Abstract
Bacillus cereus causes diarrheal and emetic food poisoning syndromes as well as a variety of mild to severe infections. A dermonecrotic vascular permeability (VP) factor has been implicated as a virulence factor in these illnesses. Hemolysin BL was previously identified as a unique tripartite hemolysin possessing VP activity. In this study, a high-yield purification scheme, which allowed quantitative characterization of hemolysin BL activity and determination of the molecular weight, pI, and N-terminal sequence of each component, was developed. Milligram quantities of the B, L1, and L2 components were highly purified by a combination of anion-exchange and hydroxylapatite chromatographies. The combined components had VP activity at low doses and were necrotic at higher doses. The toxin exhibited an unusual dose-response zone phenomenon in turbidometric hemolysis assays. Activity increased at doses up to 200 ng/ml, then decreased at doses up to 350 ng/ml, and was constant at doses up to at least 2,500 ng/ml. This behavior may provide an explanation for the unusual discontinuous pattern typical of hemolysin BL in gel diffusion assays. At high concentrations of one or two components, the presence of low amounts of the complementary component(s) resulted in full hemolytic activity. Erythrocytes were protected from lysis by Zn2+ at micromolar concentrations but not by Ca2+ and Mg2+ at concentrations up to 25 mM. These data provide guidelines for future work on this toxin and indicate that hemolysin BL is the dermonecrotic VP factor implicated as a B. cereus virulence factor.
Full text
PDF

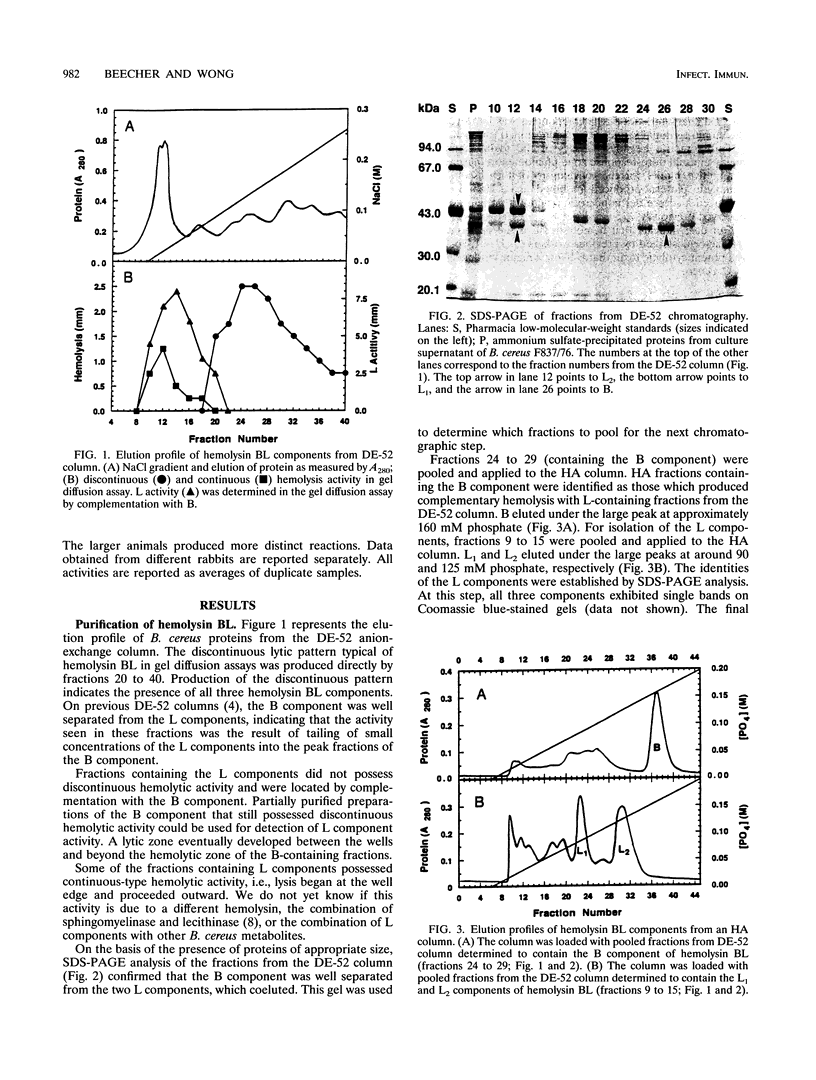
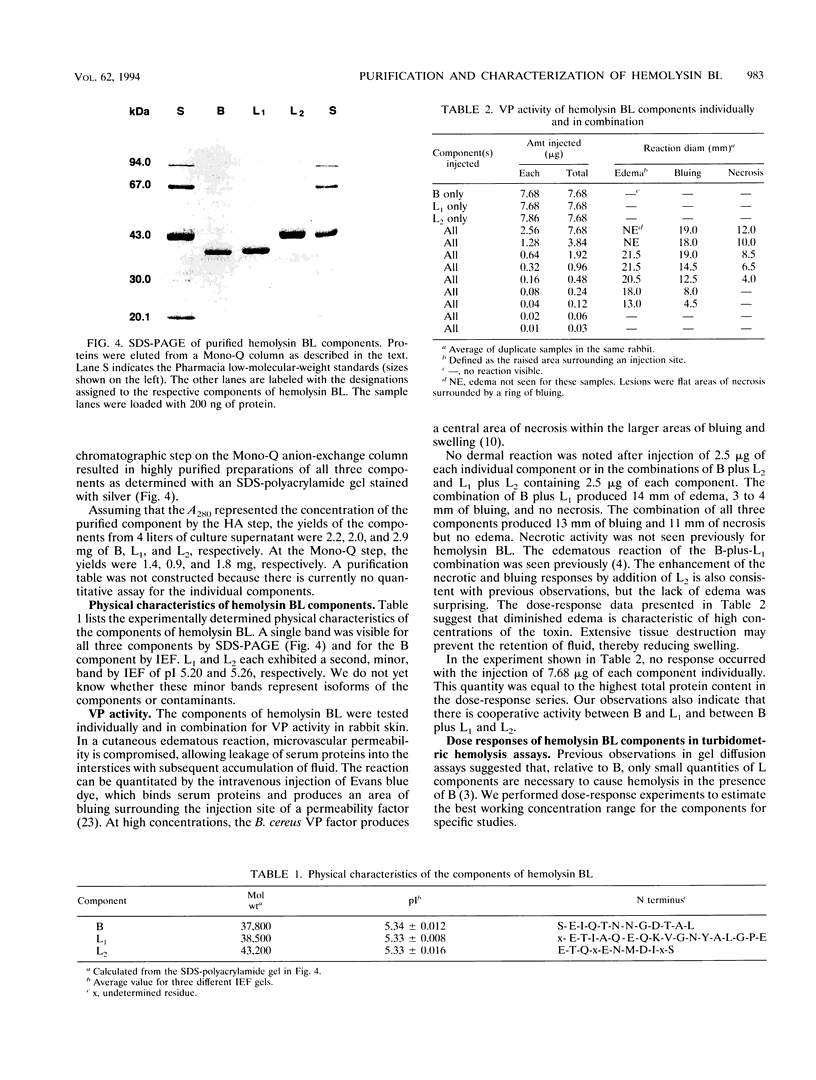
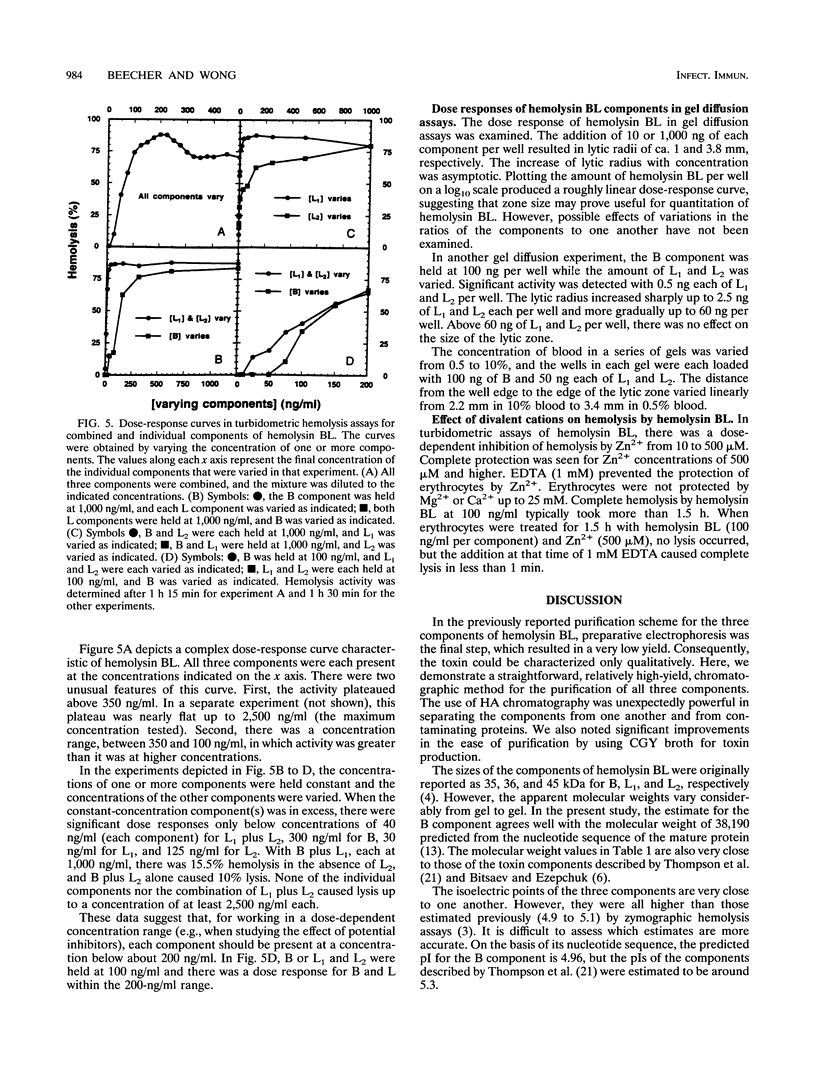


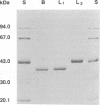
Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bashford C. L., Alder G. M., Graham J. M., Menestrina G., Pasternak C. A. Ion modulation of membrane permeability: effect of cations on intact cells and on cells and phospholipid bilayers treated with pore-forming agents. J Membr Biol. 1988 Jul;103(1):79–94. doi: 10.1007/BF01871934. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bashford C. L., Alder G. M., Menestrina G., Micklem K. J., Murphy J. J., Pasternak C. A. Membrane damage by hemolytic viruses, toxins, complement, and other cytotoxic agents. A common mechanism blocked by divalent cations. J Biol Chem. 1986 Jul 15;261(20):9300–9308. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Beecher D. J., MacMillan J. D. A novel bicomponent hemolysin from Bacillus cereus. Infect Immun. 1990 Jul;58(7):2220–2227. doi: 10.1128/iai.58.7.2220-2227.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Beecher D. J., Macmillan J. D. Characterization of the components of hemolysin BL from Bacillus cereus. Infect Immun. 1991 May;59(5):1778–1784. doi: 10.1128/iai.59.5.1778-1784.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bernheimer A. W. Assay of hemolytic toxins. Methods Enzymol. 1988;165:213–217. doi: 10.1016/s0076-6879(88)65033-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bitsaev A. R., Ezepchuk Iu V. Molekuliarnaia priroda patogennogo deistviia, vyzyvaemogo B. cereus. Mol Gen Mikrobiol Virusol. 1987 Jul;(7):18–23. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gilmore M. S., Cruz-Rodz A. L., Leimeister-Wächter M., Kreft J., Goebel W. A Bacillus cereus cytolytic determinant, cereolysin AB, which comprises the phospholipase C and sphingomyelinase genes: nucleotide sequence and genetic linkage. J Bacteriol. 1989 Feb;171(2):744–753. doi: 10.1128/jb.171.2.744-753.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Glatz B. A., Spira W. M., Goepfert J. M. Alteration of vascular permeability in rabbits by culture filtrates of Bacillus cereus and related species. Infect Immun. 1974 Aug;10(2):299–303. doi: 10.1128/iai.10.2.299-303.1974. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Granum P. E., Nissen H. Sphingomyelinase is part of the 'enterotoxin complex' produced by Bacillus cereus. FEMS Microbiol Lett. 1993 Jun 1;110(1):97–100. doi: 10.1111/j.1574-6968.1993.tb06301.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heinrichs J. H., Beecher D. J., MacMillan J. D., Zilinskas B. A. Molecular cloning and characterization of the hblA gene encoding the B component of hemolysin BL from Bacillus cereus. J Bacteriol. 1993 Nov;175(21):6760–6766. doi: 10.1128/jb.175.21.6760-6766.1993. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ikezawa H., Mori M., Taguchi R. Studies on sphingomyelinase of Bacillus cereus: hydrolytic and hemolytic actions on erythrocyte membranes. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1980 Feb;199(2):572–578. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(80)90315-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Matsudaira P. Limited N-terminal sequence analysis. Methods Enzymol. 1990;182:602–613. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(90)82047-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Menestrina G., Bashford C. L., Pasternak C. A. Pore-forming toxins: experiments with S. aureus alpha-toxin, C. perfringens theta-toxin and E. coli haemolysin in lipid bilayers, liposomes and intact cells. Toxicon. 1990;28(5):477–491. doi: 10.1016/0041-0101(90)90292-f. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shinagawa K., Sugiyama J., Terada T., Matsusaka N., Sugii S. Improved methods for purification of an enterotoxin produced by Bacillus cereus. FEMS Microbiol Lett. 1991 May 1;64(1):1–5. doi: 10.1016/0378-1097(91)90199-k. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shinagawa K., Ueno S., Konuma H., Matsusaka N., Sugii S. Purification and characterization of the vascular permeability factor produced by Bacillus cereus. J Vet Med Sci. 1991 Apr;53(2):281–286. doi: 10.1292/jvms.53.281. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thompson N. E., Ketterhagen M. J., Bergdoll M. S., Schantz E. J. Isolation and some properties of an enterotoxin produced by Bacillus cereus. Infect Immun. 1984 Mar;43(3):887–894. doi: 10.1128/iai.43.3.887-894.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tomita M., Taguchi R., Ikezawa H. Molecular properties and kinetic studies on sphingomyelinase of Bacillus cereus. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1982 May 21;704(1):90–99. doi: 10.1016/0167-4838(82)90135-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Turnbull P. C., Jørgensen K., Kramer J. M., Gilbert R. J., Parry J. M. Severe clinical conditions associated with Bacillus cereus and the apparent involvement of exotoxins. J Clin Pathol. 1979 Mar;32(3):289–293. doi: 10.1136/jcp.32.3.289. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Turnbull P. C., Kramer J. M., Jørgensen K., Gilbert R. J., Melling J. Properties and production characteristics of vomiting, diarrheal, and necrotizing toxins of Bacillus cereus. Am J Clin Nutr. 1979 Jan;32(1):219–228. doi: 10.1093/ajcn/32.1.219. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Turnbull P. C., Kramer J. M. Non-gastrointestinal Bacillus cereus infections: an analysis of exotoxin production by strains isolated over a two-year period. J Clin Pathol. 1983 Oct;36(10):1091–1096. doi: 10.1136/jcp.36.10.1091. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Young J. D., Leong L. G., DiNome M. A., Cohn Z. A. A semiautomated hemolysis microassay for membrane lytic proteins. Anal Biochem. 1986 May 1;154(2):649–654. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(86)90042-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]