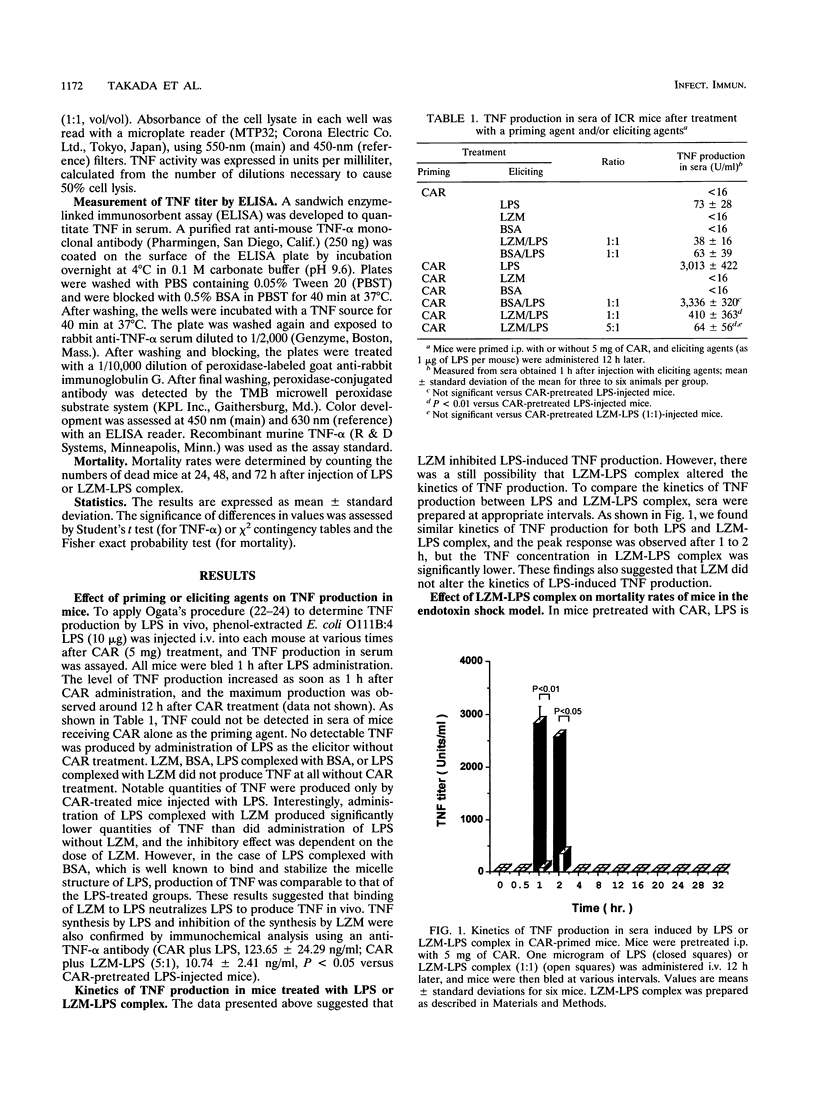
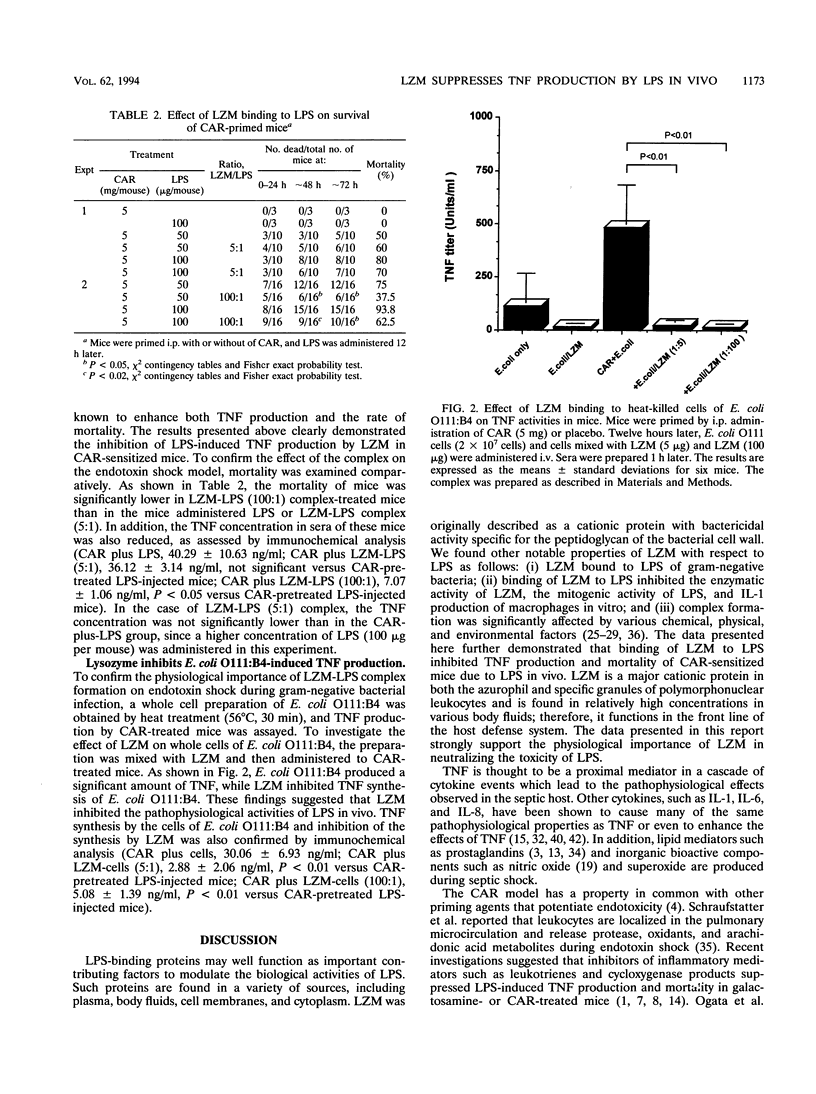
Abstract
Endotoxin (lipopolysaccharide [LPS]) released during gram-negative bacterial infection induces varieties of cytokines which directly and/or indirectly cause shock, disseminated intravascular coagulation, and death. We previously showed that lysozyme (LZM) was an LPS-binding protein and inhibited various immunomodulating activities of LPS. In this study, we examined the effect of LZM on the LPS-triggered septic shock model induced by carrageenan treatment and assessed by tumor necrosis factor production. The data presented in this report strongly suggest that LZM-LPS complex formation completely abrogates tumor necrosis factor production and the mortality caused by LPS and that LZM may be useful for the treatment of endotoxin shock.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Aketagawa J., Miyata T., Ohtsubo S., Nakamura T., Morita T., Hayashida H., Miyata T., Iwanaga S., Takao T., Shimonishi Y. Primary structure of limulus anticoagulant anti-lipopolysaccharide factor. J Biol Chem. 1986 Jun 5;261(16):7357–7365. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ball H. A., Cook J. A., Wise W. C., Halushka P. V. Role of thromboxane, prostaglandins and leukotrienes in endotoxic and septic shock. Intensive Care Med. 1986;12(3):116–126. doi: 10.1007/BF00254925. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Becker L. J., Rudbach J. A. Potentiation of endotoxicity by carrageenan. Infect Immun. 1978 Mar;19(3):1099–1100. doi: 10.1128/iai.19.3.1099-1100.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Beutler B., Milsark I. W., Cerami A. C. Passive immunization against cachectin/tumor necrosis factor protects mice from lethal effect of endotoxin. Science. 1985 Aug 30;229(4716):869–871. doi: 10.1126/science.3895437. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chajek T., Eisenberg S. Very low density lipoprotein. Metabolism of phospholipids, cholesterol, and apolipoprotein C in the isolated perfused rat heart. J Clin Invest. 1978 Jun;61(6):1654–1665. doi: 10.1172/JCI109086. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cook J. A., Wise W. C., Halushka P. V. Protective effect of a selective leukotriene antagonist in endotoxemia in the rat. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1985 Nov;235(2):470–474. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fry D. E., Pearlstein L., Fulton R. L., Polk H. C., Jr Multiple system organ failure. The role of uncontrolled infection. Arch Surg. 1980 Feb;115(2):136–140. doi: 10.1001/archsurg.1980.01380020006003. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Galanos C., Freudenberg M. A., Reutter W. Galactosamine-induced sensitization to the lethal effects of endotoxin. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Nov;76(11):5939–5943. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.11.5939. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Golenbock D. T., Hampton R. Y., Raetz C. R., Wright S. D. Human phagocytes have multiple lipid A-binding sites. Infect Immun. 1990 Dec;58(12):4069–4075. doi: 10.1128/iai.58.12.4069-4075.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kettelhut I. C., Fiers W., Goldberg A. L. The toxic effects of tumor necrosis factor in vivo and their prevention by cyclooxygenase inhibitors. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Jun;84(12):4273–4277. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.12.4273. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Le J., Vilcek J. Tumor necrosis factor and interleukin 1: cytokines with multiple overlapping biological activities. Lab Invest. 1987 Mar;56(3):234–248. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lehmann V., Freudenberg M. A., Galanos C. Lethal toxicity of lipopolysaccharide and tumor necrosis factor in normal and D-galactosamine-treated mice. J Exp Med. 1987 Mar 1;165(3):657–663. doi: 10.1084/jem.165.3.657. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lei M. G., Morrison D. C. Specific endotoxic lipopolysaccharide-binding proteins on murine splenocytes. I. Detection of lipopolysaccharide-binding sites on splenocytes and splenocyte subpopulations. J Immunol. 1988 Aug 1;141(3):996–1005. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lei M. G., Stimpson S. A., Morrison D. C. Specific endotoxic lipopolysaccharide-binding receptors on murine splenocytes. III. Binding specificity and characterization. J Immunol. 1991 Sep 15;147(6):1925–1932. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moncada S., Palmer R. M., Higgs E. A. Nitric oxide: physiology, pathophysiology, and pharmacology. Pharmacol Rev. 1991 Jun;43(2):109–142. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morrison D. C., Jacobs D. M. Inhibition of lipopolysaccharide-initiated activation of serum complement by polymyxin B. Infect Immun. 1976 Jan;13(1):298–301. doi: 10.1128/iai.13.1.298-301.1976. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Myers A. K., Robey J. W., Price R. M. Relationships between tumour necrosis factor, eicosanoids and platelet-activating factor as mediators of endotoxin-induced shock in mice. Br J Pharmacol. 1990 Mar;99(3):499–502. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1990.tb12957.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nakamura T., Furunaka H., Miyata T., Tokunaga F., Muta T., Iwanaga S., Niwa M., Takao T., Shimonishi Y. Tachyplesin, a class of antimicrobial peptide from the hemocytes of the horseshoe crab (Tachypleus tridentatus). Isolation and chemical structure. J Biol Chem. 1988 Nov 15;263(32):16709–16713. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ogata M., Matsumoto T., Kamochi M., Yoshida S. I., Mizuguchi Y., Shigematsu A. Protective effects of a leukotriene inhibitor and a leukotriene antagonist on endotoxin-induced mortality in carrageenan-pretreated mice. Infect Immun. 1992 Jun;60(6):2432–2437. doi: 10.1128/iai.60.6.2432-2437.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ogata M., Matsumoto T., Koga K., Takenaka I., Kamochi M., Sata T., Yoshida S., Shigematsu A. An antagonist of platelet-activating factor suppresses endotoxin-induced tumor necrosis factor and mortality in mice pretreated with carrageenan. Infect Immun. 1993 Feb;61(2):699–704. doi: 10.1128/iai.61.2.699-704.1993. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ogata M., Yoshida S., Kamochi M., Shigematsu A., Mizuguchi Y. Enhancement of lipopolysaccharide-induced tumor necrosis factor production in mice by carrageenan pretreatment. Infect Immun. 1991 Feb;59(2):679–683. doi: 10.1128/iai.59.2.679-683.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ohno N., Morrison D. C. Effects of lipopolysaccharide chemotype structure on binding and inactivation of hen egg lysozyme. Eur J Biochem. 1989 Dec 22;186(3):621–627. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1989.tb15252.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ohno N., Morrison D. C. Lipopolysaccharide interaction with lysozyme. Binding of lipopolysaccharide to lysozyme and inhibition of lysozyme enzymatic activity. J Biol Chem. 1989 Mar 15;264(8):4434–4441. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ohno N., Morrison D. C. Lipopolysaccharide interactions with lysozyme differentially affect lipopolysaccharide immunostimulatory activity. Eur J Biochem. 1989 Dec 22;186(3):629–636. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1989.tb15253.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ohno N., Tanida N., Yadomae T. Characterization of complex formation between lipopolysaccharide and lysozyme. Carbohydr Res. 1991 Jul 18;214(1):115–130. doi: 10.1016/s0008-6215(00)90535-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Okusawa S., Gelfand J. A., Ikejima T., Connolly R. J., Dinarello C. A. Interleukin 1 induces a shock-like state in rabbits. Synergism with tumor necrosis factor and the effect of cyclooxygenase inhibition. J Clin Invest. 1988 Apr;81(4):1162–1172. doi: 10.1172/JCI113431. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ooi C. E., Weiss J., Elsbach P., Frangione B., Mannion B. A 25-kDa NH2-terminal fragment carries all the antibacterial activities of the human neutrophil 60-kDa bactericidal/permeability-increasing protein. J Biol Chem. 1987 Nov 5;262(31):14891–14894. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Paul N. L., Ruddle N. H. Lymphotoxin. Annu Rev Immunol. 1988;6:407–438. doi: 10.1146/annurev.iy.06.040188.002203. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Raziuddin S., Morrison D. C. Binding of bacterial endotoxin (LPS) to encephalitogenic myelin basic protein and modulation of characteristic biologic activities of LPS. J Immunol. 1981 Mar;126(3):1030–1035. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schraufstatter I., Revak S. D., Cochrane C. G. Biochemical factors in pulmonary inflammatory disease. Fed Proc. 1984 Oct;43(13):2807–2810. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schumann R. R., Leong S. R., Flaggs G. W., Gray P. W., Wright S. D., Mathison J. C., Tobias P. S., Ulevitch R. J. Structure and function of lipopolysaccharide binding protein. Science. 1990 Sep 21;249(4975):1429–1431. doi: 10.1126/science.2402637. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tanida N., Ohno N., Adachi Y., Matsuura M., Nakano M., Kiso M., Hasegawa A., Yadomae T. Modification of immunopharmacological activities of synthetic monosaccharide lipid A analogue, GLA60, by lysozyme. J Biochem. 1992 Nov;112(5):616–623. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.jbchem.a123949. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tobias P. S., Soldau K., Ulevitch R. J. Isolation of a lipopolysaccharide-binding acute phase reactant from rabbit serum. J Exp Med. 1986 Sep 1;164(3):777–793. doi: 10.1084/jem.164.3.777. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tracey K. J., Beutler B., Lowry S. F., Merryweather J., Wolpe S., Milsark I. W., Hariri R. J., Fahey T. J., 3rd, Zentella A., Albert J. D. Shock and tissue injury induced by recombinant human cachectin. Science. 1986 Oct 24;234(4775):470–474. doi: 10.1126/science.3764421. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Waage A., Espevik T. Interleukin 1 potentiates the lethal effect of tumor necrosis factor alpha/cachectin in mice. J Exp Med. 1988 Jun 1;167(6):1987–1992. doi: 10.1084/jem.167.6.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wong G. G., Clark S. C. Multiple actions of interleukin 6 within a cytokine network. Immunol Today. 1988 May;9(5):137–139. doi: 10.1016/0167-5699(88)91200-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wright S. D., Ramos R. A., Hermanowski-Vosatka A., Rockwell P., Detmers P. A. Activation of the adhesive capacity of CR3 on neutrophils by endotoxin: dependence on lipopolysaccharide binding protein and CD14. J Exp Med. 1991 May 1;173(5):1281–1286. doi: 10.1084/jem.173.5.1281. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van der Poll T., Büller H. R., ten Cate H., Wortel C. H., Bauer K. A., van Deventer S. J., Hack C. E., Sauerwein H. P., Rosenberg R. D., ten Cate J. W. Activation of coagulation after administration of tumor necrosis factor to normal subjects. N Engl J Med. 1990 Jun 7;322(23):1622–1627. doi: 10.1056/NEJM199006073222302. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


