Abstract
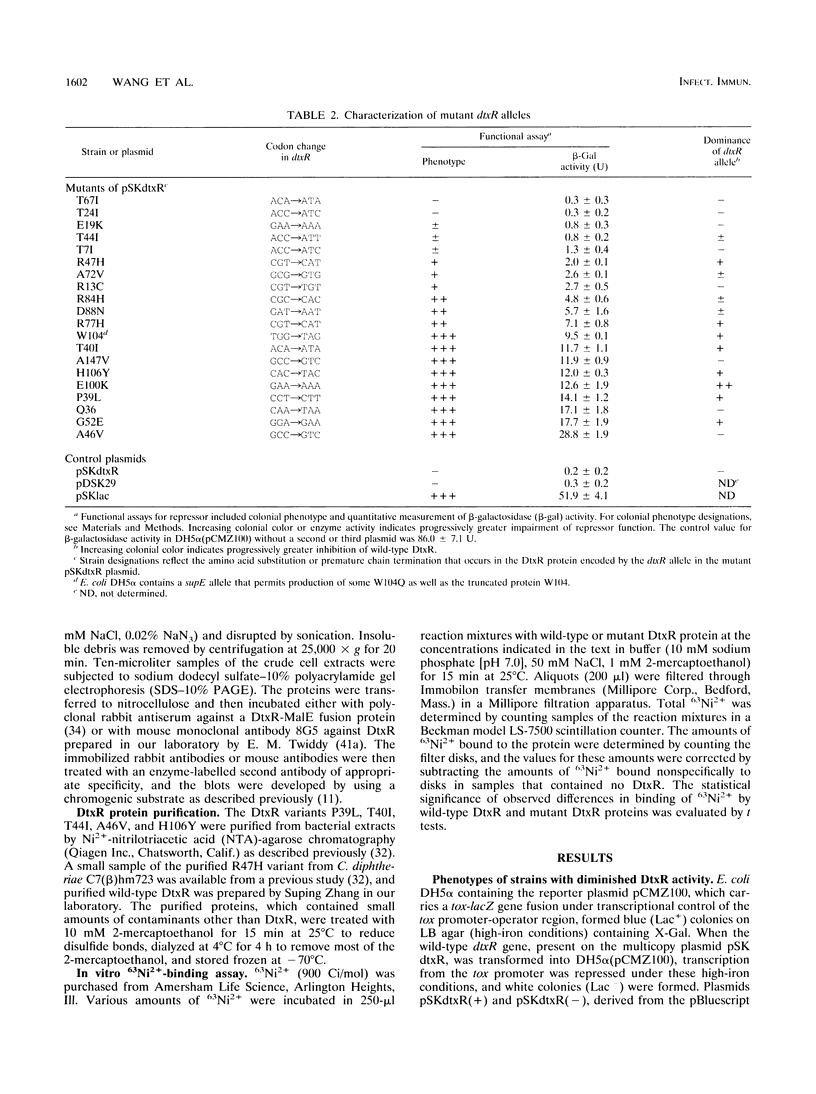
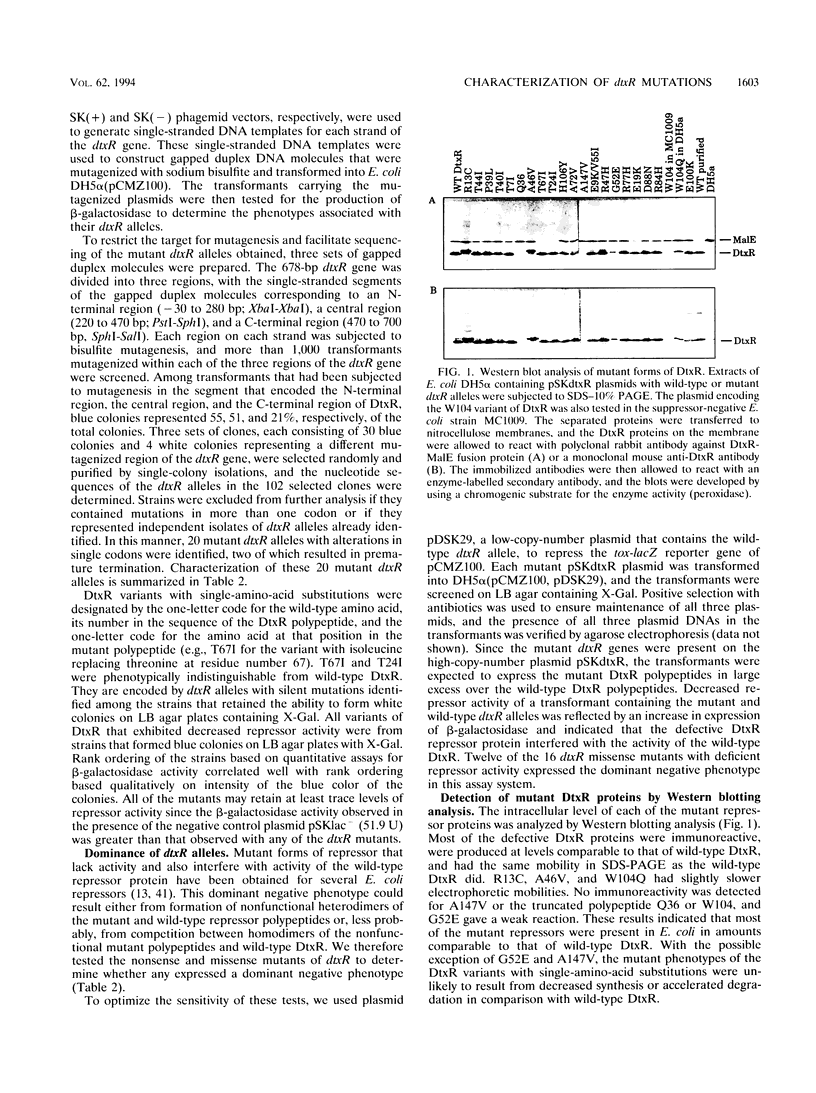
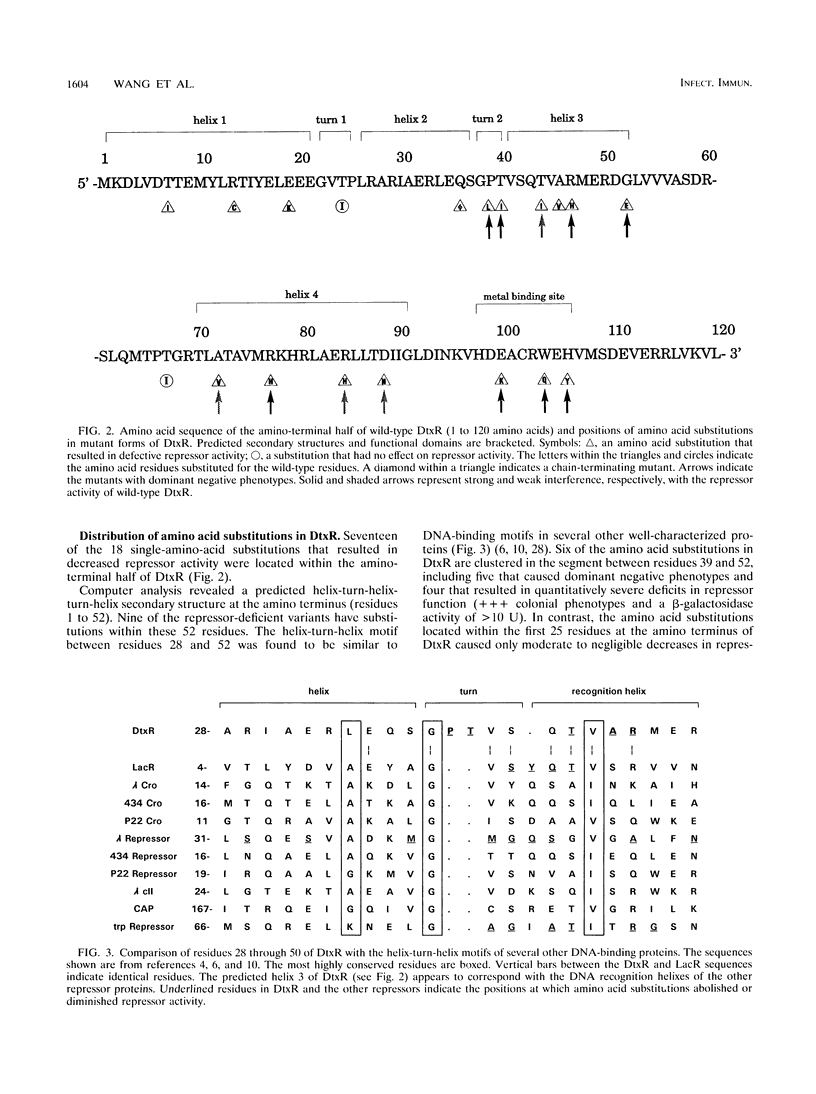
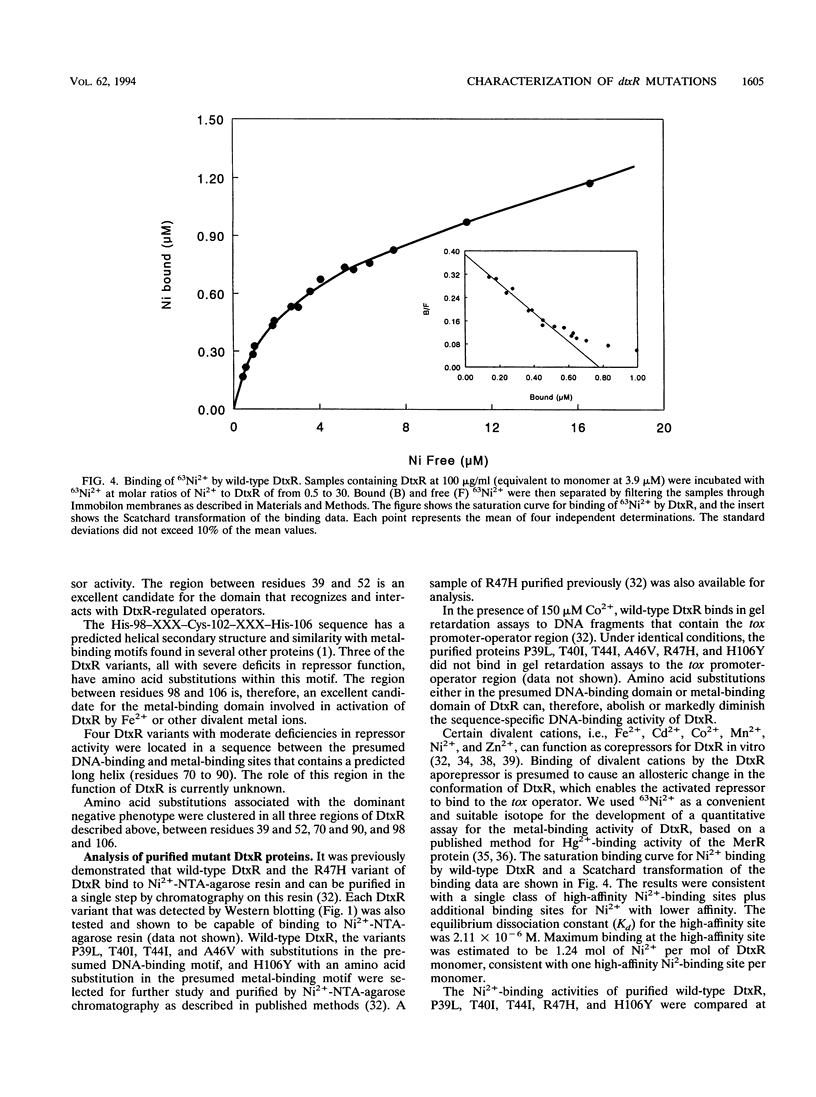
The diphtheria toxin repressor (DtxR) is an iron-dependent regulator of diphtheria toxin production and iron uptake in Corynebacterium diphtheriae. It is activated in vitro by divalent metal ions including Fe2+, Cd2+, Co2+, Mn2+, Ni2+, and Zn2+. We characterized 20 different mutations in dtxR induced by bisulfite mutagenesis, 18 of which caused single-amino-acid substitutions in DtxR and two of which were chain-terminating mutations. Six of the amino acid replacements were clustered between residues 39 and 52 in a predicted helix-turn-helix motif that exhibits homology with several other repressors and is identified as the putative DNA-binding domain of DtxR. Three substitutions occurred within a predicted alpha-helical region with the sequence His-98-X3-Cys-102-X3-His-106 that resembles metal-binding motifs in several other proteins and is identified as the putative metal-binding site of DtxR. Several purified variants of DtxR with decreased repressor activity failed to bind in gel retardation assays to DNA fragments that contained the tox operator. A quantitative assay for binding of DtxR to 63Ni2+ was also developed. Scatchard analysis revealed that DtxR has a single class of high-affinity 63Ni(2+)-binding sites with a Kd of 2.11 x 10(-6) M and a maximum binding capacity of approximately 1.2 atoms of Ni2+ per DtxR monomer. The P39L, T40I, T44I, and R47H variants of DtxR exhibited normal to slightly decreased 63Ni(2+)-binding activity, but H106Y, which has an amino acid substitution in the presumed metal-binding domain, exhibited markedly decreased 63Ni(2+)-binding activity.
Full text
PDF

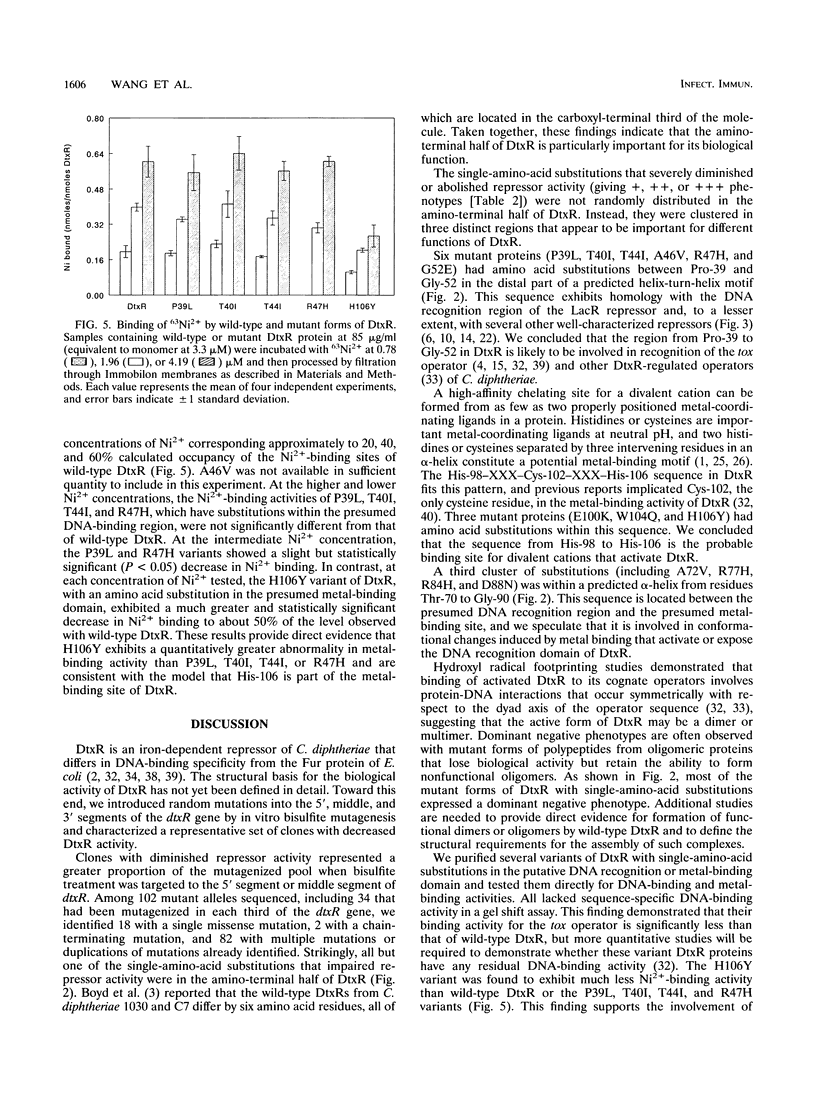


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Arnold F. H., Haymore B. L. Engineered metal-binding proteins: purification to protein folding. Science. 1991 Jun 28;252(5014):1796–1797. doi: 10.1126/science.1648261. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bagg A., Neilands J. B. Ferric uptake regulation protein acts as a repressor, employing iron (II) as a cofactor to bind the operator of an iron transport operon in Escherichia coli. Biochemistry. 1987 Aug 25;26(17):5471–5477. doi: 10.1021/bi00391a039. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boyd J. M., Hall K. C., Murphy J. R. DNA sequences and characterization of dtxR alleles from Corynebacterium diphtheriae PW8(-), 1030(-), and C7hm723(-). J Bacteriol. 1992 Feb;174(4):1268–1272. doi: 10.1128/jb.174.4.1268-1272.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boyd J., Murphy J. R. Analysis of the diphtheria tox promoter by site-directed mutagenesis. J Bacteriol. 1988 Dec;170(12):5949–5952. doi: 10.1128/jb.170.12.5949-5952.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boyd J., Oza M. N., Murphy J. R. Molecular cloning and DNA sequence analysis of a diphtheria tox iron-dependent regulatory element (dtxR) from Corynebacterium diphtheriae. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Aug;87(15):5968–5972. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.15.5968. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brennan R. G., Matthews B. W. The helix-turn-helix DNA binding motif. J Biol Chem. 1989 Feb 5;264(4):1903–1906. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Connell T. D., Holmes R. K. Molecular genetic analysis of ganglioside GD1b-binding activity of Escherichia coli type IIa heat-labile enterotoxin by use of random and site-directed mutagenesis. Infect Immun. 1992 Jan;60(1):63–70. doi: 10.1128/iai.60.1.63-70.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Coy M., Neilands J. B. Structural dynamics and functional domains of the fur protein. Biochemistry. 1991 Aug 20;30(33):8201–8210. doi: 10.1021/bi00247a016. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fourel G., Phalipon A., Kaczorek M. Evidence for direct regulation of diphtheria toxin gene transcription by an Fe2+-dependent DNA-binding repressor, DtoxR, in Corynebacterium diphtheriae. Infect Immun. 1989 Oct;57(10):3221–3225. doi: 10.1128/iai.57.10.3221-3225.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harrison S. C. A structural taxonomy of DNA-binding domains. Nature. 1991 Oct 24;353(6346):715–719. doi: 10.1038/353715a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Holmes R. K., Twiddy E. M. Characterization of monoclonal antibodies that react with unique and cross-reacting determinants of cholera enterotoxin and its subunits. Infect Immun. 1983 Dec;42(3):914–923. doi: 10.1128/iai.42.3.914-923.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaczorek M., Zettlmeissl G., Delpeyroux F., Streeck R. E. Diphtheria toxin promoter function in Corynebacterium diphtheriae and Escherichia coli. Nucleic Acids Res. 1985 May 10;13(9):3147–3159. doi: 10.1093/nar/13.9.3147. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kelley R. L., Yanofsky C. Mutational studies with the trp repressor of Escherichia coli support the helix-turn-helix model of repressor recognition of operator DNA. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Jan;82(2):483–487. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.2.483. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kolkhof P., Teichmann D., Kisters-Woike B., von Wilcken-Bergmann B., Müller-Hill B. Lac repressor with the helix-turn-helix motif of lambda cro binds to lac operator. EMBO J. 1992 Aug;11(8):3031–3038. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1992.tb05373.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Krafft A. E., Tai S. P., Coker C., Holmes R. K. Transcription analysis and nucleotide sequence of tox promoter/operator mutants of corynebacteriophage beta. Microb Pathog. 1992 Aug;13(2):85–92. doi: 10.1016/0882-4010(92)90069-z. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Matthews B. W., Ohlendorf D. H., Anderson W. F., Takeda Y. Structure of the DNA-binding region of lac repressor inferred from its homology with cro repressor. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Mar;79(5):1428–1432. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.5.1428. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Murphy J. R., Michel J. L., Teng M. Evidence that the regulation of diphtheria toxin production is directed at the level of transcription. J Bacteriol. 1978 Aug;135(2):511–516. doi: 10.1128/jb.135.2.511-516.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pabo C. O., Sauer R. T. Transcription factors: structural families and principles of DNA recognition. Annu Rev Biochem. 1992;61:1053–1095. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.61.070192.005201. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pappenheimer A. M., Jr Diphtheria toxin. Annu Rev Biochem. 1977;46:69–94. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.46.070177.000441. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pine R., Huang P. C. An improved method to obtain a large number of mutants in a defined region of DNA. Methods Enzymol. 1987;154:415–430. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(87)54088-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rogers H. J. Iron-Binding Catechols and Virulence in Escherichia coli. Infect Immun. 1973 Mar;7(3):445–456. doi: 10.1128/iai.7.3.445-456.1973. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Saito T., Wormald M. R., Williams R. J. Some structural features of the iron-uptake regulation protein. Eur J Biochem. 1991 Apr 10;197(1):29–38. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1991.tb15878.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanger F., Nicklen S., Coulson A. R. DNA sequencing with chain-terminating inhibitors. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Dec;74(12):5463–5467. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.12.5463. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sauer R. T., Yocum R. R., Doolittle R. F., Lewis M., Pabo C. O. Homology among DNA-binding proteins suggests use of a conserved super-secondary structure. Nature. 1982 Jul 29;298(5873):447–451. doi: 10.1038/298447a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schmitt M. P., Holmes R. K. Analysis of diphtheria toxin repressor-operator interactions and characterization of a mutant repressor with decreased binding activity for divalent metals. Mol Microbiol. 1993 Jul;9(1):173–181. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2958.1993.tb01679.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schmitt M. P., Holmes R. K. Characterization of a defective diphtheria toxin repressor (dtxR) allele and analysis of dtxR transcription in wild-type and mutant strains of Corynebacterium diphtheriae. Infect Immun. 1991 Nov;59(11):3903–3908. doi: 10.1128/iai.59.11.3903-3908.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schmitt M. P., Holmes R. K. Iron-dependent regulation of diphtheria toxin and siderophore expression by the cloned Corynebacterium diphtheriae repressor gene dtxR in C. diphtheriae C7 strains. Infect Immun. 1991 Jun;59(6):1899–1904. doi: 10.1128/iai.59.6.1899-1904.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schmitt M. P., Twiddy E. M., Holmes R. K. Purification and characterization of the diphtheria toxin repressor. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1992 Aug 15;89(16):7576–7580. doi: 10.1073/pnas.89.16.7576. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schäffer S., Hantke K., Braun V. Nucleotide sequence of the iron regulatory gene fur. Mol Gen Genet. 1985;200(1):110–113. doi: 10.1007/BF00383321. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shewchuk L. M., Helmann J. D., Ross W., Park S. J., Summers A. O., Walsh C. T. Transcriptional switching by the MerR protein: activation and repression mutants implicate distinct DNA and mercury(II) binding domains. Biochemistry. 1989 Mar 7;28(5):2340–2344. doi: 10.1021/bi00431a053. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shewchuk L. M., Verdine G. L., Walsh C. T. Transcriptional switching by the metalloregulatory MerR protein: initial characterization of DNA and mercury (II) binding activities. Biochemistry. 1989 Mar 7;28(5):2331–2339. doi: 10.1021/bi00431a052. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tai S. P., Krafft A. E., Nootheti P., Holmes R. K. Coordinate regulation of siderophore and diphtheria toxin production by iron in Corynebacterium diphtheriae. Microb Pathog. 1990 Oct;9(4):267–273. doi: 10.1016/0882-4010(90)90015-i. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tao X., Boyd J., Murphy J. R. Specific binding of the diphtheria tox regulatory element DtxR to the tox operator requires divalent heavy metal ions and a 9-base-pair interrupted palindromic sequence. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1992 Jul 1;89(13):5897–5901. doi: 10.1073/pnas.89.13.5897. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tao X., Murphy J. R. Binding of the metalloregulatory protein DtxR to the diphtheria tox operator requires a divalent heavy metal ion and protects the palindromic sequence from DNase I digestion. J Biol Chem. 1992 Oct 25;267(30):21761–21764. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tao X., Murphy J. R. Cysteine-102 is positioned in the metal binding activation site of the Corynebacterium diphtheriae regulatory element DtxR. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1993 Sep 15;90(18):8524–8528. doi: 10.1073/pnas.90.18.8524. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thliveris A. T., Mount D. W. Genetic identification of the DNA binding domain of Escherichia coli LexA protein. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1992 May 15;89(10):4500–4504. doi: 10.1073/pnas.89.10.4500. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Welkos S. L., Holmes R. K. Regulation of toxinogenesis in Corynebacterium diphtheriae. I. Mutations in bacteriophage beta that alter the effects of iron on toxin production. J Virol. 1981 Mar;37(3):936–945. doi: 10.1128/jvi.37.3.936-945.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



