Abstract
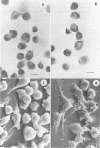
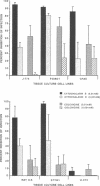
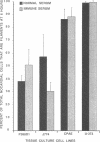
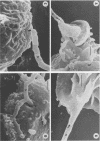
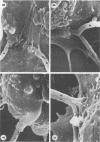
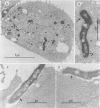
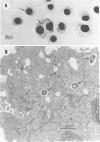
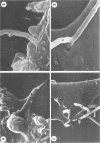
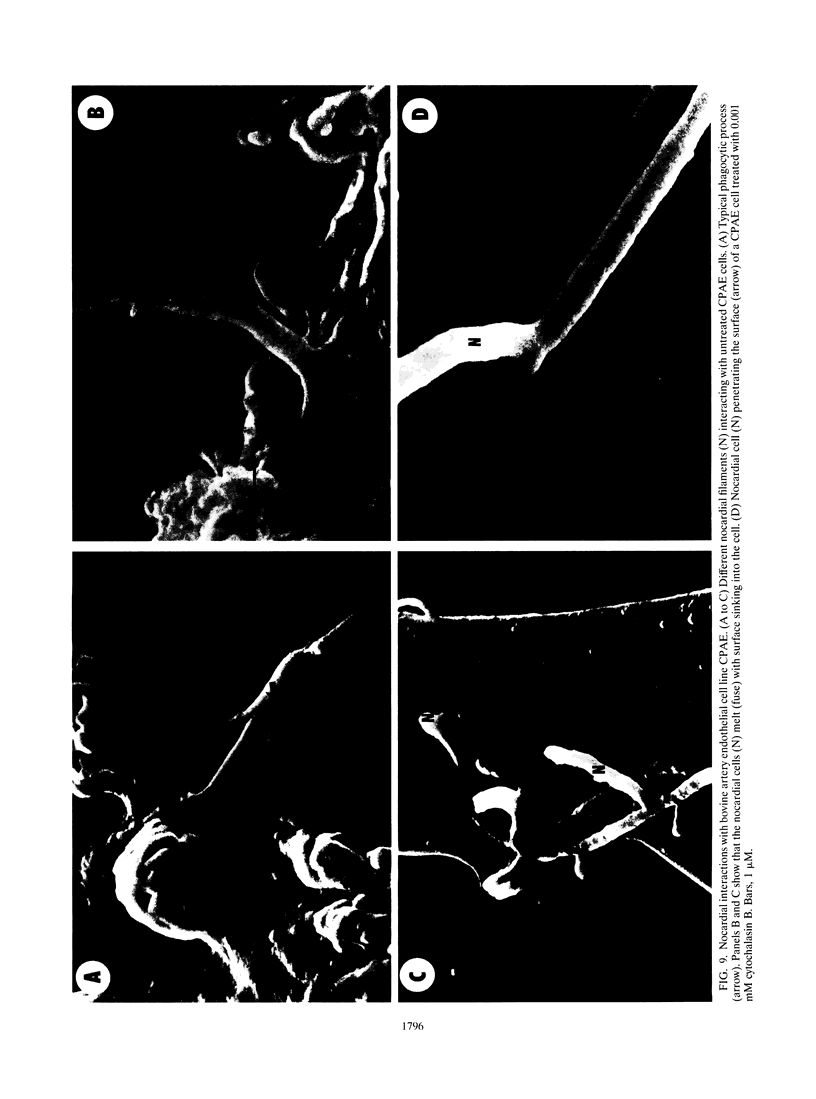
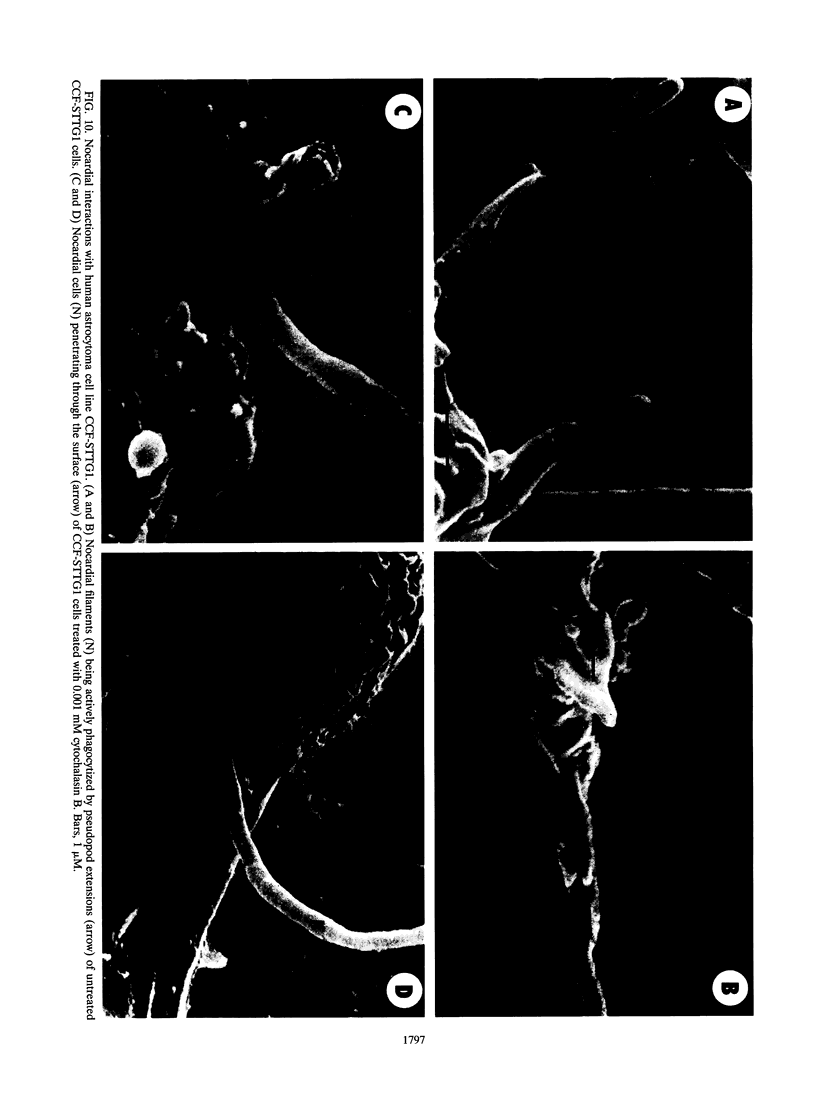
An in vitro model for studying host cell interactions with Nocardia asteroides was developed. Thus, macrophage cell lines J774A.1 and P388D1, pulmonary artery endothelium cell line CPAE, rat glial tumor cell line C6, and human astrocytoma cell lines CCF-STTG1 and U-373 MG were infected with either log- or stationary-phase cells of N. asteroides GUH-2, and the host cell-nocardia interactions were determined by light microscopy and electron microscopy. Polyclonal antinocardial antibody did not enhance uptake of nocardiae by any of these cell lines; however, log-phase cells of GUH-2 infected a higher percentage of J774A.1 and P388D1 than did stationary-phase organisms. When cells infected with stationary-phase GUH-2 were incubated for 6 h, filaments developed, which indicated that nocardial growth had occurred. In J774A.1 and P388D1, only 31 to 57% of the total stationary-phase coccobacillary cells that were phagocytized formed filaments within 6 h. This indicated that there was some inhibition of growth of the phagocytized nocardiae within these macrophage cell lines; however, the nocardiae grew within the endothelial (> 87% filaments) and astrocytoma (100% filaments) cell lines. Microfilament inhibitor cytochalasin B inhibited uptake of GUH-2 by macrophages and other cell lines, except that there was no effect on uptake of nocardial cells by astrocytoma cell line U-373 MG. Scanning and transmission electron microscopy showed phagocytosis of GUH-2 by the different cell lines. In cytochalasin B-treated cells, nocardiae were shown to penetrate through the cell surface and become internalized in a manner distinct from typical phagocytosis, suggesting that filamentous forms of this organism have a phagocytosis-independent invasion factor. The extent of this cytochalasin-resistant cellular penetration by the nocardiae differed in the different cell lines.
Full text
PDF
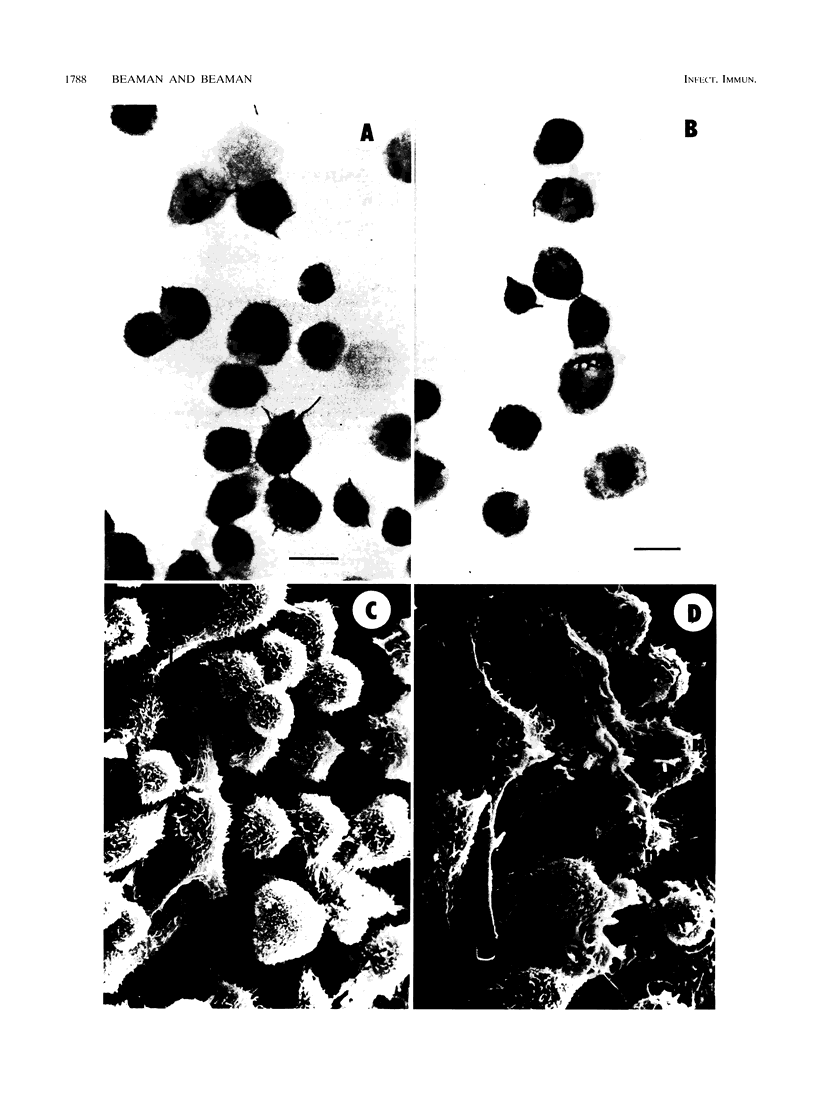
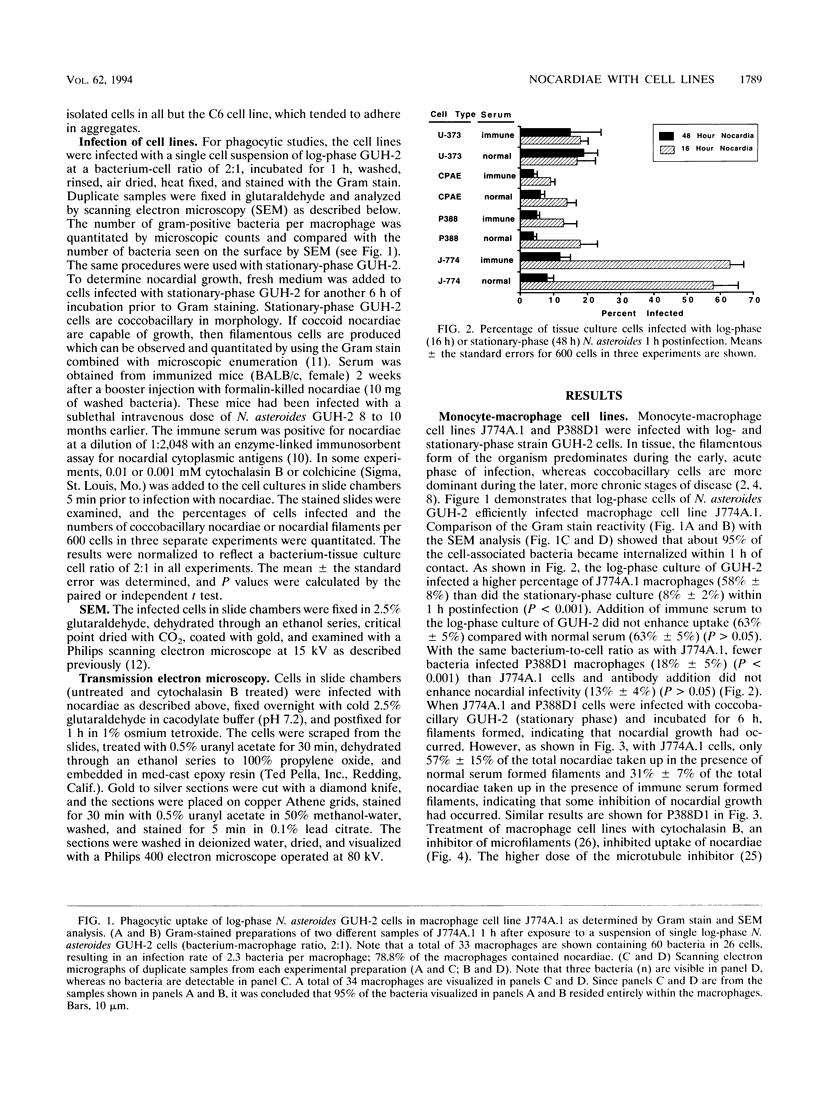
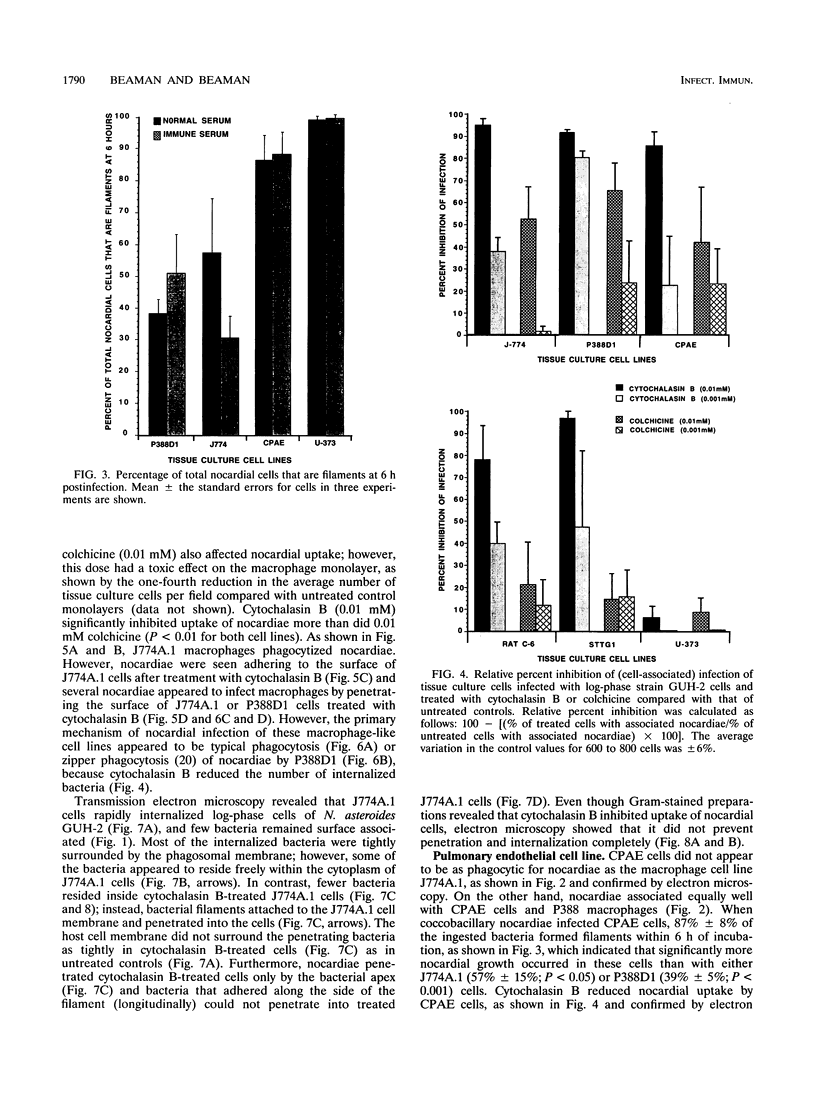
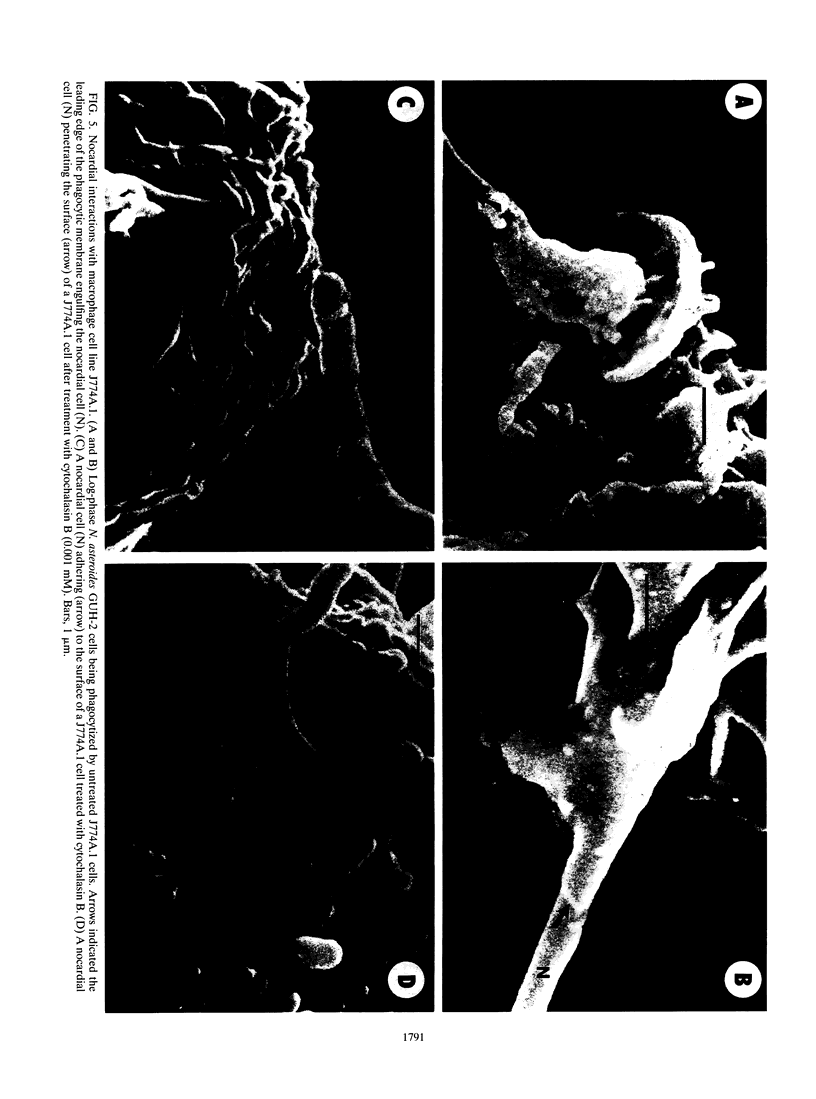
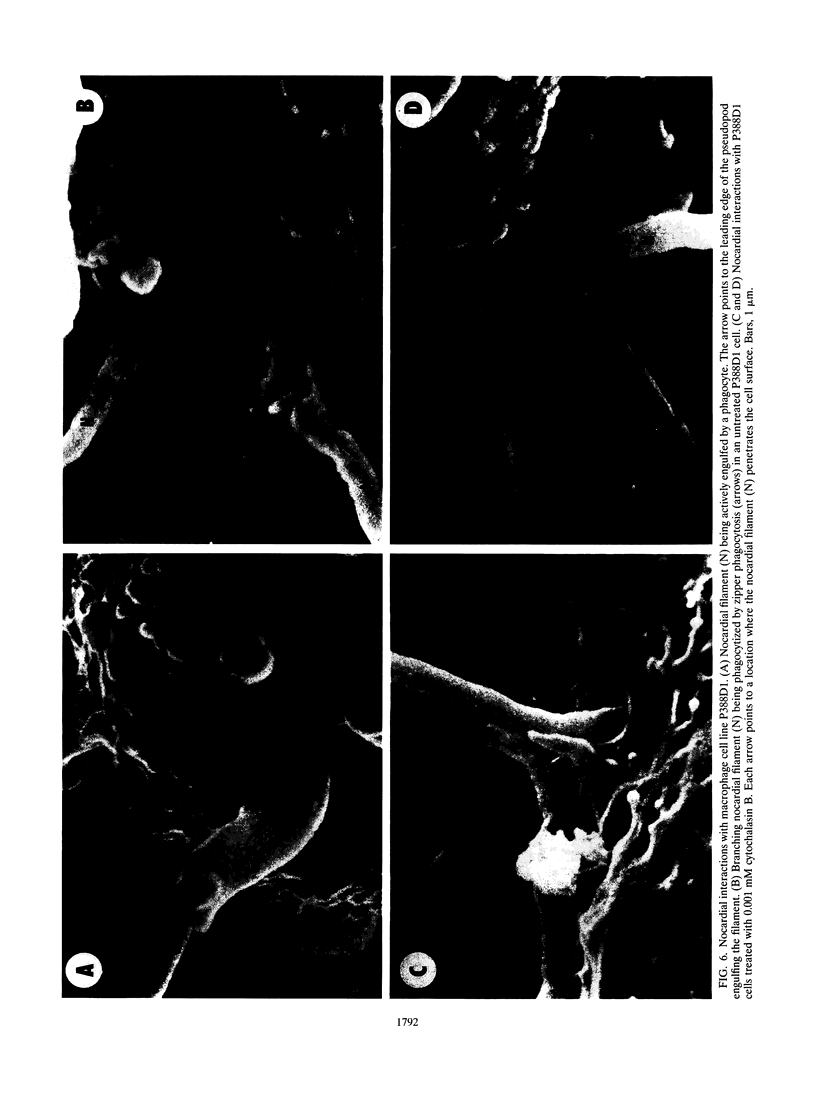
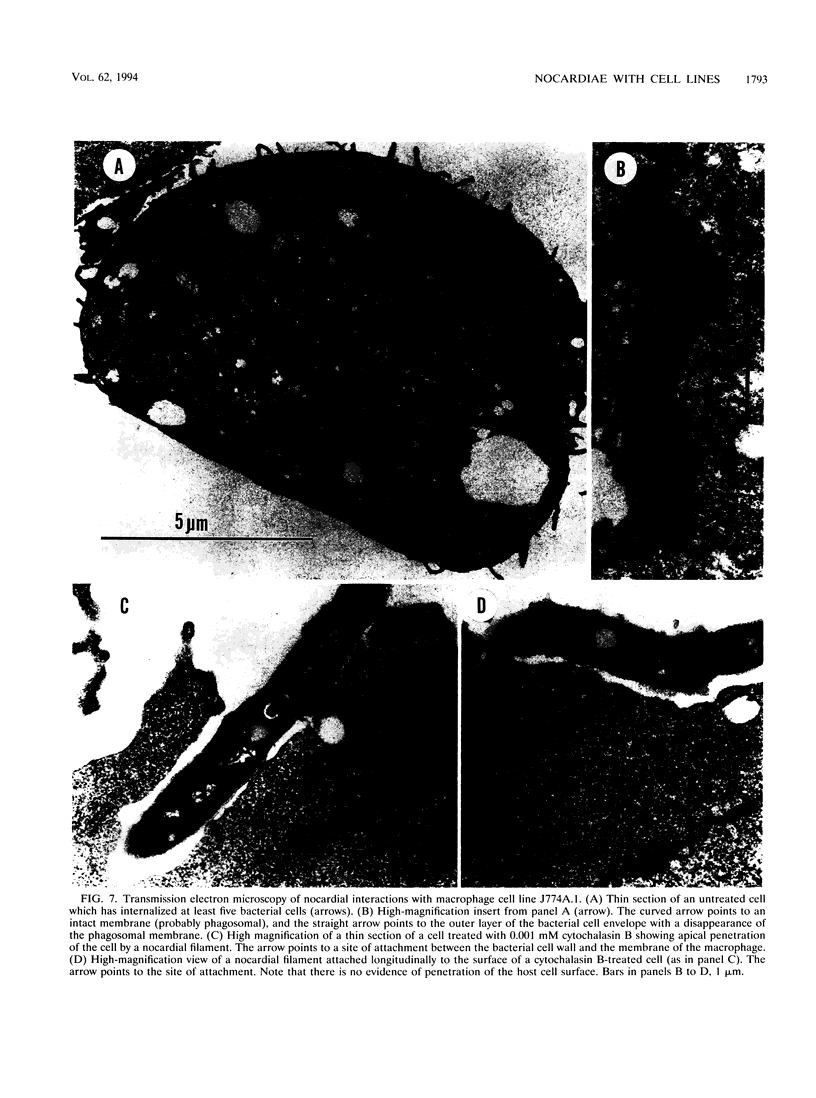
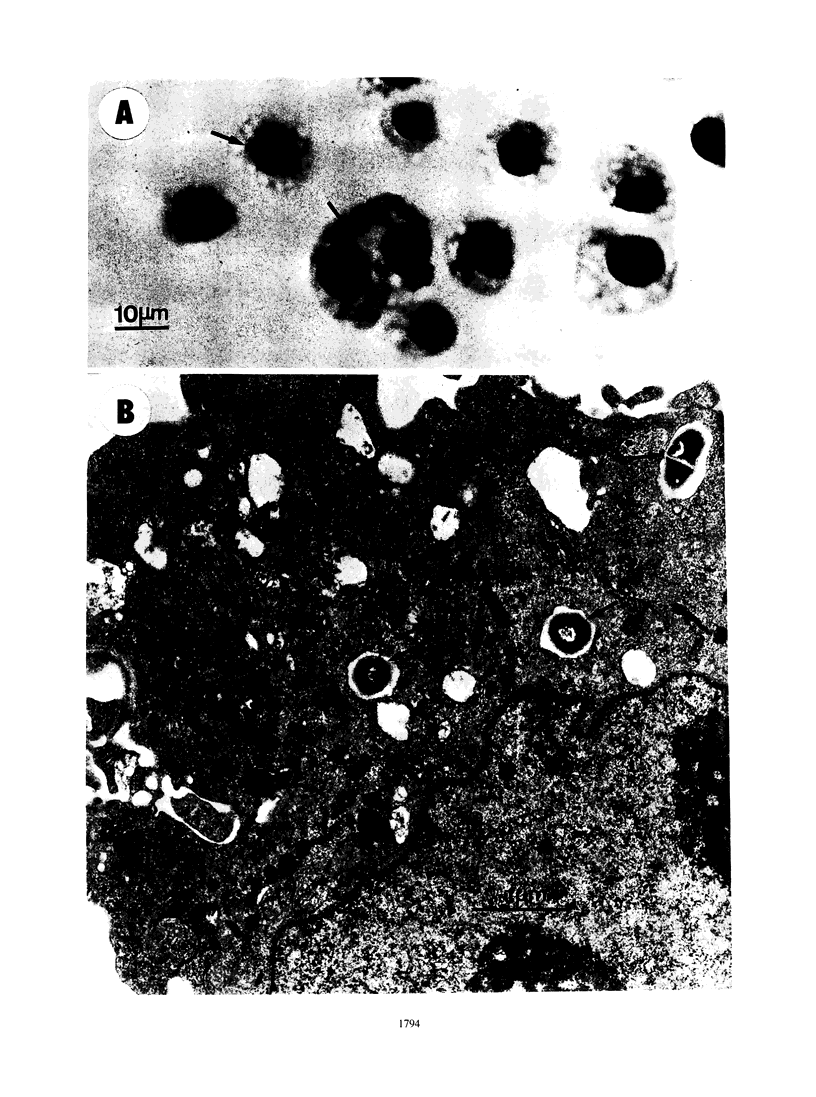


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Barna B. P., Chou S. M., Jacobs B., Ransohoff R. M., Hahn J. F., Bay J. W. Enhanced DNA synthesis of human glial cells exposed to human leukocyte products. J Neuroimmunol. 1985 Dec;10(2):151–158. doi: 10.1016/0165-5728(85)90005-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Beaman B. L., Black C. M., Doughty F., Beaman L. Role of superoxide dismutase and catalase as determinants of pathogenicity of Nocardia asteroides: importance in resistance to microbicidal activities of human polymorphonuclear neutrophils. Infect Immun. 1985 Jan;47(1):135–141. doi: 10.1128/iai.47.1.135-141.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Beaman B. L., Black C. Interaction of Nocardia asteroides in BALB/c mice: modulation of macrophage function, enzyme activity and the induction of immunologically specific T-cell bactericidal activity. Curr Top Microbiol Immunol. 1985;122:138–147. doi: 10.1007/978-3-642-70740-7_21. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Beaman B. L. In vitro response of rabbit alveolar macrophages to infection with Nocardia asteroides. Infect Immun. 1977 Mar;15(3):925–937. doi: 10.1128/iai.15.3.925-937.1977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Beaman B. L. Interaction of Nocardia asteroides at different phases of growth with in vitro-maintained macrophages obtained from the lungs of normal and immunized rabbits. Infect Immun. 1979 Oct;26(1):355–361. doi: 10.1128/iai.26.1.355-361.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Beaman B. L., Maslan S. Virulence of Nocardia asteroides during its growth cycle. Infect Immun. 1978 Apr;20(1):290–295. doi: 10.1128/iai.20.1.290-295.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Beaman B. L., Ogata S. A. Ultrastructural analysis of attachment to and penetration of capillaries in the murine pons, midbrain, thalamus, and hypothalamus by Nocardia asteroides. Infect Immun. 1993 Mar;61(3):955–965. doi: 10.1128/iai.61.3.955-965.1993. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Beaman B. L. Structural and biochemical alterations of Nocardia asteroides cell walls during its growth cycle. J Bacteriol. 1975 Sep;123(3):1235–1253. doi: 10.1128/jb.123.3.1235-1253.1975. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Beaman L., Beaman B. L. Interactions of Nocardia asteroides with murine glia cells in culture. Infect Immun. 1993 Jan;61(1):343–347. doi: 10.1128/iai.61.1.343-347.1993. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Beaman L., Beaman B. L. Monoclonal antibodies demonstrate that superoxide dismutase contributes to protection of Nocardia asteroides within the intact host. Infect Immun. 1990 Sep;58(9):3122–3128. doi: 10.1128/iai.58.9.3122-3128.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Beaman L., Beaman B. The timing of exposure of mononuclear phagocytes to recombinant interferon gamma and recombinant tumor necrosis factor alpha alters interactions with Nocardia asteroides. J Leukoc Biol. 1992 Mar;51(3):276–281. doi: 10.1002/jlb.51.3.276. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Beaman L., Paliescheskey M., Beaman B. L. Acid phosphatase stimulation of the growth of Nocardia asteroides and its possible relationship to the modification of lysosomal enzymes in macrophages. Infect Immun. 1988 Jun;56(6):1652–1654. doi: 10.1128/iai.56.6.1652-1654.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Black C. M., Beaman B. L., Donovan R. M., Goldstein E. Effect of virulent and less virulent strains of Nocardia asteroides on acid-phosphatase activity in alveolar and peritoneal macrophages maintained in vitro. J Infect Dis. 1983 Jul;148(1):117–124. doi: 10.1093/infdis/148.1.117. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Black C. M., Beaman B. L., Donovan R. M., Goldstein E. Intracellular acid phosphatase content and ability of different macrophage populations to kill Nocardia asteroides. Infect Immun. 1985 Feb;47(2):375–383. doi: 10.1128/iai.47.2.375-383.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Black C. M., Paliescheskey M., Beaman B. L., Donovan R. M., Goldstein E. Modulation of lysosomal protease-esterase and lysozyme in Kupffer cells and peritoneal macrophages infected with Nocardia asteroides. Infect Immun. 1986 Dec;54(3):917–919. doi: 10.1128/iai.54.3.917-919.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davis-Scibienski C., Beaman B. L. Interaction of Nocardia asteroides with rabbit alveolar macrophages: association of virulence, viability, ultrastructural damage, and phagosome-lysosome fusion. Infect Immun. 1980 May;28(2):610–619. doi: 10.1128/iai.28.2.610-619.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Filice G. A., Beaman B. L., Krick J. A., Remington J. S. Effects of human neutrophils and monocytes on Nocardia asteroides: failure of killing despite occurrence of the oxidative metabolic burst. J Infect Dis. 1980 Sep;142(3):432–438. doi: 10.1093/infdis/142.3.432. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Filice G. A., Beaman B. L., Remington J. S. Effects of activated macrophages on Nacardia asteroides. Infect Immun. 1980 Feb;27(2):643–649. doi: 10.1128/iai.27.2.643-649.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Griffin F. M., Jr, Griffin J. A., Leider J. E., Silverstein S. C. Studies on the mechanism of phagocytosis. I. Requirements for circumferential attachment of particle-bound ligands to specific receptors on the macrophage plasma membrane. J Exp Med. 1975 Nov 1;142(5):1263–1282. doi: 10.1084/jem.142.5.1263. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hill H. R., Augustine N. H., Williams P. A., Brown E. J., Bohnsack J. F. Mechanism of fibronectin enhancement of group B streptococcal phagocytosis by human neutrophils and culture-derived macrophages. Infect Immun. 1993 Jun;61(6):2334–2339. doi: 10.1128/iai.61.6.2334-2339.1993. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Isberg R. R. Discrimination between intracellular uptake and surface adhesion of bacterial pathogens. Science. 1991 May 17;252(5008):934–938. doi: 10.1126/science.1674624. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kluftinger J. L., Kelly N. M., Jost B. H., Hancock R. E. Fibronectin as an enhancer of nonopsonic phagocytosis of Pseudomonas aeruginosa by macrophages. Infect Immun. 1989 Sep;57(9):2782–2785. doi: 10.1128/iai.57.9.2782-2785.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lachman L. B., Brown D. C., Dinarello C. A. Growth-promoting effect of recombinant interleukin 1 and tumor necrosis factor for a human astrocytoma cell line. J Immunol. 1987 May 1;138(9):2913–2916. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Malawista S. E., Bodel P. T. The dissociation by colchicine of phagocytosis from increased oxygen consumption in human leukocytes. J Clin Invest. 1967 May;46(5):786–796. doi: 10.1172/JCI105579. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Malawista S. E., Gee J. B., Bensch K. G. Cytochalasin B reversibly inhibits phagocytosis: functional, metabolic, and ultrastructural effects in human blood leukocytes and rabbit alveolar macrophages. Yale J Biol Med. 1971 Dec;44(3):286–300. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Noske W., Lentzen H., Lange K., Keller K. Phagocytotic activity of glial cells in culture. Exp Cell Res. 1982 Dec;142(2):437–445. doi: 10.1016/0014-4827(82)90385-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Snyderman R., Pike M. C., Fischer D. G., Koren H. S. Biologic and biochemical activities of continuous macrophage cell lines P388D1 and J774.1. J Immunol. 1977 Dec;119(6):2060–2066. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tweardy D. J., Mott P. L., Glazer E. W. Monokine modulation of human astroglial cell production of granulocyte colony-stimulating factor and granulocyte-macrophage colony-stimulating factor. I. Effects of IL-1 alpha and IL-beta. J Immunol. 1990 Mar 15;144(6):2233–2241. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Walker T. S. Rickettsial interactions with human endothelial cells in vitro: adherence and entry. Infect Immun. 1984 May;44(2):205–210. doi: 10.1128/iai.44.2.205-210.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wiker H. G., Harboe M. The antigen 85 complex: a major secretion product of Mycobacterium tuberculosis. Microbiol Rev. 1992 Dec;56(4):648–661. doi: 10.1128/mr.56.4.648-661.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]