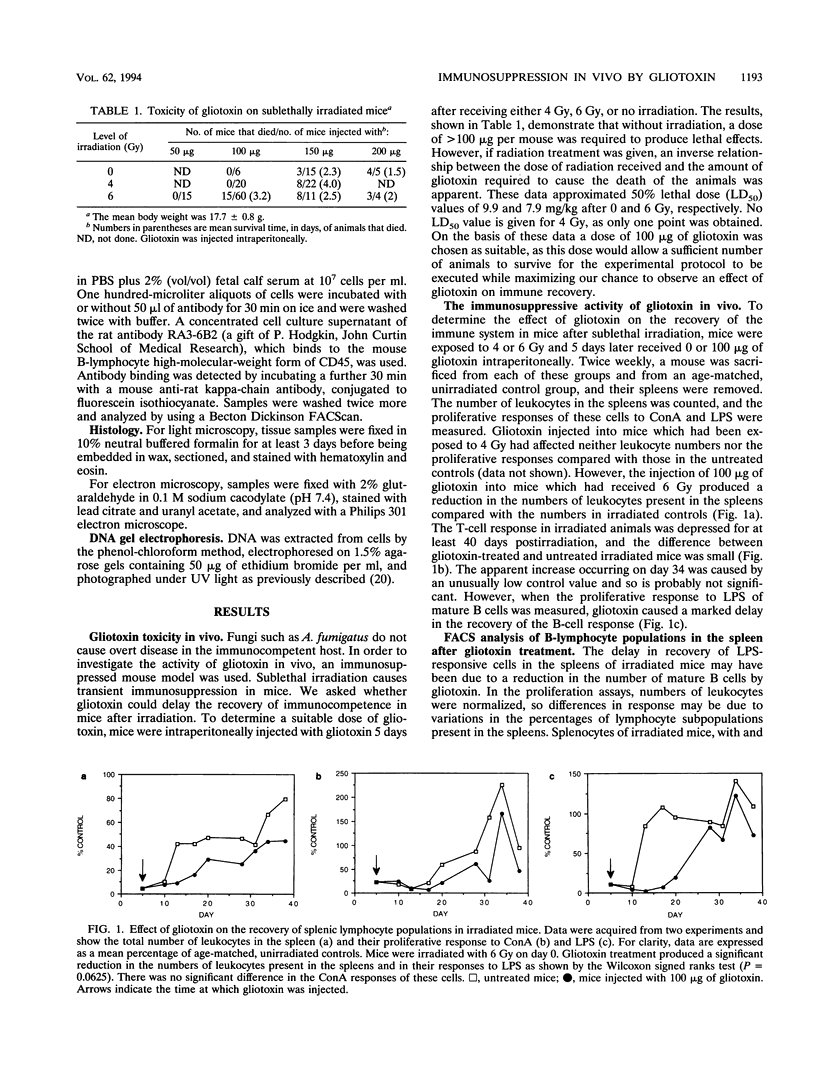
Abstract
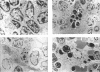
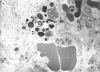
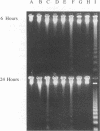
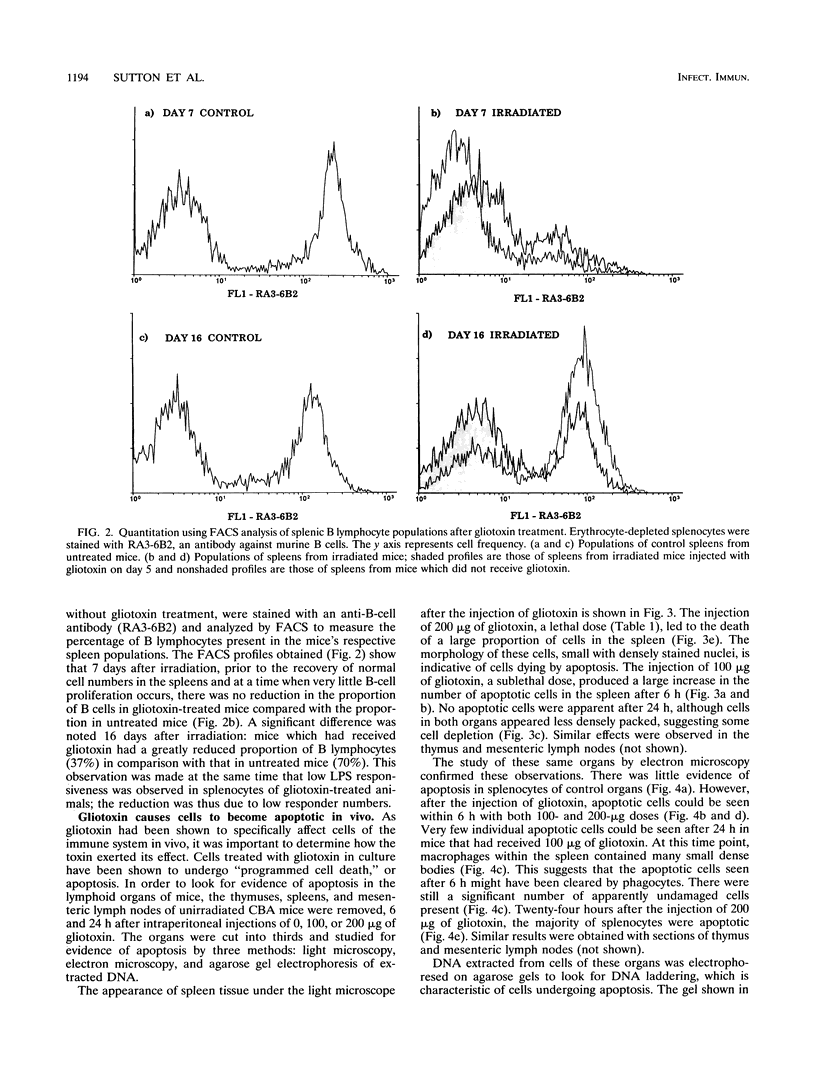
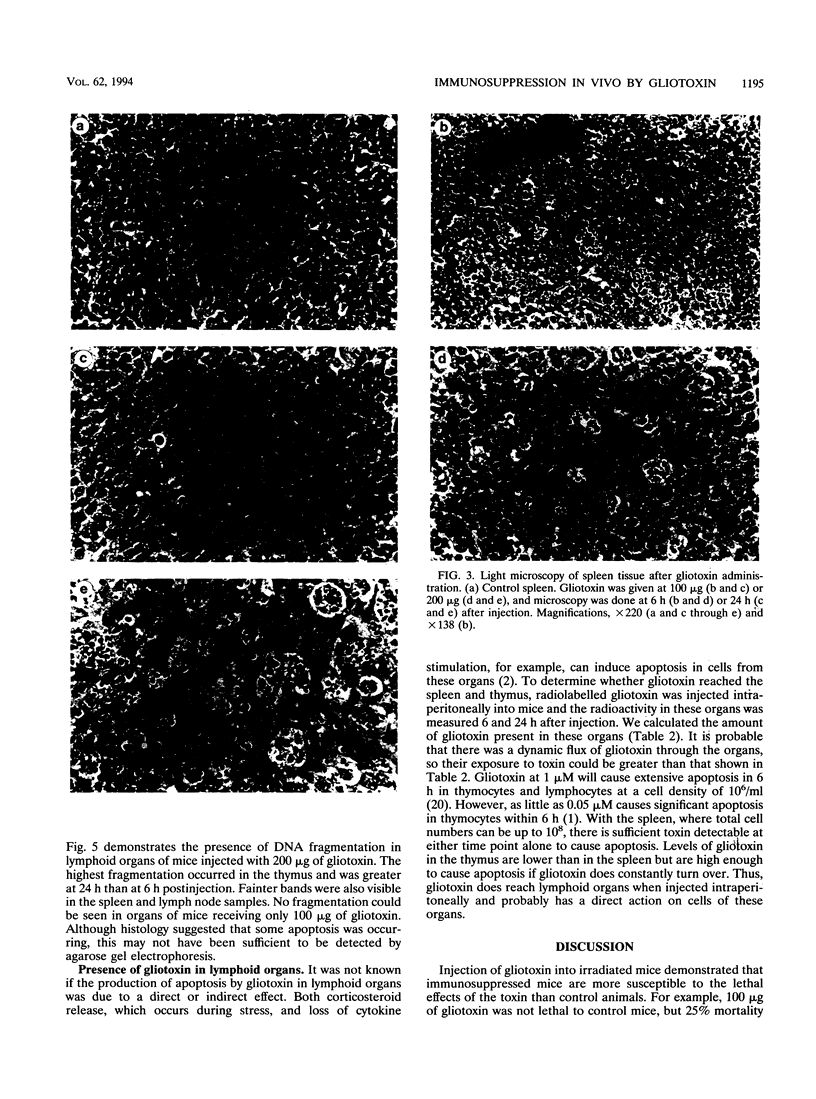
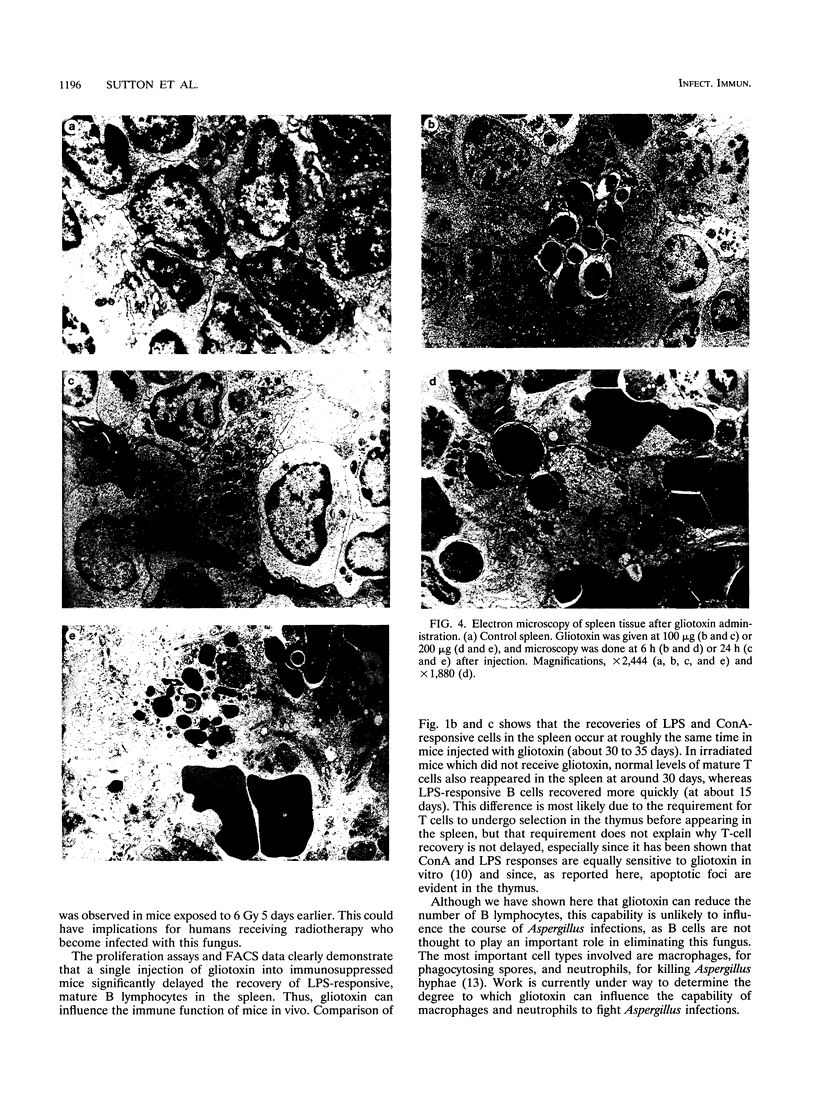
Aspergillosis is a disease caused by the opportunistic pathogen Aspergillus fumigatus and other related fungi. It occurs mainly in immunosuppressed people and causes very high mortality rates. A fumigatus and other pathogenic fungi have been shown to produce a metabolite, gliotoxin, which has immunosuppressive properties in vitro, but little is known about its in vivo activity. Here we report that gliotoxin has increased toxicity in mice after irradiation. A single injection of gliotoxin delayed the recovery of immune cells after immunosuppression by sublethal irradiation by 2 weeks. Study of the morphology of cells of the thymus, spleen, and mesenteric lymph nodes by light microscopy and electron microscopy and agarose gel electrophoresis of DNA from these organs showed that the injection of gliotoxin induced apoptosis in cells of the immune system in vivo. Thus, gliotoxin does have immunosuppressive activity in vivo and could potentially play a significant role in the pathogenesis of aspergillosis and other fungal diseases.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bodey G., Bueltmann B., Duguid W., Gibbs D., Hanak H., Hotchi M., Mall G., Martino P., Meunier F., Milliken S. Fungal infections in cancer patients: an international autopsy survey. Eur J Clin Microbiol Infect Dis. 1992 Feb;11(2):99–109. doi: 10.1007/BF01967060. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cohen J. J., Duke R. C., Fadok V. A., Sellins K. S. Apoptosis and programmed cell death in immunity. Annu Rev Immunol. 1992;10:267–293. doi: 10.1146/annurev.iy.10.040192.001411. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Denning D. W., Tucker R. M., Hanson L. H., Stevens D. A. Treatment of invasive aspergillosis with itraconazole. Am J Med. 1989 Jun;86(6 Pt 2):791–800. doi: 10.1016/0002-9343(89)90475-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eichner R. D., Al Salami M., Wood P. R., Müllbacher A. The effect of gliotoxin upon macrophage function. Int J Immunopharmacol. 1986;8(7):789–797. doi: 10.1016/0192-0561(86)90016-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kusne S., Torre-Cisneros J., Mañez R., Irish W., Martin M., Fung J., Simmons R. L., Starzl T. E. Factors associated with invasive lung aspergillosis and the significance of positive Aspergillus culture after liver transplantation. J Infect Dis. 1992 Dec;166(6):1379–1383. doi: 10.1093/infdis/166.6.1379. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Murphy J. W. Immunity to fungi. Curr Opin Immunol. 1989;2(3):360–367. doi: 10.1016/0952-7915(89)90142-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Müllbacher A., Eichner R. D. Immunosuppression in vitro by a metabolite of a human pathogenic fungus. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Jun;81(12):3835–3837. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.12.3835. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Müllbacher A., Hume D., Braithwaite A. W., Waring P., Eichner R. D. Selective resistance of bone marrow-derived hemopoietic progenitor cells to gliotoxin. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Jun;84(11):3822–3825. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.11.3822. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Müllbacher A., Moreland A. F., Waring P., Sjaarda A., Eichner R. D. Prevention of graft-versus-host disease by treatment of bone marrow with gliotoxin in fully allogeneic chimeras and their cytotoxic T cell repertoire. Transplantation. 1988 Jul;46(1):120–125. doi: 10.1097/00007890-198807000-00022. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Müllbacher A., Waring P., Tiwari-Palni U., Eichner R. D. Structural relationship of epipolythiodioxopiperazines and their immunomodulating activity. Mol Immunol. 1986 Feb;23(2):231–235. doi: 10.1016/0161-5890(86)90047-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shah D. T., Larsen B. Clinical isolates of yeast produce a gliotoxin-like substance. Mycopathologia. 1991 Dec;116(3):203–208. doi: 10.1007/BF00436836. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Torre-Cisneros J., Mañez R., Kusne S., Alessiani M., Martin M., Starzl T. E. The spectrum of aspergillosis in liver transplant patients: comparison of FK 506 and cyclosporine immunosuppression. Transplant Proc. 1991 Dec;23(6):3040–3041. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wajszczuk C. P., Dummer J. S., Ho M., Van Thiel D. H., Starzl T. E., Iwatsuki S., Shaw B., Jr Fungal infections in liver transplant recipients. Transplantation. 1985 Oct;40(4):347–353. doi: 10.1097/00007890-198510000-00002. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Waring P. DNA fragmentation induced in macrophages by gliotoxin does not require protein synthesis and is preceded by raised inositol triphosphate levels. J Biol Chem. 1990 Aug 25;265(24):14476–14480. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]