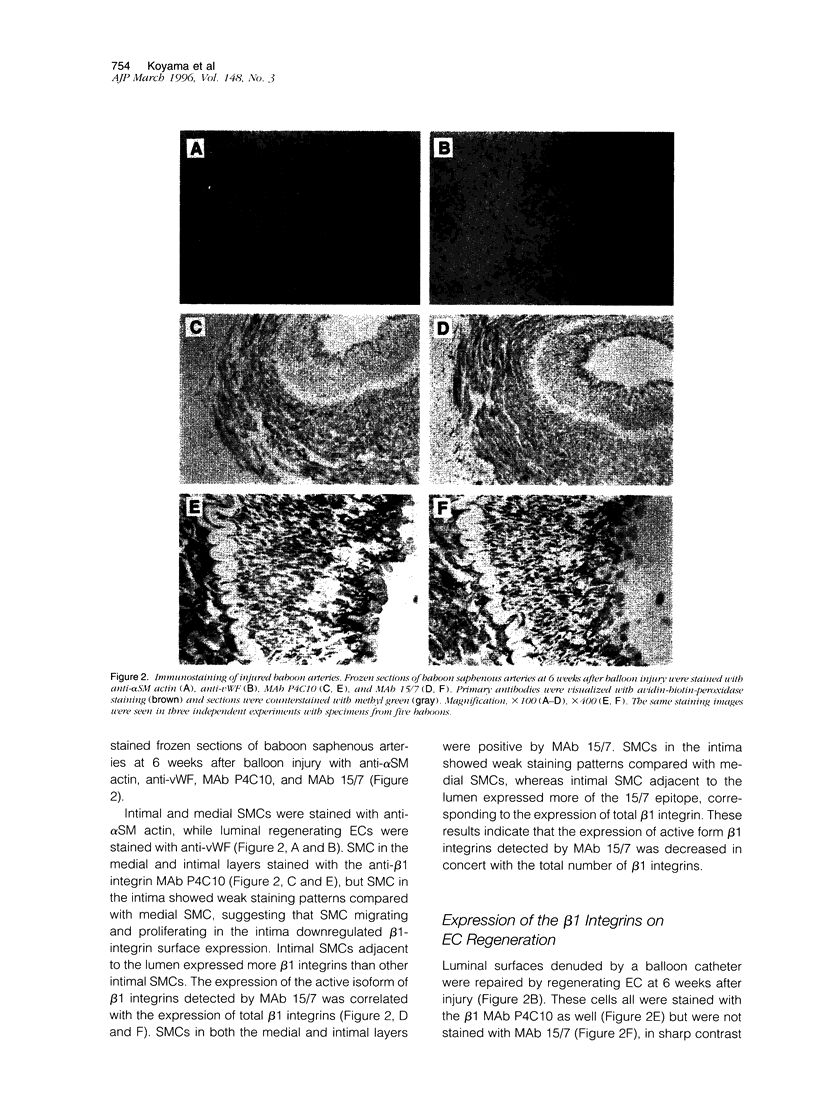
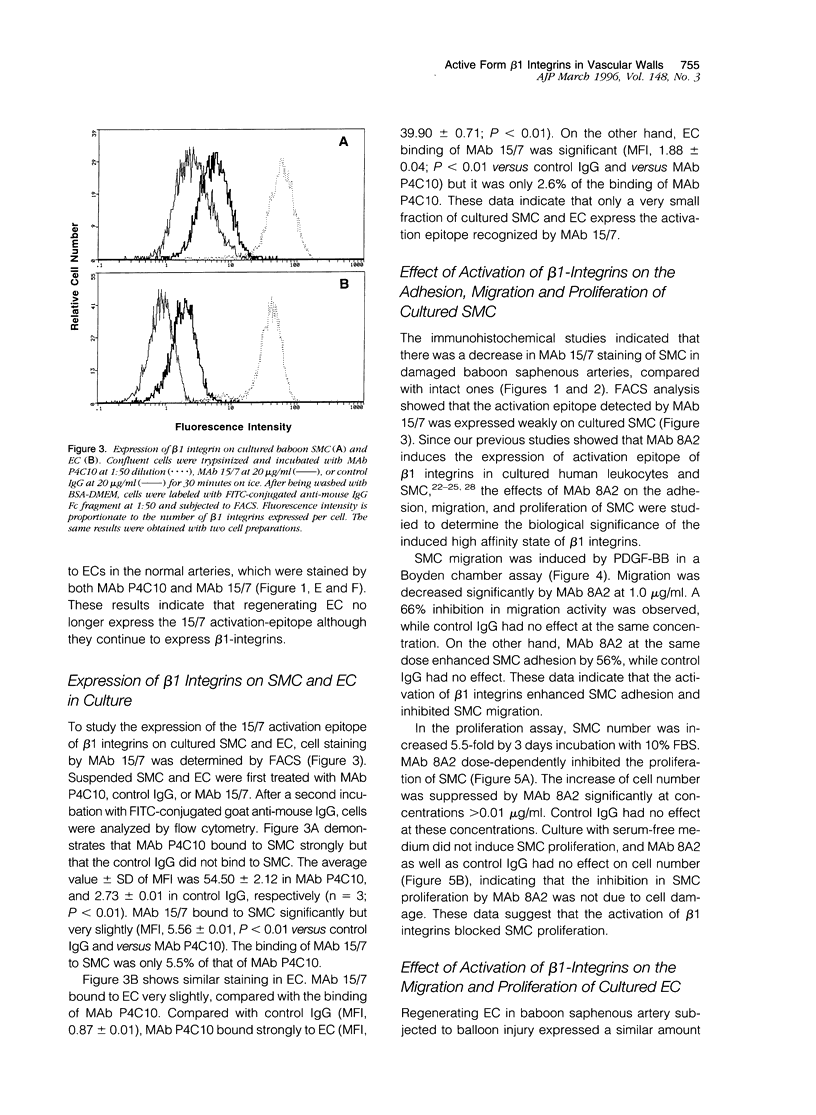
Abstract
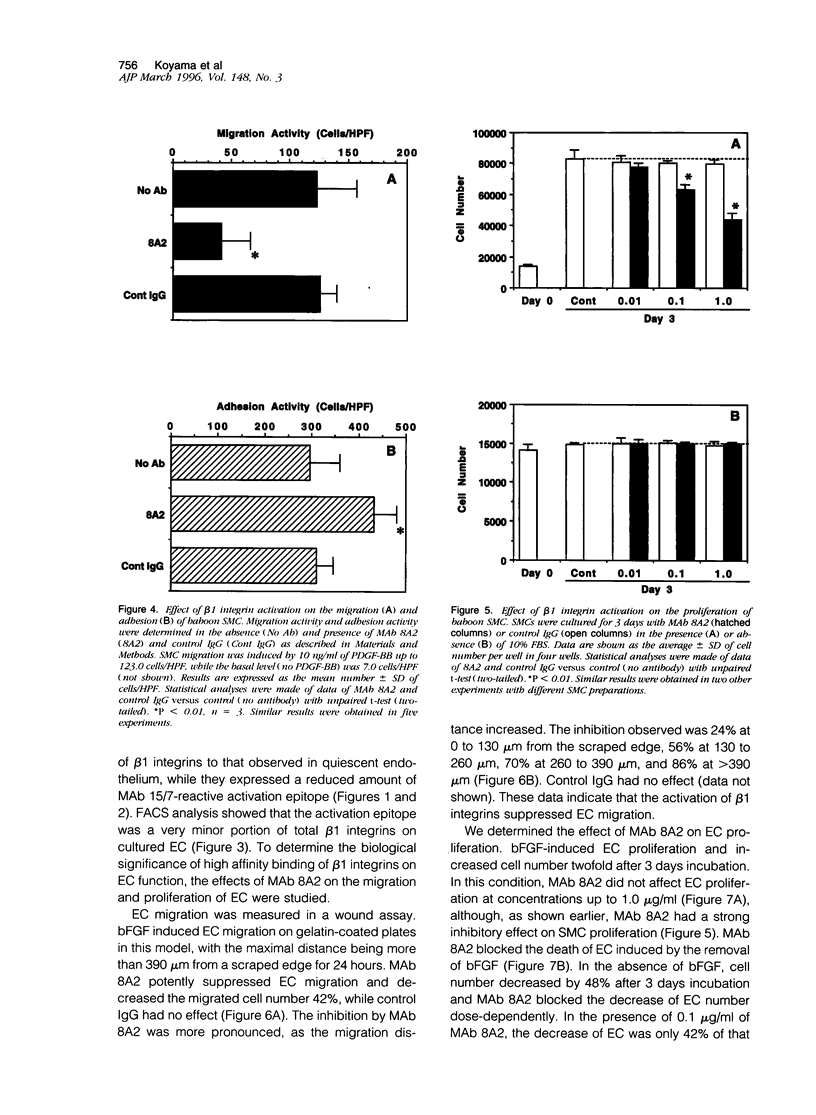
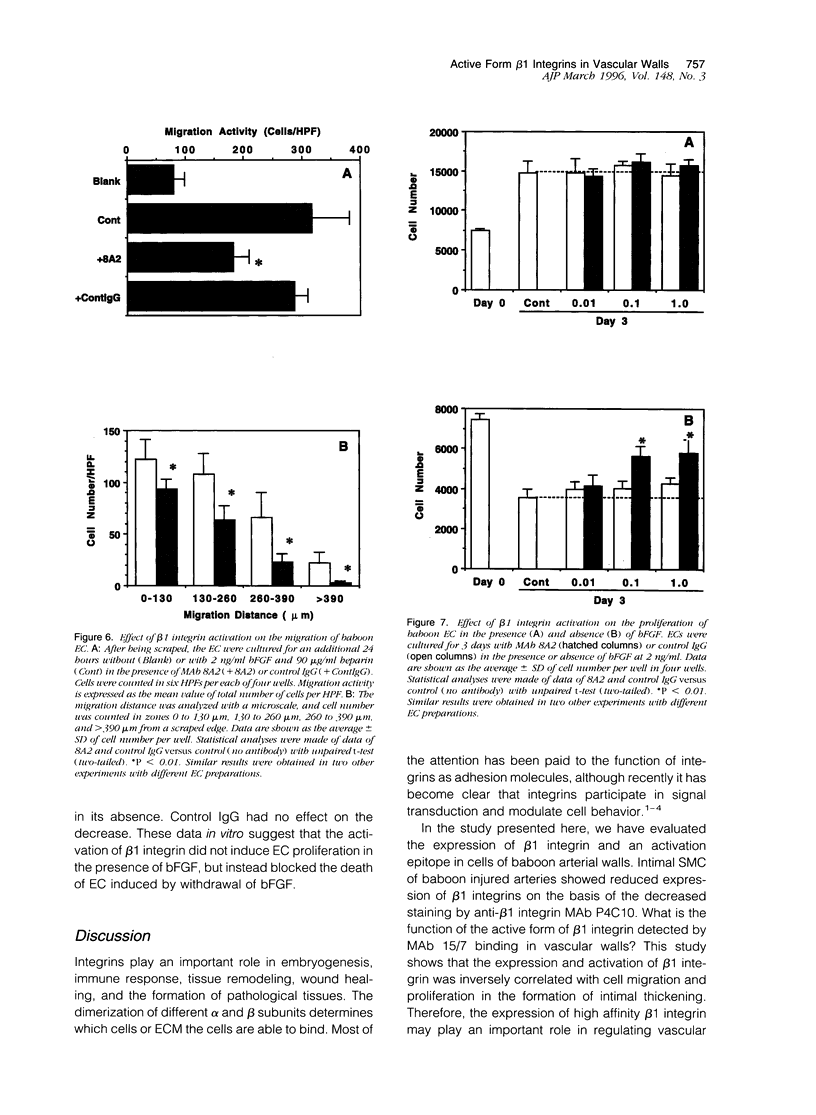
Migration and proliferation of endothelial cells (ECs) and smooth muscle cells (SMCs) contribute to the response to injury in damaged and atherosclerotic vessels. These events might be regulated by cellular interactions with extracellular matrix through the expression and activation of integrins. To study the functions of beta 1 integrins in the vessel wall, we used monoclonal antibody (MAb) 15/7, which recognizes an activation epitope of beta 1 integrin subunits, and MAb 8A2, which induces a high affinity form of beta 1 integrins recognized by MAb 15/7. Immunohistochemical analyses were done on samples of normal baboon saphenous arteries and from arteries subjected to balloon injury. EC and SMC expressed the activation epitope of beta 1 integrin in uninjured arteries. By contrast, in balloon-injured arteries 6 weeks after injury, regenerating EC did not express the activation epitope, and there was no decrease in the expression of total beta 1 integrin, whereas SMC migrating into the intima exhibited decreased expression of the total and activated beta 1 integrin. Flow cytometer analysis of cultured cells indicated that baboon EC and SMC weakly express the activation epitope of beta 1 integrin. Next, we determined by utilizing MAb 8A2 the effects of increased expression of activation epitope of beta 1 integrin on the functions of SMC and EC. The activation of beta 1 integrins on SMC induced by MAb 8A2 enhanced SMC adhesion and suppressed SMC migration in a Boyden chamber assay. SMC proliferation was inhibited by MAb 8A2 dose-dependently. Similarly, MAb 8A2-induced activation of beta 1 integrins on EC suppressed EC migration into a wound. However, MAb 8A2 did not affect the basic fibroblast growth factor-induced proliferation of EC, although it blocked the decrease in EC number caused by the removal of basic fibroblast growth factor. These results suggest that activation of beta 1 integrins in vascular cells is regulated in a cell-type dependent manner and plays an important role in modulating vascular cell functions.
Full text
PDF








Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Arroyo A. G., García-Vicuña R., Marazuela M., Yednock T. A., González-Amaro R., Sánchez-Madrid F. Expression and functional significance of an activation-dependent epitope of the beta 1 integrins in chronic inflammatory diseases. Eur J Immunol. 1995 Jun;25(6):1720–1728. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830250635. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Arroyo A. G., Sánchez-Mateos P., Campanero M. R., Martín-Padura I., Dejana E., Sánchez-Madrid F. Regulation of the VLA integrin-ligand interactions through the beta 1 subunit. J Cell Biol. 1992 May;117(3):659–670. doi: 10.1083/jcb.117.3.659. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Basson C. T., Kocher O., Basson M. D., Asis A., Madri J. A. Differential modulation of vascular cell integrin and extracellular matrix expression in vitro by TGF-beta 1 correlates with reciprocal effects on cell migration. J Cell Physiol. 1992 Oct;153(1):118–128. doi: 10.1002/jcp.1041530116. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Belkin V. M., Belkin A. M., Koteliansky V. E. Human smooth muscle VLA-1 integrin: purification, substrate specificity, localization in aorta, and expression during development. J Cell Biol. 1990 Nov;111(5 Pt 1):2159–2170. doi: 10.1083/jcb.111.5.2159. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blaschuk K. L., Holland P. C. The regulation of alpha 5 beta 1 integrin expression in human muscle cells. Dev Biol. 1994 Aug;164(2):475–483. doi: 10.1006/dbio.1994.1217. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bretscher M. S. Endocytosis and recycling of the fibronectin receptor in CHO cells. EMBO J. 1989 May;8(5):1341–1348. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1989.tb03514.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brooks P. C., Clark R. A., Cheresh D. A. Requirement of vascular integrin alpha v beta 3 for angiogenesis. Science. 1994 Apr 22;264(5158):569–571. doi: 10.1126/science.7512751. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Choi E. T., Engel L., Callow A. D., Sun S., Trachtenberg J., Santoro S., Ryan U. S. Inhibition of neointimal hyperplasia by blocking alpha V beta 3 integrin with a small peptide antagonist GpenGRGDSPCA. J Vasc Surg. 1994 Jan;19(1):125–134. doi: 10.1016/s0741-5214(94)70127-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clowes A. W., Clowes M. M., Au Y. P., Reidy M. A., Belin D. Smooth muscle cells express urokinase during mitogenesis and tissue-type plasminogen activator during migration in injured rat carotid artery. Circ Res. 1990 Jul;67(1):61–67. doi: 10.1161/01.res.67.1.61. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DiMilla P. A., Stone J. A., Quinn J. A., Albelda S. M., Lauffenburger D. A. Maximal migration of human smooth muscle cells on fibronectin and type IV collagen occurs at an intermediate attachment strength. J Cell Biol. 1993 Aug;122(3):729–737. doi: 10.1083/jcb.122.3.729. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Diamond M. S., Springer T. A. A subpopulation of Mac-1 (CD11b/CD18) molecules mediates neutrophil adhesion to ICAM-1 and fibrinogen. J Cell Biol. 1993 Jan;120(2):545–556. doi: 10.1083/jcb.120.2.545. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Drake C. J., Davis L. A., Little C. D. Antibodies to beta 1-integrins cause alterations of aortic vasculogenesis, in vivo. Dev Dyn. 1992 Jan;193(1):83–91. doi: 10.1002/aja.1001930111. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Faull R. J., Kovach N. L., Harlan J. M., Ginsberg M. H. Affinity modulation of integrin alpha 5 beta 1: regulation of the functional response by soluble fibronectin. J Cell Biol. 1993 Apr;121(1):155–162. doi: 10.1083/jcb.121.1.155. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Faull R. J., Kovach N. L., Harlan J. M., Ginsberg M. H. Stimulation of integrin-mediated adhesion of T lymphocytes and monocytes: two mechanisms with divergent biological consequences. J Exp Med. 1994 Apr 1;179(4):1307–1316. doi: 10.1084/jem.179.4.1307. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Geary R. L., Koyama N., Wang T. W., Vergel S., Clowes A. W. Failure of heparin to inhibit intimal hyperplasia in injured baboon arteries. The role of heparin-sensitive and -insensitive pathways in the stimulation of smooth muscle cell migration and proliferation. Circulation. 1995 Jun 15;91(12):2972–2981. doi: 10.1161/01.cir.91.12.2972. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Geng Y. J., Libby P. Evidence for apoptosis in advanced human atheroma. Colocalization with interleukin-1 beta-converting enzyme. Am J Pathol. 1995 Aug;147(2):251–266. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Giancotti F. G., Ruoslahti E. Elevated levels of the alpha 5 beta 1 fibronectin receptor suppress the transformed phenotype of Chinese hamster ovary cells. Cell. 1990 Mar 9;60(5):849–859. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90098-y. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Golden M. A., Au Y. P., Kirkman T. R., Wilcox J. N., Raines E. W., Ross R., Clowes A. W. Platelet-derived growth factor activity and mRNA expression in healing vascular grafts in baboons. Association in vivo of platelet-derived growth factor mRNA and protein with cellular proliferation. J Clin Invest. 1991 Feb;87(2):406–414. doi: 10.1172/JCI115011. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Han D. K., Haudenschild C. C., Hong M. K., Tinkle B. T., Leon M. B., Liau G. Evidence for apoptosis in human atherogenesis and in a rat vascular injury model. Am J Pathol. 1995 Aug;147(2):267–277. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hynes R. O. Integrins: versatility, modulation, and signaling in cell adhesion. Cell. 1992 Apr 3;69(1):11–25. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(92)90115-s. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Janat M. F., Argraves W. S., Liau G. Regulation of vascular smooth muscle cell integrin expression by transforming growth factor beta1 and by platelet-derived growth factor-BB. J Cell Physiol. 1992 Jun;151(3):588–595. doi: 10.1002/jcp.1041510319. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jones J. L., Critchley D. R., Walker R. A. Alteration of stromal protein and integrin expression in breast--a marker of premalignant change? J Pathol. 1992 Aug;167(4):399–406. doi: 10.1002/path.1711670409. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Juliano R. L., Haskill S. Signal transduction from the extracellular matrix. J Cell Biol. 1993 Feb;120(3):577–585. doi: 10.1083/jcb.120.3.577. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kovach N. L., Carlos T. M., Yee E., Harlan J. M. A monoclonal antibody to beta 1 integrin (CD29) stimulates VLA-dependent adherence of leukocytes to human umbilical vein endothelial cells and matrix components. J Cell Biol. 1992 Jan;116(2):499–509. doi: 10.1083/jcb.116.2.499. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Koyama N., Hart C. E., Clowes A. W. Different functions of the platelet-derived growth factor-alpha and -beta receptors for the migration and proliferation of cultured baboon smooth muscle cells. Circ Res. 1994 Oct;75(4):682–691. doi: 10.1161/01.res.75.4.682. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kuijpers T. W., Mul E. P., Blom M., Kovach N. L., Gaeta F. C., Tollefson V., Elices M. J., Harlan J. M. Freezing adhesion molecules in a state of high-avidity binding blocks eosinophil migration. J Exp Med. 1993 Jul 1;178(1):279–284. doi: 10.1084/jem.178.1.279. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lange T. S., Bielinsky A. K., Kirchberg K., Bank I., Herrmann K., Krieg T., Scharffetter-Kochanek K. Mg2+ and Ca2+ differentially regulate beta 1 integrin-mediated adhesion of dermal fibroblasts and keratinocytes to various extracellular matrix proteins. Exp Cell Res. 1994 Sep;214(1):381–388. doi: 10.1006/excr.1994.1271. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meredith J. E., Jr, Fazeli B., Schwartz M. A. The extracellular matrix as a cell survival factor. Mol Biol Cell. 1993 Sep;4(9):953–961. doi: 10.1091/mbc.4.9.953. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Muschler J. L., Horwitz A. F. Down-regulation of the chicken alpha 5 beta 1 integrin fibronectin receptor during development. Development. 1991 Sep;113(1):327–337. doi: 10.1242/dev.113.1.327. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Neugebauer K. M., Reichardt L. F. Cell-surface regulation of beta 1-integrin activity on developing retinal neurons. Nature. 1991 Mar 7;350(6313):68–71. doi: 10.1038/350068a0. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Picker L. J., Treer J. R., Nguyen M., Terstappen L. W., Hogg N., Yednock T. Coordinate expression of beta 1 and beta 2 integrin "activation" epitopes during T cell responses in secondary lymphoid tissue. Eur J Immunol. 1993 Nov;23(11):2751–2757. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830231105. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Postigo A. A., Pulido R., Campanero M. R., Acevedo A., García-Pardo A., Corbi A. L., Sanchez-Madrid F., De Landazuri M. O. Differential expression of VLA-4 integrin by resident and peripheral blood B lymphocytes. Acquisition of functionally active alpha 4 beta 1-fibronectin receptors upon B cell activation. Eur J Immunol. 1991 Oct;21(10):2437–2445. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830211021. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Qian F., Vaux D. L., Weissman I. L. Expression of the integrin alpha 4 beta 1 on melanoma cells can inhibit the invasive stage of metastasis formation. Cell. 1994 May 6;77(3):335–347. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(94)90149-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Risau W., Lemmon V. Changes in the vascular extracellular matrix during embryonic vasculogenesis and angiogenesis. Dev Biol. 1988 Feb;125(2):441–450. doi: 10.1016/0012-1606(88)90225-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ross R. The pathogenesis of atherosclerosis: a perspective for the 1990s. Nature. 1993 Apr 29;362(6423):801–809. doi: 10.1038/362801a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roth T., Podestá F., Stepp M. A., Boeri D., Lorenzi M. Integrin overexpression induced by high glucose and by human diabetes: potential pathway to cell dysfunction in diabetic microangiopathy. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1993 Oct 15;90(20):9640–9644. doi: 10.1073/pnas.90.20.9640. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schmidt C. E., Horwitz A. F., Lauffenburger D. A., Sheetz M. P. Integrin-cytoskeletal interactions in migrating fibroblasts are dynamic, asymmetric, and regulated. J Cell Biol. 1993 Nov;123(4):977–991. doi: 10.1083/jcb.123.4.977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schreiner C., Fisher M., Hussein S., Juliano R. L. Increased tumorigenicity of fibronectin receptor deficient Chinese hamster ovary cell variants. Cancer Res. 1991 Mar 15;51(6):1738–1740. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shattil S. J., Hoxie J. A., Cunningham M., Brass L. F. Changes in the platelet membrane glycoprotein IIb.IIIa complex during platelet activation. J Biol Chem. 1985 Sep 15;260(20):11107–11114. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Skinner M. P., Raines E. W., Ross R. Dynamic expression of alpha 1 beta 1 and alpha 2 beta 1 integrin receptors by human vascular smooth muscle cells. Alpha 2 beta 1 integrin is required for chemotaxis across type I collagen-coated membranes. Am J Pathol. 1994 Nov;145(5):1070–1081. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smyth S. S., Joneckis C. C., Parise L. V. Regulation of vascular integrins. Blood. 1993 Jun 1;81(11):2827–2843. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Springer T. A. Traffic signals for lymphocyte recirculation and leukocyte emigration: the multistep paradigm. Cell. 1994 Jan 28;76(2):301–314. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(94)90337-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stallmach A., von Lampe B., Matthes H., Bornhöft G., Riecken E. O. Diminished expression of integrin adhesion molecules on human colonic epithelial cells during the benign to malign tumour transformation. Gut. 1992 Mar;33(3):342–346. doi: 10.1136/gut.33.3.342. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Takada Y., Puzon W. Identification of a regulatory region of integrin beta 1 subunit using activating and inhibiting antibodies. J Biol Chem. 1993 Aug 15;268(23):17597–17601. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yabkowitz R., Mansfield P. J., Ryan U. S., Suchard S. J. Thrombospondin mediates migration and potentiates platelet-derived growth factor-dependent migration of calf pulmonary artery smooth muscle cells. J Cell Physiol. 1993 Oct;157(1):24–32. doi: 10.1002/jcp.1041570104. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yang J. T., Rayburn H., Hynes R. O. Embryonic mesodermal defects in alpha 5 integrin-deficient mice. Development. 1993 Dec;119(4):1093–1105. doi: 10.1242/dev.119.4.1093. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]