Abstract
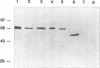
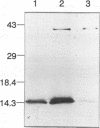
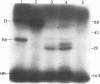
We report the sequencing of a 2,242-bp region of the Streptococcus mutants NG5 genome containing the genes for ptsH and ptsI, which encode HPr and enzyme I (EI), respectively, of the phosphoenolpyruvate-dependent phosphotransferase transport system. The sequence was obtained from two cloned overlapping genomic fragments; one expresses HPr and a truncated EI, while the other expresses a full-length EI in Escherichia coli, as determined by Western immunoblotting. The ptsI gene appeared to be expressed from a region located in the ptsH gene. The S. mutans NG5 pts operon does not appear to be linked to other phosphotransferase transport system proteins as has been found in other bacteria. A positive fermentation pattern on MacConkey-glucose plates by an E. coli ptsI mutant harboring the S. mutans NG5 ptsI gene on a plasmid indicated that the S. mutans NG5 EI can complement a defect in the E. coli gene. This was confirmed by protein phosphorylation experiments with 32P-labeled phosphoenolpyruvate indicating phosphotransfer from the S. mutans NG5 EI to the E. coli HPr. Two forms of the cloned EI, both truncated to varying degrees in the C-terminal region, were inefficiently phosphorylated and unable to complement fully the ptsI defect in the E. coli mutant. The deduced amino acid sequence of HPr shows a high degree of homology, particularly around the active site, to the same protein from other gram-positive bacteria, notably, S. salivarius, and to a lesser extent with those of gram-negative bacteria. The deduced amino acid sequence of S. mutans NG5 EI also shares several regions of homology with other sequenced EIs, notably, with the region around the active site, a region that contains the only conserved cystidyl residue among the various proteins and which may be involved in substrate binding.
Full text
PDF







Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Anderson J. W., Pullen K., Georges F., Klevit R. E., Waygood E. B. The involvement of the arginine 17 residue in the active site of the histidine-containing protein, HPr, of the phosphoenolpyruvate:sugar phosphotransferase system of Escherichia coli. J Biol Chem. 1993 Jun 15;268(17):12325–12333. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Beyreuther K., Raufuss H., Schrecker O., Hengstenberg W. The phosphoenolpyruvate-dependent phosphotransferase system of Staphylococcus aureus. 1. Amino-acid sequence of the phosphocarrier protein HPr. Eur J Biochem. 1977 May 2;75(1):275–286. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1977.tb11527.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Birnboim H. C. A rapid alkaline extraction method for the isolation of plasmid DNA. Methods Enzymol. 1983;100:243–255. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(83)00059-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bourassa S., Gauthier L., Giguère R., Vadeboncoeur C. A IIIman protein is involved in the transport of glucose, mannose and fructose by oral streptococci. Oral Microbiol Immunol. 1990 Oct;5(5):288–297. doi: 10.1111/j.1399-302x.1990.tb00427.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dayhoff M. O., Barker W. C., Hunt L. T. Establishing homologies in protein sequences. Methods Enzymol. 1983;91:524–545. doi: 10.1016/s0076-6879(83)91049-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- De Reuse H., Danchin A. The ptsH, ptsI, and crr genes of the Escherichia coli phosphoenolpyruvate-dependent phosphotransferase system: a complex operon with several modes of transcription. J Bacteriol. 1988 Sep;170(9):3827–3837. doi: 10.1128/jb.170.9.3827-3837.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- De Reuse H., Roy A., Danchin A. Analysis of the ptsH-ptsI-crr region in Escherichia coli K-12: nucleotide sequence of the ptsH gene. Gene. 1985;35(1-2):199–207. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(85)90172-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Deutscher J., Pevec B., Beyreuther K., Kiltz H. H., Hengstenberg W. Streptococcal phosphoenolpyruvate-sugar phosphotransferase system: amino acid sequence and site of ATP-dependent phosphorylation of HPr. Biochemistry. 1986 Oct 21;25(21):6543–6551. doi: 10.1021/bi00369a031. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dillard J. P., Yother J. Analysis of Streptococcus pneumoniae sequences cloned into Escherichia coli: effect of promoter strength and transcription terminators. J Bacteriol. 1991 Aug;173(16):5105–5109. doi: 10.1128/jb.173.16.5105-5109.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dower W. J., Miller J. F., Ragsdale C. W. High efficiency transformation of E. coli by high voltage electroporation. Nucleic Acids Res. 1988 Jul 11;16(13):6127–6145. doi: 10.1093/nar/16.13.6127. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eisermann R., Fischer R., Kessler U., Neubauer A., Hengstenberg W. Staphylococcal phosphoenolpyruvate-dependent phosphotransferase system. Purification and protein sequencing of the Staphylococcus carnosus histidine-containing protein, and cloning and DNA sequencing of the ptsH gene. Eur J Biochem. 1991 Apr 10;197(1):9–14. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1991.tb15875.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Frischauf A. M., Lehrach H., Poustka A., Murray N. Lambda replacement vectors carrying polylinker sequences. J Mol Biol. 1983 Nov 15;170(4):827–842. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(83)80190-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gagnon G., Vadeboncoeur C., Levesque R. C., Frenette M. Cloning, sequencing and expression in Escherichia coli of the ptsI gene encoding enzyme I of the phosphoenolpyruvate:sugar phosphotransferase transport system from Streptococcus salivarius. Gene. 1992 Nov 2;121(1):71–78. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(92)90163-j. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gauthier L., Mayrand D., Vadeboncoeur C. Isolation of a novel protein involved in the transport of fructose by an inducible phosphoenolpyruvate fructose phosphotransferase system in Streptococcus mutans. J Bacteriol. 1984 Nov;160(2):755–763. doi: 10.1128/jb.160.2.755-763.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gonzy-Tréboul G., Steinmetz M. Phosphoenolpyruvate:sugar phosphotransferase system of Bacillus subtilis: cloning of the region containing the ptsH and ptsI genes and evidence for a crr-like gene. J Bacteriol. 1987 May;169(5):2287–2290. doi: 10.1128/jb.169.5.2287-2290.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gonzy-Tréboul G., Zagorec M., Rain-Guion M. C., Steinmetz M. Phosphoenolpyruvate:sugar phosphotransferase system of Bacillus subtilis: nucleotide sequence of ptsX, ptsH and the 5'-end of ptsI and evidence for a ptsHI operon. Mol Microbiol. 1989 Jan;3(1):103–112. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2958.1989.tb00109.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gottesman M. M., Hicks M. L., Gellert M. Genetics and function of DNA ligase in Escherichia coli. J Mol Biol. 1973 Jul 15;77(4):531–547. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(73)90221-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Graves M. C., Rabinowitz J. C. In vivo and in vitro transcription of the Clostridium pasteurianum ferredoxin gene. Evidence for "extended" promoter elements in gram-positive organisms. J Biol Chem. 1986 Aug 25;261(24):11409–11415. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hamada S., Slade H. D. Biology, immunology, and cariogenicity of Streptococcus mutans. Microbiol Rev. 1980 Jun;44(2):331–384. doi: 10.1128/mr.44.2.331-384.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hamilton I. R., Gauthier L., Desjardins B., Vadeboncoeur C. Concentration-dependent repression of the soluble and membrane components of the Streptococcus mutans phosphoenolpyruvate: sugar phosphotransferase system by glucose. J Bacteriol. 1989 Jun;171(6):2942–2948. doi: 10.1128/jb.171.6.2942-2948.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Henikoff S. Unidirectional digestion with exonuclease III creates targeted breakpoints for DNA sequencing. Gene. 1984 Jun;28(3):351–359. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(84)90153-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Higgins D. G., Bleasby A. J., Fuchs R. CLUSTAL V: improved software for multiple sequence alignment. Comput Appl Biosci. 1992 Apr;8(2):189–191. doi: 10.1093/bioinformatics/8.2.189. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaslow D. C. A rapid biochemical method for purifying lambda DNA from phage lysates. Nucleic Acids Res. 1986 Aug 26;14(16):6767–6767. doi: 10.1093/nar/14.16.6767. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kohlbrecher D., Eisermann R., Hengstenberg W. Staphylococcal phosphoenolpyruvate-dependent phosphotransferase system: molecular cloning and nucleotide sequence of the Staphylococcus carnosus ptsI gene and expression and complementation studies of the gene product. J Bacteriol. 1992 Apr;174(7):2208–2214. doi: 10.1128/jb.174.7.2208-2214.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kruse R., Hengstenberg W., Beneicke W., Kalbitzer H. R. Involvement of various amino- and carboxyl-terminal residues in the active site of the histidine-containing protein HPr of the phosphoenolpyruvate-dependent phosphotransferase system of Staphylococcus carnosus: site-directed mutagenesis with the ptsH gene, biochemical characterization and NMR studies of the mutant proteins. Protein Eng. 1993 Jun;6(4):417–423. doi: 10.1093/protein/6.4.417. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LOWRY O. H., ROSEBROUGH N. J., FARR A. L., RANDALL R. J. Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem. 1951 Nov;193(1):265–275. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Loesche W. J. Role of Streptococcus mutans in human dental decay. Microbiol Rev. 1986 Dec;50(4):353–380. doi: 10.1128/mr.50.4.353-380.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Macrina F. L., Evans R. P., Tobian J. A., Hartley D. L., Clewell D. B., Jones K. R. Novel shuttle plasmid vehicles for Escherichia-Streptococcus transgeneric cloning. Gene. 1983 Nov;25(1):145–150. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(83)90176-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mattoo R. L., Waygood E. B. An enzymatic method for [32P]phosphoenolpyruvate synthesis. Anal Biochem. 1983 Jan;128(1):245–249. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(83)90372-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mulligan M. E., McClure W. R. Analysis of the occurrence of promoter-sites in DNA. Nucleic Acids Res. 1986 Jan 10;14(1):109–126. doi: 10.1093/nar/14.1.109. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pocalyko D. J., Carroll L. J., Martin B. M., Babbitt P. C., Dunaway-Mariano D. Analysis of sequence homologies in plant and bacterial pyruvate phosphate dikinase, enzyme I of the bacterial phosphoenolpyruvate: sugar phosphotransferase system and other PEP-utilizing enzymes. Identification of potential catalytic and regulatory motifs. Biochemistry. 1990 Dec 4;29(48):10757–10765. doi: 10.1021/bi00500a006. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Postma P. W., Lengeler J. W. Phosphoenolpyruvate:carbohydrate phosphotransferase system of bacteria. Microbiol Rev. 1985 Sep;49(3):232–269. doi: 10.1128/mr.49.3.232-269.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pries A., Priefert H., Krüger N., Steinbüchel A. Identification and characterization of two Alcaligenes eutrophus gene loci relevant to the poly(beta-hydroxybutyric acid)-leaky phenotype which exhibit homology to ptsH and ptsI of Escherichia coli. J Bacteriol. 1991 Sep;173(18):5843–5853. doi: 10.1128/jb.173.18.5843-5853.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reizer J., Hoischen C., Reizer A., Pham T. N., Saier M. H., Jr Sequence analyses and evolutionary relationships among the energy-coupling proteins Enzyme I and HPr of the bacterial phosphoenolpyruvate: sugar phosphotransferase system. Protein Sci. 1993 Apr;2(4):506–521. doi: 10.1002/pro.5560020403. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Robitaille D., Gauthier L., Vadeboncoeur C. The presence of two forms of the phosphocarrier protein HPr of the phosphoenolpyruvate:sugar phosphotransferase system in streptococci. Biochimie. 1991 May;73(5):573–581. doi: 10.1016/0300-9084(91)90025-v. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roeske C. A., Kutny R. M., Budde R. J., Chollet R. Sequence of the phosphothreonyl regulatory site peptide from inactive maize leaf pyruvate, orthophosphate dikinase. J Biol Chem. 1988 May 15;263(14):6683–6687. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Saffen D. W., Presper K. A., Doering T. L., Roseman S. Sugar transport by the bacterial phosphotransferase system. Molecular cloning and structural analysis of the Escherichia coli ptsH, ptsI, and crr genes. J Biol Chem. 1987 Nov 25;262(33):16241–16253. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanger F., Nicklen S., Coulson A. R. DNA sequencing with chain-terminating inhibitors. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Dec;74(12):5463–5467. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.12.5463. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thibault L., Vadeboncoeur C. Phosphoenolpyruvate-sugar phosphotransferase transport system of Streptococcus mutans: purification of HPr and enzyme I and determination of their intracellular concentrations by rocket immunoelectrophoresis. Infect Immun. 1985 Dec;50(3):817–825. doi: 10.1128/iai.50.3.817-825.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tinoco I., Jr, Borer P. N., Dengler B., Levin M. D., Uhlenbeck O. C., Crothers D. M., Bralla J. Improved estimation of secondary structure in ribonucleic acids. Nat New Biol. 1973 Nov 14;246(150):40–41. doi: 10.1038/newbio246040a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Towbin H., Staehelin T., Gordon J. Electrophoretic transfer of proteins from polyacrylamide gels to nitrocellulose sheets: procedure and some applications. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Sep;76(9):4350–4354. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.9.4350. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vadeboncoeur C., Gauthier L. The phosphoenolpyruvate: sugar phosphotransferase system of Streptococcus salivarius. Identification of a IIIman protein. Can J Microbiol. 1987 Feb;33(2):118–122. doi: 10.1139/m87-020. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vadeboncoeur C., Konishi Y., Dumas F., Gauthier L., Frenette M. HPr polymorphism in oral streptococci is caused by the partial removal of the N-terminal methionine. Biochimie. 1991 Nov;73(11):1427–1430. doi: 10.1016/0300-9084(91)90174-y. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vadeboncoeur C., Proulx M. Lactose transport in Streptococcus mutans: isolation and characterization of factor IIIlac, a specific protein component of the phosphoenolpyruvate-lactose phosphotransferase system. Infect Immun. 1984 Oct;46(1):213–219. doi: 10.1128/iai.46.1.213-219.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vadeboncoeur C., Proulx M., Trahan L. Purification of proteins similar to HPr and enzyme I from the oral bacterium Streptococcus salivarius. Biochemical and immunochemical properties. Can J Microbiol. 1983 Dec;29(12):1694–1705. doi: 10.1139/m83-260. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vadeboncoeur C., St Martin S., Brochu D., Hamilton I. R. Effect of growth rate and pH on intracellular levels and activities of the components of the phosphoenolpyruvate: sugar phosphotransferase system in Streptococcus mutans Ingbritt. Infect Immun. 1991 Mar;59(3):900–906. doi: 10.1128/iai.59.3.900-906.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vadeboncoeur C., Thibault L., Neron S., Halvorson H., Hamilton I. R. Effect of growth conditions on levels of components of the phosphoenolpyruvate:sugar phosphotransferase system in Streptococcus mutans and Streptococcus sobrinus grown in continuous culture. J Bacteriol. 1987 Dec;169(12):5686–5691. doi: 10.1128/jb.169.12.5686-5691.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vieira J., Messing J. The pUC plasmids, an M13mp7-derived system for insertion mutagenesis and sequencing with synthetic universal primers. Gene. 1982 Oct;19(3):259–268. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(82)90015-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wu L. F., Tomich J. M., Saier M. H., Jr Structure and evolution of a multidomain multiphosphoryl transfer protein. Nucleotide sequence of the fruB(HI) gene in Rhodobacter capsulatus and comparisons with homologous genes from other organisms. J Mol Biol. 1990 Jun 20;213(4):687–703. doi: 10.1016/S0022-2836(05)80256-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]