Abstract
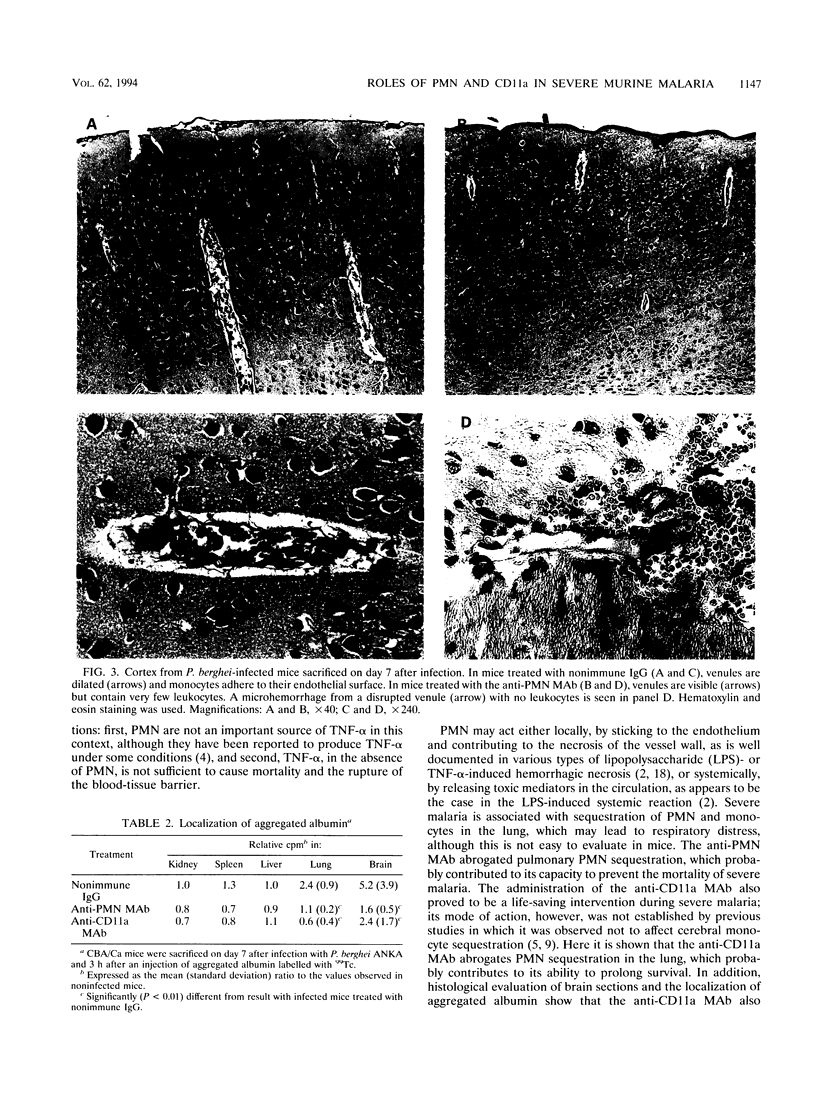
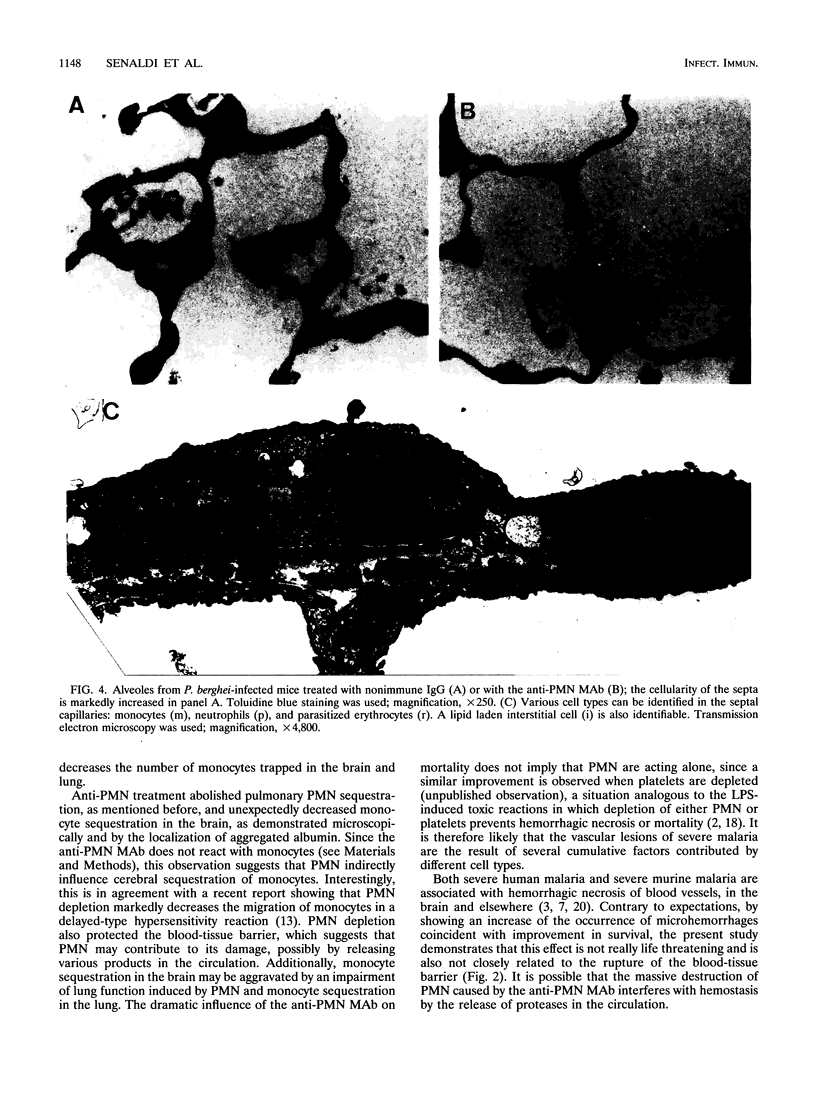
Infection of CBA mice with Plasmodium berghei ANKA results in severe malaria, which is characterized by mortality 6 to 10 days after infection and is associated with alterations of the brain microcirculation. These alterations consist of (i) intravascular sequestration of monocytes, (ii) an increase in vascular permeability as documented by Evans blue diffusion, and (iii) microhemorrhages. This syndrome may be due to an increase of production of tumor necrosis factor alpha which upregulates the endothelial expression of ICAM-1 and thus leads to adhesion of CD11a/CD18 (LFA-1)-bearing cells. During severe malaria, we found an important sequestration of the CD11a-bearing polymorphonuclear neutrophil leukocytes (PMN) in the lung but not in the brain. Treatment with a monoclonal antibody (MAb) against PMN, which induces profound neutropenia, prevented mortality and Evans blue diffusion in the brain and the lung, while it unexpectedly increased the occurrence of microhemorrhages. The anti-PMN MAb abolished PMN sequestration in the lung and also partially decreased monocyte sequestration in the brain and the lung. Treatment with an anti-CD11a MAb also prevented mortality, Evans blue diffusion, and PMN and monocyte sequestration. This study shows that PMN contribute to the mortality and the microvascular lesions resulting from severe malaria. This may be due to their CD11a-dependent sequestration in the lung and also to their indirect influence on vascular permeability and the sequestration of monocytes.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Chang H. R., Vesin C., Grau G. E., Pointaire P., Arsenijevic D., Strath M., Pechère J. C., Piguet P. F. Respective role of polymorphonuclear leukocytes and their integrins (CD-11/18) in the local or systemic toxicity of lipopolysaccharide. J Leukoc Biol. 1993 Jun;53(6):636–639. doi: 10.1002/jlb.53.6.636. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clark I. A., MacMicking J. D., Gray K. M., Rockett K. A., Cowden W. B. Malaria mimicry with tumor necrosis factor. Contrasts between species of murine malaria and Plasmodium falciparum. Am J Pathol. 1992 Feb;140(2):325–336. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dubravec D. B., Spriggs D. R., Mannick J. A., Rodrick M. L. Circulating human peripheral blood granulocytes synthesize and secrete tumor necrosis factor alpha. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Sep;87(17):6758–6761. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.17.6758. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Falanga P. B., Butcher E. C. Late treatment with anti-LFA-1 (CD11a) antibody prevents cerebral malaria in a mouse model. Eur J Immunol. 1991 Sep;21(9):2259–2263. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830210938. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goldblum S. E., Wu K. M., Jay M. Lung myeloperoxidase as a measure of pulmonary leukostasis in rabbits. J Appl Physiol (1985) 1985 Dec;59(6):1978–1985. doi: 10.1152/jappl.1985.59.6.1978. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grau G. E., Fajardo L. F., Piguet P. F., Allet B., Lambert P. H., Vassalli P. Tumor necrosis factor (cachectin) as an essential mediator in murine cerebral malaria. Science. 1987 Sep 4;237(4819):1210–1212. doi: 10.1126/science.3306918. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grau G. E., Piguet P. F., Engers H. D., Louis J. A., Vassalli P., Lambert P. H. L3T4+ T lymphocytes play a major role in the pathogenesis of murine cerebral malaria. J Immunol. 1986 Oct 1;137(7):2348–2354. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grau G. E., Pointaire P., Piguet P. F., Vesin C., Rosen H., Stamenkovic I., Takei F., Vassalli P. Late administration of monoclonal antibody to leukocyte function-antigen 1 abrogates incipient murine cerebral malaria. Eur J Immunol. 1991 Sep;21(9):2265–2267. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830210939. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grau G. E., Taylor T. E., Molyneux M. E., Wirima J. J., Vassalli P., Hommel M., Lambert P. H. Tumor necrosis factor and disease severity in children with falciparum malaria. N Engl J Med. 1989 Jun 15;320(24):1586–1591. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198906153202404. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kishimoto T. K., Larson R. S., Corbi A. L., Dustin M. L., Staunton D. E., Springer T. A. The leukocyte integrins. Adv Immunol. 1989;46:149–182. doi: 10.1016/s0065-2776(08)60653-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kudo C., Yamashita T., Terashita M., Sendo F. Modulation of in vivo immune response by selective depletion of neutrophils using a monoclonal antibody, RP-3. II. Inhibition by RP-3 treatment of mononuclear leukocyte recruitment in delayed-type hypersensitivity to sheep red blood cells in rats. J Immunol. 1993 May 1;150(9):3739–3746. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lopez A. F., Strath M., Sanderson C. J. Differentiation antigens on mouse eosinophils and neutrophils identified by monoclonal antibodies. Br J Haematol. 1984 Jul;57(3):489–494. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2141.1984.tb02923.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mackey L. J., Hochmann A., June C. H., Contreras C. E., Lambert P. H. Immunopathological aspects of Plasmodium berghei infection in five strains of mice. II. Immunopathology of cerebral and other tissue lesions during the infection. Clin Exp Immunol. 1980 Dec;42(3):412–420. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McCaffery P. J., Berridge M. V. Expression of the leukocyte functional molecule (LFA-1) on mouse platelets. Blood. 1986 Jun;67(6):1757–1764. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pierres M., Goridis C., Golstein P. Inhibition of murine T cell-mediated cytolysis and T cell proliferation by a rat monoclonal antibody immunoprecipitating two lymphoid cell surface polypeptides of 94 000 and 180 000 molecular weight. Eur J Immunol. 1982 Jan;12(1):60–69. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830120112. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Piguet P. F., Vesin C., Ryser J. E., Senaldi G., Grau G. E., Tacchini-Cottier F. An effector role for platelets in systemic and local lipopolysaccharide-induced toxicity in mice, mediated by a CD11a- and CD54-dependent interaction with endothelium. Infect Immun. 1993 Oct;61(10):4182–4187. doi: 10.1128/iai.61.10.4182-4187.1993. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pukrittayakamee S., Clemens R., Pramoolsinsap C., Karges H. E., Vanijanonta S., Bunnag D., White N. J. Polymorphonuclear leucocyte elastase in Plasmodium falciparum malaria. Trans R Soc Trop Med Hyg. 1992 Nov-Dec;86(6):598–601. doi: 10.1016/0035-9203(92)90143-z. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rest J. R. Cerebral malaria in inbred mice. I. A new model and its pathology. Trans R Soc Trop Med Hyg. 1982;76(3):410–415. doi: 10.1016/0035-9203(82)90203-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Román G. C. Cerebral malaria: the unsolved riddle. J Neurol Sci. 1991 Jan;101(1):1–6. doi: 10.1016/0022-510x(91)90012-v. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sheehan K. C., Ruddle N. H., Schreiber R. D. Generation and characterization of hamster monoclonal antibodies that neutralize murine tumor necrosis factors. J Immunol. 1989 Jun 1;142(11):3884–3893. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]