Abstract
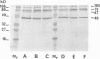
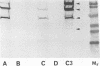
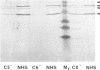
The deposition and degradation of human complement component C3 on the cell surfaces of Neisseria meningitidis and Neisseria gonorrhoeae were studied. Bacteria were incubated in human serum, and ester-linked C3 fragments were analyzed by hydroxylamine release and immunoblot detection. Similar patterns of C3 degradation were found for both serum-resistant and serum-sensitive meningococcal strains of serogroups A, B, C, Y, and W135, as well as for serum-sensitive gonococcal strains and their sialylated serum-resistant variants. The predominant fragments in all cases were the 40-kDa alpha' 2 chain of iC3b and the 75-kDa beta chain common to both C3b and iC3b. The 67-kDa alpha' 1 chain of iC3b was also detected. The 105-kDa alpha' chain of intact C3b represented a minor proportion of deposited C3. Capsule-specific immunoglobulin G or immunoglobulin A1 did not alter the observed degradation patterns, nor did incubation of meningococci in properdin-deficient serum. The degradation of C3 in C5-, C6-, or C8-deficient serum was the same as that in normal serum, although the deposition of C3 was severely limited, based as indicated by the intensity of the fragments. With the use of an enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay that measured total iC3b and C3, I found that both iC3b deposition and C3 deposition varied among meningococcal and gonococcal strains and that the amounts of iC3b and C3 were independent of the relative quantities of cell surface sialic acid and of serum sensitivity for meningococci but not for gonococci. I conclude that complement activation on neisserial cell surface results in the formation of an identical repertoire of predominantly iC3b fragments of ester-linked C3b molecules regardless of the presence of sialic acid in either the capsule or the lipooligosaccharide or of the sensitivity of the organism to complement-mediated lysis but that the quantities of both ester- and amide-linked iC3b molecules deposited exhibit strain variability.
Full text
PDF





Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Brown E. J. Complement receptors and phagocytosis. Curr Opin Immunol. 1991 Feb;3(1):76–82. doi: 10.1016/0952-7915(91)90081-b. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Campbell J. R., Baker C. J., Edwards M. S. Influence of serotype of group B streptococci on C3 degradation. Infect Immun. 1992 Nov;60(11):4558–4562. doi: 10.1128/iai.60.11.4558-4562.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Densen P., McRill C. M., Ross S. C. Assembly of the membrane attack complex promotes decay of the alternative pathway C3 convertase on Neisseria gonorrhoeae. J Immunol. 1988 Dec 1;141(11):3902–3909. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Densen P., Weiler J. M., Griffiss J. M., Hoffmann L. G. Familial properdin deficiency and fatal meningococcemia. Correction of the bactericidal defect by vaccination. N Engl J Med. 1987 Apr 9;316(15):922–926. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198704093161506. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Estabrook M. M., Christopher N. C., Griffiss J. M., Baker C. J., Mandrell R. E. Sialylation and human neutrophil killing of group C Neisseria meningitidis. J Infect Dis. 1992 Nov;166(5):1079–1088. doi: 10.1093/infdis/166.5.1079. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Figueroa J. E., Densen P. Infectious diseases associated with complement deficiencies. Clin Microbiol Rev. 1991 Jul;4(3):359–395. doi: 10.1128/cmr.4.3.359. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fries L. F., Gaither T. A., Hammer C. H., Frank M. M. C3b covalently bound to IgG demonstrates a reduced rate of inactivation by factors H and I. J Exp Med. 1984 Dec 1;160(6):1640–1655. doi: 10.1084/jem.160.6.1640. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Griffiss J. M., Brandt B. L. Disease due to serogroup W135 Neisseria meningitidis. Pediatrics. 1979 Aug;64(2):218–221. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Griffiss J. M., Jarvis G. A., O'Brien J. P., Eads M. M., Schneider H. Lysis of Neisseria gonorrhoeae initiated by binding of normal human IgM to a hexosamine-containing lipooligosaccharide epitope(s) is augmented by strain-specific, properdin-binding-dependent alternative complement pathway activation. J Immunol. 1991 Jul 1;147(1):298–305. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hamadeh R. M., Jarvis G. A., Galili U., Mandrell R. E., Zhou P., Griffiss J. M. Human natural anti-Gal IgG regulates alternative complement pathway activation on bacterial surfaces. J Clin Invest. 1992 Apr;89(4):1223–1235. doi: 10.1172/JCI115706. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hostetter M. K., Gordon D. L. Biochemistry of C3 and related thiolester proteins in infection and inflammation. Rev Infect Dis. 1987 Jan-Feb;9(1):97–109. doi: 10.1093/clinids/9.1.97. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Isenman D. E., Kells D. I., Cooper N. R., Müller-Eberhard H. J., Pangburn M. K. Nucleophilic modification of human complement protein C3: correlation of conformational changes with acquisition of C3b-like functional properties. Biochemistry. 1981 Jul 21;20(15):4458–4467. doi: 10.1021/bi00518a034. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jarvis G. A., Griffiss J. M. Human IgA1 blockade of IgG-initiated lysis of Neisseria meningitidis is a function of antigen-binding fragment binding to the polysaccharide capsule. J Immunol. 1991 Sep 15;147(6):1962–1967. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jarvis G. A., Griffiss J. M. Human IgA1 initiates complement-mediated killing of Neisseria meningitidis. J Immunol. 1989 Sep 1;143(5):1703–1709. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jarvis G. A., Vedros N. A. Sialic acid of group B Neisseria meningitidis regulates alternative complement pathway activation. Infect Immun. 1987 Jan;55(1):174–180. doi: 10.1128/iai.55.1.174-180.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- John C. M., Griffiss J. M., Apicella M. A., Mandrell R. E., Gibson B. W. The structural basis for pyocin resistance in Neisseria gonorrhoeae lipooligosaccharides. J Biol Chem. 1991 Oct 15;266(29):19303–19311. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Joiner K. A., Warren K. A., Hammer C., Frank M. M. Bactericidal but not nonbactericidal C5b-9 is associated with distinctive outer membrane proteins in Neisseria gonorrhoeae. J Immunol. 1985 Mar;134(3):1920–1925. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kim J. J., Mandrell R. E., Griffiss J. M. Neisseria lactamica and Neisseria meningitidis share lipooligosaccharide epitopes but lack common capsular and class 1, 2, and 3 protein epitopes. Infect Immun. 1989 Feb;57(2):602–608. doi: 10.1128/iai.57.2.602-608.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Koistinen V. Effect of complement-protein-C3b density on the binding of complement factor H to surface-bound C3b. Biochem J. 1991 Nov 15;280(Pt 1):255–259. doi: 10.1042/bj2800255. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mandrell R. E., Griffiss J. M., Macher B. A. Lipooligosaccharides (LOS) of Neisseria gonorrhoeae and Neisseria meningitidis have components that are immunochemically similar to precursors of human blood group antigens. Carbohydrate sequence specificity of the mouse monoclonal antibodies that recognize crossreacting antigens on LOS and human erythrocytes. J Exp Med. 1988 Jul 1;168(1):107–126. doi: 10.1084/jem.168.1.107. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mandrell R. E., Lesse A. J., Sugai J. V., Shero M., Griffiss J. M., Cole J. A., Parsons N. J., Smith H., Morse S. A., Apicella M. A. In vitro and in vivo modification of Neisseria gonorrhoeae lipooligosaccharide epitope structure by sialylation. J Exp Med. 1990 May 1;171(5):1649–1664. doi: 10.1084/jem.171.5.1649. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meri S., Pangburn M. K. Discrimination between activators and nonactivators of the alternative pathway of complement: regulation via a sialic acid/polyanion binding site on factor H. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 May;87(10):3982–3986. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.10.3982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nairn C. A., Cole J. A., Patel P. V., Parsons N. J., Fox J. E., Smith H. Cytidine 5'-monophospho-N-acetylneuraminic acid or a related compound is the low Mr factor from human red blood cells which induces gonococcal resistance to killing by human serum. J Gen Microbiol. 1988 Dec;134(12):3295–3306. doi: 10.1099/00221287-134-12-3295. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ross S. C., Rosenthal P. J., Berberich H. M., Densen P. Killing of Neisseria meningitidis by human neutrophils: implications for normal and complement-deficient individuals. J Infect Dis. 1987 Jun;155(6):1266–1275. doi: 10.1093/infdis/155.6.1266. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schneider H., Griffiss J. M., Mandrell R. E., Jarvis G. A. Elaboration of a 3.6-kilodalton lipooligosaccharide, antibody against which is absent from human sera, is associated with serum resistance of Neisseria gonorrhoeae. Infect Immun. 1985 Dec;50(3):672–677. doi: 10.1128/iai.50.3.672-677.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sidberry H., Kaufman B., Wright D. C., Sadoff J. Immunoenzymatic analysis by monoclonal antibodies of bacterial lipopolysaccharides after transfer to nitrocellulose. J Immunol Methods. 1985 Feb 11;76(2):299–305. doi: 10.1016/0022-1759(85)90307-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WHITE L. A., KELLOGG D. S., Jr NEISSERIA GONORRHOEAE IDENTIFICATION IN DIRECT SMEARS BY A FLUORESCENT ANTIBODY-COUNTERSTAIN METHOD. Appl Microbiol. 1965 Mar;13:171–174. doi: 10.1128/am.13.2.171-174.1965. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wilson C. B., Weaver W. M. Comparative susceptibility of group B streptococci and Staphylococcus aureus to killing by oxygen metabolites. J Infect Dis. 1985 Aug;152(2):323–329. doi: 10.1093/infdis/152.2.323. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yamasaki R., Bacon B. Three-dimensional structural analysis of the group B polysaccharide of Neisseria meningitidis 6275 by two-dimensional NMR: the polysaccharide is suggested to exist in helical conformations in solution. Biochemistry. 1991 Jan 22;30(3):851–857. doi: 10.1021/bi00217a039. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yamasaki R., Griffiss J. M., Quinn K. P., Mandrell R. E. Neuraminic acid is alpha 2-->3 linked in the lipooligosaccharide of Neisseria meningitidis serogroup B strain 6275. J Bacteriol. 1993 Jul;175(14):4565–4568. doi: 10.1128/jb.175.14.4565-4568.1993. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]