Abstract
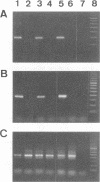
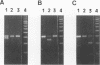
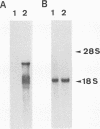
Pneumocystis carinii surface glycoprotein A (gpA) exhibits host species-specific phenotypic and genotypic variation. Despite this heterogeneity, the gpAs of P. carinii isolated from different host species appear to be homologous molecules sharing certain biochemical and antigenic characteristics. Using two degenerate oligodeoxyribonucleotide primers corresponding to conserved cysteine regions from ferret and rat P. carinii gpAs, a PCR product of approximately 300 bp was amplified from ferret, rat, and SCID mouse P. carinii-infected lung genomic DNA. Northern (RNA) hybridization revealed a transcript of 3,450 nucleotides in P. carinii-infected SCID mouse lung mRNA, which is similar in size to the transcripts for ferret and rat P. carinii gpAs. Nucleotide sequence analysis of SCID mouse P. carinii gpA subclones derived from the PCR products identified two isoforms, which were 89% identical to each other in the amplified region and 73 and 54% identical to the rat- and ferret-derived P. carinii gpA genes, respectively. Comparison of the deduced amino acid sequences of mouse, ferret, and rat P. carinii gpAs revealed striking similarity in residues adjacent to and including the conserved cysteines. Furthermore, the spacing of two proline residues is invariant, and a potential N-linked glycosylation site is found at a similar position in all of the gpAs. Despite the heterogeneity observed in P. carinii gpAs, the conservation of cysteine residues and adjacent sequences implies similar secondary structure and, most likely, similar function for the gpAs of P. carinii isolated from different host species.
Full text
PDF





Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Borst P. Molecular genetics of antigenic variation. Immunol Today. 1991 Mar;12(3):A29–A33. doi: 10.1016/S0167-5699(05)80009-X. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brown J. P., Twardzik D. R., Marquardt H., Todaro G. J. Vaccinia virus encodes a polypeptide homologous to epidermal growth factor and transforming growth factor. Nature. 1985 Feb 7;313(6002):491–492. doi: 10.1038/313491a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Devereux J., Haeberli P., Smithies O. A comprehensive set of sequence analysis programs for the VAX. Nucleic Acids Res. 1984 Jan 11;12(1 Pt 1):387–395. doi: 10.1093/nar/12.1part1.387. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ezekowitz R. A., Williams D. J., Koziel H., Armstrong M. Y., Warner A., Richards F. F., Rose R. M. Uptake of Pneumocystis carinii mediated by the macrophage mannose receptor. Nature. 1991 May 9;351(6322):155–158. doi: 10.1038/351155a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fisher D. J., Gigliotti F., Zauderer M., Harmsen A. G. Specific T-cell response to a Pneumocystis carinii surface glycoprotein (gp120) after immunization and natural infection. Infect Immun. 1991 Oct;59(10):3372–3376. doi: 10.1128/iai.59.10.3372-3376.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gigliotti F., Ballou L. R., Hughes W. T., Mosley B. D. Purification and initial characterization of a ferret Pneumocystis carinii surface antigen. J Infect Dis. 1988 Oct;158(4):848–854. doi: 10.1093/infdis/158.4.848. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gigliotti F., Haidaris P. J., Haidaris C. G., Wright T. W., Van der Meid K. R. Further evidence of host species-specific variation in antigens of Pneumocystis carinii using the polymerase chain reaction. J Infect Dis. 1993 Jul;168(1):191–194. doi: 10.1093/infdis/168.1.191. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gigliotti F., Harmsen A. G., Haidaris C. G., Haidaris P. J. Pneumocystis carinii is not universally transmissible between mammalian species. Infect Immun. 1993 Jul;61(7):2886–2890. doi: 10.1128/iai.61.7.2886-2890.1993. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gigliotti F. Host species-specific antigenic variation of a mannosylated surface glycoprotein of Pneumocystis carinii. J Infect Dis. 1992 Feb;165(2):329–336. doi: 10.1093/infdis/165.2.329. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gigliotti F., Hughes W. T. Passive immunoprophylaxis with specific monoclonal antibody confers partial protection against Pneumocystis carinii pneumonitis in animal models. J Clin Invest. 1988 Jun;81(6):1666–1668. doi: 10.1172/JCI113503. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gigliotti F., Stokes D. C., Cheatham A. B., Davis D. S., Hughes W. T. Development of murine monoclonal antibodies to Pneumocystis carinii. J Infect Dis. 1986 Aug;154(2):315–322. doi: 10.1093/infdis/154.2.315. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Graves D. C., McNabb S. J., Worley M. A., Downs T. D., Ivey M. H. Analyses of rat Pneumocystis carinii antigens recognized by human and rat antibodies by using western immunoblotting. Infect Immun. 1986 Oct;54(1):96–103. doi: 10.1128/iai.54.1.96-103.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gunning P., Ponte P., Okayama H., Engel J., Blau H., Kedes L. Isolation and characterization of full-length cDNA clones for human alpha-, beta-, and gamma-actin mRNAs: skeletal but not cytoplasmic actins have an amino-terminal cysteine that is subsequently removed. Mol Cell Biol. 1983 May;3(5):787–795. doi: 10.1128/mcb.3.5.787. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Haidaris P. J., Wright T. W., Gigliotti F., Haidaris C. G. Expression and characterization of a cDNA clone encoding an immunodominant surface glycoprotein of Pneumocystis carinii. J Infect Dis. 1992 Nov;166(5):1113–1123. doi: 10.1093/infdis/166.5.1113. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hong S. T., Steele P. E., Cushion M. T., Walzer P. D., Stringer S. L., Stringer J. R. Pneumocystis carinii karyotypes. J Clin Microbiol. 1990 Aug;28(8):1785–1795. doi: 10.1128/jcm.28.8.1785-1795.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kovacs J. A., Halpern J. L., Lundgren B., Swan J. C., Parrillo J. E., Masur H. Monoclonal antibodies to Pneumocystis carinii: identification of specific antigens and characterization of antigenic differences between rat and human isolates. J Infect Dis. 1989 Jan;159(1):60–70. doi: 10.1093/infdis/159.1.60. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kovacs J. A., Powell F., Edman J. C., Lundgren B., Martinez A., Drew B., Angus C. W. Multiple genes encode the major surface glycoprotein of Pneumocystis carinii. J Biol Chem. 1993 Mar 15;268(8):6034–6040. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Linke M. J., Cushion M. T., Walzer P. D. Properties of the major antigens of rat and human Pneumocystis carinii. Infect Immun. 1989 May;57(5):1547–1555. doi: 10.1128/iai.57.5.1547-1555.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lundgren B., Lipschik G. Y., Kovacs J. A. Purification and characterization of a major human Pneumocystis carinii surface antigen. J Clin Invest. 1991 Jan;87(1):163–170. doi: 10.1172/JCI114966. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Murray J. F., Garay S. M., Hopewell P. C., Mills J., Snider G. L., Stover D. E. NHLBI workshop summary. Pulmonary complications of the acquired immunodeficiency syndrome: an update. Report of the second National Heart, Lung and Blood Institute workshop. Am Rev Respir Dis. 1987 Feb;135(2):504–509. doi: 10.1164/arrd.1987.135.2.504. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nash T. E., Mowatt M. R. Characterization of a Giardia lamblia variant-specific surface protein (VSP) gene from isolate GS/M and estimation of the VSP gene repertoire size. Mol Biochem Parasitol. 1992 Apr;51(2):219–227. doi: 10.1016/0166-6851(92)90072-r. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nudel U., Zakut R., Shani M., Neuman S., Levy Z., Yaffe D. The nucleotide sequence of the rat cytoplasmic beta-actin gene. Nucleic Acids Res. 1983 Mar 25;11(6):1759–1771. doi: 10.1093/nar/11.6.1759. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pearson W. R., Lipman D. J. Improved tools for biological sequence comparison. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Apr;85(8):2444–2448. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.8.2444. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pottratz S. T., Paulsrud J., Smith J. S., Martin W. J., 2nd Pneumocystis carinii attachment to cultured lung cells by pneumocystis gp 120, a fibronectin binding protein. J Clin Invest. 1991 Aug;88(2):403–407. doi: 10.1172/JCI115318. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Radding J. A., Armstrong M. Y., Ullu E., Richards F. F. Identification and isolation of a major cell surface glycoprotein of Pneumocystis carinii. Infect Immun. 1989 Jul;57(7):2149–2157. doi: 10.1128/iai.57.7.2149-2157.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reisner A. H. Similarity between the vaccinia virus 19K early protein and epidermal growth factor. 1985 Feb 28-Mar 6Nature. 313(6005):801–803. doi: 10.1038/313801a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Simpson P. J. An improved method for mRNA isolation and characterization of in vitro translation products by Western blotting. Gene. 1987;56(2-3):161–171. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(87)90134-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sinclair K., Wakefield A. E., Banerji S., Hopkin J. M. Pneumocystis carinii organisms derived from rat and human hosts are genetically distinct. Mol Biochem Parasitol. 1991 Mar;45(1):183–184. doi: 10.1016/0166-6851(91)90042-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tanabe K., Takasaki S., Watanabe J., Kobata A., Egawa K., Nakamura Y. Glycoproteins composed of major surface immunodeterminants of Pneumocystis carinii. Infect Immun. 1989 May;57(5):1363–1368. doi: 10.1128/iai.57.5.1363-1368.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Twardzik D. R., Brown J. P., Ranchalis J. E., Todaro G. J., Moss B. Vaccinia virus-infected cells release a novel polypeptide functionally related to transforming and epidermal growth factors. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Aug;82(16):5300–5304. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.16.5300. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vogel P., Miller C. J., Lowenstine L. L., Lackner A. A. Evidence of horizontal transmission of Pneumocystis carinii pneumonia in simian immunodeficiency virus-infected rhesus macaques. J Infect Dis. 1993 Oct;168(4):836–843. doi: 10.1093/infdis/168.4.836. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wada M., Kitada K., Saito M., Egawa K., Nakamura Y. cDNA sequence diversity and genomic clusters of major surface glycoprotein genes of Pneumocystis carinii. J Infect Dis. 1993 Oct;168(4):979–985. doi: 10.1093/infdis/168.4.979. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wakefield A. E., Peters S. E., Banerji S., Bridge P. D., Hall G. S., Hawksworth D. L., Guiver L. A., Allen A. G., Hopkin J. M. Pneumocystis carinii shows DNA homology with the ustomycetous red yeast fungi. Mol Microbiol. 1992 Jul;6(14):1903–1911. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2958.1992.tb01363.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wakefield A. E., Pixley F. J., Banerji S., Sinclair K., Miller R. F., Moxon E. R., Hopkin J. M. Detection of Pneumocystis carinii with DNA amplification. Lancet. 1990 Aug 25;336(8713):451–453. doi: 10.1016/0140-6736(90)92008-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Walzer P. D., Linke M. J. A comparison of the antigenic characteristics of rat and human Pneumocystis carinii by immunoblotting. J Immunol. 1987 Apr 1;138(7):2257–2265. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Walzer P. D., Rutledge M. E. Comparison of rat, mouse, and human Pneumocystis carinii by immunofluorescence. J Infect Dis. 1980 Sep;142(3):449–449. doi: 10.1093/infdis/142.3.449. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Walzer P. D., Stanforth D., Linke M. J., Cushion M. T. Pneumocystis carinii: immunoblotting and immunofluorescent analyses of serum antibodies during experimental rat infection and recovery. Exp Parasitol. 1987 Jun;63(3):319–328. doi: 10.1016/0014-4894(87)90179-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weinberg G. A., Bartlett M. S. Comparison of pulsed field gel electrophoresis karyotypes of Pneumocystis carinii derived from rat lung, cell culture, and ferret lung. J Protozool. 1991 Nov-Dec;38(6):64S–65S. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zimmerman P. E., Voelker D. R., McCormack F. X., Paulsrud J. R., Martin W. J., 2nd 120-kD surface glycoprotein of Pneumocystis carinii is a ligand for surfactant protein A. J Clin Invest. 1992 Jan;89(1):143–149. doi: 10.1172/JCI115554. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]