Abstract
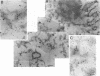
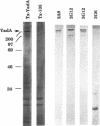
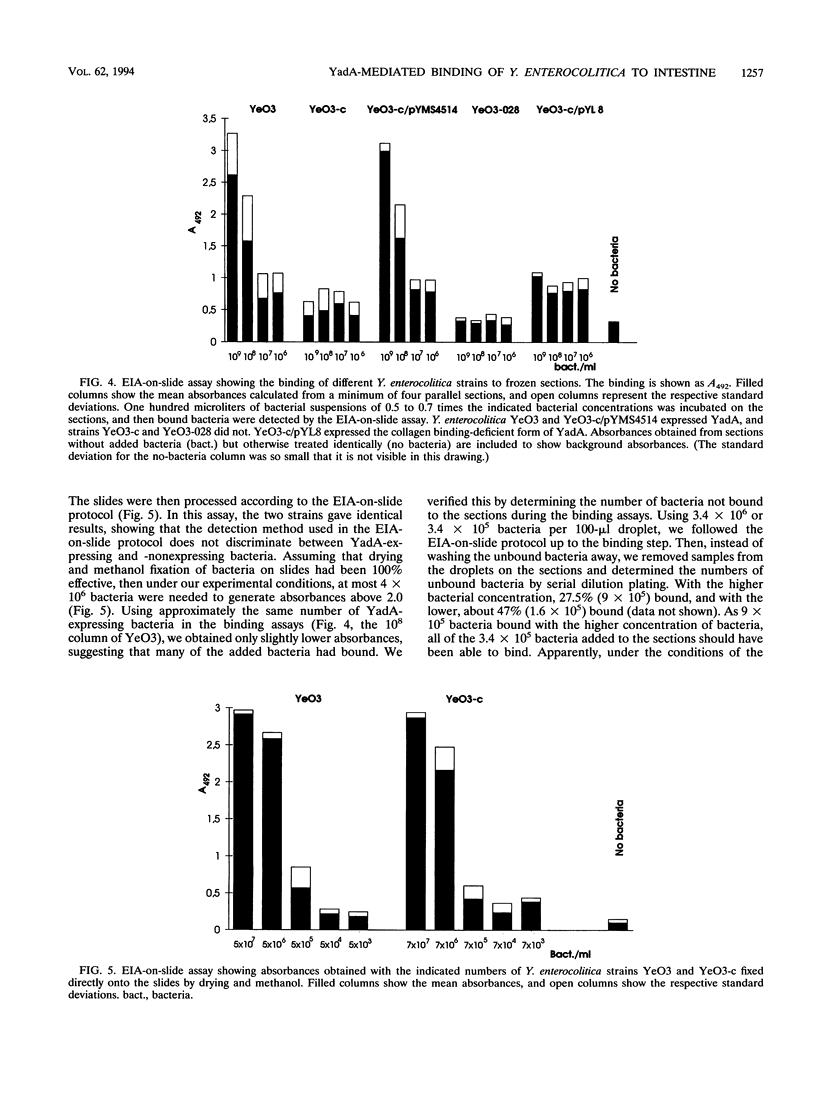
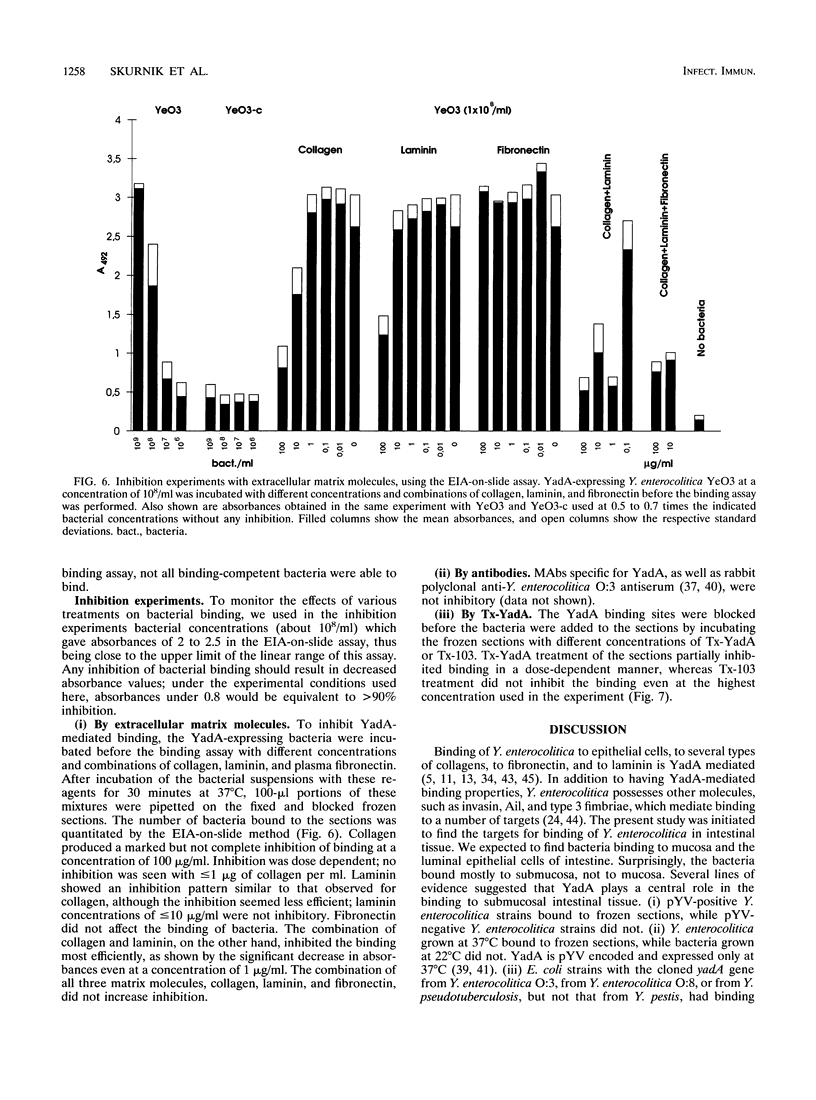
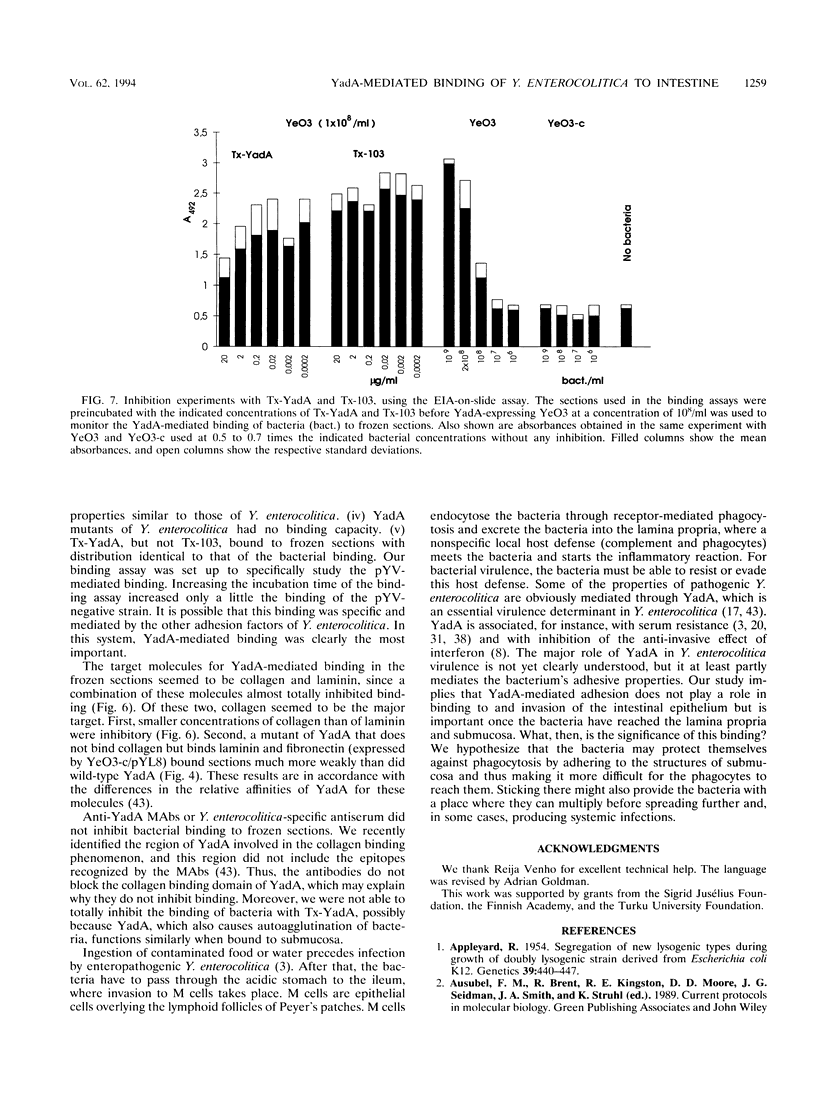
The binding of live Yersinia enterocolitica to frozen sections of human intestine was investigated qualitatively by monitoring the binding of bacteria by using Gram or immunoperoxidase staining as well as quantitatively by a new enzyme immunoassay-on-slide method. We have demonstrated that the binding of various Y. enterocolitica serotypes and Escherichia coli clones to frozen sections of human intestine is mediated by the Yersinia adhesin, YadA. The YadA-mediated binding occurs mainly at the submucosal layer of the intestinal wall and only to a limited extent at the mucosal layer; there binding is mostly to the mucin threads. In addition, partially purified YadA binds to frozen sections with a pattern similar to that of intact bacteria. Collagen, laminin, or partially purified YadA only partially inhibited the YadA-mediated binding of bacteria, presumably because YadA is multifunctional. A combination of collagen and laminin inhibited the binding more efficiently. Therefore, YadA may be involved in the interactions with the extracellular matrix molecules after the invasion of the intestinal tissue.
Full text
PDF




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Appleyard R K. Segregation of New Lysogenic Types during Growth of a Doubly Lysogenic Strain Derived from Escherichia Coli K12. Genetics. 1954 Jul;39(4):440–452. doi: 10.1093/genetics/39.4.440. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Balligand G., Laroche Y., Cornelis G. Genetic analysis of virulence plasmid from a serogroup 9 Yersinia enterocolitica strain: role of outer membrane protein P1 in resistance to human serum and autoagglutination. Infect Immun. 1985 Jun;48(3):782–786. doi: 10.1128/iai.48.3.782-786.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bliska J. B., Copass M. C., Falkow S. The Yersinia pseudotuberculosis adhesin YadA mediates intimate bacterial attachment to and entry into HEp-2 cells. Infect Immun. 1993 Sep;61(9):3914–3921. doi: 10.1128/iai.61.9.3914-3921.1993. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bordier C. Phase separation of integral membrane proteins in Triton X-114 solution. J Biol Chem. 1981 Feb 25;256(4):1604–1607. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brubaker R. R. The genus Yersinia: biochemistry and genetics of virulence. Curr Top Microbiol Immunol. 1972;57:111–158. doi: 10.1007/978-3-642-65297-4_4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bukholm G., Kapperud G., Skurnik M. Genetic evidence that the yopA gene-encoded Yersinia outer membrane protein Yop1 mediates inhibition of the anti-invasive effect of interferon. Infect Immun. 1990 Jul;58(7):2245–2251. doi: 10.1128/iai.58.7.2245-2251.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bölin I., Forsberg A., Norlander L., Skurnik M., Wolf-Watz H. Identification and mapping of the temperature-inducible, plasmid-encoded proteins of Yersinia spp. Infect Immun. 1988 Feb;56(2):343–348. doi: 10.1128/iai.56.2.343-348.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- China B., Sory M. P., N'Guyen B. T., De Bruyere M., Cornelis G. R. Role of the YadA protein in prevention of opsonization of Yersinia enterocolitica by C3b molecules. Infect Immun. 1993 Aug;61(8):3129–3136. doi: 10.1128/iai.61.8.3129-3136.1993. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cover T. L., Aber R. C. Yersinia enterocolitica. N Engl J Med. 1989 Jul 6;321(1):16–24. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198907063210104. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Emödy L., Heesemann J., Wolf-Watz H., Skurnik M., Kapperud G., O'Toole P., Wadström T. Binding to collagen by Yersinia enterocolitica and Yersinia pseudotuberculosis: evidence for yopA-mediated and chromosomally encoded mechanisms. J Bacteriol. 1989 Dec;171(12):6674–6679. doi: 10.1128/jb.171.12.6674-6679.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hanski C., Kutschka U., Schmoranzer H. P., Naumann M., Stallmach A., Hahn H., Menge H., Riecken E. O. Immunohistochemical and electron microscopic study of interaction of Yersinia enterocolitica serotype O8 with intestinal mucosa during experimental enteritis. Infect Immun. 1989 Mar;57(3):673–678. doi: 10.1128/iai.57.3.673-678.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Isberg R. R., Falkow S. A single genetic locus encoded by Yersinia pseudotuberculosis permits invasion of cultured animal cells by Escherichia coli K-12. Nature. 1985 Sep 19;317(6034):262–264. doi: 10.1038/317262a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Isberg R. R. Pathways for the penetration of enteroinvasive Yersinia into mammalian cells. Mol Biol Med. 1990 Feb;7(1):73–82. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Isberg R. R., Voorhis D. L., Falkow S. Identification of invasin: a protein that allows enteric bacteria to penetrate cultured mammalian cells. Cell. 1987 Aug 28;50(5):769–778. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90335-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kapperud G., Namork E., Skurnik M., Nesbakken T. Plasmid-mediated surface fibrillae of Yersinia pseudotuberculosis and Yersinia enterocolitica: relationship to the outer membrane protein YOP1 and possible importance for pathogenesis. Infect Immun. 1987 Sep;55(9):2247–2254. doi: 10.1128/iai.55.9.2247-2254.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LOWRY O. H., ROSEBROUGH N. J., FARR A. L., RANDALL R. J. Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem. 1951 Nov;193(1):265–275. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Martinez R. J. Thermoregulation-dependent expression of Yersinia enterocolitica protein 1 imparts serum resistance to Escherichia coli K-12. J Bacteriol. 1989 Jul;171(7):3732–3739. doi: 10.1128/jb.171.7.3732-3739.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meacock P. A., Cohen S. N. Partitioning of bacterial plasmids during cell division: a cis-acting locus that accomplishes stable plasmid inheritance. Cell. 1980 Jun;20(2):529–542. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(80)90639-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Messing J., Crea R., Seeburg P. H. A system for shotgun DNA sequencing. Nucleic Acids Res. 1981 Jan 24;9(2):309–321. doi: 10.1093/nar/9.2.309. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miller V. L., Falkow S. Evidence for two genetic loci in Yersinia enterocolitica that can promote invasion of epithelial cells. Infect Immun. 1988 May;56(5):1242–1248. doi: 10.1128/iai.56.5.1242-1248.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miller V. L., Farmer J. J., 3rd, Hill W. E., Falkow S. The ail locus is found uniquely in Yersinia enterocolitica serotypes commonly associated with disease. Infect Immun. 1989 Jan;57(1):121–131. doi: 10.1128/iai.57.1.121-131.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Paerregaard A., Espersen F., Baker N. The influence of properties encoded by the Yersinia virulence plasmid on adhesion of Yersinia enterocolitica to ileal brush border membrane vesicles. APMIS. 1990 Oct;98(10):927–932. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Paerregaard A., Espersen F., Hannover Larsen J., Høiby N. Adhesion of Yersinia enterocolitica to human epithelial cell lines and to rabbit and human small intestinal tissue. APMIS. 1990 Jan;98(1):53–60. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Paerregaard A., Espersen F., Jensen O. M., Skurnik M. Interactions between Yersinia enterocolitica and rabbit ileal mucus: growth, adhesion, penetration, and subsequent changes in surface hydrophobicity and ability to adhere to ileal brush border membrane vesicles. Infect Immun. 1991 Jan;59(1):253–260. doi: 10.1128/iai.59.1.253-260.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Paerregaard A., Espersen F., Skurnik M. Role of the Yersinia outer membrane protein YadA in adhesion to rabbit intestinal tissue and rabbit intestinal brush border membrane vesicles. APMIS. 1991 Mar;99(3):226–232. doi: 10.1111/j.1699-0463.1991.tb05143.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pekkola-Heino K., Viljanen M. K., Ståhlberg T. H., Granfors K., Toivanen A. Monoclonal antibodies reacting selectively with core and O-polysaccharide of Yersinia enterocolitica O:3 lipopolysaccharide. Acta Pathol Microbiol Immunol Scand C. 1987 Feb;95(1):27–34. doi: 10.1111/j.1699-0463.1987.tb00005.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pepe J. C., Miller V. L. The Yersinia enterocolitica inv gene product is an outer membrane protein that shares epitopes with Yersinia pseudotuberculosis invasin. J Bacteriol. 1990 Jul;172(7):3780–3789. doi: 10.1128/jb.172.7.3780-3789.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pilz D., Vocke T., Heesemann J., Brade V. Mechanism of YadA-mediated serum resistance of Yersinia enterocolitica serotype O3. Infect Immun. 1992 Jan;60(1):189–195. doi: 10.1128/iai.60.1.189-195.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Portnoy D. A., Moseley S. L., Falkow S. Characterization of plasmids and plasmid-associated determinants of Yersinia enterocolitica pathogenesis. Infect Immun. 1981 Feb;31(2):775–782. doi: 10.1128/iai.31.2.775-782.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rosqvist R., Skurnik M., Wolf-Watz H. Increased virulence of Yersinia pseudotuberculosis by two independent mutations. Nature. 1988 Aug 11;334(6182):522–524. doi: 10.1038/334522a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schulze-Koops H., Burkhardt H., Heesemann J., Kirsch T., Swoboda B., Bull C., Goodman S., Emmrich F. Outer membrane protein YadA of enteropathogenic yersiniae mediates specific binding to cellular but not plasma fibronectin. Infect Immun. 1993 Jun;61(6):2513–2519. doi: 10.1128/iai.61.6.2513-2519.1993. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schulze-Koops H., Burkhardt H., Heesemann J., von der Mark K., Emmrich F. Plasmid-encoded outer membrane protein YadA mediates specific binding of enteropathogenic yersiniae to various types of collagen. Infect Immun. 1992 Jun;60(6):2153–2159. doi: 10.1128/iai.60.6.2153-2159.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Skurnik M., Bölin I., Heikkinen H., Piha S., Wolf-Watz H. Virulence plasmid-associated autoagglutination in Yersinia spp. J Bacteriol. 1984 Jun;158(3):1033–1036. doi: 10.1128/jb.158.3.1033-1036.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Skurnik M. Expression of antigens encoded by the virulence plasmid of Yersinia enterocolitica under different growth conditions. Infect Immun. 1985 Jan;47(1):183–190. doi: 10.1128/iai.47.1.183-190.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Skurnik M. Lack of correlation between the presence of plasmids and fimbriae in Yersinia enterocolitica and Yersinia pseudotuberculosis. J Appl Bacteriol. 1984 Jun;56(3):355–363. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2672.1984.tb01362.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Skurnik M., Poikonen K. Experimental intestinal infection of rats by Yersinia enterocolitica 0:3. A follow-up study with specific antibodies to the virulence plasmid specified antigens. Scand J Infect Dis. 1986;18(4):355–364. doi: 10.3109/00365548609032347. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Skurnik M., Toivanen P. LcrF is the temperature-regulated activator of the yadA gene of Yersinia enterocolitica and Yersinia pseudotuberculosis. J Bacteriol. 1992 Mar;174(6):2047–2051. doi: 10.1128/jb.174.6.2047-2051.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Skurnik M., Wolf-Watz H. Analysis of the yopA gene encoding the Yop1 virulence determinants of Yersinia spp. Mol Microbiol. 1989 Apr;3(4):517–529. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2958.1989.tb00198.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tamm A., Tarkkanen A. M., Korhonen T. K., Kuusela P., Toivanen P., Skurnik M. Hydrophobic domains affect the collagen-binding specificity and surface polymerization as well as the virulence potential of the YadA protein of Yersinia enterocolitica. Mol Microbiol. 1993 Dec;10(5):995–1011. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2958.1993.tb00971.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tarkkanen A. M., Allen B. L., Westerlund B., Holthöfer H., Kuusela P., Risteli L., Clegg S., Korhonen T. K. Type V collagen as the target for type-3 fimbriae, enterobacterial adherence organelles. Mol Microbiol. 1990 Aug;4(8):1353–1361. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2958.1990.tb00714.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tertti R., Skurnik M., Vartio T., Kuusela P. Adhesion protein YadA of Yersinia species mediates binding of bacteria to fibronectin. Infect Immun. 1992 Jul;60(7):3021–3024. doi: 10.1128/iai.60.7.3021-3024.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Une T. Studies on the pathogenicity of Yersinia enterocolitica. I. Experimental infection in rabbits. Microbiol Immunol. 1977;21(7):341–363. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Valtonen V. V., Leirisalo M., Pentikäinen P. J., Räsänen T., Seppälä I., Larinkari U., Ranki M., Koskimies S., Malkamäki M., Mäkelä P. H. Triggering infections in reactive arthritis. Ann Rheum Dis. 1985 Jun;44(6):399–405. doi: 10.1136/ard.44.6.399. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Viitanen A. M., Toivanen P., Skurnik M. The lcrE gene is part of an operon in the lcr region of Yersinia enterocolitica O:3. J Bacteriol. 1990 Jun;172(6):3152–3162. doi: 10.1128/jb.172.6.3152-3162.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yang Y., Isberg R. R. Cellular internalization in the absence of invasin expression is promoted by the Yersinia pseudotuberculosis yadA product. Infect Immun. 1993 Sep;61(9):3907–3913. doi: 10.1128/iai.61.9.3907-3913.1993. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]