Abstract
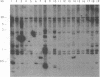
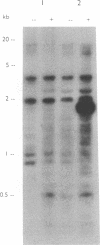
There has been considerable speculation regarding the possible relationship between the phenotypic and genotypic heterogeneity seen among human isolates of Giardia lamblia and the wide clinical spectrum of human giardiasis. Several workers have suggested that human giardiasis may be a mixed infection consisting of variant strains or subgroups which are present in the same infection and which are selectable, but it is not clear whether these apparent variant strains represent a truly heterogeneous infection or whether the genotypic heterogeneity observed is due to the susceptibility of the Giardia genome to a high rate of structural genetic rearrangement. We have therefore studied variation in Giardia intestinalis genotypes in 19 isolates in vitro and in vivo by using the technique of M13 DNA fingerprinting. Genotypes of isolates changed with time when cultured under standard conditions and when pressured with bile. Sequential isolates and their clones taken from a patient with chronic giardiasis both before and after several treatments with metronidazole had different genotypes. Finally, clones of isolate WB had different initial genotypes, which changed after 4 months in culture. These findings suggest that the apparent genotypic heterogeneity at least in these G. intestinalis isolates is more likely to be due to the plasticity of the Giardia genome than to the presence of a truly mixed population of strains within the same infection.
Full text
PDF





Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Adam R. D., Aggarwal A., Lal A. A., de La Cruz V. F., McCutchan T., Nash T. E. Antigenic variation of a cysteine-rich protein in Giardia lamblia. J Exp Med. 1988 Jan 1;167(1):109–118. doi: 10.1084/jem.167.1.109. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Adam R. D. Chromosome-size variation in Giardia lamblia: the role of rDNA repeats. Nucleic Acids Res. 1992 Jun 25;20(12):3057–3061. doi: 10.1093/nar/20.12.3057. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Andrews R. H., Adams M., Boreham P. F., Mayrhofer G., Meloni B. P. Giardia intestinalis: electrophoretic evidence for a species complex. Int J Parasitol. 1989 Apr;19(2):183–190. doi: 10.1016/0020-7519(89)90006-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Andrews R. H., Chilton N. B., Mayrhofer G. Selection of specific genotypes of Giardia intestinalis by growth in vitro and in vivo. Parasitology. 1992 Dec;105(Pt 3):375–386. doi: 10.1017/s0031182000074540. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baum K. F., Berens R. L., Jones R. H., Marr J. J. A new method for cloning Giardia lamblia, with a discussion of the statistical considerations of limiting dilution. J Parasitol. 1988 Apr;74(2):267–269. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bertram M. A., Meyer E. A., Lile J. D., Morse S. A. A comparison of isozymes of five axenic Giardia isolates. J Parasitol. 1983 Oct;69(5):793–801. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bhatia V. N., Warhurst D. C. Hatching and subsequent cultivation of cysts of Giardia intestinalis in Diamond's medium. J Trop Med Hyg. 1981 Feb;84(1):45–45. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Borst P., Greaves D. R. Programmed gene rearrangements altering gene expression. Science. 1987 Feb 6;235(4789):658–667. doi: 10.1126/science.3544215. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cowman A. F., Saint R. B., Coppel R. L., Brown G. V., Anders R. F., Kemp D. J. Conserved sequences flank variable tandem repeats in two S-antigen genes of Plasmodium falciparum. Cell. 1985 Apr;40(4):775–783. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(85)90337-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- De Jonckheere J. F., Majewska A. C., Kasprzak W. Giardia isolates from primates and rodents display the same molecular polymorphism as human isolates. Mol Biochem Parasitol. 1990 Feb;39(1):23–29. doi: 10.1016/0166-6851(90)90004-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Farthing M. J., Keusch G. T., Carey M. C. Effects of bile and bile salts on growth and membrane lipid uptake by Giardia lamblia. Possible implications for pathogenesis of intestinal disease. J Clin Invest. 1985 Nov;76(5):1727–1732. doi: 10.1172/JCI112162. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Feinberg A. P., Vogelstein B. A technique for radiolabeling DNA restriction endonuclease fragments to high specific activity. Anal Biochem. 1983 Jul 1;132(1):6–13. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(83)90418-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fortess E., Meyer E. A. Isolation and axenic cultivation of Giardia trophozoites from the guinea pig. J Parasitol. 1976 Oct;62(5):689–689. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Keister D. B. Axenic culture of Giardia lamblia in TYI-S-33 medium supplemented with bile. Trans R Soc Trop Med Hyg. 1983;77(4):487–488. doi: 10.1016/0035-9203(83)90120-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kemp D. J., Coppel R. L., Anders R. F. Repetitive proteins and genes of malaria. Annu Rev Microbiol. 1987;41:181–208. doi: 10.1146/annurev.mi.41.100187.001145. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Le Blancq S. M., Korman S. H., Van der Ploeg L. H. Frequent rearrangements of rRNA-encoding chromosomes in Giardia lamblia. Nucleic Acids Res. 1991 Aug 25;19(16):4405–4412. doi: 10.1093/nar/19.16.4405. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mayrhofer G., Andrews R. H., Ey P. L., Albert M. J., Grimmond T. R., Merry D. J. The use of suckling mice to isolate and grow Giardia from mammalian faecal specimens for genetic analysis. Parasitology. 1992 Oct;105(Pt 2):255–263. doi: 10.1017/s0031182000074187. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meloni B. P., Lymbery A. J., Thompson R. C. Isoenzyme electrophoresis of 30 isolates of Giardia from humans and felines. Am J Trop Med Hyg. 1988 Jan;38(1):65–73. doi: 10.4269/ajtmh.1988.38.65. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meyer E. A. Giardia lamblia: isolation and axenic cultivation. Exp Parasitol. 1976 Feb;39(1):101–105. doi: 10.1016/0014-4894(76)90016-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith P. D., Gillin F. D., Spira W. M., Nash T. E. Chronic giardiasis: studies on drug sensitivity, toxin production, and host immune response. Gastroenterology. 1982 Oct;83(4):797–803. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sogin M. L., Gunderson J. H., Elwood H. J., Alonso R. A., Peattie D. A. Phylogenetic meaning of the kingdom concept: an unusual ribosomal RNA from Giardia lamblia. Science. 1989 Jan 6;243(4887):75–77. doi: 10.1126/science.2911720. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Southern E. M. Detection of specific sequences among DNA fragments separated by gel electrophoresis. J Mol Biol. 1975 Nov 5;98(3):503–517. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(75)80083-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tanaka M., Gu H. M., Bzik D. J., Li W. B., Inselburg J. Mutant dihydrofolate reductase-thymidylate synthase genes in pyrimethamine-resistant Plasmodium falciparum with polymorphic chromosome duplications. Mol Biochem Parasitol. 1990 Aug;42(1):83–91. doi: 10.1016/0166-6851(90)90115-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Triglia T., Foote S. J., Kemp D. J., Cowman A. F. Amplification of the multidrug resistance gene pfmdr1 in Plasmodium falciparum has arisen as multiple independent events. Mol Cell Biol. 1991 Oct;11(10):5244–5250. doi: 10.1128/mcb.11.10.5244. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Upcroft J. A., Healey A., Murray D. G., Boreham P. F., Upcroft P. A gene associated with cell division and drug resistance in Giardia duodenalis. Parasitology. 1992 Jun;104(Pt 3):397–405. doi: 10.1017/s0031182000063642. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Van der Ploeg L. H., Schwartz D. C., Cantor C. R., Borst P. Antigenic variation in Trypanosoma brucei analyzed by electrophoretic separation of chromosome-sized DNA molecules. Cell. 1984 May;37(1):77–84. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(84)90302-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vassart G., Georges M., Monsieur R., Brocas H., Lequarre A. S., Christophe D. A sequence in M13 phage detects hypervariable minisatellites in human and animal DNA. Science. 1987 Feb 6;235(4789):683–684. doi: 10.1126/science.2880398. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weiss J. B., van Keulen H., Nash T. E. Classification of subgroups of Giardia lamblia based upon ribosomal RNA gene sequence using the polymerase chain reaction. Mol Biochem Parasitol. 1992 Aug;54(1):73–86. doi: 10.1016/0166-6851(92)90096-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]