Abstract
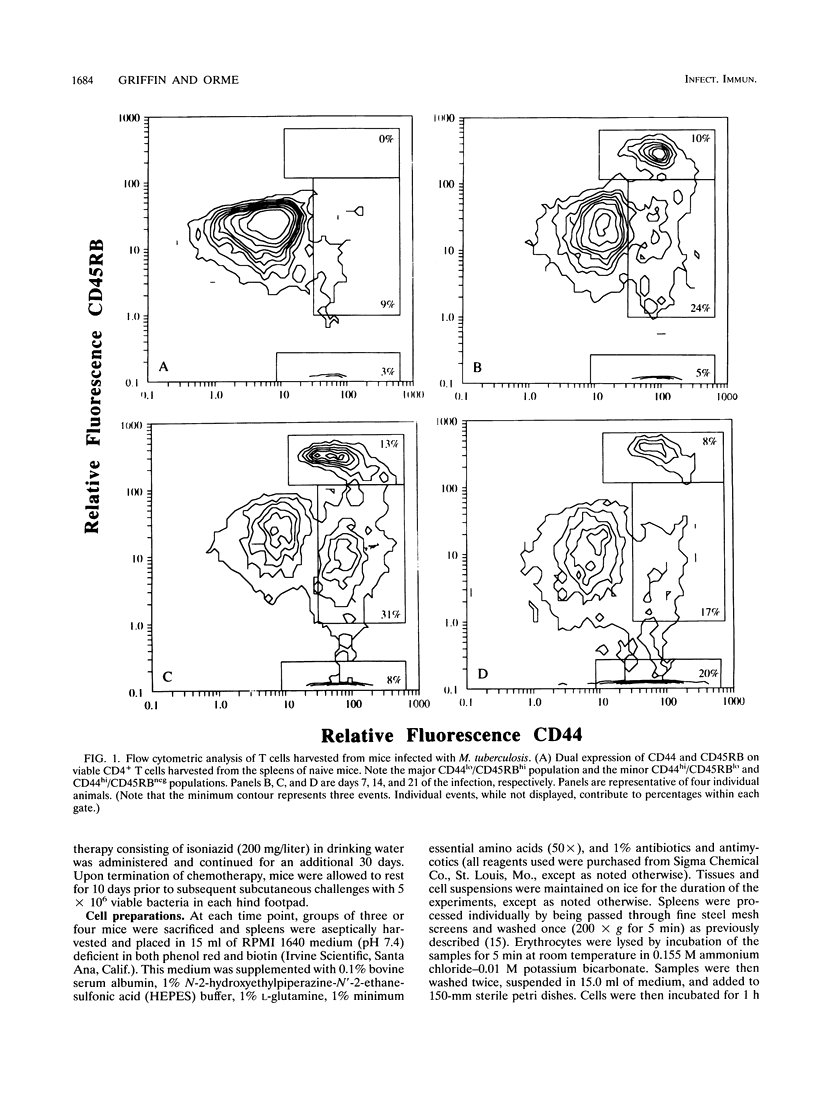
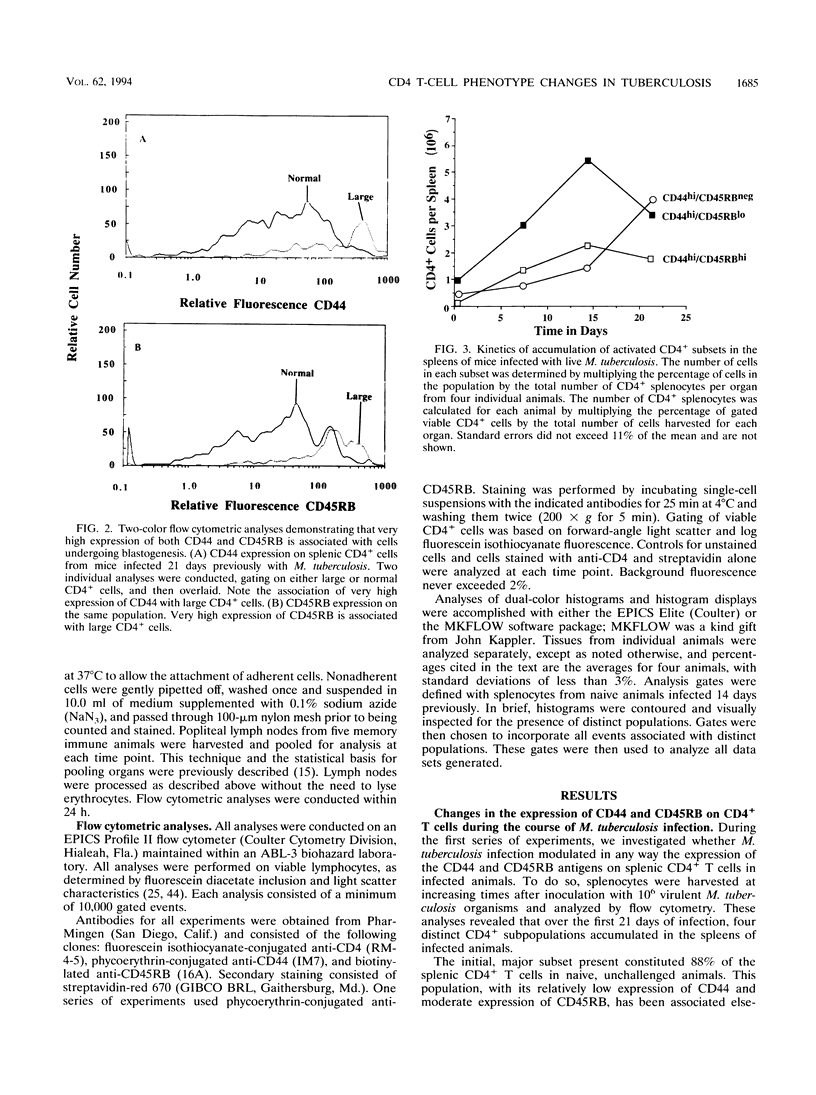
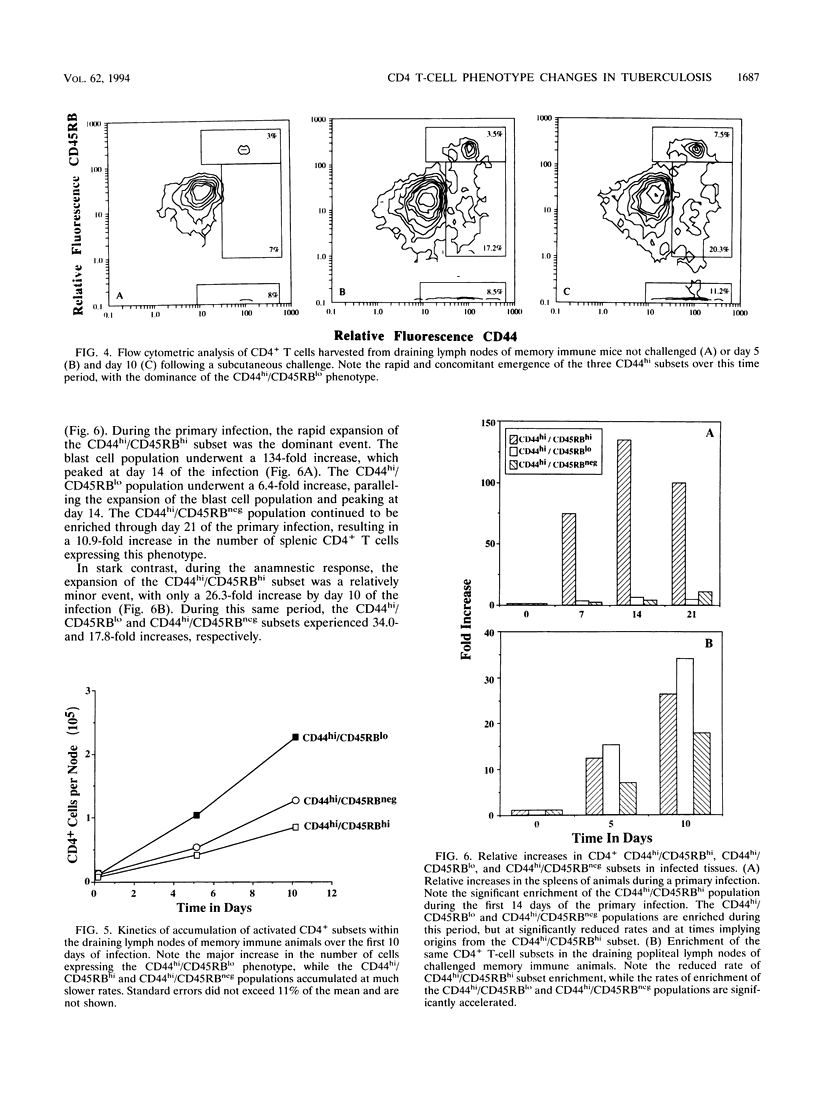
We report here that during the course of an experimental infection of mice with Mycobacterium tuberculosis, the differential expression of the cell surface antigens CD44 and CD45RB could be used to delineate CD4+ T cells into four phenotypically distinct subsets. The major subset present was designated CD44lo/CD45RBhi and is associated with naive or resting T cells. The three remaining subsets expressed increased levels of the CD44 antigen as the infection progressed and could therefore be considered to be in an activated state. These activated populations could be further divided on the basis of their variable expression of the CD45RB antigen. These populations were designated CD44hi/CD45RBhi, CD44hi/CD45RBlo, and CD44hi/CD45RBneg. Kinetic studies of the emergence of these populations indicated that these subsets arose sequentially from the naive population at times associated with the peak expression of acquired specific resistance. In further studies, in an attempt to associate either the CD44hi/CD45RBlo or the CD44hi/CD45RBneg population with acquired immunologic memory of tuberculosis infection, draining lymph nodes of challenged memory immune animals were analyzed for the accumulation of the CD4+ subsets. The accumulation of both the CD44hi/CD45RBlo and the CD44hi/CD45RBneg populations was observed, but the CD44hi/CD45RBlo population was enriched in a manner consistent with the rapid accumulation of memory T cells during the anamnestic response. While functional roles for each of these subsets remain to be determined, these data provide the first evidence for the evolution of multiple, phenotypically distinct CD4+ T-cell subsets during the in vivo response to an experimental mycobacterial infection.
Full text
PDF




Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Akbar A. N., Timms A., Janossy G. Cellular events during memory T-cell activation in vitro: the UCHL1 (180,000 MW) determinant is newly synthesized after mitosis. Immunology. 1989 Feb;66(2):213–218. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Andersen P., Askgaard D., Ljungqvist L., Bentzon M. W., Heron I. T-cell proliferative response to antigens secreted by Mycobacterium tuberculosis. Infect Immun. 1991 Apr;59(4):1558–1563. doi: 10.1128/iai.59.4.1558-1563.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bell E. B., Sparshott S. M. Interconversion of CD45R subsets of CD4 T cells in vivo. Nature. 1990 Nov 8;348(6297):163–166. doi: 10.1038/348163a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bell E. B., Yang C. P., Sarawar S. R., Sparshott S. M. The cyclic expression of CD45R isoforms on CD4 T cells. Biochem Soc Trans. 1992 Feb;20(1):198–202. doi: 10.1042/bst0200198. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Birkeland M. L., Johnson P., Trowbridge I. S., Puré E. Changes in CD45 isoform expression accompany antigen-induced murine T-cell activation. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Sep;86(17):6734–6738. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.17.6734. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Birkeland M. L., Kraus T., Tardelli L., Puré E. Progressive changes in CD45RB phenotype and lymphokine production by murine CD4+ T cells after alloantigen exposure. Immunology. 1992 Apr;75(4):632–638. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bloom B. R., Murray C. J. Tuberculosis: commentary on a reemergent killer. Science. 1992 Aug 21;257(5073):1055–1064. doi: 10.1126/science.257.5073.1055. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Budd R. C., Cerottini J. C., Horvath C., Bron C., Pedrazzini T., Howe R. C., MacDonald H. R. Distinction of virgin and memory T lymphocytes. Stable acquisition of the Pgp-1 glycoprotein concomitant with antigenic stimulation. J Immunol. 1987 May 15;138(10):3120–3129. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Butterfield K., Fathman C. G., Budd R. C. A subset of memory CD4+ helper T lymphocytes identified by expression of Pgp-1. J Exp Med. 1989 Apr 1;169(4):1461–1466. doi: 10.1084/jem.169.4.1461. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chatterjee D., Roberts A. D., Lowell K., Brennan P. J., Orme I. M. Structural basis of capacity of lipoarabinomannan to induce secretion of tumor necrosis factor. Infect Immun. 1992 Mar;60(3):1249–1253. doi: 10.1128/iai.60.3.1249-1253.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clement L. T., Yamashita N., Martin A. M. The functionally distinct subpopulations of human CD4+ helper/inducer T lymphocytes defined by anti-CD45R antibodies derive sequentially from a differentiation pathway that is regulated by activation-dependent post-thymic differentiation. J Immunol. 1988 Sep 1;141(5):1464–1470. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dianzani U., Luqman M., Rojo J., Yagi J., Baron J. L., Woods A., Janeway C. A., Jr, Bottomly K. Molecular associations on the T cell surface correlate with immunological memory. Eur J Immunol. 1990 Oct;20(10):2249–2257. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830201014. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ernst D. N., Hobbs M. V., Torbett B. E., Glasebrook A. L., Rehse M. A., Bottomly K., Hayakawa K., Hardy R. R., Weigle W. O. Differences in the expression profiles of CD45RB, Pgp-1, and 3G11 membrane antigens and in the patterns of lymphokine secretion by splenic CD4+ T cells from young and aged mice. J Immunol. 1990 Sep 1;145(5):1295–1302. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Flesch I. E., Kaufmann S. H. Activation of tuberculostatic macrophage functions by gamma interferon, interleukin-4, and tumor necrosis factor. Infect Immun. 1990 Aug;58(8):2675–2677. doi: 10.1128/iai.58.8.2675-2677.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Griffin J. P., Harshan K. V., Born W. K., Orme I. M. Kinetics of accumulation of gamma delta receptor-bearing T lymphocytes in mice infected with live mycobacteria. Infect Immun. 1991 Nov;59(11):4263–4265. doi: 10.1128/iai.59.11.4263-4265.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Haynes B. F., Telen M. J., Hale L. P., Denning S. M. CD44--a molecule involved in leukocyte adherence and T-cell activation. Immunol Today. 1989 Dec;10(12):423–428. doi: 10.1016/0167-5699(89)90040-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Huet S., Groux H., Caillou B., Valentin H., Prieur A. M., Bernard A. CD44 contributes to T cell activation. J Immunol. 1989 Aug 1;143(3):798–801. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Huygen K., Abramowicz D., Vandenbussche P., Jacobs F., De Bruyn J., Kentos A., Drowart A., Van Vooren J. P., Goldman M. Spleen cell cytokine secretion in Mycobacterium bovis BCG-infected mice. Infect Immun. 1992 Jul;60(7):2880–2886. doi: 10.1128/iai.60.7.2880-2886.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kawamura I., Tsukada H., Yoshikawa H., Fujita M., Nomoto K., Mitsuyama M. IFN-gamma-producing ability as a possible marker for the protective T cells against Mycobacterium bovis BCG in mice. J Immunol. 1992 May 1;148(9):2887–2893. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lee W. T., Vitetta E. S. Limiting dilution analysis of CD45Rhi and CD45Rlo T cells: further evidence that CD45Rlo cells are memory cells. Cell Immunol. 1990 Oct 15;130(2):459–471. doi: 10.1016/0008-8749(90)90287-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lee W. T., Vitetta E. S. The differential expression of homing and adhesion molecules on virgin and memory T cells in the mouse. Cell Immunol. 1991 Jan;132(1):215–222. doi: 10.1016/0008-8749(91)90020-c. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lee W. T., Yin X. M., Vitetta E. S. Functional and ontogenetic analysis of murine CD45Rhi and CD45Rlo CD4+ T cells. J Immunol. 1990 May 1;144(9):3288–3295. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lerner A., Yamada T., Miller R. A. Pgp-1hi T lymphocytes accumulate with age in mice and respond poorly to concanavalin A. Eur J Immunol. 1989 Jun;19(6):977–982. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830190604. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lesley J., Schulte R., Trotter J., Hyman R. Qualitative and quantitative heterogeneity in Pgp-1 expression among murine thymocytes. Cell Immunol. 1988 Mar;112(1):40–54. doi: 10.1016/0008-8749(88)90274-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Loken M. R., Sweet R. G., Herzenberg L. A. Cell discrimination by multiangle light scattering. J Histochem Cytochem. 1976 Jan;24(1):284–291. doi: 10.1177/24.1.1254923. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lynch F., Ceredig R. Ly-24 (Pgp-1) expression by thymocytes and peripheral T cells. Immunol Today. 1988 Jan;9(1):7–10. doi: 10.1016/0167-5699(88)91347-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lynch F., Ceredig R. Mouse strain variation in Ly-24 (Pgp-1) expression by peripheral T cells and thymocytes: implications for T cell differentiation. Eur J Immunol. 1989 Feb;19(2):223–229. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830190202. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lynch F., Chaudhri G., Allan J. E., Doherty P. C., Ceredig R. Expression of Pgp-1 (or Ly24) by subpopulations of mouse thymocytes and activated peripheral T lymphocytes. Eur J Immunol. 1987 Jan;17(1):137–140. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830170123. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Murray H. W. Interferon-gamma, the activated macrophage, and host defense against microbial challenge. Ann Intern Med. 1988 Apr;108(4):595–608. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-108-4-595. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nathan C. F., Kaplan G., Levis W. R., Nusrat A., Witmer M. D., Sherwin S. A., Job C. K., Horowitz C. R., Steinman R. M., Cohn Z. A. Local and systemic effects of intradermal recombinant interferon-gamma in patients with lepromatous leprosy. N Engl J Med. 1986 Jul 3;315(1):6–15. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198607033150102. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nathan C. F., Murray H. W., Wiebe M. E., Rubin B. Y. Identification of interferon-gamma as the lymphokine that activates human macrophage oxidative metabolism and antimicrobial activity. J Exp Med. 1983 Sep 1;158(3):670–689. doi: 10.1084/jem.158.3.670. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Orme I. M., Andersen P., Boom W. H. T cell response to Mycobacterium tuberculosis. J Infect Dis. 1993 Jun;167(6):1481–1497. doi: 10.1093/infdis/167.6.1481. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Orme I. M. Characteristics and specificity of acquired immunologic memory to Mycobacterium tuberculosis infection. J Immunol. 1988 May 15;140(10):3589–3593. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Orme I. M. Induction of nonspecific acquired resistance and delayed-type hypersensitivity, but not specific acquired resistance in mice inoculated with killed mycobacterial vaccines. Infect Immun. 1988 Dec;56(12):3310–3312. doi: 10.1128/iai.56.12.3310-3312.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Orme I. M., Miller E. S., Roberts A. D., Furney S. K., Griffin J. P., Dobos K. M., Chi D., Rivoire B., Brennan P. J. T lymphocytes mediating protection and cellular cytolysis during the course of Mycobacterium tuberculosis infection. Evidence for different kinetics and recognition of a wide spectrum of protein antigens. J Immunol. 1992 Jan 1;148(1):189–196. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Orme I. M., Roberts A. D., Griffin J. P., Abrams J. S. Cytokine secretion by CD4 T lymphocytes acquired in response to Mycobacterium tuberculosis infection. J Immunol. 1993 Jul 1;151(1):518–525. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Orme I. M. The kinetics of emergence and loss of mediator T lymphocytes acquired in response to infection with Mycobacterium tuberculosis. J Immunol. 1987 Jan 1;138(1):293–298. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Powrie F., Mason D. Subsets of rat CD4+ T cells defined by their differential expression of variants of the CD45 antigen: developmental relationships and in vitro and in vivo functions. Curr Top Microbiol Immunol. 1990;159:79–96. doi: 10.1007/978-3-642-75244-5_5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rook G. A., Champion B. R., Steele J., Varey A. M., Stanford J. L. I-A restricted activation by T cell lines of anti-tuberculosis activity in murine macrophages. Clin Exp Immunol. 1985 Feb;59(2):414–420. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Serra H. M., Krowka J. F., Ledbetter J. A., Pilarski L. M. Loss of CD45R (Lp220) represents a post-thymic T cell differentiation event. J Immunol. 1988 Mar 1;140(5):1435–1441. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shimizu Y., Van Seventer G. A., Siraganian R., Wahl L., Shaw S. Dual role of the CD44 molecule in T cell adhesion and activation. J Immunol. 1989 Oct 15;143(8):2457–2463. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sparshott S. M., Bell E. B., Sarawar S. R. CD45R CD4 T cell subset-reconstituted nude rats: subset-dependent survival of recipients and bi-directional isoform switching. Eur J Immunol. 1991 Apr;21(4):993–1000. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830210420. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thomas M. L., Lefrançois L. Differential expression of the leucocyte-common antigen family. Immunol Today. 1988 Oct;9(10):320–326. doi: 10.1016/0167-5699(88)91326-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


