Abstract
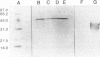
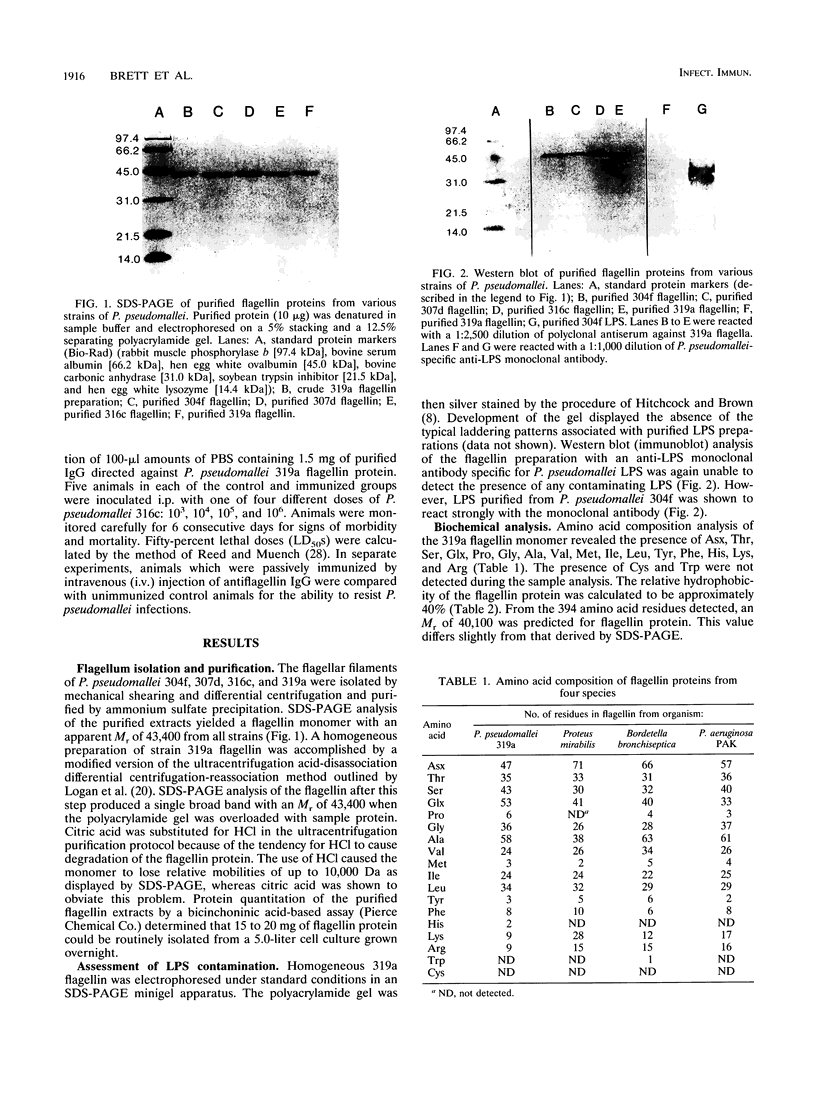
Flagellin proteins from several different strains of Pseudomonas pseudomallei have been isolated and purified to homogeneity by mechanical shearing and differential centrifugation techniques. Analysis by sodium dodecyl sulfate-polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis yielded flagellin monomer protein bands with an estimated M(r) of 43,400. No lipopolysaccharide contamination of the purified protein preparations was detectable by silver staining of flagellin displayed on polyacrylamide gels and by Western immunoblotting with P. pseudomallei antilipopolysaccharide monoclonal antibody. NH2-terminal amino acid sequence analysis of the flagellin protein of P. pseudomallei 319a revealed significant homology with flagellins from Proteus mirabilis, Bordetella bronchiseptica, and Pseudomonas aeruginosa PAK. Rabbit polyclonal antiserum raised against the 319a flagellin protein reacted with 64 of 65 P. pseudomallei strains tested. The polyclonal antiserum proved effective in inhibiting the motility of these organisms in motility agar plates. Passive immunization studies demonstrated that 319a flagellin-specific antiserum was capable of protecting diabetic rats from challenge with a heterologous P. pseudomallei strain.
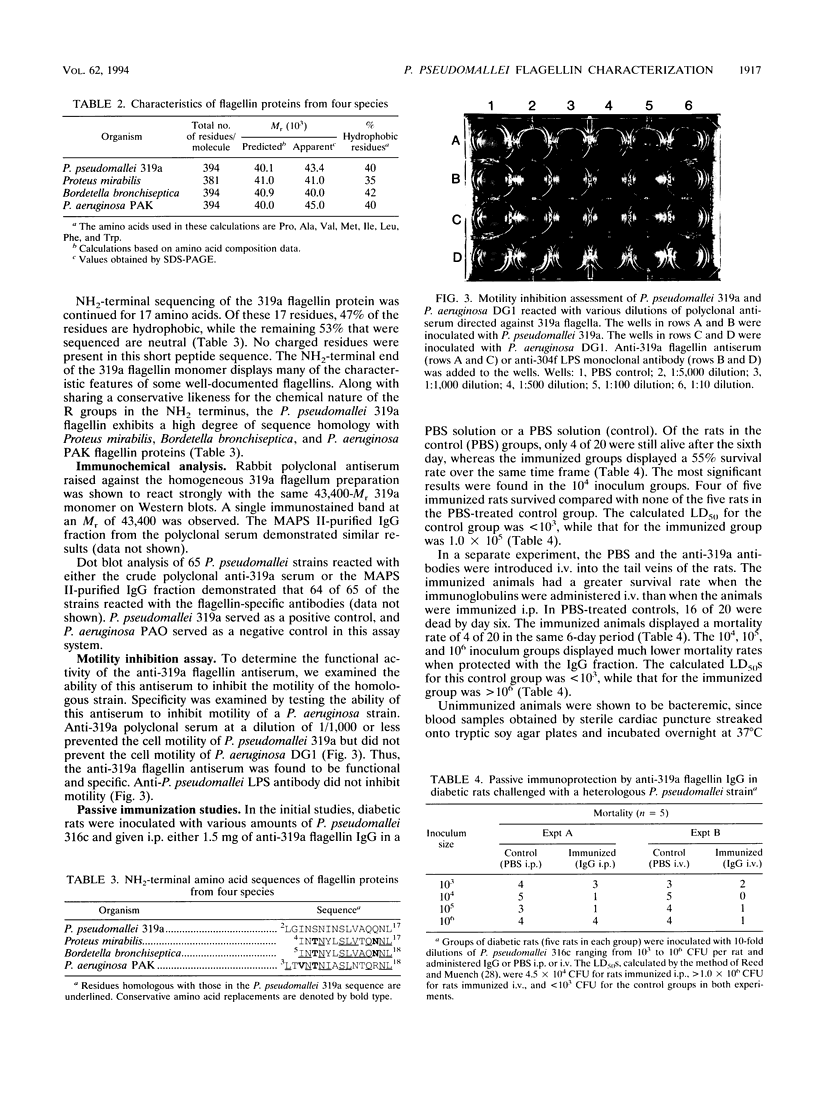
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bahrani F. K., Johnson D. E., Robbins D., Mobley H. L. Proteus mirabilis flagella and MR/P fimbriae: isolation, purification, N-terminal analysis, and serum antibody response following experimental urinary tract infection. Infect Immun. 1991 Oct;59(10):3574–3580. doi: 10.1128/iai.59.10.3574-3580.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- COLLING M., NIGG C., HECKLY R. J. Toxins of Pseudomonas pseudomallei. I. Production in vitro. J Bacteriol. 1958 Oct;76(4):422–426. doi: 10.1128/jb.76.4.422-426.1958. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chaowagul W., White N. J., Dance D. A., Wattanagoon Y., Naigowit P., Davis T. M., Looareesuwan S., Pitakwatchara N. Melioidosis: a major cause of community-acquired septicemia in northeastern Thailand. J Infect Dis. 1989 May;159(5):890–899. doi: 10.1093/infdis/159.5.890. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ellison D. W., Baker H. J., Mariappan M. Melioidosis in Malaysia. I. A method for isolation of Pseudomonas pseudomallei from soil and surface water. Am J Trop Med Hyg. 1969 Sep;18(5):694–697. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HECKLY R. J., NIGG C. Toxins of Pseudomonas pseudomallei. II. Characterization. J Bacteriol. 1958 Oct;76(4):427–436. doi: 10.1128/jb.76.4.427-436.1958. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hitchcock P. J., Brown T. M. Morphological heterogeneity among Salmonella lipopolysaccharide chemotypes in silver-stained polyacrylamide gels. J Bacteriol. 1983 Apr;154(1):269–277. doi: 10.1128/jb.154.1.269-277.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Howe C., Sampath A., Spotnitz M. The pseudomallei group: a review. J Infect Dis. 1971 Dec;124(6):598–606. doi: 10.1093/infdis/124.6.598. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Joys T. M. The covalent structure of the phase-1 flagellar filament protein of Salmonella typhimurium and its comparison with other flagellins. J Biol Chem. 1985 Dec 15;260(29):15758–15761. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Joys T. M. The flagellar filament protein. Can J Microbiol. 1988 Apr;34(4):452–458. doi: 10.1139/m88-078. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KOBAYASHI T., RINKER J. N., KOFFLER H. Purification and and chemical properties of flagellin. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1959 Oct;84:342–362. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(59)90598-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KOFFLER H., KOBAYASHI T. Purification of flagella and flagellin with ammonium sulfate. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1957 Mar;67(1):246–248. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(57)90266-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kanto S., Okino H., Aizawa S., Yamaguchi S. Amino acids responsible for flagellar shape are distributed in terminal regions of flagellin. J Mol Biol. 1991 Jun 5;219(3):471–480. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(91)90187-b. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kelly-Wintenberg K., Anderson T., Montie T. C. Phosphorylated tyrosine in the flagellum filament protein of Pseudomonas aeruginosa. J Bacteriol. 1990 Sep;172(9):5135–5139. doi: 10.1128/jb.172.9.5135-5139.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kirschenbaum D. M. A compilation of amino acid analyses of proteins. VII. Residues per molecule-5. Anal Biochem. 1975 May 26;66(1):123–150. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(75)90732-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kostrzynska M., Betts J. D., Austin J. W., Trust T. J. Identification, characterization, and spatial localization of two flagellin species in Helicobacter pylori flagella. J Bacteriol. 1991 Feb;173(3):937–946. doi: 10.1128/jb.173.3.937-946.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Logan S. M., Harris L. A., Trust T. J. Isolation and characterization of Campylobacter flagellins. J Bacteriol. 1987 Nov;169(11):5072–5077. doi: 10.1128/jb.169.11.5072-5077.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mays E. E., Ricketts E. A. Melioidosis: recrudescence associated with bronchogenic carcinoma twenty-six years following initial geographic exposure. Chest. 1975 Aug;68(2):261–263. doi: 10.1378/chest.68.2.261. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Minnich S. A., Newton A. Promoter mapping and cell cycle regulation of flagellin gene transcription in Caulobacter crescentus. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Mar;84(5):1142–1146. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.5.1142. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Montie T. C., Craven R. C., Holder I. A. Flagellar preparations from Pseudomonas aeruginosa: isolation and characterization. Infect Immun. 1982 Jan;35(1):281–288. doi: 10.1128/iai.35.1.281-288.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Montie T. C., Stover G. B. Isolation and characterization of flagellar preparations from Pseudomonas species. J Clin Microbiol. 1983 Sep;18(3):452–456. doi: 10.1128/jcm.18.3.452-456.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Puthucheary S. D., Parasakthi N., Lee M. K. Septicaemic melioidosis: a review of 50 cases from Malaysia. Trans R Soc Trop Med Hyg. 1992 Nov-Dec;86(6):683–685. doi: 10.1016/0035-9203(92)90191-e. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Richardson K., Parker C. D. Identification and occurrence of Vibrio cholerae flagellar core proteins in isolated outer membrane. Infect Immun. 1985 Mar;47(3):674–679. doi: 10.1128/iai.47.3.674-679.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schmitt R., Raska I., Mayer F. Plain and complex flagella of Pseudomonas rhodos: analysis of fine structure and composition. J Bacteriol. 1974 Feb;117(2):844–857. doi: 10.1128/jb.117.2.844-857.1974. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sexton M. M., Goebel L. A., Godfrey A. J., Choawagul W., White N. J., Woods D. E. Ribotype analysis of Pseudomonas pseudomallei isolates. J Clin Microbiol. 1993 Feb;31(2):238–243. doi: 10.1128/jcm.31.2.238-243.1993. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Totten P. A., Lory S. Characterization of the type a flagellin gene from Pseudomonas aeruginosa PAK. J Bacteriol. 1990 Dec;172(12):7188–7199. doi: 10.1128/jb.172.12.7188-7199.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Towbin H., Staehelin T., Gordon J. Electrophoretic transfer of proteins from polyacrylamide gels to nitrocellulose sheets: procedure and some applications. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Sep;76(9):4350–4354. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.9.4350. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Woods D. E., Jones A. L., Hill P. J. Interaction of insulin with Pseudomonas pseudomallei. Infect Immun. 1993 Oct;61(10):4045–4050. doi: 10.1128/iai.61.10.4045-4050.1993. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yabuuchi E., Kosako Y., Oyaizu H., Yano I., Hotta H., Hashimoto Y., Ezaki T., Arakawa M. Proposal of Burkholderia gen. nov. and transfer of seven species of the genus Pseudomonas homology group II to the new genus, with the type species Burkholderia cepacia (Palleroni and Holmes 1981) comb. nov. Microbiol Immunol. 1992;36(12):1251–1275. doi: 10.1111/j.1348-0421.1992.tb02129.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]