Abstract
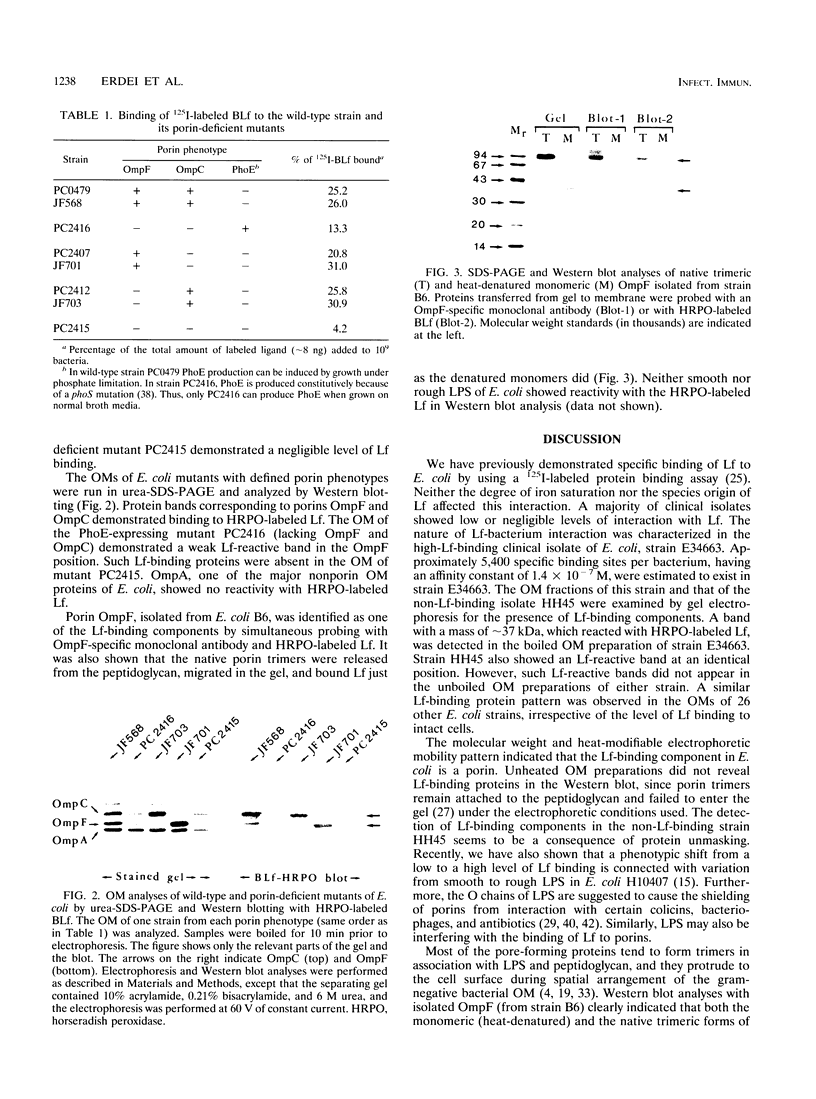
Lactoferrin (Lf) is an iron-binding antimicrobial protein present in milk and on mucosal surfaces, with a suggested role in preimmune host defense. Certain strains of Escherichia coli (bacterial whole cells) demonstrate specific interaction with 125I-labeled Lf. A band with a mass of approximately 37 kDa, which was reactive with horseradish peroxidase-labeled Lf, was identified in the boiled cell envelope and outer membrane preparations of an Lf-binding E. coli strain, E34663, and a non-Lf-binding strain, HH45, by sodium dodecyl sulfate-polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis (SDS-PAGE) and Western blotting (immunoblotting). Such a band was not detected in the unboiled native cell envelope and outer membrane preparations. The molecular mass and the property of heat modifiability suggested that the Lf-binding proteins were porins. The native trimeric form of porin OmpF isolated from strain B6 and its dissociated monomeric form both reacted with horseradish peroxidase-labeled Lf and with monoclonal antibodies specific for OmpF. Furthermore, by using E. coli constructs with defined porin phenotypes, OmpF and OmpC were identified as the Lf-binding proteins by urea-SDS-PAGE and Western blotting and by 125I-Lf binding studies with intact bacteria. These data establish that Lf binds to porins, a class of well-conserved molecules common in E. coli and many other gram-negative bacteria. However, in certain strains of E. coli these pore-forming proteins are shielded from Lf interaction.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Arnold R. R., Cole M. F., McGhee J. R. A bactericidal effect for human lactoferrin. Science. 1977 Jul 15;197(4300):263–265. doi: 10.1126/science.327545. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baggiolini M., De Duve C., Masson P. L., Heremans J. F. Association of lactoferrin with specific granules in rabbit heterophil leukocytes. J Exp Med. 1970 Mar 1;131(3):559–570. doi: 10.1084/jem.131.3.559. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bennett R. M., Davis J. Lactoferrin binding to human peripheral blood cells: an interaction with a B-enriched population of lymphocytes and a subpopulation of adherent mononuclear cells. J Immunol. 1981 Sep;127(3):1211–1216. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Benz R. Structure and function of porins from gram-negative bacteria. Annu Rev Microbiol. 1988;42:359–393. doi: 10.1146/annurev.mi.42.100188.002043. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Birgens H. S. The biological significance of lactoferrin in haematology. Scand J Haematol. 1984 Sep;33(3):225–230. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-0609.1984.tb02220.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Broxmeyer H. E., Smithyman A., Eger R. R., Meyers P. A., de Sousa M. Identification of lactoferrin as the granulocyte-derived inhibitor of colony-stimulating activity production. J Exp Med. 1978 Oct 1;148(4):1052–1067. doi: 10.1084/jem.148.4.1052. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bullen J. J., Rogers H. J., Leigh L. Iron-binding proteins in milk and resistance to Escherichia coli infection in infants. Br Med J. 1972 Jan 8;1(5792):69–75. doi: 10.1136/bmj.1.5792.69. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dalmastri C., Valenti P., Visca P., Vittorioso P., Orsi N. Enhanced antimicrobial activity of lactoferrin by binding to the bacterial surface. Microbiologica. 1988 Jul;11(3):225–230. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Duncan R. L., Jr, McArthur W. P. Lactoferrin-mediated modulation of mononuclear cell activities. I. Suppression of the murine in vitro primary antibody responses. Cell Immunol. 1981 Sep 15;63(2):308–320. doi: 10.1016/0008-8749(81)90010-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ellison R. T., 3rd, Giehl T. J., LaForce F. M. Damage of the outer membrane of enteric gram-negative bacteria by lactoferrin and transferrin. Infect Immun. 1988 Nov;56(11):2774–2781. doi: 10.1128/iai.56.11.2774-2781.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Filip C., Fletcher G., Wulff J. L., Earhart C. F. Solubilization of the cytoplasmic membrane of Escherichia coli by the ionic detergent sodium-lauryl sarcosinate. J Bacteriol. 1973 Sep;115(3):717–722. doi: 10.1128/jb.115.3.717-722.1973. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Foulds J., Chai T. Isolation and characterization of isogenic E. coli strains with alterations in the level of one or more major outer membrane proteins. Can J Microbiol. 1979 Mar;25(3):423–427. doi: 10.1139/m79-065. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gadó I., Erdei J., Laszlo V. G., Pászti J., Czirók E., Kontrohr T., Tóth I., Forsgren A., Naidu A. S. Correlation between human lactoferrin binding and colicin susceptibility in Escherichia coli. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1991 Dec;35(12):2538–2543. doi: 10.1128/aac.35.12.2538. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kishore A. R., Erdei J., Naidu S. S., Falsen E., Forsgren A., Naidu A. S. Specific binding of lactoferrin to Aeromonas hydrophila. FEMS Microbiol Lett. 1991 Sep 15;67(1):115–119. doi: 10.1016/0378-1097(91)90454-i. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Law B. A., Reiter B. The isolation and bacteriostatic properties of lactoferrin from bovine milk whey. J Dairy Res. 1977 Oct;44(3):595–599. doi: 10.1017/s0022029900020550. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lugtenberg B., Van Alphen L. Molecular architecture and functioning of the outer membrane of Escherichia coli and other gram-negative bacteria. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1983 Mar 21;737(1):51–115. doi: 10.1016/0304-4157(83)90014-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maneva A. I., Sirakov L. M., Manev V. V. Lactoferrin binding to neutrophilic polymorphonuclear leucocytes. Int J Biochem. 1983;15(7):981–984. doi: 10.1016/0020-711x(83)90179-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miyazawa K., Mantel C., Lu L., Morrison D. C., Broxmeyer H. E. Lactoferrin-lipopolysaccharide interactions. Effect on lactoferrin binding to monocyte/macrophage-differentiated HL-60 cells. J Immunol. 1991 Jan 15;146(2):723–729. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Naidu A. S., Miedzobrodzki J., Andersson M., Nilsson L. E., Forsgren A., Watts J. L. Bovine lactoferrin binding to six species of coagulase-negative staphylococci isolated from bovine intramammary infections. J Clin Microbiol. 1990 Oct;28(10):2312–2319. doi: 10.1128/jcm.28.10.2312-2319.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Naidu A. S., Miedzobrodzki J., Musser J. M., Rosdahl V. T., Hedström S. A., Forsgren A. Human lactoferrin binding in clinical isolates of Staphylococcus aureus. J Med Microbiol. 1991 Jun;34(6):323–328. doi: 10.1099/00222615-34-6-323. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Naidu S. S., Erdei J., Czirók E., Kalfas S., Gadó I., Thorén A., Forsgren A., Naidu A. S. Specific binding of lactoferrin to Escherichia coli isolated from human intestinal infections. APMIS. 1991 Dec;99(12):1142–1150. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Naidu S. S., Svensson U., Kishore A. R., Naidu A. S. Relationship between antibacterial activity and porin binding of lactoferrin in Escherichia coli and Salmonella typhimurium. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1993 Feb;37(2):240–245. doi: 10.1128/aac.37.2.240. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nakamura K., Mizushima S. Effects of heating in dodecyl sulfate solution on the conformation and electrophoretic mobility of isolated major outer membrane proteins from Escherichia coli K-12. J Biochem. 1976 Dec;80(6):1411–1422. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.jbchem.a131414. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nakane P. K., Kawaoi A. Peroxidase-labeled antibody. A new method of conjugation. J Histochem Cytochem. 1974 Dec;22(12):1084–1091. doi: 10.1177/22.12.1084. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nikaido H. Outer membrane barrier as a mechanism of antimicrobial resistance. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1989 Nov;33(11):1831–1836. doi: 10.1128/aac.33.11.1831. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oseas R., Yang H. H., Baehner R. L., Boxer L. A. Lactoferrin: a promoter of polymorphonuclear leukocyte adhesiveness. Blood. 1981 May;57(5):939–945. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reite B., Oram J. D. Bacterial inhibitors in milk and other biological fluids. Nature. 1967 Oct 28;216(5113):328–330. doi: 10.1038/216328a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rochard E., Legrand D., Mazurier J., Montreuil J., Spik G. The N-terminal domain I of human lactotransferrin binds specifically to phytohemagglutinin-stimulated peripheral blood human lymphocyte receptors. FEBS Lett. 1989 Sep 11;255(1):201–204. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(89)81091-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rocque W. J., Coughlin R. T., McGroarty E. J. Lipopolysaccharide tightly bound to porin monomers and trimers from Escherichia coli K-12. J Bacteriol. 1987 Sep;169(9):4003–4010. doi: 10.1128/jb.169.9.4003-4010.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rosenbusch J. P. Characterization of the major envelope protein from Escherichia coli. Regular arrangement on the peptidoglycan and unusual dodecyl sulfate binding. J Biol Chem. 1974 Dec 25;249(24):8019–8029. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schnaitman C. A. Outer membrane proteins of Escherichia coli. I. Effect of preparative conditions on the migration of protein in polyacrylamide gels. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1973 Aug;157(2):541–552. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(73)90673-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stuart J., Norrell S., Harrington J. P. Kinetic effect of human lactoferrin on the growth of Escherichia coli 0111. Int J Biochem. 1984;16(10):1043–1047. doi: 10.1016/0020-711x(84)90085-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tigyi Z., Kishore A. R., Maeland J. A., Forsgren A., Naidu A. S. Lactoferrin-binding proteins in Shigella flexneri. Infect Immun. 1992 Jul;60(7):2619–2626. doi: 10.1128/iai.60.7.2619-2626.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tommassen J., Lugtenberg B. Outer membrane protein e of Escherichia coli K-12 is co-regulated with alkaline phosphatase. J Bacteriol. 1980 Jul;143(1):151–157. doi: 10.1128/jb.143.1.151-157.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Van Snick J. L., Masson P. L. The binding of human lactoferrin to mouse peritoneal cells. J Exp Med. 1976 Dec 1;144(6):1568–1580. doi: 10.1084/jem.144.6.1568. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yu F., Mizushima S. Roles of lipopolysaccharide and outer membrane protein OmpC of Escherichia coli K-12 in the receptor function for bacteriophage T4. J Bacteriol. 1982 Aug;151(2):718–722. doi: 10.1128/jb.151.2.718-722.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van Alphen W., van Seim N., Lugtenberg B. Pores in the outer membrane of Escherichia coli K12: involvement of proteins b and e in the functioning of pores for nucleotides. Mol Gen Genet. 1978 Feb 7;159(1):75–83. doi: 10.1007/BF00401750. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van der Ley P., de Graaff P., Tommassen J. Shielding of Escherichia coli outer membrane proteins as receptors for bacteriophages and colicins by O-antigenic chains of lipopolysaccharide. J Bacteriol. 1986 Oct;168(1):449–451. doi: 10.1128/jb.168.1.449-451.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]






