Abstract
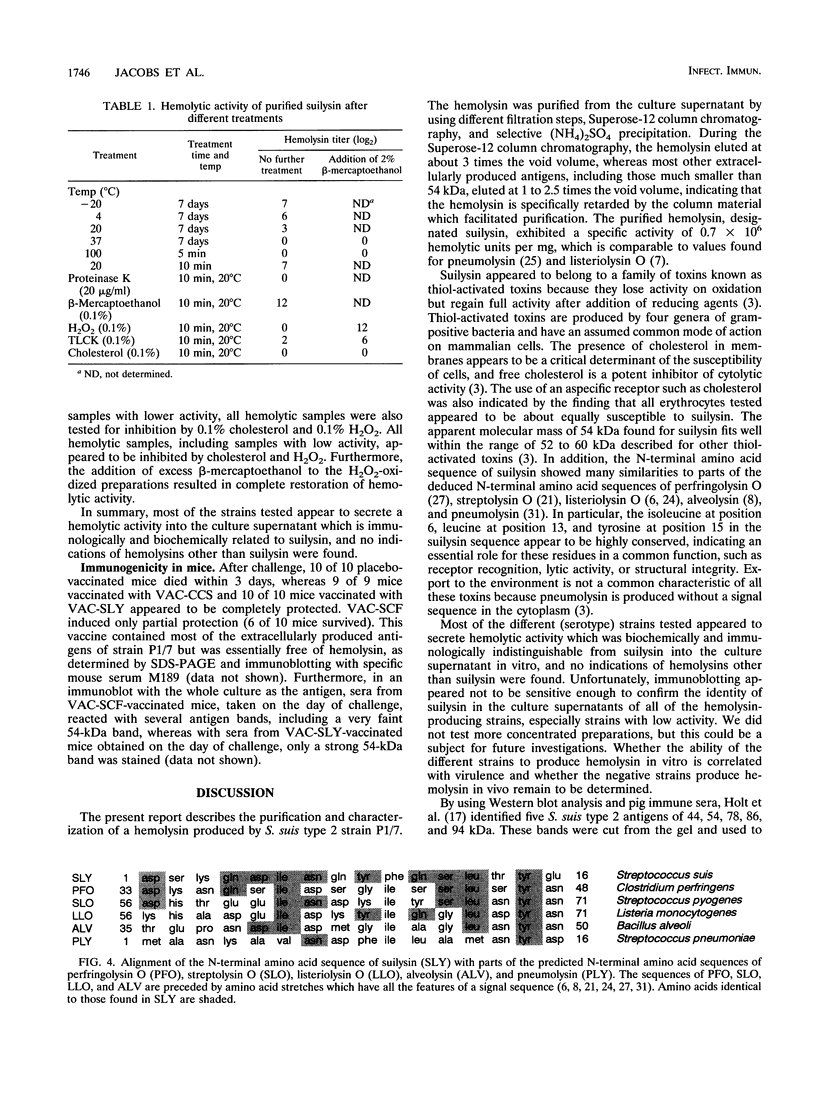
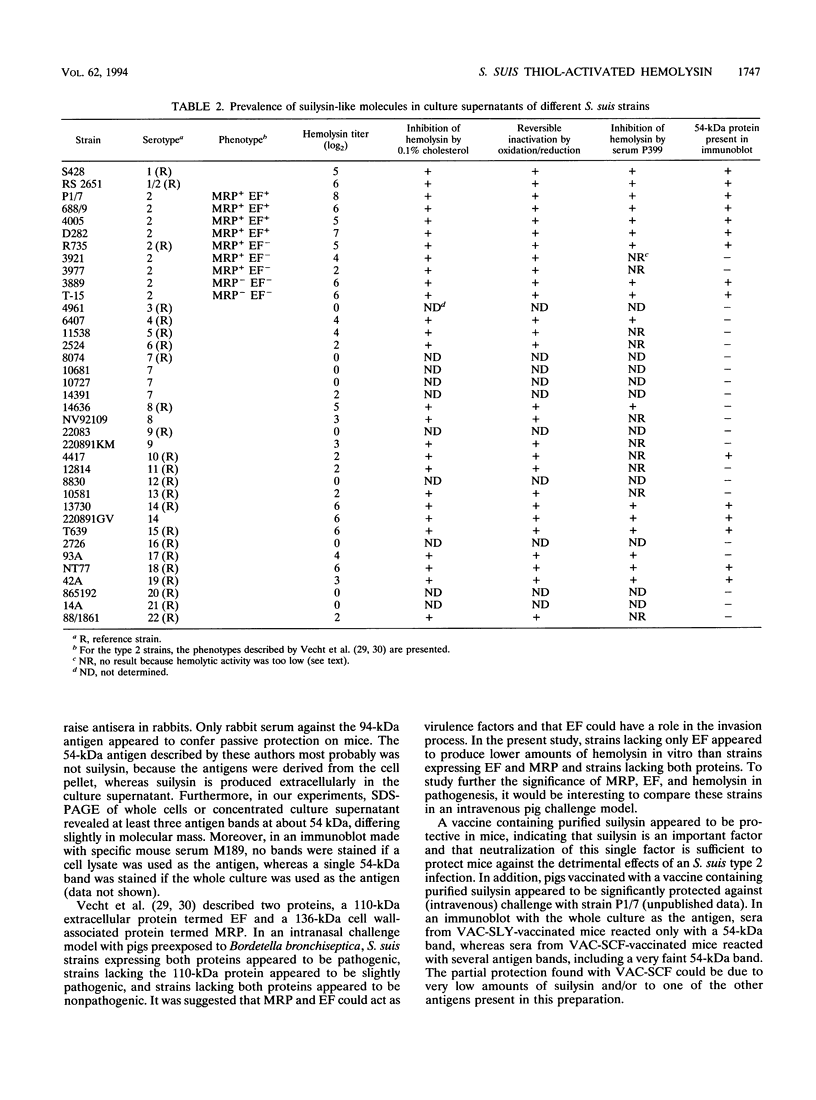
The present report describes the identification, purification, and characterization of a hemolysin produced by Streptococcus suis type 2. The hemolysin was purified from the culture supernatant by using different filtration steps, Superose-12 column chromatography, and selective (NH4)2SO4 precipitation. The purified hemolysin, designated suilysin, had an apparent molecular mass of 54,000 Da and exhibited a specific activity of 0.7 x 10(6) hemolytic units per mg. Suilysin appeared to belong to a family of toxins known as the thiol-activated toxins, with which it had several characteristics in common: loss of activity upon oxidation, reactivation upon reduction, and inhibition of activity by small amounts of cholesterol. The N-terminal amino acid sequence of suilysin showed many similarities with parts of the deduced N-terminal amino acid sequences of perfringolysin O, streptolysin O, listeriolysin O, alveolysin, and pneumolysin. Mice immunized with a vaccine containing purified suilysin appeared to be completely protected against a lethal S. suis type 2 challenge, indicating that suilysin is an important factor and that the neutralization of this single factor is sufficient to protect mice against the detrimental effects of an S. suis type 2 infection. Most of the different (serotype) strains appeared to secrete hemolytic activity which was biochemically and immunologically indistinguishable from suilysin into the culture supernatant in vitro, indicating that suilysin might be a cross-protection factor.
Full text
PDF




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Arends J. P., Zanen H. C. Meningitis caused by Streptococcus suis in humans. Rev Infect Dis. 1988 Jan-Feb;10(1):131–137. doi: 10.1093/clinids/10.1.131. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boetner A. G., Binder M., Bille-Hansen V. Streptococcus suis infections in Danish pigs and experimental infection with Streptococcus suis serotype 7. Acta Pathol Microbiol Immunol Scand B. 1987 Aug;95(4):233–239. doi: 10.1111/j.1699-0463.1987.tb03118.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boulnois G. J., Paton J. C., Mitchell T. J., Andrew P. W. Structure and function of pneumolysin, the multifunctional, thiol-activated toxin of Streptococcus pneumoniae. Mol Microbiol. 1991 Nov;5(11):2611–2616. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2958.1991.tb01969.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clifton-Hadley F. A. Streptococcus suis type 2 infections. Br Vet J. 1983 Jan-Feb;139(1):1–5. doi: 10.1016/s0007-1935(17)30581-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Devriese L. A., Sustronck B., Maenhout T., Haesebrouck F. Streptococcus suis meningitis in a horse. Vet Rec. 1990 Jul 21;127(3):68–68. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Domann E., Chakraborty T. Nucleotide sequence of the listeriolysin gene from a Listeria monocytogenes serotype 1/2a strain. Nucleic Acids Res. 1989 Aug 11;17(15):6406–6406. doi: 10.1093/nar/17.15.6406. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Geoffroy C., Gaillard J. L., Alouf J. E., Berche P. Purification, characterization, and toxicity of the sulfhydryl-activated hemolysin listeriolysin O from Listeria monocytogenes. Infect Immun. 1987 Jul;55(7):1641–1646. doi: 10.1128/iai.55.7.1641-1646.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Geoffroy C., Mengaud J., Alouf J. E., Cossart P. Alveolysin, the thiol-activated toxin of Bacillus alvei, is homologous to listeriolysin O, perfringolysin O, pneumolysin, and streptolysin O and contains a single cysteine. J Bacteriol. 1990 Dec;172(12):7301–7305. doi: 10.1128/jb.172.12.7301-7305.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gogolewski R. P., Cook R. W., O'Connell C. J. Streptococcus suis serotypes associated with disease in weaned pigs. Aust Vet J. 1990 Jun;67(6):202–204. doi: 10.1111/j.1751-0813.1990.tb07759.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gottschalk M., Higgins R., Jacques M., Beaudoin M., Henrichsen J. Characterization of six new capsular types (23 through 28) of Streptococcus suis. J Clin Microbiol. 1991 Nov;29(11):2590–2594. doi: 10.1128/jcm.29.11.2590-2594.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gottschalk M., Higgins R., Jacques M., Dubreuil D. Production and characterization of two Streptococcus suis capsular type 2 mutants. Vet Microbiol. 1992 Jan;30(1):59–71. doi: 10.1016/0378-1135(92)90094-a. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gottschalk M., Higgins R., Jacques M., Mittal K. R., Henrichsen J. Description of 14 new capsular types of Streptococcus suis. J Clin Microbiol. 1989 Dec;27(12):2633–2636. doi: 10.1128/jcm.27.12.2633-2636.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gottschalk M., Lebrun A., Jacques M., Higgins R. Hemagglutination properties of Streptococcus suis. J Clin Microbiol. 1990 Sep;28(9):2156–2158. doi: 10.1128/jcm.28.9.2156-2158.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Higgins R., Gottschalk M., Beaudoin M., Rawluk S. A. Distribution of Streptococcus suis capsular types in Quebec and western Canada. Can Vet J. 1992 Jan;33(1):27–30. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Higgins R., Gottschalk M., Mittal K. R., Beaudoin M. Streptococcus suis infection in swine. A sixteen month study. Can J Vet Res. 1990 Jan;54(1):170–173. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Holt M. E., Enright M. R., Alexander T. J. Immunisation of pigs with killed cultures of Streptococcus suis type 2. Res Vet Sci. 1990 Jan;48(1):23–27. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hommez J., Wullepit J., Cassimon P., Castryck F., Ceyssens K., Devriese L. A. Streptococcus suis and other streptococcal species as a cause of extramammary infection in ruminants. Vet Rec. 1988 Dec 10;123(24):626–627. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jacques M., Gottschalk M., Foiry B., Higgins R. Ultrastructural study of surface components of Streptococcus suis. J Bacteriol. 1990 Jun;172(6):2833–2838. doi: 10.1128/jb.172.6.2833-2838.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kebede M., Chengappa M. M., Stuart J. G. Isolation and characterization of temperature-sensitive mutants of Streptococcus suis: efficacy trial of the mutant vaccine in mice. Vet Microbiol. 1990 Apr;22(2-3):249–257. doi: 10.1016/0378-1135(90)90112-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kehoe M. A., Miller L., Walker J. A., Boulnois G. J. Nucleotide sequence of the streptolysin O (SLO) gene: structural homologies between SLO and other membrane-damaging, thiol-activated toxins. Infect Immun. 1987 Dec;55(12):3228–3232. doi: 10.1128/iai.55.12.3228-3232.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LOWRY O. H., ROSEBROUGH N. J., FARR A. L., RANDALL R. J. Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem. 1951 Nov;193(1):265–275. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mengaud J., Vicente M. F., Chenevert J., Pereira J. M., Geoffroy C., Gicquel-Sanzey B., Baquero F., Perez-Diaz J. C., Cossart P. Expression in Escherichia coli and sequence analysis of the listeriolysin O determinant of Listeria monocytogenes. Infect Immun. 1988 Apr;56(4):766–772. doi: 10.1128/iai.56.4.766-772.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Paton J. C., Lock R. A., Hansman D. J. Effect of immunization with pneumolysin on survival time of mice challenged with Streptococcus pneumoniae. Infect Immun. 1983 May;40(2):548–552. doi: 10.1128/iai.40.2.548-552.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Paton J. C., Lock R. A., Lee C. J., Li J. P., Berry A. M., Mitchell T. J., Andrew P. W., Hansman D., Boulnois G. J. Purification and immunogenicity of genetically obtained pneumolysin toxoids and their conjugation to Streptococcus pneumoniae type 19F polysaccharide. Infect Immun. 1991 Jul;59(7):2297–2304. doi: 10.1128/iai.59.7.2297-2304.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tweten R. K. Nucleotide sequence of the gene for perfringolysin O (theta-toxin) from Clostridium perfringens: significant homology with the genes for streptolysin O and pneumolysin. Infect Immun. 1988 Dec;56(12):3235–3240. doi: 10.1128/iai.56.12.3235-3240.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vecht U., Wisselink H. J., Jellema M. L., Smith H. E. Identification of two proteins associated with virulence of Streptococcus suis type 2. Infect Immun. 1991 Sep;59(9):3156–3162. doi: 10.1128/iai.59.9.3156-3162.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vecht U., Wisselink H. J., van Dijk J. E., Smith H. E. Virulence of Streptococcus suis type 2 strains in newborn germfree pigs depends on phenotype. Infect Immun. 1992 Feb;60(2):550–556. doi: 10.1128/iai.60.2.550-556.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vecht U., van Leengoed L. A., Verheijen E. R. Streptococcus suis infections in pigs in the Netherlands (Part I). Vet Q. 1985 Oct;7(4):315–321. doi: 10.1080/01652176.1985.9694005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Walker J. A., Allen R. L., Falmagne P., Johnson M. K., Boulnois G. J. Molecular cloning, characterization, and complete nucleotide sequence of the gene for pneumolysin, the sulfhydryl-activated toxin of Streptococcus pneumoniae. Infect Immun. 1987 May;55(5):1184–1189. doi: 10.1128/iai.55.5.1184-1189.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Windsor R. S. Meningitis in pigs caused by Streptococcus suis type II. Vet Rec. 1977 Nov 5;101(19):378–379. doi: 10.1136/vr.101.19.378. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]





