Abstract
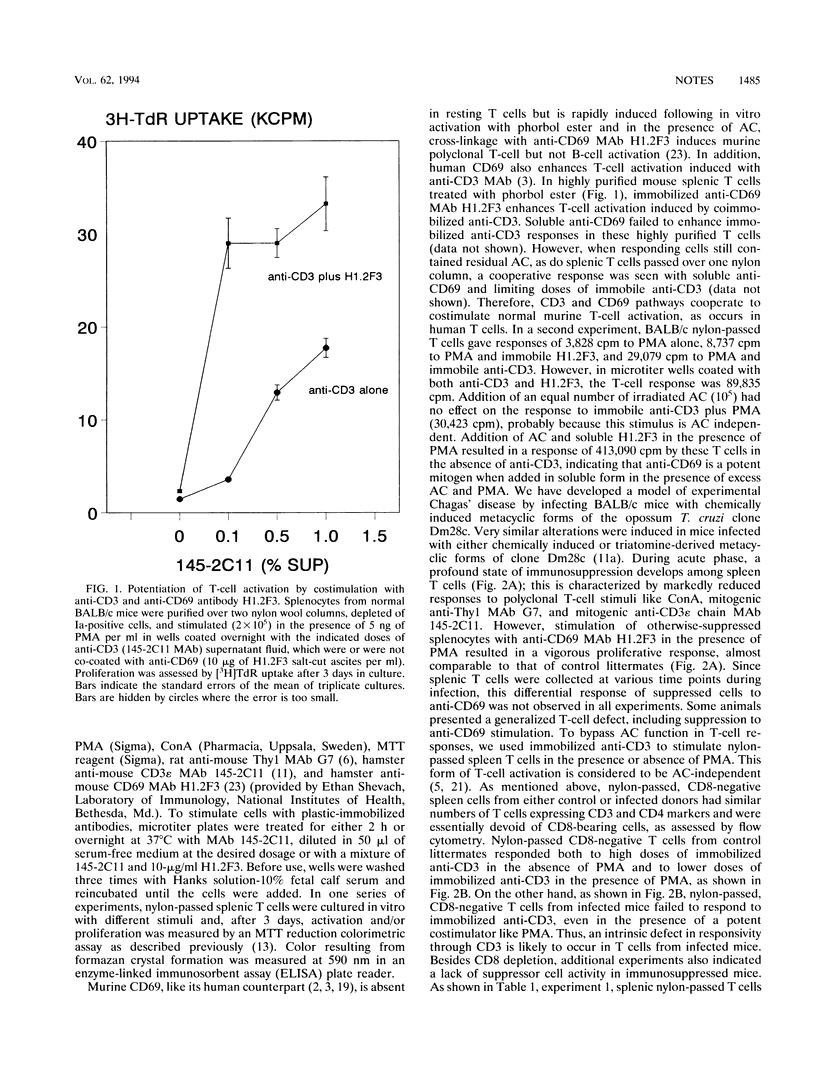
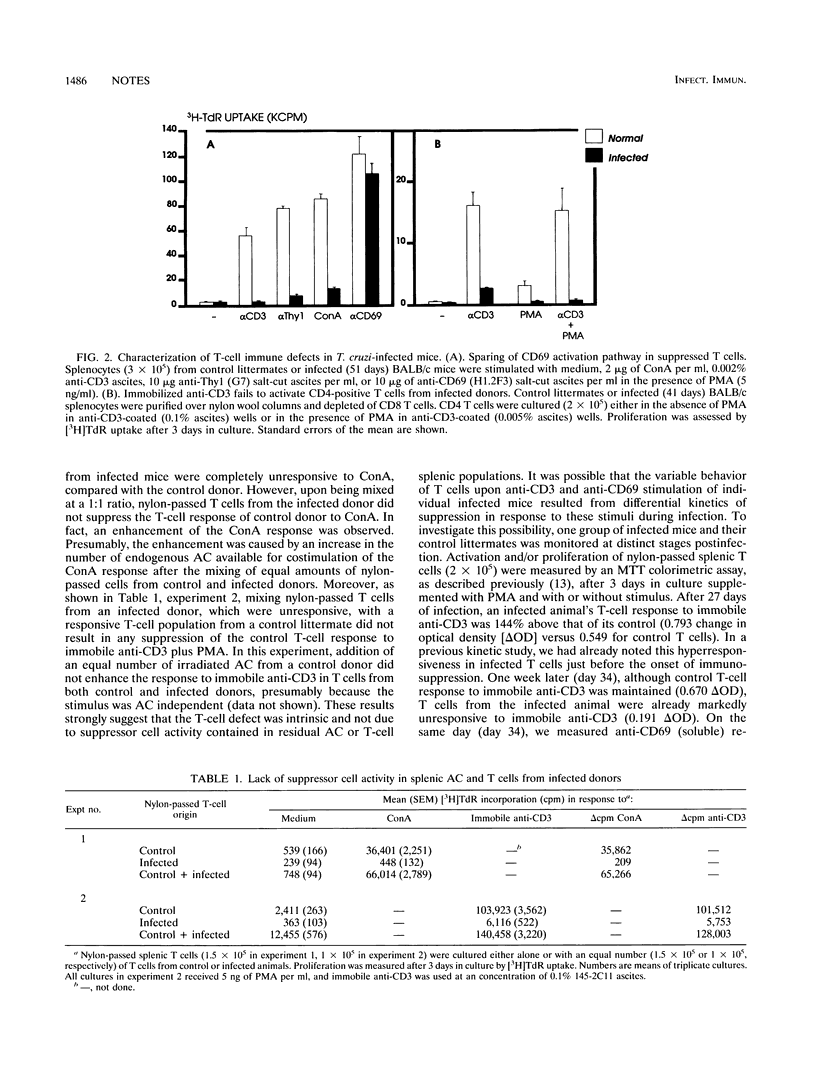
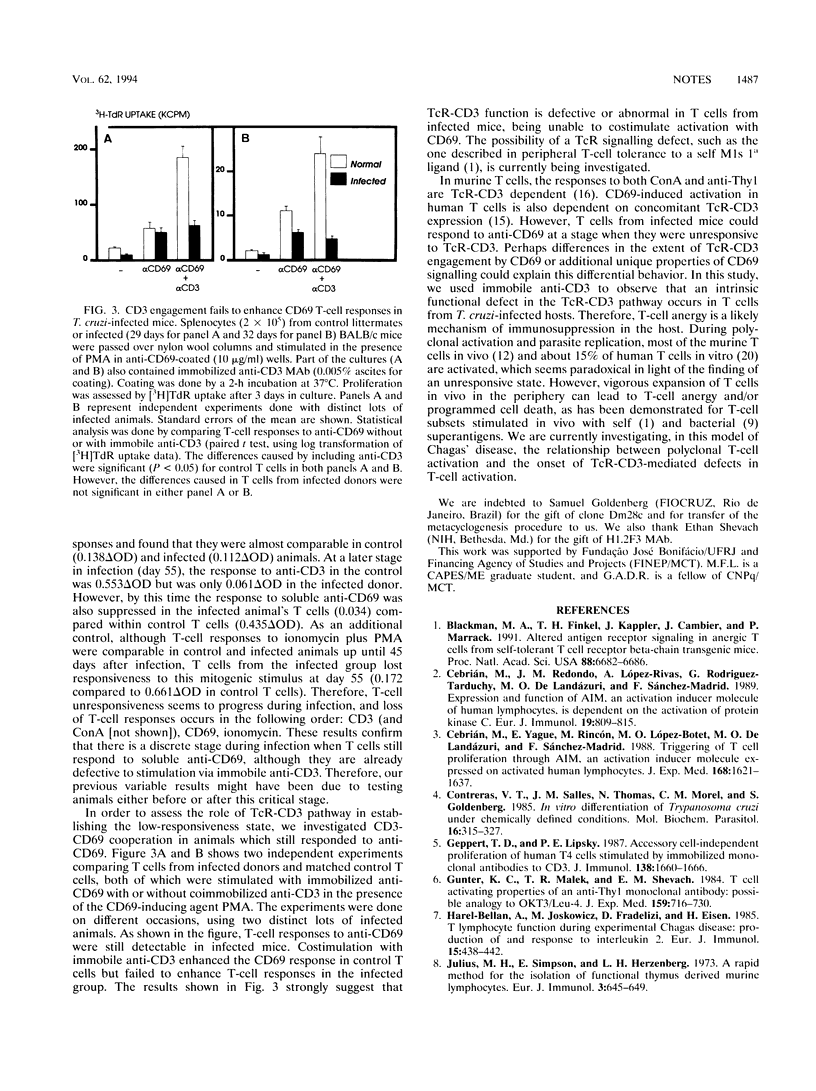
A model of experimental Trypanosoma cruzi murine infection with chemically induced metacyclic forms (opossum clone Dm28c) showed a marked state of T-cell unresponsiveness during acute phase, but lacked evidence of suppressor cell activity. Spleen cells from infected mice were suppressed in vitro in responses to T-cell activators concanavalin A, anti-Thy1 monoclonal antibody (MAb), and anti-CD3 MAb compared with spleen cells from control littermates. Activation with accessory cell-independent stimulus provided by immobilized anti-CD3 was defective in splenic CD4-positive T cells from infected mice, but not in such cells from control mice. No evidence of splenic suppressor cell activity was found in cell-mixing experiments using nylon-passed T cells from control and infected donors. Kinetic experiments showed that there was a discrete stage in infection when T cells were already suppressed in response to anti-CD3 but still responded to anti-CD69 MAb. In these T cells, immobilized anti-CD3 failed to enhance simultaneous CD69 responses, although anti-CD3 enhanced CD69 responses in control T cells from uninfected donors. These results demonstrate an intrinsic defect in T-cell receptor-mediated T-cell activation, which could be a mechanism generating T-cell suppression during infection by T. cruzi.
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Blackman M. A., Finkel T. H., Kappler J., Cambier J., Marrack P. Altered antigen receptor signaling in anergic T cells from self-tolerant T-cell receptor beta-chain transgenic mice. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Aug 1;88(15):6682–6686. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.15.6682. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cebrián M., Redondo J. M., López-Rivas A., Rodríguez-Tarduchy G., De Landázuri M. O., Sánchez-Madrid F. Expression and function of AIM, an activation inducer molecule of human lymphocytes, is dependent on the activation of protein kinase C. Eur J Immunol. 1989 May;19(5):809–815. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830190505. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cebrián M., Yagüe E., Rincón M., López-Botet M., de Landázuri M. O., Sánchez-Madrid F. Triggering of T cell proliferation through AIM, an activation inducer molecule expressed on activated human lymphocytes. J Exp Med. 1988 Nov 1;168(5):1621–1637. doi: 10.1084/jem.168.5.1621. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Contreras V. T., Salles J. M., Thomas N., Morel C. M., Goldenberg S. In vitro differentiation of Trypanosoma cruzi under chemically defined conditions. Mol Biochem Parasitol. 1985 Sep;16(3):315–327. doi: 10.1016/0166-6851(85)90073-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Geppert T. D., Lipsky P. E. Accessory cell independent proliferation of human T4 cells stimulated by immobilized monoclonal antibodies to CD3. J Immunol. 1987 Mar 15;138(6):1660–1666. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gunter K. C., Malek T. R., Shevach E. M. T cell-activating properties of an anti-Thy-1 monoclonal antibody. Possible analogy to OKT3/Leu-4. J Exp Med. 1984 Mar 1;159(3):716–730. doi: 10.1084/jem.159.3.716. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harel-Bellan A., Joskowicz M., Fradelizi D., Eisen H. T lymphocyte function during experimental Chagas' disease: production of and response to interleukin 2. Eur J Immunol. 1985 May;15(5):438–442. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830150505. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Julius M. H., Simpson E., Herzenberg L. A. A rapid method for the isolation of functional thymus-derived murine lymphocytes. Eur J Immunol. 1973 Oct;3(10):645–649. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830031011. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kawabe Y., Ochi A. Programmed cell death and extrathymic reduction of Vbeta8+ CD4+ T cells in mice tolerant to Staphylococcus aureus enterotoxin B. Nature. 1991 Jan 17;349(6306):245–248. doi: 10.1038/349245a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kierszenbaum F. On evasion of Trypanosoma cruzi from the host immune response. Lymphoproliferative responses to trypanosomal antigens during acute and chronic experimental Chagas' disease. Immunology. 1981 Nov;44(3):641–648. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leo O., Foo M., Sachs D. H., Samelson L. E., Bluestone J. A. Identification of a monoclonal antibody specific for a murine T3 polypeptide. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Mar;84(5):1374–1378. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.5.1374. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mosmann T. Rapid colorimetric assay for cellular growth and survival: application to proliferation and cytotoxicity assays. J Immunol Methods. 1983 Dec 16;65(1-2):55–63. doi: 10.1016/0022-1759(83)90303-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reed S. G., Pihl D. L., Grabstein K. H. Immune deficiency in chronic Trypanosoma cruzi infection. Recombinant IL-1 restores Th function for antibody production. J Immunol. 1989 Mar 15;142(6):2067–2071. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rincón M., Cebrián M., Sánchez-Madrid F., López-Botet M. Induction of T cell function via the gp33/27 activation inducer molecule (AIM) requires co-expression of the CD3/TcR complex. Eur J Immunol. 1989 May;19(5):959–962. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830190528. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schmitt-Verhulst A. M., Guimezanes A., Boyer C., Poenie M., Tsien R., Buferne M., Hua C., Leserman L. Pleiotropic loss of activation pathways in a T-cell receptor alpha-chain deletion variant of a cytolytic T-cell clone. Nature. 1987 Feb 12;325(6105):628–631. doi: 10.1038/325628a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tarleton R. L., Koller B. H., Latour A., Postan M. Susceptibility of beta 2-microglobulin-deficient mice to Trypanosoma cruzi infection. Nature. 1992 Mar 26;356(6367):338–340. doi: 10.1038/356338a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tarleton R. L. Trypanosoma cruzi-induced suppression of IL-2 production. II. Evidence for a role for suppressor cells. J Immunol. 1988 Apr 15;140(8):2769–2773. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Testi R., Phillips J. H., Lanier L. L. Leu 23 induction as an early marker of functional CD3/T cell antigen receptor triggering. Requirement for receptor cross-linking, prolonged elevation of intracellular [Ca++] and stimulation of protein kinase C. J Immunol. 1989 Mar 15;142(6):1854–1860. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Van Voorhis W. C. Coculture of human peripheral blood mononuclear cells with Trypanosoma cruzi leads to proliferation of lymphocytes and cytokine production. J Immunol. 1992 Jan 1;148(1):239–248. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Williams I. R., Unanue E. R. Costimulatory requirements of murine Th1 clones. The role of accessory cell-derived signals in responses to anti-CD3 antibody. J Immunol. 1990 Jul 1;145(1):85–93. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yokoyama W. M., Koning F., Kehn P. J., Pereira G. M., Stingl G., Coligan J. E., Shevach E. M. Characterization of a cell surface-expressed disulfide-linked dimer involved in murine T cell activation. J Immunol. 1988 Jul 15;141(2):369–376. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yokoyama W. M., Maxfield S. R., Shevach E. M. Very early (VEA) and very late (VLA) activation antigens have distinct functions in T lymphocyte activation. Immunol Rev. 1989 Jun;109:153–176. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-065x.1989.tb00024.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



