained in the adult PNS. Development. 1994 Feb;120(2):301–311. doi: 10.1242/dev.120.2.301. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Minna J. D. The molecular biology of lung cancer pathogenesis. Chest. 1993 Apr;103(4 Suppl):449S–456S. doi: 10.1378/chest.103.4_supplement.449s. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miyake Y., Kodama T., Yamaguchi K. Pro-gastrin-releasing peptide(31-98) is a specific tumor marker in patients with small cell lung carcinoma. Cancer Res. 1994 Apr 15;54(8):2136–2140. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miyashita T., Reed J. C. bcl-2 gene transfer increases relative resistance of S49.1 and WEHI7.2 lymphoid cells to cell death and DNA fragmentation induced by glucocorticoids and multiple chemotherapeutic drugs. Cancer Res. 1992 Oct 1;52(19):5407–5411. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pezzella F., Tse A. G., Cordell J. L., Pulford K. A., Gatter K. C., Mason D. Y. Expression of the bcl-2 oncogene protein is not specific for the 14;18 chromosomal translocation. Am J Pathol. 1990 Aug;137(2):225–232. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pezzella F., Turley H., Kuzu I., Tungekar M. F., Dunnill M. S., Pierce C. B., Harris A., Gatter K. C., Mason D. Y. bcl-2 protein in non-small-cell lung carcinoma. N Engl J Med. 1993 Sep 2;329(10):690–694. doi: 10.1056/NEJM199309023291003. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ramani P., Lu Q. L. Expression of bcl-2 gene product in neuroblastoma. J Pathol. 1994 Mar;172(3):273–278. doi: 10.1002/path.1711720308. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reed J. C., Cuddy M., Slabiak T., Croce C. M., Nowell P. C. Oncogenic potential of bcl-2 demonstrated by gene transfer. Nature. 1988 Nov 17;336(6196):259–261. doi: 10.1038/336259a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reed J. C., Meister L., Tanaka S., Cuddy M., Yum S., Geyer C., Pleasure D. Differential expression of bcl2 protooncogene in neuroblastoma and other human tumor cell lines of neural origin. Cancer Res. 1991 Dec 15;51(24):6529–6538. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sentman C. L., Shutter J. R., Hockenbery D., Kanagawa O., Korsmeyer S. J. bcl-2 inhibits multiple forms of apoptosis but not negative selection in thymocytes. Cell. 1991 Nov 29;67(5):879–888. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(91)90361-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tahara E. Molecular mechanism of stomach carcinogenesis. J Cancer Res Clin Oncol. 1993;119(5):265–272. doi: 10.1007/BF01212724. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thompson R. J., Doran J. F., Jackson P., Dhillon A. P., Rode J. PGP 9.5--a new marker for vertebrate neurons and neuroendocrine cells. Brain Res. 1983 Nov 14;278(1-2):224–228. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(83)90241-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Travis W. D., Linnoila R. I., Tsokos M. G., Hitchcock C. L., Cutler G. B., Jr, Nieman L., Chrousos G., Pass H., Doppman J. Neuroendocrine tumors of the lung with proposed criteria for large-cell neuroendocrine carcinoma. An ultrastructural, immunohistochemical, and flow cytometric study of 35 cases. Am J Surg Pathol. 1991 Jun;15(6):529–553. doi: 10.1097/00000478-199106000-00003. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tsujimoto Y., Croce C. M. Analysis of the structure, transcripts, and protein products of bcl-2, the gene involved in human follicular lymphoma. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Jul;83(14):5214–5218. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.14.5214. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tsujimoto Y., Finger L. R., Yunis J., Nowell P. C., Croce C. M. Cloning of the chromosome breakpoint of neoplastic B cells with the t(14;18) chromosome translocation. Science. 1984 Nov 30;226(4678):1097–1099. doi: 10.1126/science.6093263. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vaux D. L., Cory S., Adams J. M. Bcl-2 gene promotes haemopoietic cell survival and cooperates with c-myc to immortalize pre-B cells. Nature. 1988 Sep 29;335(6189):440–442. doi: 10.1038/335440a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van den Oord J. J., Vandeghinste N., De Ley M., De Wolf-Peeters C. Bcl-2 expression in human melanocytes and melanocytic tumors. Am J Pathol. 1994 Aug;145(2):294–300. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]