Abstract
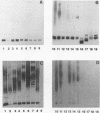
A hybridoma secreting a monoclonal antibody (MAb) directed against Klebsiella lipopolysaccharide (LPS) was derived from spleen cells of mice immunized a smooth, nonencapsulated Klebsiella strain (Friedländer 201; serogroup O1). The MAb, called V/9-5 (immunoglobulin G2a), cross-reacted with LPS preparations produced from reference strains for the Klebsiella O serogroups O1, O2ab, O2ac, O3, O4, O5, and O12. Furthermore, the MAb reacted with LPSs from serogroup reference strains O6/O8, O9, and O11, which are regarded as being identical to O1, O2, and O4, respectively. When testing the supernatant of clinically isolated Klebsiella strains by means of an inhibition enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay, we found that 86 (92.4%) of 93 Klebsiella pneumoniae subsp. pneumoniae isolates and 24 (96.0%) of 25 K. oxytoca isolates harbored the cross-reactive epitope. By contrast, two laboratory strains of K. pneumoniae subsp. rhinoscleromatis did not react with MAb V/9-5. The MAb proved to be specific for the genus Klebsiella, since it did not react with any of a total of 73 strains belonging to other gram-negative bacterial genera. In conjunction with other LPS-specific MAbs, MAb V/9-5 might become a useful reagent for rapid identification of klebsiellae in clinical specimens. Furthermore, the epitope recognized by MAb V/9-5 might serve as a target epitope for the production of human MAbs for immunotherapeutic purposes.
Full text
PDF





Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- BAER H., EHRENWORTH L. The pathogenicity of Klebsiella pneumoniae for mice: the relationship to the quantity and rate of production of type-specific capsular polysaccharide. J Bacteriol. 1956 Nov;72(5):713–717. doi: 10.1128/jb.72.5.713-717.1956. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Björndal H., Lindberg B., Lönngren J., Nilsson K., Nimmich W. Structural studies on the klebsiella O group 4 lipopolysaccharide. Acta Chem Scand. 1972;26(3):1269–1271. doi: 10.3891/acta.chem.scand.26-1269. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Björndal H., Lindberg B., Nimmich W. Structural studies on the lipopolysaccharide from Klebsiella K73-O10. I. Methylation analysis, identification and location of 3-O-methyl-L-rhamnose. Acta Chem Scand. 1970;24(9):3414–3415. doi: 10.3891/acta.chem.scand.24-3414. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bodey G. P., Elting L. S., Rodriquez S., Hernandez M. Klebsiella bacteremia. A 10-year review in a cancer institution. Cancer. 1989 Dec 1;64(11):2368–2376. doi: 10.1002/1097-0142(19891201)64:11<2368::aid-cncr2820641129>3.0.co;2-h. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bogard W. C., Jr, Dunn D. L., Abernethy K., Kilgarriff C., Kung P. C. Isolation and characterization of murine monoclonal antibodies specific for gram-negative bacterial lipopolysaccharide: association of cross-genus reactivity with lipid A specificity. Infect Immun. 1987 Apr;55(4):899–908. doi: 10.1128/iai.55.4.899-908.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brade H., Brade L., Nano F. E. Chemical and serological investigations on the genus-specific lipopolysaccharide epitope of Chlamydia. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Apr;84(8):2508–2512. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.8.2508. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Caldwell H. D., Hitchcock P. J. Monoclonal antibody against a genus-specific antigen of Chlamydia species: location of the epitope on chlamydial lipopolysaccharide. Infect Immun. 1984 May;44(2):306–314. doi: 10.1128/iai.44.2.306-314.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carlin N. I., Lindberg A. A. Monoclonal antibodies specific for Shigella flexneri lipopolysaccharides: clones binding to type IV, V, and VI antigens, group 3,4 antigen, and an epitope common to all Shigella flexneri and Shigella dysenteriae type 1 stains. Infect Immun. 1987 Jun;55(6):1412–1420. doi: 10.1128/iai.55.6.1412-1420.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carpenter J. L. Klebsiella pulmonary infections: occurrence at one medical center and review. Rev Infect Dis. 1990 Jul-Aug;12(4):672–682. doi: 10.1093/clinids/12.4.672. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cryz S. J., Jr, Mortimer P. M., Mansfield V., Germanier R. Seroepidemiology of Klebsiella bacteremic isolates and implications for vaccine development. J Clin Microbiol. 1986 Apr;23(4):687–690. doi: 10.1128/jcm.23.4.687-690.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Curvall M., Lindberg B., Lönngren J., Nimmich W. Structural studies on the Klebsiella O group 3 lipopolysaccharide. Acta Chem Scand. 1973;27(7):2645–2649. doi: 10.3891/acta.chem.scand.27-2645. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Curvall M., Lindberg B., Lönngren J., Rudén U., Nimmich W. Structural studies of the Klebsiella O group 8 lipopolysaccharide. Acta Chem Scand. 1973 Oct;27(10):4019–4021. doi: 10.3891/acta.chem.scand.27-4019. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dale P. A., McQuillen D. P., Gulati S., Rice P. A. Human vaccination with Escherichia coli J5 mutant induces cross-reactive bactericidal antibody against Neisseria gonorrhoeae lipooligosaccharide. J Infect Dis. 1992 Aug;166(2):316–325. doi: 10.1093/infdis/166.2.316. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Erbing C., Lindberg B., Lönngren J. Structural studies on the Klebsiella O group 12 lipopolysaccharide. Carbohydr Res. 1977 Jul;56(2):377–381. doi: 10.1016/s0008-6215(00)83359-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eriksen J. Immunochemical studies on some serological cross-reactions in the Klebsiella group. 16. Neutral polysaccharide antigens. Acta Pathol Microbiol Scand. 1966;66(1):71–78. doi: 10.1111/apm.1966.66.1.71. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Feldman C., Smith C., Levy H., Ginsburg P., Miller S. D., Koornhof H. J. Klebsiella pneumoniae bacteraemia at an urban general hospital. J Infect. 1990 Jan;20(1):21–31. doi: 10.1016/s0163-4453(90)92258-m. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fujihara Y., Lei M. G., Morrison D. C. Characterization of specific binding of a human immunoglobulin M monoclonal antibody to lipopolysaccharide and its lipid A domain. Infect Immun. 1993 Mar;61(3):910–918. doi: 10.1128/iai.61.3.910-918.1993. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fujita S., Matsubara F. Latex agglutination text for O serogrouping of Klebsiella species. Microbiol Immunol. 1984;28(6):731–734. doi: 10.1111/j.1348-0421.1984.tb00728.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Held T. K., Trautmann M., Mielke M. E., Neudeck H., Cryz S. J., Jr, Cross A. S. Monoclonal antibody against Klebsiella capsular polysaccharide reduces severity and hematogenic spread of experimental Klebsiella pneumoniae pneumonia. Infect Immun. 1992 May;60(5):1771–1778. doi: 10.1128/iai.60.5.1771-1778.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaluzewski S. Antygeny somatyczne szczepów Klebsiella K 63-K 72. Med Dosw Mikrobiol. 1965;17(4):283–290. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kol O., Wieruszeski J. M., Strecker G., Fournet B., Zalisz R., Smets P. Structure of the O-specific polysaccharide chain of Klebsiella pneumoniae O1K2 (NCTC 5055) lipopolysaccharide. A complementary elucidation. Carbohydr Res. 1992 Dec 15;236:339–344. doi: 10.1016/0008-6215(92)85028-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kol O., Wieruszeski J. M., Strecker G., Montreuil J., Fournet B., Zalisz R., Smets P. Structure of the O-specific polysaccharide chain from Klebsiella pneumoniae O1K2 (NCTC 5055) lipopolysaccharide. Carbohydr Res. 1991 Sep 18;217:117–125. doi: 10.1016/0008-6215(91)84122-u. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lang A. B., Bruderer U., Senyk G., Pitt T. L., Larrick J. W., Cryz S. J., Jr Human monoclonal antibodies specific for capsular polysaccharides of Klebsiella recognize clusters of multiple serotypes. J Immunol. 1991 May 1;146(9):3160–3164. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lindberg B., Lönngren J., Nimmich W., Rudén U. Structural studies on the Klebsiella O group 7 lipopolysaccharide. Acta Chem Scand. 1973 Oct;27(10):3787–3790. doi: 10.3891/acta.chem.scand.27-3787. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lindberg B., Lönngren J., Nimmich W. Structural studies on Klebsiella O group 5 lipopolysaccharides. Acta Chem Scand. 1972;26(6):2231–2236. doi: 10.3891/acta.chem.scand.26-2231. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lindberg B., Lönngren J. Structural studies of the Klebsiella O group 9 lipopolysaccharide. Carbohydr Res. 1972 Jun;23(1):47–55. doi: 10.1016/s0008-6215(00)81576-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MacLean L. L., Whitfield C., Perry M. B. Characterization of the polysaccharide antigen of Klebsiella pneumoniae O:9 lipopolysaccharide. Carbohydr Res. 1993 Feb 1;239:325–328. doi: 10.1016/0008-6215(93)84231-t. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mandine E., Salles M. F., Zalisz R., Guenounou M., Smets P. Murine monoclonal antibodies to Klebsiella pneumoniae protect against lethal endotoxemia and experimental infection with capsulated K. pneumoniae. Infect Immun. 1990 Sep;58(9):2828–2833. doi: 10.1128/iai.58.9.2828-2833.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marks M. I., Ziegler E. J., Douglas H., Corbeil L. B., Braude A. I. Induction of immunity against lethal Haemophilus influenzae type b infection by Escherichia coli core lipopolysaccharide. J Clin Invest. 1982 Apr;69(4):742–749. doi: 10.1172/JCI110512. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mattsby-Baltzer I., Lindgren K., Lindholm B., Edebo L. Endotoxin shedding by enterobacteria: free and cell-bound endotoxin differ in Limulus activity. Infect Immun. 1991 Feb;59(2):689–695. doi: 10.1128/iai.59.2.689-695.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McCallum K. L., Schoenhals G., Laakso D., Clarke B., Whitfield C. A high-molecular-weight fraction of smooth lipopolysaccharide in Klebsiella serotype O1:K20 contains a unique O-antigen epitope and determines resistance to nonspecific serum killing. Infect Immun. 1989 Dec;57(12):3816–3822. doi: 10.1128/iai.57.12.3816-3822.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mutharia L. M., Crockford G., Bogard W. C., Jr, Hancock R. E. Monoclonal antibodies specific for Escherichia coli J5 lipopolysaccharide: cross-reaction with other gram-negative bacterial species. Infect Immun. 1984 Sep;45(3):631–636. doi: 10.1128/iai.45.3.631-636.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nimmich W., Korten G. Die chemische Zusammensetzung der Klebsiella-Lipopolysaccharide (O-Antigene) Pathol Microbiol (Basel) 1970;36(3):179–190. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- PICKETT M. J., CABELLI V. J. The precipitating antigens of Friedländer's Bacillus. J Gen Microbiol. 1953 Oct;9(2):249–256. doi: 10.1099/00221287-9-2-249. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pollack M., Raubitschek A. A., Larrick J. W. Human monoclonal antibodies that recognize conserved epitopes in the core-lipid A region of lipopolysaccharides. J Clin Invest. 1987 May;79(5):1421–1430. doi: 10.1172/JCI112970. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pyle S. W., Schill W. B. Rapid serological analysis of bacterial lipopolysaccharides by electrotransfer to nitrocellulose. J Immunol Methods. 1985 Dec 27;85(2):371–382. doi: 10.1016/0022-1759(85)90146-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sidberry H., Kaufman B., Wright D. C., Sadoff J. Immunoenzymatic analysis by monoclonal antibodies of bacterial lipopolysaccharides after transfer to nitrocellulose. J Immunol Methods. 1985 Feb 11;76(2):299–305. doi: 10.1016/0022-1759(85)90307-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Teng N. N., Kaplan H. S., Hebert J. M., Moore C., Douglas H., Wunderlich A., Braude A. I. Protection against gram-negative bacteremia and endotoxemia with human monoclonal IgM antibodies. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Mar;82(6):1790–1794. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.6.1790. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tomás J. M., Camprubi S., Merino S., Davey M. R., Williams P. Surface exposure of O1 serotype lipopolysaccharide in Klebsiella pneumoniae strains expressing different K antigens. Infect Immun. 1991 Jun;59(6):2006–2011. doi: 10.1128/iai.59.6.2006-2011.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Trautmann M., Cryz S. J., Jr, Sadoff J. C., Cross A. S. A murine monoclonal antibody against Klebsiella capsular polysaccharide is opsonic in vitro and protects against experimental Klebsiella pneumoniae infection. Microb Pathog. 1988 Sep;5(3):177–187. doi: 10.1016/0882-4010(88)90020-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tsai C. M., Civin C. I. Eight lipooligosaccharides of Neisseria meningitidis react with a monoclonal antibody which binds lacto-N-neotetraose (Gal beta 1-4GlcNAc beta 1-3Gal beta 1-4Glc). Infect Immun. 1991 Oct;59(10):3604–3609. doi: 10.1128/iai.59.10.3604-3609.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Whitfield C., Perry M. B., MacLean L. L., Yu S. H. Structural analysis of the O-antigen side chain polysaccharides in the lipopolysaccharides of Klebsiella serotypes O2(2a), O2(2a,2b), and O2(2a,2c). J Bacteriol. 1992 Aug;174(15):4913–4919. doi: 10.1128/jb.174.15.4913-4919.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Whitfield C., Richards J. C., Perry M. B., Clarke B. R., MacLean L. L. Expression of two structurally distinct D-galactan O antigens in the lipopolysaccharide of Klebsiella pneumoniae serotype O1. J Bacteriol. 1991 Feb;173(4):1420–1431. doi: 10.1128/jb.173.4.1420-1431.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- ØRSKOV I. O antigens in the Klebsiella group. Acta Pathol Microbiol Scand. 1954;34(2):145–156. doi: 10.1111/j.1699-0463.1954.tb00811.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]