Abstract
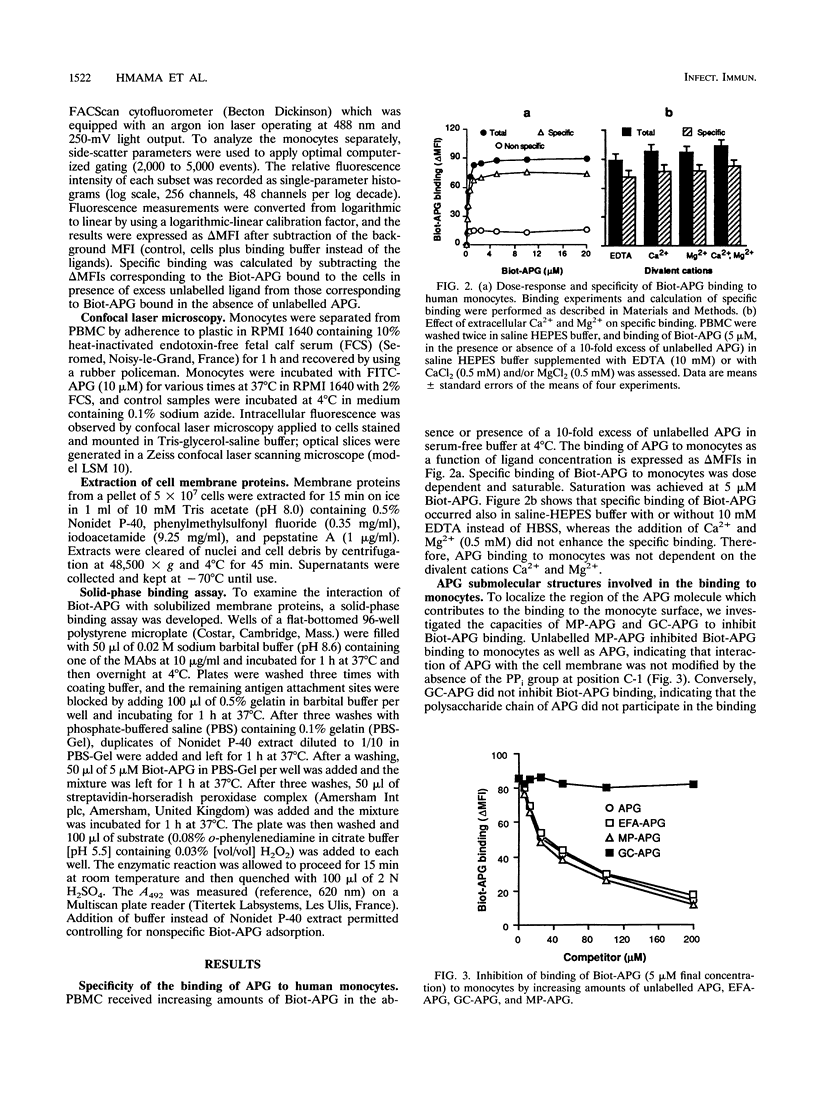
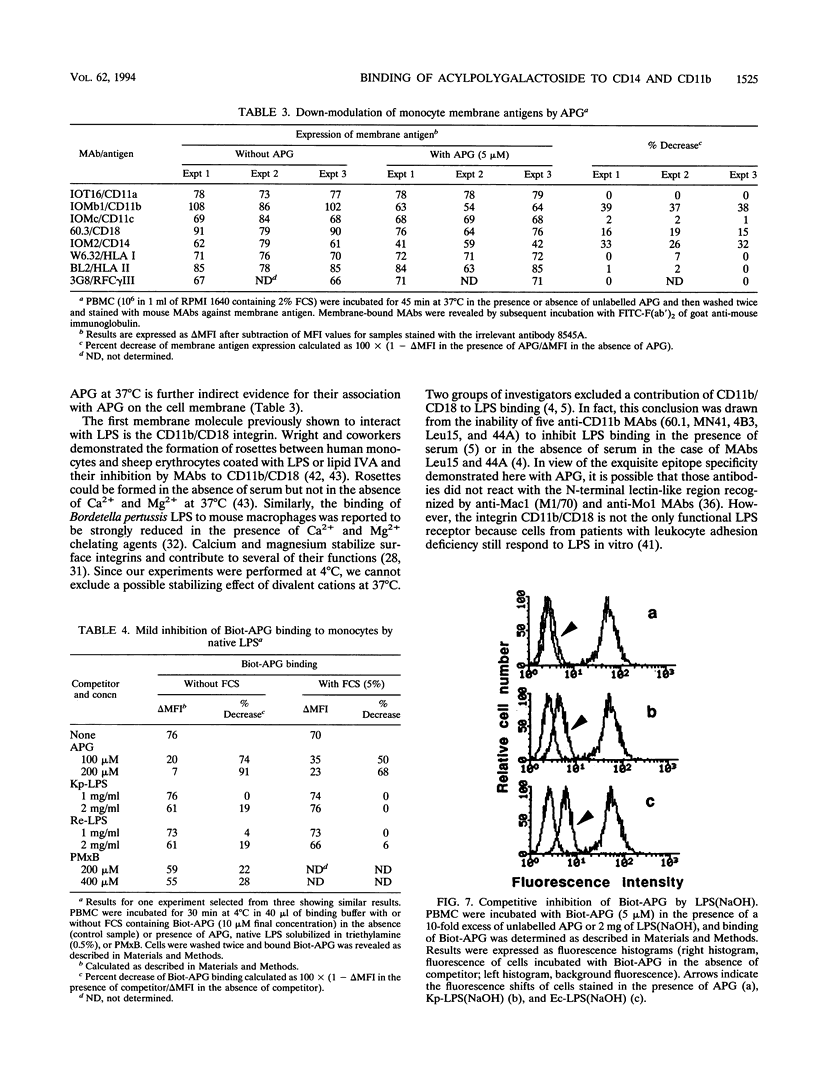
A water-soluble acylpolygalactosyl (APG) of 34 kDa was obtained from the Klebsiella pneumoniae membrane by alkaline hydrolysis and delipidation. APG comprises a poly(1,3)galactose chain, a core, and a lipid moiety made of a glucosamine disaccharide with two N-linked beta OH-myristates. The monocyte binding sites for APG were investigated by flow cytometry. Biotin-labelled APG (Biot-APG) bound to monocytes at 4 degrees C in the absence of serum, calcium, and magnesium. The binding was dose dependent, saturable, and displaced by unlabelled APG. Neither the polysaccharide chain present in APG-related molecules nor the PPi group or additional ester-linked myristates and palmitates were required for APG binding. The role of CD11b and CD14 was demonstrated by competitive inhibition with monoclonal antibodies and by the uptake of APG by these solubilized proteins. APG was rapidly internalized into monocytes at 37 degrees C while CD14 and CD11b/CD18 molecules were partially down-modulated. Lipopolysaccharides (LPS) from the same K. pneumoniae strain and from Escherichia coli and Salmonella minnesota partially competed for Biot-APG binding in the absence but not in the presence of serum. When altered by alkaline hydrolysis, those LPS became strong competitors for APG binding. It was concluded that alkaline hydrolysis of the K. pneumoniae membrane yielded molecules structurally related to LPS which bind to LPS membrane receptors in the absence of serum.
Full text
PDF





Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bagasra O., Wright S. D., Seshamma T., Oakes J. W., Pomerantz R. J. CD14 is involved in control of human immunodeficiency virus type 1 expression in latently infected cells by lipopolysaccharide. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1992 Jul 15;89(14):6285–6289. doi: 10.1073/pnas.89.14.6285. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bullock W. E., Wright S. D. Role of the adherence-promoting receptors, CR3, LFA-1, and p150,95, in binding of Histoplasma capsulatum by human macrophages. J Exp Med. 1987 Jan 1;165(1):195–210. doi: 10.1084/jem.165.1.195. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Corrales I., Weersink A. J., Verhoef J., van Kessel K. P. Serum-independent binding of lipopolysaccharide to human monocytes is trypsin sensitive and does not involve CD14. Immunology. 1993 Sep;80(1):84–89. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Couturier C., Haeffner-Cavaillon N., Caroff M., Kazatchkine M. D. Binding sites for endotoxins (lipopolysaccharides) on human monocytes. J Immunol. 1991 Sep 15;147(6):1899–1904. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Graham I. L., Brown E. J. Extracellular calcium results in a conformational change in Mac-1 (CD11b/CD18) on neutrophils. Differentiation of adhesion and phagocytosis functions of Mac-1. J Immunol. 1991 Jan 15;146(2):685–691. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Haeffner-Cavaillon N., Caroff M., Cavaillon J. M. Interleukin-1 induction by lipopolysaccharides: structural requirements of the 3-deoxy-D-manno-2-octulosonic acid (KDO). Mol Immunol. 1989 May;26(5):485–494. doi: 10.1016/0161-5890(89)90108-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Haeffner-Cavaillon N., Cavaillon J. M., Etievant M., Lebbar S., Szabo L. Specific binding of endotoxin to human monocytes and mouse macrophages: serum requirement. Cell Immunol. 1985 Mar;91(1):119–131. doi: 10.1016/0008-8749(85)90037-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Haeffner-Cavaillon N., Cavaillon J. M., Szabo L. Macrophage-dependent polyclonal activation of splenocytes by Bordetella pertussis endotoxin and its isolated polysaccharide and Lipid A regions. Cell Immunol. 1982 Nov 15;74(1):1–13. doi: 10.1016/0008-8749(82)90001-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hailman E., Lichenstein H. S., Wurfel M. M., Miller D. S., Johnson D. A., Kelley M., Busse L. A., Zukowski M. M., Wright S. D. Lipopolysaccharide (LPS)-binding protein accelerates the binding of LPS to CD14. J Exp Med. 1994 Jan 1;179(1):269–277. doi: 10.1084/jem.179.1.269. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Halling J. L., Hamill D. R., Lei M. G., Morrison D. C. Identification and characterization of lipopolysaccharide-binding proteins on human peripheral blood cell populations. Infect Immun. 1992 Mar;60(3):845–852. doi: 10.1128/iai.60.3.845-852.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hampton R. Y., Golenbock D. T., Penman M., Krieger M., Raetz C. R. Recognition and plasma clearance of endotoxin by scavenger receptors. Nature. 1991 Jul 25;352(6333):342–344. doi: 10.1038/352342a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hmama Z., Kouassi E., Panaye G., Delassan S., Normier G., Binz H., Revillard J. P. Binding of a bacterial acylpoly(1,3)galactoside to human blood leucocytes. Scand J Immunol. 1992 Jul;36(1):11–20. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-3083.1992.tb02935.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hmama Z., Lina G., Normier G., Binz H., Revillard J. P. Role of acyl residues in polyclonal murine B cell activation by acylpoly(1,3)galactosides from Klebsiella pneumoniae. J Immunol. 1993 Nov 15;151(10):5440–5449. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hmama Z., Lina G., Vincent C., Wijdenes J., Normier G., Binz H., Revillard J. P. Monocyte cytokine secretion induced by chemically-defined derivatives of Klebsiella pneumoniae. Clin Exp Immunol. 1992 Jul;89(1):104–109. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2249.1992.tb06886.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hmama Z., Normier G., Kouassi E., Flacher M., Binz H., Revillard J. P. Binding of a membrane proteoglycan from Klebsiella pneumoniae and its derivatives to human leukocytes. Immunobiology. 1992 Nov;186(3-4):183–198. doi: 10.1016/S0171-2985(11)80249-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kang Y. H., Dwivedi R. S., Lee C. H. Ultrastructural and immunocytochemical study of the uptake and distribution of bacterial lipopolysaccharide in human monocytes. J Leukoc Biol. 1990 Oct;48(4):316–332. doi: 10.1002/jlb.48.4.316. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Keller G. E., 3rd, Dey R. D., Burrell R. Immunocytochemical determination of the role of alveolar macrophages in endotoxin processing in vitro and in vivo. Int Arch Allergy Appl Immunol. 1991;96(2):149–155. doi: 10.1159/000235486. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kitchens R. L., Ulevitch R. J., Munford R. S. Lipopolysaccharide (LPS) partial structures inhibit responses to LPS in a human macrophage cell line without inhibiting LPS uptake by a CD14-mediated pathway. J Exp Med. 1992 Aug 1;176(2):485–494. doi: 10.1084/jem.176.2.485. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kouassi E., Hmama Z., Lina G., Vial J., Faure-Barba F., Normier G., Binz H., Revillard J. P. Activation of human monocyte chemiluminescence response by acylpoly(1,3)galactosides derived from Klebsiella pneumoniae. J Leukoc Biol. 1992 Nov;52(5):529–536. doi: 10.1002/jlb.52.5.529. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lei M. G., Morrison D. C. Specific endotoxic lipopolysaccharide-binding proteins on murine splenocytes. II. Membrane localization and binding characteristics. J Immunol. 1988 Aug 1;141(3):1006–1011. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lei M. G., Stimpson S. A., Morrison D. C. Specific endotoxic lipopolysaccharide-binding receptors on murine splenocytes. III. Binding specificity and characterization. J Immunol. 1991 Sep 15;147(6):1925–1932. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Luchi M., Munford R. S. Binding, internalization, and deacylation of bacterial lipopolysaccharide by human neutrophils. J Immunol. 1993 Jul 15;151(2):959–969. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morrison D. C., Jacobs D. M. Binding of polymyxin B to the lipid A portion of bacterial lipopolysaccharides. Immunochemistry. 1976 Oct;13(10):813–818. doi: 10.1016/0019-2791(76)90181-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Municio A. M., Abarca S., Carrascosa J. L., Garcia R., Diaz-Laviada I., Ainaga M. J., Portoles M. T., Pagani R., Risco C., Bosch M. A. Immunocytochemical localization of bacterial lipopolysaccharide with colloidal-gold probes in different target cells. Adv Exp Med Biol. 1990;256:199–202. doi: 10.1007/978-1-4757-5140-6_17. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Raetz C. R. Biochemistry of endotoxins. Annu Rev Biochem. 1990;59:129–170. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.59.070190.001021. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schumann R. R., Leong S. R., Flaggs G. W., Gray P. W., Wright S. D., Mathison J. C., Tobias P. S., Ulevitch R. J. Structure and function of lipopolysaccharide binding protein. Science. 1990 Sep 21;249(4975):1429–1431. doi: 10.1126/science.2402637. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Springer T. A. Adhesion receptors of the immune system. Nature. 1990 Aug 2;346(6283):425–434. doi: 10.1038/346425a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tahri-Jouti M. A., Chaby R. Specific binding of lipopolysaccharides to mouse macrophages--I. Characteristics of the interaction and inefficiency of the polysaccharide region. Mol Immunol. 1990 Aug;27(8):751–761. doi: 10.1016/0161-5890(90)90084-d. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tahri-Jouti M. A., Mondange M., Le Dur A., Auzanneau F. I., Charon D., Girard R., Chaby R. Specific binding of lipopolysaccharides to mouse macrophages--II. Involvement of distinct lipid a substructures. Mol Immunol. 1990 Aug;27(8):763–770. doi: 10.1016/0161-5890(90)90085-e. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Talamás-Rohana P., Wright S. D., Lennartz M. R., Russell D. G. Lipophosphoglycan from Leishmania mexicana promastigotes binds to members of the CR3, p150,95 and LFA-1 family of leukocyte integrins. J Immunol. 1990 Jun 15;144(12):4817–4824. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tobias P. S., Soldau K., Kline L., Lee J. D., Kato K., Martin T. P., Ulevitch R. J. Cross-linking of lipopolysaccharide (LPS) to CD14 on THP-1 cells mediated by LPS-binding protein. J Immunol. 1993 Apr 1;150(7):3011–3021. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vincent C., Revillard J. P. Sandwich-type ELISA for free and bound secretory component in human biological fluids. J Immunol Methods. 1988 Feb 10;106(2):153–160. doi: 10.1016/0022-1759(88)90191-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weersink A. J., van Kessel K. P., van den Tol M. E., van Strijp J. A., Torensma R., Verhoef J., Elsbach P., Weiss J. Human granulocytes express a 55-kDa lipopolysaccharide-binding protein on the cell surface that is identical to the bactericidal/permeability-increasing protein. J Immunol. 1993 Jan 1;150(1):253–263. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wright S. D., Detmers P. A., Aida Y., Adamowski R., Anderson D. C., Chad Z., Kabbash L. G., Pabst M. J. CD18-deficient cells respond to lipopolysaccharide in vitro. J Immunol. 1990 Apr 1;144(7):2566–2571. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wright S. D., Jong M. T. Adhesion-promoting receptors on human macrophages recognize Escherichia coli by binding to lipopolysaccharide. J Exp Med. 1986 Dec 1;164(6):1876–1888. doi: 10.1084/jem.164.6.1876. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wright S. D., Levin S. M., Jong M. T., Chad Z., Kabbash L. G. CR3 (CD11b/CD18) expresses one binding site for Arg-Gly-Asp-containing peptides and a second site for bacterial lipopolysaccharide. J Exp Med. 1989 Jan 1;169(1):175–183. doi: 10.1084/jem.169.1.175. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wright S. D. Multiple receptors for endotoxin. Curr Opin Immunol. 1991 Feb;3(1):83–90. doi: 10.1016/0952-7915(91)90082-c. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wright S. D., Ramos R. A., Patel M., Miller D. S. Septin: a factor in plasma that opsonizes lipopolysaccharide-bearing particles for recognition by CD14 on phagocytes. J Exp Med. 1992 Sep 1;176(3):719–727. doi: 10.1084/jem.176.3.719. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wright S. D., Ramos R. A., Tobias P. S., Ulevitch R. J., Mathison J. C. CD14, a receptor for complexes of lipopolysaccharide (LPS) and LPS binding protein. Science. 1990 Sep 21;249(4975):1431–1433. doi: 10.1126/science.1698311. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]




