Abstract
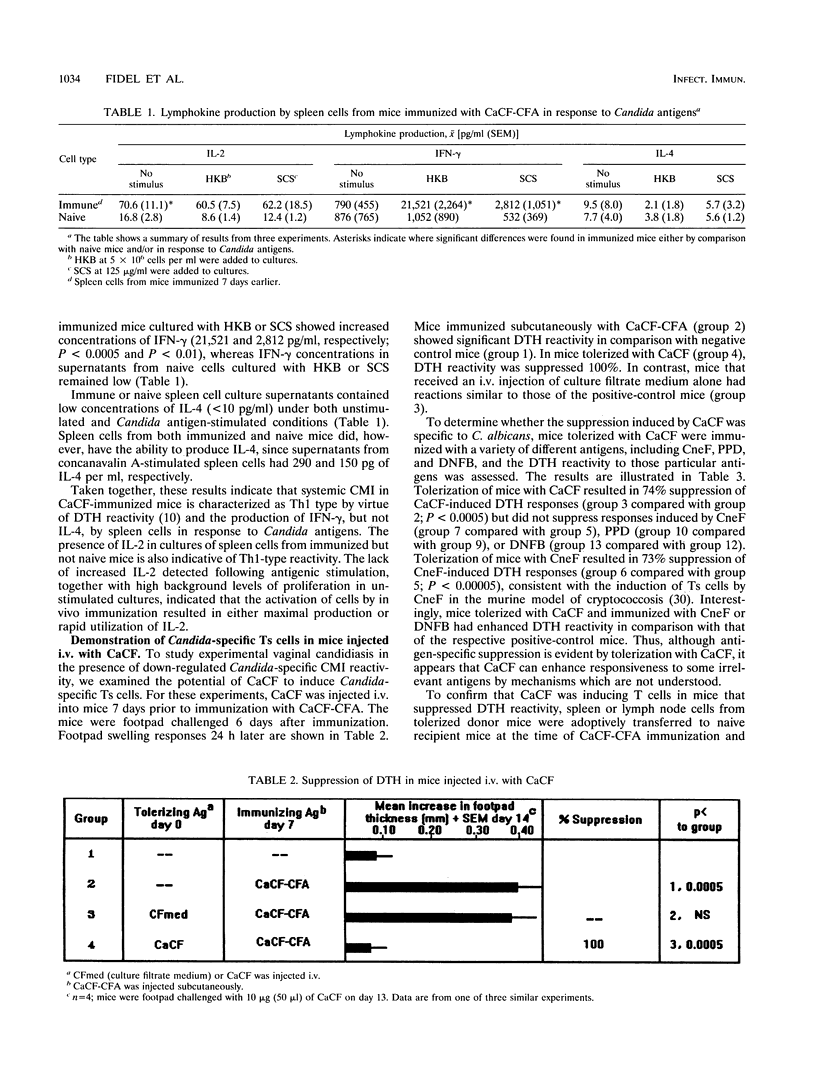
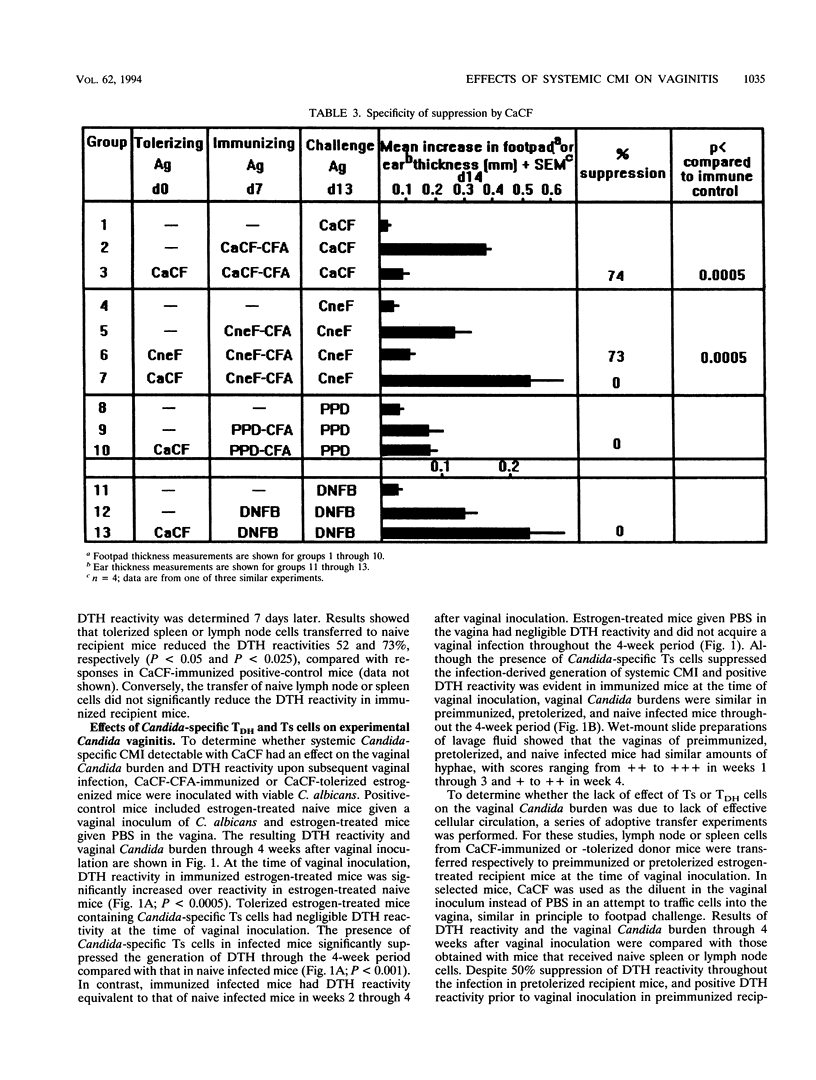
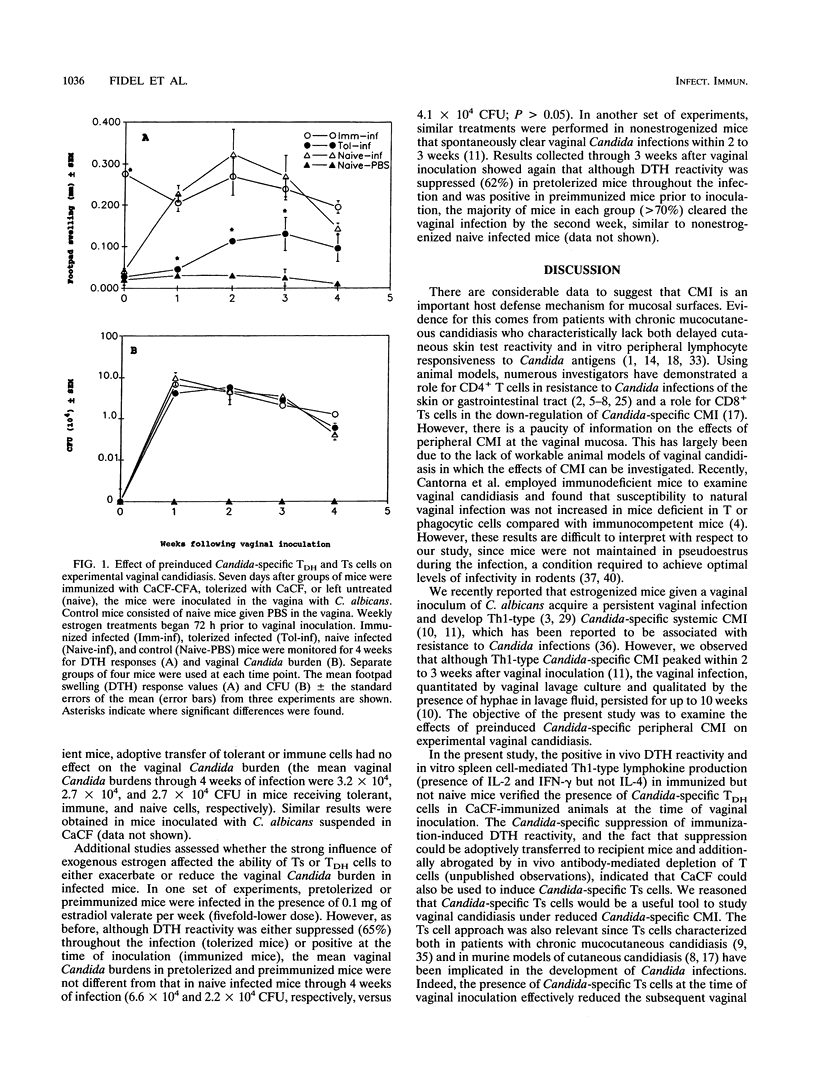
It has been postulated that systemic cell-mediated immunity (CMI) is an important host defense factor against recurrent vaginal infections caused by Candida albicans. Using an estrogen-dependent murine model of vaginal candidiasis, we have previously shown that mice inoculated vaginally with C. albicans acquire a persistent vaginal infection and develop Candida-specific Th1-type systemic CMI. In the present study, experimental vaginitis was monitored in the presence of preinduced systemic Candida-specific CMI. Mice immunized systemically with C. albicans culture filtrate antigens (CaCF) in complete Freund's adjuvant (CFA) had Th1-type reactivity similar to that of vaginally infected mice. CaCF given to mice intravenously induced Candida-specific suppressor T (Ts) cells. Mice preimmunized with CaCF-CFA and given a vaginal inoculum of C. albicans had positive delayed-type hypersensitivity (DTH) reactivity from the time of vaginal inoculation through 4 weeks. Conversely, mice infected in the presence of Ts cells had significantly reduced DTH responses throughout the 4-week period in comparison with naive infected mice. However, the presence of Th1-type Candida-specific DTH cells or Ts cells, either induced in mice prior to vaginal inoculation or adoptively transferred at the time of inoculation, had no effect on the vaginal Candida burden through 4 weeks of infection. A similar lack of effects was obtained in animals with lower Candida population levels resulting from a reduction in or absence of exogenous estrogen. These results suggest that systemic Th1-type CMI demonstrable with CaCF is unrelated to protective events at the level of the vaginal mucosa.
Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Aronson I. K., Rieger C. H., Soltani K., Tkalcevic V., Chan W. C., Lorincz A. L., Matz G. Late onset chronic mucocutaneous candidiasis with lymphoma and specific serum inhibitory factor. Cancer. 1979 Jan;43(1):101–108. doi: 10.1002/1097-0142(197901)43:1<101::aid-cncr2820430116>3.0.co;2-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Balish E., Filutowicz H., Oberley T. D. Correlates of cell-mediated immunity in Candida albicans-colonized gnotobiotic mice. Infect Immun. 1990 Jan;58(1):107–113. doi: 10.1128/iai.58.1.107-113.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bottomly K. A functional dichotomy in CD4+ T lymphocytes. Immunol Today. 1988 Sep;9(9):268–274. doi: 10.1016/0167-5699(88)91308-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cantorna M. T., Balish E. Mucosal and systemic candidiasis in congenitally immunodeficient mice. Infect Immun. 1990 Apr;58(4):1093–1100. doi: 10.1128/iai.58.4.1093-1100.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cantorna M. T., Balish E. Role of CD4+ lymphocytes in resistance to mucosal candidiasis. Infect Immun. 1991 Jul;59(7):2447–2455. doi: 10.1128/iai.59.7.2447-2455.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cantorna M., Mook D., Balish E. Resistance of congenitally immunodeficient gnotobiotic mice to vaginal candidiasis. Infect Immun. 1990 Nov;58(11):3813–3815. doi: 10.1128/iai.58.11.3813-3815.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carrow E. W., Domer J. E. Immunoregulation in experimental murine candidiasis: specific suppression induced by Candida albicans cell wall glycoprotein. Infect Immun. 1985 Jul;49(1):172–181. doi: 10.1128/iai.49.1.172-181.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Domer J. E., Garner R. E., Befidi-Mengue R. N. Mannan as an antigen in cell-mediated immunity (CMI) assays and as a modulator of mannan-specific CMI. Infect Immun. 1989 Mar;57(3):693–700. doi: 10.1128/iai.57.3.693-700.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Durandy A., Fischer A., Le Deist F., Drouhet E., Griscelli C. Mannan-specific and mannan-induced T-cell suppressive activity in patients with chronic mucocutaneous candidiasis. J Clin Immunol. 1987 Sep;7(5):400–409. doi: 10.1007/BF00917018. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fidel P. L., Jr, Lynch M. E., Redondo-Lopez V., Sobel J. D., Robinson R. Systemic cell-mediated immune reactivity in women with recurrent vulvovaginal candidiasis. J Infect Dis. 1993 Dec;168(6):1458–1465. doi: 10.1093/infdis/168.6.1458. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fidel P. L., Jr, Lynch M. E., Sobel J. D. Candida-specific Th1-type responsiveness in mice with experimental vaginal candidiasis. Infect Immun. 1993 Oct;61(10):4202–4207. doi: 10.1128/iai.61.10.4202-4207.1993. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fidel P. L., Jr, Lynch M. E., Sobel J. D. Candida-specific cell-mediated immunity is demonstrable in mice with experimental vaginal candidiasis. Infect Immun. 1993 May;61(5):1990–1995. doi: 10.1128/iai.61.5.1990-1995.1993. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fiorentino D. F., Bond M. W., Mosmann T. R. Two types of mouse T helper cell. IV. Th2 clones secrete a factor that inhibits cytokine production by Th1 clones. J Exp Med. 1989 Dec 1;170(6):2081–2095. doi: 10.1084/jem.170.6.2081. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fischer A., Ballet J. J., Griscelli C. Specific inhibition of in vitro Candida-induced lymphocyte proliferation by polysaccharidic antigens present in the serum of patients with chronic mucocutaneous candidiasis. J Clin Invest. 1978 Nov;62(5):1005–1013. doi: 10.1172/JCI109204. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fleury F. J. Adult vaginitis. Clin Obstet Gynecol. 1981 Jun;24(2):407–438. doi: 10.1097/00003081-198106000-00008. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fong I. W., McCleary P., Read S. Cellular immunity of patients with recurrent or refractory vulvovaginal moniliasis. Am J Obstet Gynecol. 1992 Mar;166(3):887–890. doi: 10.1016/0002-9378(92)91356-f. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Garner R. E., Childress A. M., Human L. G., Domer J. E. Characterization of Candida albicans mannan-induced, mannan-specific delayed hypersensitivity suppressor cells. Infect Immun. 1990 Aug;58(8):2613–2620. doi: 10.1128/iai.58.8.2613-2620.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gatenby P., Basten A., Adams E. Thymoma and late onset mucocutaneous candidiasis associated with a plasma inhibitor of cell-mediated immune function. J Clin Lab Immunol. 1980 May;3(3):209–216. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gillis S., Ferm M. M., Ou W., Smith K. A. T cell growth factor: parameters of production and a quantitative microassay for activity. J Immunol. 1978 Jun;120(6):2027–2032. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hobbs J. R., Brigden D., Davidson F., Kahan M., Oates J. K. Immunological aspects of candidal vaginitis. Proc R Soc Med. 1977;70 (Suppl 4):11–14. doi: 10.1177/00359157770700S404. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hu-Li J., Ohara J., Watson C., Tsang W., Paul W. E. Derivation of a T cell line that is highly responsive to IL-4 and IL-2 (CT.4R) and of an IL-2 hyporesponsive mutant of that line (CT.4S). J Immunol. 1989 Feb 1;142(3):800–807. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hurley R. Candidal vaginitis. Proc R Soc Med. 1977;70 (Suppl 4):1–2. doi: 10.1177/00359157770700S401. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hurley R., De Louvois J. Candida vaginitis. Postgrad Med J. 1979 Sep;55(647):645–647. doi: 10.1136/pgmj.55.647.645. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hurley R. Recurrent Candida infection. Clin Obstet Gynaecol. 1981 Apr;8(1):209–214. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jensen J., Warner T., Balish E. Resistance of SCID mice to Candida albicans administered intravenously or colonizing the gut: role of polymorphonuclear leukocytes and macrophages. J Infect Dis. 1993 Apr;167(4):912–919. doi: 10.1093/infdis/167.4.912. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Koga T., Mitsuyama M., Handa T., Yayama T., Muramori K., Nomoto K. Induction by killed Listeria monocytogenes of effector T cells mediating delayed-type hypersensitivity but not protection in mice. Immunology. 1987 Oct;62(2):241–248. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mitsuyama M., Nomoto K., Takeya K. Direct correlation between delayed footpad reaction and resistance to local bacterial infection. Infect Immun. 1982 Apr;36(1):72–79. doi: 10.1128/iai.36.1.72-79.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morton R. S., Rashid S. Candidal vaginitis: natural history, predisposing factors and prevention. Proc R Soc Med. 1977;70 (Suppl 4):3–6. doi: 10.1177/00359157770700S402. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mosmann T. R., Cherwinski H., Bond M. W., Giedlin M. A., Coffman R. L. Two types of murine helper T cell clone. I. Definition according to profiles of lymphokine activities and secreted proteins. J Immunol. 1986 Apr 1;136(7):2348–2357. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Murphy J. W., Moorhead J. W. Regulation of cell-mediated immunity in cryptococcosis. I. Induction of specific afferent T suppressor cells by cryptococcal antigen. J Immunol. 1982 Jan;128(1):276–283. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nandi D., Allison J. P. Phenotypic analysis and gamma delta-T cell receptor repertoire of murine T cells associated with the vaginal epithelium. J Immunol. 1991 Sep 15;147(6):1773–1778. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Paterson P. Y., Semo R., Blumenschein G., Swelstad J. Mucocutaneous candidiasis, anergy and a plasma inhibitor of cellular immunity: reversal after amphotericin B therapy. Clin Exp Immunol. 1971 Nov;9(5):595–602. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Phanuphak P., Moorhead J. W., Claman H. N. Tolerance and contact sensitivity to DNFB in mice. I. In vivo detection by ear swelling and correlation with in vitro cell stimulation. J Immunol. 1974 Jan;112(1):115–123. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Piccolella E., Lombardi G., Morelli R. Generation of suppressor cells in the response of human lymphocytes to a polysaccharide from Candida albicans. J Immunol. 1981 Jun;126(6):2151–2155. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Romani L., Mocci S., Bietta C., Lanfaloni L., Puccetti P., Bistoni F. Th1 and Th2 cytokine secretion patterns in murine candidiasis: association of Th1 responses with acquired resistance. Infect Immun. 1991 Dec;59(12):4647–4654. doi: 10.1128/iai.59.12.4647-4654.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ryley J. F., McGregor S. Quantification of vaginal Candida albicans infections in rodents. J Med Vet Mycol. 1986 Dec;24(6):455–460. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sobel J. D., Muller G., McCormick J. F. Experimental chronic vaginal candidosis in rats. Sabouraudia. 1985 Jun;23(3):199–206. doi: 10.1080/00362178585380301. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sobel J. D. Pathogenesis and epidemiology of vulvovaginal candidiasis. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1988;544:547–557. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1988.tb40450.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Syverson R. E., Buckley H., Gibian J., Ryan G. M., Jr Cellular and humoral immune status in women with chronic Candida vaginitis. Am J Obstet Gynecol. 1979 Jul 15;134(6):624–627. doi: 10.1016/0002-9378(79)90641-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Witkin S. S., Hirsch J., Ledger W. J. A macrophage defect in women with recurrent Candida vaginitis and its reversal in vitro by prostaglandin inhibitors. Am J Obstet Gynecol. 1986 Oct;155(4):790–795. doi: 10.1016/s0002-9378(86)80022-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Witkin S. S. Inhibition of Candida-induced lymphocyte proliferation by antibody to Candida albicans. Obstet Gynecol. 1986 Nov;68(5):696–699. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


