Abstract
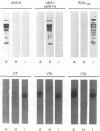
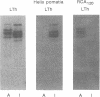
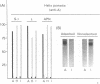
The ability of glycoproteins from pig intestinal brush border membranes (BBM) to bind cholera toxin (CT) or heat-labile toxins from strains of Escherichia coli isolated from human (LTh) or pig (LTp) intestines was studied. Glycoproteins capable of binding the toxins are also recognized by antibodies or lectins specific for ABO(H) blood group and related antigens. Pigs expressing A, H, or I antigenic determinants were used for comparison. The toxin-binding capacity of a glycoprotein depends on the toxin type and the blood group epitope borne by the glycoprotein. LTh and LTp preferably bound to several blood group A-active glycoproteins rather than H-active glycoproteins. By contrast, CT practically did not recognize either blood group A- or blood group H-active glycoproteins, while glycoproteins from pigs expressing I antigenic determinants were able to interact with LTh, LTp, and CT. LTh, LTp, or CT glycoprotein binding was selectively inhibited by specific lectins or monosaccharides. Affinity purification of the toxin binding brush border glycoproteins on the basis of their blood group reactivity suggests that such glycoproteins are hydrolytic enzymes. BBM from A+ pigs contain about 27 times more LTh binding sites, in addition to those recognized by CT, than an equivalent membrane preparation from H+ pigs. The present findings may help clarify some previous unclear results on LTh binding to intestinal BBM glycoproteins obtained by use of animals not typed by their ABO(H) blood group phenotype.
Full text
PDF




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Barra J. L., Monferran C. G., Balanzino L. E., Cumar F. A. Escherichia coli heat-labile enterotoxin preferentially interacts with blood group A-active glycolipids from pig intestinal mucosa and A- and B-active glycolipids from human red cells compared to H-active glycolipids. Mol Cell Biochem. 1992 Sep 22;115(1):63–70. doi: 10.1007/BF00229097. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bennun F. R., Roth G. A., Monferran C. G., Cumar F. A. Binding of cholera toxin to pig intestinal mucosa glycosphingolipids: relationship with the ABO blood group system. Infect Immun. 1989 Mar;57(3):969–974. doi: 10.1128/iai.57.3.969-974.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Björk S., Breimer M. E., Hansson G. C., Karlsson K. A., Leffler H. Structures of blood group glycosphingolipids of human small intestine. A relation between the expression of fucolipids of epithelial cells and the ABO, Le and Se phenotype of the donor. J Biol Chem. 1987 May 15;262(14):6758–6765. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clausen H., Hakomori S. ABH and related histo-blood group antigens; immunochemical differences in carrier isotypes and their distribution. Vox Sang. 1989;56(1):1–20. doi: 10.1111/j.1423-0410.1989.tb03040.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DAHLQVIST A. METHOD FOR ASSAY OF INTESTINAL DISACCHARIDASES. Anal Biochem. 1964 Jan;7:18–25. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(64)90115-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Danielsen E. M., Cowell G. M., Norén O., Sjöström H. Biosynthesis of microvillar proteins. Biochem J. 1984 Jul 1;221(1):1–14. doi: 10.1042/bj2210001. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Finkelstein R. A., Burks M. F., Zupan A., Dallas W. S., Jacob C. O., Ludwig D. S. Epitopes of the cholera family of enterotoxins. Rev Infect Dis. 1987 May-Jun;9(3):544–561. doi: 10.1093/clinids/9.3.544. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Finne J., Breimer M. E., Hansson G. C., Karlsson K. A., Leffler H., Vliegenthart J. F., van Halbeek H. Novel polyfucosylated N-linked glycopeptides with blood group A, H, X, and Y determinants from human small intestinal epithelial cells. J Biol Chem. 1989 Apr 5;264(10):5720–5735. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gorvel J. P., Wisner-Provost A., Maroux S. Identification of glycoproteins bearing human blood group A determinants in rabbit enterocyte plasma membranes. FEBS Lett. 1982 Jun 21;143(1):17–20. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(82)80263-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Griffiths S. L., Critchley D. R. Characterisation of the binding sites for Escherichia coli heat-labile toxin type I in intestinal brush borders. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1991 Oct 10;1075(2):154–161. doi: 10.1016/0304-4165(91)90246-d. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Griffiths S. L., Finkelstein R. A., Critchley D. R. Characterization of the receptor for cholera toxin and Escherichia coli heat-labile toxin in rabbit intestinal brush borders. Biochem J. 1986 Sep 1;238(2):313–322. doi: 10.1042/bj2380313. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hauser H., Howell K., Dawson R. M., Bowyer D. E. Rabbit small intestinal brush border membrane preparation and lipid composition. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1980 Nov 18;602(3):567–577. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(80)90335-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Holmgren J., Fredman P., Lindblad M., Svennerholm A. M., Svennerholm L. Rabbit intestinal glycoprotein receptor for Escherichia coli heat-labile enterotoxin lacking affinity for cholera toxin. Infect Immun. 1982 Nov;38(2):424–433. doi: 10.1128/iai.38.2.424-433.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Holmgren J., Lindblad M., Fredman P., Svennerholm L., Myrvold H. Comparison of receptors for cholera and Escherichia coli enterotoxins in human intestine. Gastroenterology. 1985 Jul;89(1):27–35. doi: 10.1016/0016-5085(85)90741-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kelly J. J., Alpers D. H. Blood group antigenicity of purified human intestinal disaccharidases. J Biol Chem. 1973 Dec 10;248(23):8216–8221. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- King C. A., Van Heyningen W. E. Deactivation of cholera toxin by a sialidase-resistant monosialosylganglioside. J Infect Dis. 1973 Jun;127(6):639–647. doi: 10.1093/infdis/127.6.639. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maestracci D. Enzymic solubilization of the human intestinal brush border membrane enzymes. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1976 May 21;433(3):469–481. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(76)90274-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McKibbin J. M. Fucolipids. J Lipid Res. 1978 Feb;19(2):131–147. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Monferran C. G., Roth G. A., Cumar F. A. Inhibition of cholera toxin binding to membrane receptors by pig gastric mucin-derived glycopeptides: differential effect depending on the ABO blood group antigenic determinants. Infect Immun. 1990 Dec;58(12):3966–3972. doi: 10.1128/iai.58.12.3966-3972.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moss J., Vaughan M. Mechanism of action of choleragen and E. coli heat-labile enterotoxin: activation of adenylate cyclase by ADP-ribosylation. Mol Cell Biochem. 1981 Jul 7;37(2):75–90. doi: 10.1007/BF02354931. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oriol R. Tissular expression of ABH and Lewis antigens in humans and animals: expected value of different animal models in the study of ABO-incompatible organ transplants. Transplant Proc. 1987 Dec;19(6):4416–4420. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Panzetta P., Gravotta D., Maccioni H. J. Biosynthesis and expression of gangliosides during differentiation of chick embryo retina cells in vitro. J Neurochem. 1987 Dec;49(6):1763–1771. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1987.tb02434.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sjöström H., Norén O., Jeppesen L., Staun M., Svensson B., Christiansen L. Purification of different amphiphilic forms of a microvillus aminopeptidase from pig small intestine using immunoadsorbent chromatography. Eur J Biochem. 1978 Aug 1;88(2):503–511. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1978.tb12476.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Towbin H., Staehelin T., Gordon J. Electrophoretic transfer of proteins from polyacrylamide gels to nitrocellulose sheets: procedure and some applications. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Sep;76(9):4350–4354. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.9.4350. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Triadou N., Audran E., Rousset M., Zweibaum A., Oriol R. Relationship between the secretor status and the expression of ABH blood group antigenic determinants in human intestinal brush-border membrane hydrolases. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1983 Dec 27;761(3):231–236. doi: 10.1016/0304-4165(83)90070-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]