Abstract
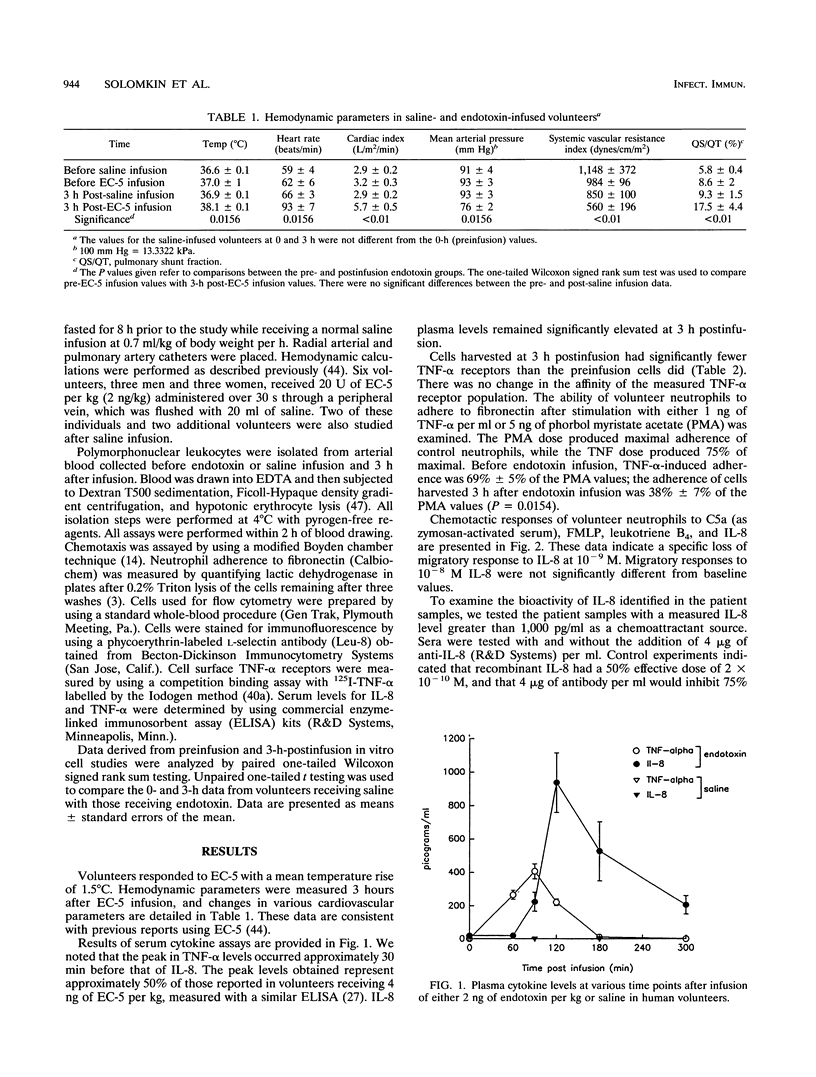
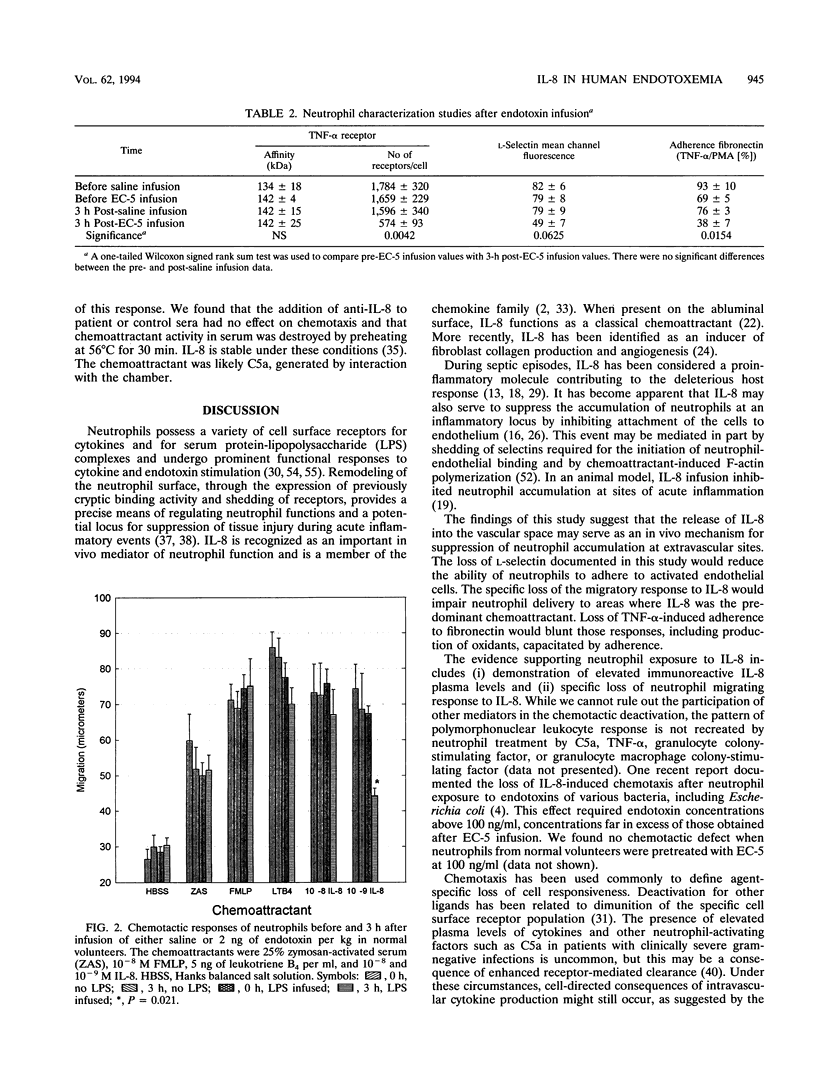
Interleukin-8 (IL-8), a neutrophil chemoattractant and activating cytokine, has been implicated as a proinflammatory mediator in gram-negative sepsis. In vitro data support the notion of IL-8 as an endothelial adherence inhibitor. To evaluate this issue, we infused six volunteers with reference endotoxin and measured plasma levels of IL-8, neutrophil tumor necrosis factor alpha (TNF-alpha) receptors, TNF-alpha-induced adherence to fibronectin, and neutrophil chemotaxis to IL-8 and other attractants. We found that, at 3 h postinfusion, IL-8 but not TNF-alpha plasma levels were elevated. Neutrophils had shed L-selectin (mean channel fluorescence decrease, 79 +/- 9 to 49 +/- 7; P = 0.0625) and TNF-alpha receptors (decrease in number of receptors per cell, 1,596 +/- 340 to 574 +/- 93; P = 0.004). Cells were chemotactically desensitized to IL-8. TNF-alpha-induced adherence to fibronectin was suppressed from 69% +/- 5% of the phorbol myristate acetate response to 38% +/- 7% (P = 0.0154). These findings support the notion that release of IL-8 into the vascular space may be an in vivo mechanism for suppression of neutrophil accumulation at extravascular sites. L-Selectin loss would reduce the ability of neutrophils to adhere to activated endothelial cells. The specific loss of migratory response to IL-8 would impair neutrophil delivery to areas where IL-8 was the predominant chemoattractant. Loss of TNF-alpha-induced adherence to fibronectin would blunt those responses, including production of oxidants, capacitated by adherence.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bachofen M., Weibel E. R. Alterations of the gas exchange apparatus in adult respiratory insufficiency associated with septicemia. Am Rev Respir Dis. 1977 Oct;116(4):589–615. doi: 10.1164/arrd.1977.116.4.589. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baggiolini M., Imboden P., Detmers P. Neutrophil activation and the effects of interleukin-8/neutrophil-activating peptide 1 (IL-8/NAP-1). Cytokines. 1992;4:1–17. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bignold L. P., Rogers S. D., Siaw T. M., Bahnisch J. Inhibition of chemotaxis of neutrophil leukocytes to interleukin-8 by endotoxins of various bacteria. Infect Immun. 1991 Nov;59(11):4255–4258. doi: 10.1128/iai.59.11.4255-4258.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bone R. C. Modulators of coagulation. A critical appraisal of their role in sepsis. Arch Intern Med. 1992 Jul;152(7):1381–1389. doi: 10.1001/archinte.152.7.1381. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brown C. C., Malech H. L., Gallin J. I. Intravenous endotoxin recruits a distinct subset of human neutrophils, defined by monoclonal antibody 31D8, from bone marrow to the peripheral circulation. Cell Immunol. 1989 Oct 15;123(2):294–306. doi: 10.1016/0008-8749(89)90290-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Campbell E. J., Senior R. M., McDonald J. A., Cox D. L. Proteolysis by neutrophils. Relative importance of cell-substrate contact and oxidative inactivation of proteinase inhibitors in vitro. J Clin Invest. 1982 Oct;70(4):845–852. doi: 10.1172/JCI110681. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Campbell E. J., Senior R. M., Welgus H. G. Extracellular matrix injury during lung inflammation. Chest. 1987 Jul;92(1):161–167. doi: 10.1378/chest.92.1.161. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cannon J. G., Tompkins R. G., Gelfand J. A., Michie H. R., Stanford G. G., van der Meer J. W., Endres S., Lonnemann G., Corsetti J., Chernow B. Circulating interleukin-1 and tumor necrosis factor in septic shock and experimental endotoxin fever. J Infect Dis. 1990 Jan;161(1):79–84. doi: 10.1093/infdis/161.1.79. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carveth H. J., Bohnsack J. F., McIntyre T. M., Baggiolini M., Prescott S. M., Zimmerman G. A. Neutrophil activating factor (NAF) induces polymorphonuclear leukocyte adherence to endothelial cells and to subendothelial matrix proteins. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1989 Jul 14;162(1):387–393. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(89)92009-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cochrane C. G., Spragg R., Revak S. D. Pathogenesis of the adult respiratory distress syndrome. Evidence of oxidant activity in bronchoalveolar lavage fluid. J Clin Invest. 1983 Mar;71(3):754–761. doi: 10.1172/JCI110823. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cybulsky M. I., Chan M. K., Movat H. Z. Acute inflammation and microthrombosis induced by endotoxin, interleukin-1, and tumor necrosis factor and their implication in gram-negative infection. Lab Invest. 1988 Apr;58(4):365–378. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Donnelly S. C., Strieter R. M., Kunkel S. L., Walz A., Robertson C. R., Carter D. C., Grant I. S., Pollok A. J., Haslett C. Interleukin-8 and development of adult respiratory distress syndrome in at-risk patient groups. Lancet. 1993 Mar 13;341(8846):643–647. doi: 10.1016/0140-6736(93)90416-e. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Driscoll K. E., Schlesinger R. B. Alveolar macrophage-stimulated neutrophil and monocyte migration: effects of in vitro ozone exposure. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol. 1988 Apr;93(2):312–318. doi: 10.1016/0041-008x(88)90131-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Friedland J. S., Suputtamongkol Y., Remick D. G., Chaowagul W., Strieter R. M., Kunkel S. L., White N. J., Griffin G. E. Prolonged elevation of interleukin-8 and interleukin-6 concentrations in plasma and of leukocyte interleukin-8 mRNA levels during septicemic and localized Pseudomonas pseudomallei infection. Infect Immun. 1992 Jun;60(6):2402–2408. doi: 10.1128/iai.60.6.2402-2408.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gimbrone M. A., Jr, Obin M. S., Brock A. F., Luis E. A., Hass P. E., Hébert C. A., Yip Y. K., Leung D. W., Lowe D. G., Kohr W. J. Endothelial interleukin-8: a novel inhibitor of leukocyte-endothelial interactions. Science. 1989 Dec 22;246(4937):1601–1603. doi: 10.1126/science.2688092. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gresham H. D., Goodwin J. L., Allen P. M., Anderson D. C., Brown E. J. A novel member of the integrin receptor family mediates Arg-Gly-Asp-stimulated neutrophil phagocytosis. J Cell Biol. 1989 May;108(5):1935–1943. doi: 10.1083/jcb.108.5.1935. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hack C. E., Hart M., van Schijndel R. J., Eerenberg A. J., Nuijens J. H., Thijs L. G., Aarden L. A. Interleukin-8 in sepsis: relation to shock and inflammatory mediators. Infect Immun. 1992 Jul;60(7):2835–2842. doi: 10.1128/iai.60.7.2835-2842.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hechtman D. H., Cybulsky M. I., Fuchs H. J., Baker J. B., Gimbrone M. A., Jr Intravascular IL-8. Inhibitor of polymorphonuclear leukocyte accumulation at sites of acute inflammation. J Immunol. 1991 Aug 1;147(3):883–892. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hoch R. C., Rodriguez R., Manning T., Bishop M., Mead P., Shoemaker W. C., Abraham E. Effects of accidental trauma on cytokine and endotoxin production. Crit Care Med. 1993 Jun;21(6):839–845. doi: 10.1097/00003246-199306000-00010. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hochstein H. D., Mills D. F., Outschoorn A. S., Rastogi S. C. The processing and collaborative assay of a reference endotoxin. J Biol Stand. 1983 Oct;11(4):251–260. doi: 10.1016/s0092-1157(83)80013-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Huber A. R., Kunkel S. L., Todd R. F., 3rd, Weiss S. J. Regulation of transendothelial neutrophil migration by endogenous interleukin-8. Science. 1991 Oct 4;254(5028):99–102. doi: 10.1126/science.1718038. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hyers T. M., Tricomi S. M., Dettenmeier P. A., Fowler A. A. Tumor necrosis factor levels in serum and bronchoalveolar lavage fluid of patients with the adult respiratory distress syndrome. Am Rev Respir Dis. 1991 Aug;144(2):268–271. doi: 10.1164/ajrccm/144.2.268. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Koch A. E., Polverini P. J., Kunkel S. L., Harlow L. A., DiPietro L. A., Elner V. M., Elner S. G., Strieter R. M. Interleukin-8 as a macrophage-derived mediator of angiogenesis. Science. 1992 Dec 11;258(5089):1798–1801. doi: 10.1126/science.1281554. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kunkel S. L., Standiford T., Kasahara K., Strieter R. M. Interleukin-8 (IL-8): the major neutrophil chemotactic factor in the lung. Exp Lung Res. 1991 Jan-Feb;17(1):17–23. doi: 10.3109/01902149109063278. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Luscinskas F. W., Kiely J. M., Ding H., Obin M. S., Hébert C. A., Baker J. B., Gimbrone M. A., Jr In vitro inhibitory effect of IL-8 and other chemoattractants on neutrophil-endothelial adhesive interactions. J Immunol. 1992 Sep 15;149(6):2163–2171. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Martich G. D., Danner R. L., Ceska M., Suffredini A. F. Detection of interleukin 8 and tumor necrosis factor in normal humans after intravenous endotoxin: the effect of antiinflammatory agents. J Exp Med. 1991 Apr 1;173(4):1021–1024. doi: 10.1084/jem.173.4.1021. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Martin M. A., Silverman H. J. Gram-negative sepsis and the adult respiratory distress syndrome. Clin Infect Dis. 1992 Jun;14(6):1213–1228. doi: 10.1093/clinids/14.6.1213. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miller E. J., Cohen A. B., Nagao S., Griffith D., Maunder R. J., Martin T. R., Weiner-Kronish J. P., Sticherling M., Christophers E., Matthay M. A. Elevated levels of NAP-1/interleukin-8 are present in the airspaces of patients with the adult respiratory distress syndrome and are associated with increased mortality. Am Rev Respir Dis. 1992 Aug;146(2):427–432. doi: 10.1164/ajrccm/146.2.427. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nathan C., Srimal S., Farber C., Sanchez E., Kabbash L., Asch A., Gailit J., Wright S. D. Cytokine-induced respiratory burst of human neutrophils: dependence on extracellular matrix proteins and CD11/CD18 integrins. J Cell Biol. 1989 Sep;109(3):1341–1349. doi: 10.1083/jcb.109.3.1341. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nelson R. D., Hasslen S. R., Ahrenholz D. H., Solem L. D. Mechanisms of loss of human neutrophil chemotaxis following thermal injury. J Burn Care Rehabil. 1987 Nov-Dec;8(6):496–502. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Neote K., Darbonne W., Ogez J., Horuk R., Schall T. J. Identification of a promiscuous inflammatory peptide receptor on the surface of red blood cells. J Biol Chem. 1993 Jun 15;268(17):12247–12249. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oppenheim J. J., Zachariae C. O., Mukaida N., Matsushima K. Properties of the novel proinflammatory supergene "intercrine" cytokine family. Annu Rev Immunol. 1991;9:617–648. doi: 10.1146/annurev.iy.09.040191.003153. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Parrillo J. E., Parker M. M., Natanson C., Suffredini A. F., Danner R. L., Cunnion R. E., Ognibene F. P. Septic shock in humans. Advances in the understanding of pathogenesis, cardiovascular dysfunction, and therapy. Ann Intern Med. 1990 Aug 1;113(3):227–242. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-113-3-227. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Peveri P., Walz A., Dewald B., Baggiolini M. A novel neutrophil-activating factor produced by human mononuclear phagocytes. J Exp Med. 1988 May 1;167(5):1547–1559. doi: 10.1084/jem.167.5.1547. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Richardson R. P., Rhyne C. D., Fong Y., Hesse D. G., Tracey K. J., Marano M. A., Lowry S. F., Antonacci A. C., Calvano S. E. Peripheral blood leukocyte kinetics following in vivo lipopolysaccharide (LPS) administration to normal human subjects. Influence of elicited hormones and cytokines. Ann Surg. 1989 Aug;210(2):239–245. doi: 10.1097/00000658-198908000-00018. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schleiffenbaum B., Fehr J. The tumor necrosis factor receptor and human neutrophil function. Deactivation and cross-deactivation of tumor necrosis factor-induced neutrophil responses by receptor down-regulation. J Clin Invest. 1990 Jul;86(1):184–195. doi: 10.1172/JCI114683. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Singer I. I., Scott S., Kawka D. W., Kazazis D. M. Adhesomes: specific granules containing receptors for laminin, C3bi/fibrinogen, fibronectin, and vitronectin in human polymorphonuclear leukocytes and monocytes. J Cell Biol. 1989 Dec;109(6 Pt 1):3169–3182. doi: 10.1083/jcb.109.6.3169. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith C. W., Kishimoto T. K., Abbassi O., Hughes B., Rothlein R., McIntire L. V., Butcher E., Anderson D. C., Abbass O. Chemotactic factors regulate lectin adhesion molecule 1 (LECAM-1)-dependent neutrophil adhesion to cytokine-stimulated endothelial cells in vitro. J Clin Invest. 1991 Feb;87(2):609–618. doi: 10.1172/JCI115037. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Solomkin J. S., Cotta L. A., Satoh P. S., Hurst J. M., Nelson R. D. Complement activation and clearance in acute illness and injury: evidence for C5a as a cell-directed mediator of the adult respiratory distress syndrome in man. Surgery. 1985 Jun;97(6):668–678. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spertini O., Luscinskas F. W., Kansas G. S., Munro J. M., Griffin J. D., Gimbrone M. A., Jr, Tedder T. F. Leukocyte adhesion molecule-1 (LAM-1, L-selectin) interacts with an inducible endothelial cell ligand to support leukocyte adhesion. J Immunol. 1991 Oct 15;147(8):2565–2573. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spinas G. A., Keller U., Brockhaus M. Release of soluble receptors for tumor necrosis factor (TNF) in relation to circulating TNF during experimental endotoxinemia. J Clin Invest. 1992 Aug;90(2):533–536. doi: 10.1172/JCI115891. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Standiford T. J., Kunkel S. L., Basha M. A., Chensue S. W., Lynch J. P., 3rd, Toews G. B., Westwick J., Strieter R. M. Interleukin-8 gene expression by a pulmonary epithelial cell line. A model for cytokine networks in the lung. J Clin Invest. 1990 Dec;86(6):1945–1953. doi: 10.1172/JCI114928. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Suffredini A. F., Fromm R. E., Parker M. M., Brenner M., Kovacs J. A., Wesley R. A., Parrillo J. E. The cardiovascular response of normal humans to the administration of endotoxin. N Engl J Med. 1989 Aug 3;321(5):280–287. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198908033210503. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Suter P. M., Suter S., Girardin E., Roux-Lombard P., Grau G. E., Dayer J. M. High bronchoalveolar levels of tumor necrosis factor and its inhibitors, interleukin-1, interferon, and elastase, in patients with adult respiratory distress syndrome after trauma, shock, or sepsis. Am Rev Respir Dis. 1992 May;145(5):1016–1022. doi: 10.1164/ajrccm/145.5.1016. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sylvester I., Suffredini A. F., Boujoukos A. J., Martich G. D., Danner R. L., Yoshimura T., Leonard E. J. Neutrophil attractant protein-1 and monocyte chemoattractant protein-1 in human serum. Effects of intravenous lipopolysaccharide on free attractants, specific IgG autoantibodies and immune complexes. J Immunol. 1993 Sep 15;151(6):3292–3298. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tennenberg S. D., Zemlan F. P., Solomkin J. S. Characterization of N-formyl-methionyl-leucyl-phenylalanine receptors on human neutrophils. Effects of isolation and temperature on receptor expression and functional activity. J Immunol. 1988 Dec 1;141(11):3937–3944. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tilg H., Shapiro L., Atkins M. B., Dinarello C. A., Mier J. W. Induction of circulating and erythrocyte-bound IL-8 by IL-2 immunotherapy and suppression of its in vitro production by IL-1 receptor antagonist and soluble tumor necrosis factor receptor (p75) chimera. J Immunol. 1993 Sep 15;151(6):3299–3307. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Westlin W. F., Kiely J. M., Gimbrone M. A., Jr Interleukin-8 induces changes in human neutrophil actin conformation and distribution: relationship to inhibition of adhesion to cytokine-activated endothelium. J Leukoc Biol. 1992 Jul;52(1):43–51. doi: 10.1002/jlb.52.1.43. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wewers M. D., Herzyk D. J., Gadek J. E. Alveolar fluid neutrophil elastase activity in the adult respiratory distress syndrome is complexed to alpha-2-macroglobulin. J Clin Invest. 1988 Oct;82(4):1260–1267. doi: 10.1172/JCI113724. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wright S. D. Multiple receptors for endotoxin. Curr Opin Immunol. 1991 Feb;3(1):83–90. doi: 10.1016/0952-7915(91)90082-c. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wright S. D., Ramos R. A., Hermanowski-Vosatka A., Rockwell P., Detmers P. A. Activation of the adhesive capacity of CR3 on neutrophils by endotoxin: dependence on lipopolysaccharide binding protein and CD14. J Exp Med. 1991 May 1;173(5):1281–1286. doi: 10.1084/jem.173.5.1281. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van Deventer S. J., Büller H. R., ten Cate J. W., Aarden L. A., Hack C. E., Sturk A. Experimental endotoxemia in humans: analysis of cytokine release and coagulation, fibrinolytic, and complement pathways. Blood. 1990 Dec 15;76(12):2520–2526. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- von Andrian U. H., Chambers J. D., McEvoy L. M., Bargatze R. F., Arfors K. E., Butcher E. C. Two-step model of leukocyte-endothelial cell interaction in inflammation: distinct roles for LECAM-1 and the leukocyte beta 2 integrins in vivo. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Sep 1;88(17):7538–7542. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.17.7538. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



