Abstract
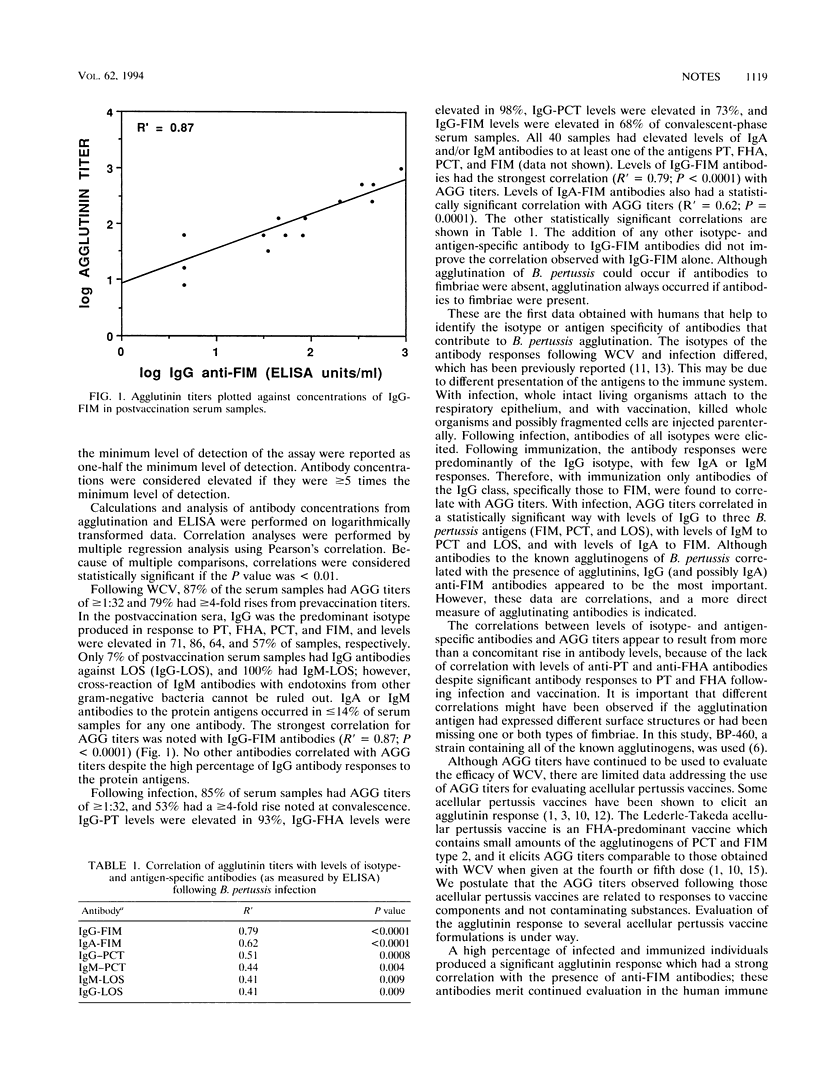
Elevated agglutinin titers have been shown to correlate with protection from disease following whole-cell pertussis vaccination, but the isotype and antigen specificity of human agglutinating antibodies is unknown. In 13 immunoassays, immunoglobulin G antifimbria antibodies had the strongest correlation with agglutinin titers following culture-proven infection with Bordetella pertussis (R' = 0.79; P < 0.0001) and following whole-cell pertussis vaccination (R' = 0.87, P < 0.0001).
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Blumberg D. A., Mink C. M., Cherry J. D., Reisinger K. S., Blatter M. M., Congeni B. L., Dekker C. L., Stout M. G., Mezzatesta J. R., Scott J. V. Comparison of an acellular pertussis-component diphtheria-tetanus-pertussis (DTP) vaccine with a whole-cell pertussis-component DTP vaccine in 17- to 24-month-old children, with measurement of 69-kilodalton outer membrane protein antibody. J Pediatr. 1990 Jul;117(1 Pt 1):46–51. doi: 10.1016/s0022-3476(05)82442-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brennan M. J., Li Z. M., Cowell J. L., Bisher M. E., Steven A. C., Novotny P., Manclark C. R. Identification of a 69-kilodalton nonfimbrial protein as an agglutinogen of Bordetella pertussis. Infect Immun. 1988 Dec;56(12):3189–3195. doi: 10.1128/iai.56.12.3189-3195.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Edwards K. M., Bradley R. B., Decker M. D., Palmer P. S., Van Savage J., Taylor J. C., Dupont W. D., Hager C. C., Wright P. F. Evaluation of a new highly purified pertussis vaccine in infants and children. J Infect Dis. 1989 Nov;160(5):832–837. doi: 10.1093/infdis/160.5.832. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Li Z. M., Brennan M. J., David J. L., Carter P. H., Cowell J. L., Manclark C. R. Comparison of type 2 and type 6 fimbriae of Bordetella pertussis by using agglutinating monoclonal antibodies. Infect Immun. 1988 Dec;56(12):3184–3188. doi: 10.1128/iai.56.12.3184-3188.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Li Z. M., Cowell J. L., Brennan M. J., Burns D. L., Manclark C. R. Agglutinating monoclonal antibodies that specifically recognize lipooligosaccharide A of Bordetella pertussis. Infect Immun. 1988 Mar;56(3):699–702. doi: 10.1128/iai.56.3.699-702.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morgan C. M., Blumberg D. A., Cherry J. D., Reisinger K. S., Blatter M. M., Blumer J. L., Dekker C. L., Stout M. G., Christenson P. D. Comparison of acellular and whole-cell pertussis-component DTP vaccines. A multicenter double-blind study in 4- to 6-year-old children. Am J Dis Child. 1990 Jan;144(1):41–45. doi: 10.1001/archpedi.1990.02150250047029. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nagel J., Poot-Scholtens E. J. Serum IgA antibody to Bordetella pertussis as an indicator of infection. J Med Microbiol. 1983 Nov;16(4):417–426. doi: 10.1099/00222615-16-4-417. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ruuskanen O., Viljanen M. K., Salmi T. T., Lehtonen O. P., Kouvalainen K., Peltonen T. DTP and DTP-inactivated polio vaccines: comparison of adverse reactions and IGG, IGM and IGA antibody responses to DTP. Acta Paediatr Scand. 1980 Mar;69(2):177–182. doi: 10.1111/j.1651-2227.1980.tb07056.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sato Y., Kimura M., Fukumi H. Development of a pertussis component vaccine in Japan. Lancet. 1984 Jan 21;1(8369):122–126. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(84)90061-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Steketee R. W., Burstyn D. G., Wassilak S. G., Adkins W. N., Jr, Polyak M. B., Davis J. P., Manclark C. R. A comparison of laboratory and clinical methods for diagnosing pertussis in an outbreak in a facility for the developmentally disabled. J Infect Dis. 1988 Mar;157(3):441–449. doi: 10.1093/infdis/157.3.441. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



