Abstract
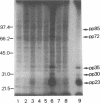
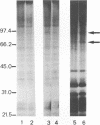
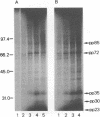
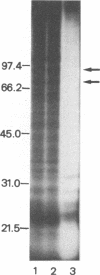
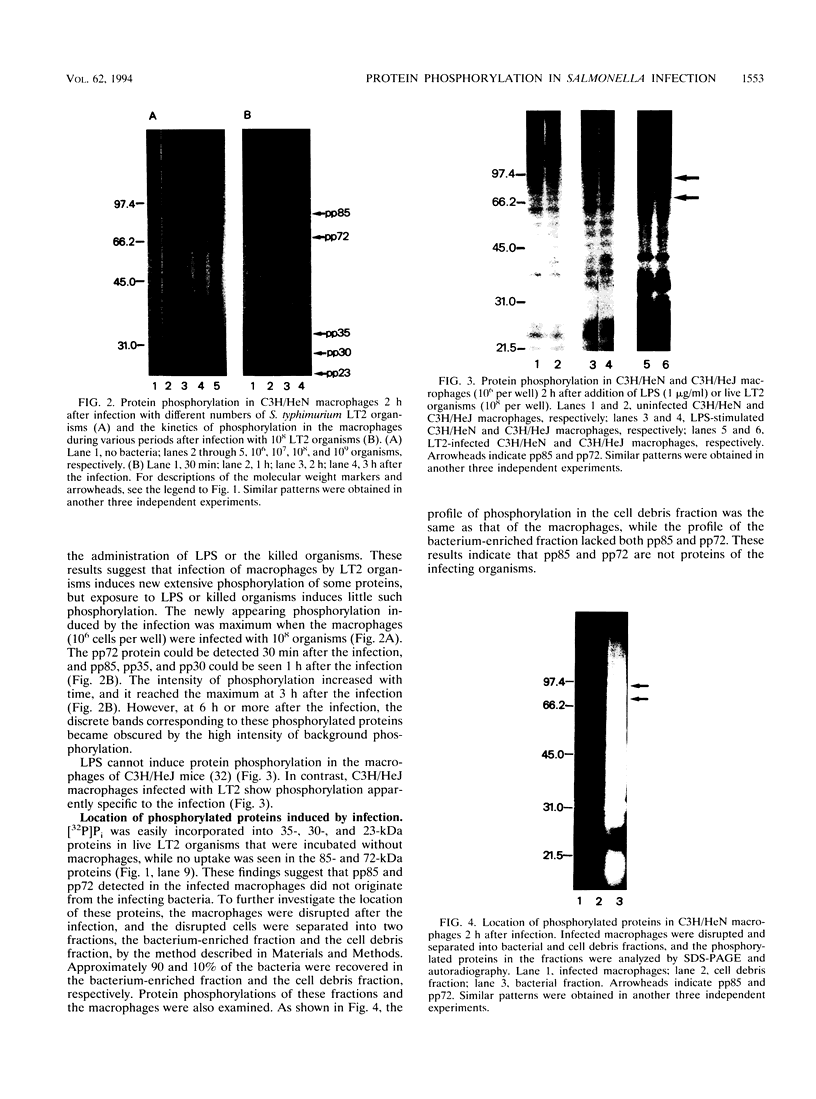
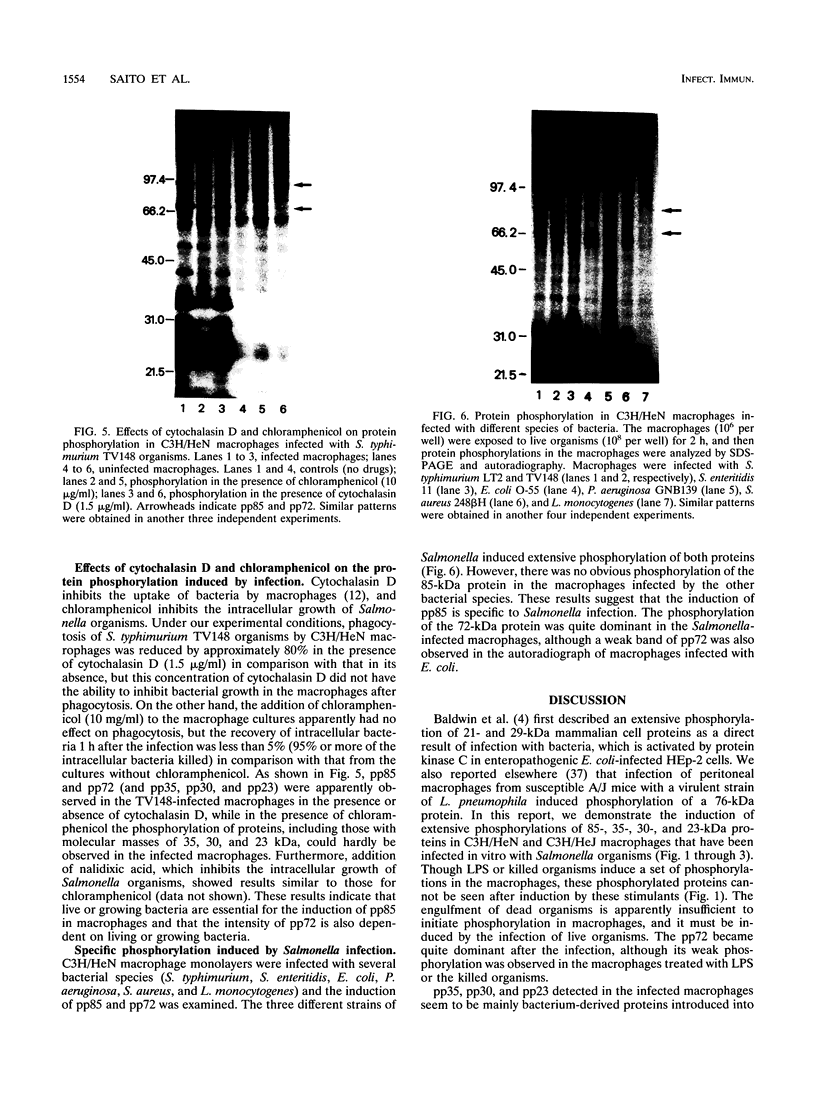
Infection of peritoneal macrophages from C3H/HeN and C3H/HeJ mice with Salmonella typhimurium or S. enteritidis induced extensive phosphorylation in a set of proteins with molecular masses of 85, 72, 35, 30, and 23 kDa, which were different from those induced by bacterial lipopolysaccharide. The phosphorylated proteins of 35, 30, and 23 kDa (pp35, pp30, and pp23, respectively) originated from the infecting bacteria, because living bacteria could induce these phosphorylated proteins themselves, and no induction of the proteins occurred in macrophages after phagocytosis of heat-killed or UV-irradiated organisms. When the infected macrophages were disrupted and separated into bacterial and macrophage debris fractions, pp85 and pp72 remained in the macrophage debris fraction, with none in the bacterial fraction. Induction of pp85 and pp72 in infected macrophages was inhibited in the presence of chloramphenicol but not cytochalasin D, suggesting that bacterial growth in the macrophages is necessary for induction of both proteins. Neither of these proteins could be detected in macrophages infected with Escherichia coli, Pseudomonas aeruginosa, Staphylococcus aureus, or Listeria monocytogenes. These results support the view that phosphorylation of the 85- and 72-kDa proteins occurs in the macrophages during the early phases of the interaction between Salmonella organisms and macrophages. The functions of specific proteins remain to be clarified.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Ahn N. G., Krebs E. G. Evidence for an epidermal growth factor-stimulated protein kinase cascade in Swiss 3T3 cells. Activation of serine peptide kinase activity by myelin basic protein kinases in vitro. J Biol Chem. 1990 Jul 15;265(20):11495–11501. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ahn N. G., Weiel J. E., Chan C. P., Krebs E. G. Identification of multiple epidermal growth factor-stimulated protein serine/threonine kinases from Swiss 3T3 cells. J Biol Chem. 1990 Jul 15;265(20):11487–11494. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baeuerle P. A., Baltimore D. Activation of DNA-binding activity in an apparently cytoplasmic precursor of the NF-kappa B transcription factor. Cell. 1988 Apr 22;53(2):211–217. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(88)90382-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baldwin T. J., Brooks S. F., Knutton S., Manjarrez Hernandez H. A., Aitken A., Williams P. H. Protein phosphorylation by protein kinase C in HEp-2 cells infected with enteropathogenic Escherichia coli. Infect Immun. 1990 Mar;58(3):761–765. doi: 10.1128/iai.58.3.761-765.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Becker S., Devlin R. B., Haskill J. S. Differential production of tumor necrosis factor, macrophage colony stimulating factor, and interleukin 1 by human alveolar macrophages. J Leukoc Biol. 1989 Apr;45(4):353–361. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chokri M., Freudenberg M., Galanos C., Poindron P., Bartholeyns J. Antitumoral effects of lipopolysaccharides, tumor necrosis factor, interferon and activated macrophages: synergism and tissue distribution. Anticancer Res. 1989 Jul-Aug;9(4):1185–1190. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cohen P. The role of protein phosphorylation in neural and hormonal control of cellular activity. Nature. 1982 Apr 15;296(5858):613–620. doi: 10.1038/296613a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Collart M. A., Baeuerle P., Vassalli P. Regulation of tumor necrosis factor alpha transcription in macrophages: involvement of four kappa B-like motifs and of constitutive and inducible forms of NF-kappa B. Mol Cell Biol. 1990 Apr;10(4):1498–1506. doi: 10.1128/mcb.10.4.1498. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Collins F. M. Vaccines and cell-mediated immunity. Bacteriol Rev. 1974 Dec;38(4):371–402. doi: 10.1128/br.38.4.371-402.1974. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Decker T., Lohmann-Matthes M. L., Karck U., Peters T., Decker K. Comparative study of cytotoxicity, tumor necrosis factor, and prostaglandin release after stimulation of rat Kupffer cells, murine Kupffer cells, and murine inflammatory liver macrophages. J Leukoc Biol. 1989 Feb;45(2):139–146. doi: 10.1002/jlb.45.2.139. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ding A. H., Nathan C. F. Trace levels of bacterial lipopolysaccharide prevent interferon-gamma or tumor necrosis factor-alpha from enhancing mouse peritoneal macrophage respiratory burst capacity. J Immunol. 1987 Sep 15;139(6):1971–1977. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Elliott J. A., Winn W. C., Jr Treatment of alveolar macrophages with cytochalasin D inhibits uptake and subsequent growth of Legionella pneumophila. Infect Immun. 1986 Jan;51(1):31–36. doi: 10.1128/iai.51.1.31-36.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Galán J. E., Pace J., Hayman M. J. Involvement of the epidermal growth factor receptor in the invasion of cultured mammalian cells by Salmonella typhimurium. Nature. 1992 Jun 18;357(6379):588–589. doi: 10.1038/357588a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Haslett C., Guthrie L. A., Kopaniak M. M., Johnston R. B., Jr, Henson P. M. Modulation of multiple neutrophil functions by preparative methods or trace concentrations of bacterial lipopolysaccharide. Am J Pathol. 1985 Apr;119(1):101–110. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hunter T. A thousand and one protein kinases. Cell. 1987 Sep 11;50(6):823–829. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90509-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Krebs E. G., Beavo J. A. Phosphorylation-dephosphorylation of enzymes. Annu Rev Biochem. 1979;48:923–959. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.48.070179.004423. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Manthey C. L., Brandes M. E., Perera P. Y., Vogel S. N. Taxol increases steady-state levels of lipopolysaccharide-inducible genes and protein-tyrosine phosphorylation in murine macrophages. J Immunol. 1992 Oct 1;149(7):2459–2465. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mathison J. C., Virca G. D., Wolfson E., Tobias P. S., Glaser K., Ulevitch R. J. Adaptation to bacterial lipopolysaccharide controls lipopolysaccharide-induced tumor necrosis factor production in rabbit macrophages. J Clin Invest. 1990 Apr;85(4):1108–1118. doi: 10.1172/JCI114542. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Matsumura H., Onozuka K., Terada Y., Nakano Y., Nakano M. Effect of murine recombinant interferon-gamma in the protection of mice against Salmonella. Int J Immunopharmacol. 1990;12(1):49–56. doi: 10.1016/0192-0561(90)90067-w. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nakano M., Saito K. Chemical components in the cell wall of Salmonella typhimurium affecting its virulence and immunogenicity in mice. Nature. 1969 Jun 14;222(5198):1085–1086. doi: 10.1038/2221085a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nakano M., Saito S., Nakano Y., Yamasu H., Matsuura M., Shinomiya H. Intracellular protein phosphorylation in murine peritoneal macrophages in response to bacterial lipopolysaccharide (LPS): effects of kinase-inhibitors and LPS-induced tolerance. Immunobiology. 1993 Apr;187(3-5):272–282. doi: 10.1016/S0171-2985(11)80344-X. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nakano Y., Onozuka K., Terada Y., Shinomiya H., Nakano M. Protective effect of recombinant tumor necrosis factor-alpha in murine salmonellosis. J Immunol. 1990 Mar 1;144(5):1935–1941. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nel A. E., Hanekom C., Hultin L. Protein kinase C plays a role in the induction of tyrosine phosphorylation of lymphoid microtubule-associated protein-2 kinase. Evidence for a CD3-associated cascade that includes pp56lck and that is defective in HPB-ALL. J Immunol. 1991 Sep 15;147(6):1933–1939. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nichols F. C., Garrison S. W., Davis H. W. Prostaglandin E2 and thromboxane B2 release from human monocytes treated with bacterial lipopolysaccharide. J Leukoc Biol. 1988 Nov;44(5):376–384. doi: 10.1002/jlb.44.5.376. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- O'Brien A. D., Metcalf E. S. Control of early Salmonella typhimurium growth in innately Salmonella-resistant mice does not require functional T lymphocytes. J Immunol. 1982 Oct;129(4):1349–1351. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pace J., Hayman M. J., Galán J. E. Signal transduction and invasion of epithelial cells by S. typhimurium. Cell. 1993 Feb 26;72(4):505–514. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(93)90070-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rossomando A. J., Payne D. M., Weber M. J., Sturgill T. W. Evidence that pp42, a major tyrosine kinase target protein, is a mitogen-activated serine/threonine protein kinase. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Sep;86(18):6940–6943. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.18.6940. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shinomiya H., Hirata H., Nakano M. Purification and characterization of the 65-kDa protein phosphorylated in murine macrophages by stimulation with bacterial lipopolysaccharide. J Immunol. 1991 May 15;146(10):3617–3625. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sturgill T. W., Ray L. B., Erikson E., Maller J. L. Insulin-stimulated MAP-2 kinase phosphorylates and activates ribosomal protein S6 kinase II. Nature. 1988 Aug 25;334(6184):715–718. doi: 10.1038/334715a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weiel J. E., Hamilton T. A., Adams D. O. LPS induces altered phosphate labeling of proteins in murine peritoneal macrophages. J Immunol. 1986 Apr 15;136(8):3012–3018. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weinstein S. L., Gold M. R., DeFranco A. L. Bacterial lipopolysaccharide stimulates protein tyrosine phosphorylation in macrophages. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 May 15;88(10):4148–4152. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.10.4148. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yamamoto Y., Klein T. W., Shinomiya H., Nakano M., Friedman H. Infection of macrophages with Legionella pneumophila induces phosphorylation of a 76-kilodalton protein. Infect Immun. 1992 Aug;60(8):3452–3455. doi: 10.1128/iai.60.8.3452-3455.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van Dissel J. T., Leijh P. C., van Furth R. Differences in initial rate of intracellular killing of Salmonella typhimurium by resident peritoneal macrophages from various mouse strains. J Immunol. 1985 May;134(5):3404–3410. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]