Abstract
We recently identified a functionally important disulfide bridge between C255 and C511 of the human Na+/glucose cotransporter SGLT1. In this study, voltage-clamp fluorometry was used to characterize the fluorescence of four different dyes attached to C255 and C511 under various ionic and substrate/inhibitor conditions. State-dependent fluorescence changes (ΔF) were observed when TMR5M or TMR6M dyes were attached to C255 and C511 or when Alexa488 was bound to C511. TMR5M-C511 was extremely sensitive to membrane potential (Vm) and to external Na+ and αMG (a nonmetabolizable glucose analog) concentrations. A progressive increase in αMG concentration drastically changed the maximal voltage-dependent ΔF and produced a positive shift in the midpoint of the ΔF-Vm curve. By determining specific fluorescence intensity for each state of the cotransporter, our steady-state fluorescence data could be reproduced using the rate constants previously proposed for a five-state kinetic model exclusively derived from electrophysiological measurements. Our results bring an independent support to the proposed kinetic model and show that the binding of αMG substrate significantly modifies the environment of C255 and C511.
INTRODUCTION
The classical distinction between ion channels and transporters is the contention that, for the latter group, a significant conformational change is required during each transport cycle. This is generally associated with larger activation energies for transporters (cotransporter and exchanger, Ea ∼ 25 kcal/mol in the case of SGLT1 (1)) versus channels (∼4–7 kcal/mol; (2,3)). In recent years, this distinction has become less stringent because ligand-gated ((4); for reviews see Keramidas et al. (5)) and voltage-gated channels (for review see Bezanilla (6)) must experience conformational changes to become activated and because transporters and pumps have been shown to present channel-like behavior (7,8). Nevertheless, whereas most channels are merely gated, transporters require conformational changes to create directed binding sites, implying a set of distinct conformational states.
In the absence of crystal structures for the different forms of a transporter, fluorescence spectroscopy coupled to electrophysiology is the most powerful way of determining conformational change in a time-resolved manner and it has been used since 1996 for studying movement of the voltage sensor in voltage-gated channels (9,10). In general, the amplitude of the fluorescence variation after a conformational change depends on the degree to which the conformational change affects the environment of the fluorophore at the molecular level. For cotransporters, voltage-clamp fluorometry (VCF) was first employed in 1998 (11) for the Na+/glucose cotransporter SGLT1, which is a member of the SLC5A family of Na+ coupled cotransporters (for review see Wright and Turk (12)). A fluorescent dye, tetramethylrhodamine-6-maleimide (TMR6M), was attached to a cysteine residue replacing amino acid Q457 and fluorescence changes were recorded simultaneously with pre-steady-state currents in the absence of glucose. Since then, it has been applied to a few other cotransporters such as the GABA transporter GAT1 (13), the serotonin transporter SERT (14), the glutamate transporter EAAT3 (15), and more recently, the Na+/Pi cotransporter (16). Additional studies of SGLT1 have also been performed using this method, with the mutant Q457C and with the mutant D454C labeled with tetramethylrhodamine-5-maleimide (TMR5M) or/and TMR6M (17–19). The studies with SGLT1 were compromised by near-complete loss of function in the labeled proteins, which diminishes the relevance of the data obtained to the normal cotransport cycle.
We have previously introduced cysteine residues into 14 different locations in the loop joining transmembrane segments (TMS) XIII and XIV of human SGLT1 (20) but none of the mutant proteins exhibits both full functionality and voltage- or substrate-dependent fluorescence changes when labeled with TMR5M. More recently, we have identified a disulfide bridge between C255 and C511 (21). We have characterized the steady-state and pre-steady-state kinetics of SGLT1 after site-directed mutagenesis at either of these two residues (C255A and C511A) and have proposed a five-state kinetic model (22) that reproduces the functional characteristics of the normal and mutated proteins. The mutants C255A and C511A, lacking this disulfide bridge, are fully functional with near-normal voltage dependence, Na+ affinities, and αMG affinities. We have also shown that C511 and C255 can be specifically labeled with a maleimide-attached fluorophore in the C255A and C511A mutants, respectively, without affecting their kinetics.
In this study we examined conformational changes using VCF via labeling of these two cysteine residues, which report the same local environment in SGLT1, using four different fluorescent dyes. In particular, TMR5M attached to C511 was found to be extremely sensitive to conformational states attained when two Na+ ions and one substrate molecule are bound to the external site. The fluorescence changes observed are fully consistent with the five-state model, and its quantitative rate constants, previously proposed on the basis of electrophysiological data.
MATERIALS AND METHODS
Oocyte preparation and injection
Oocytes were surgically removed from Xenopus laevis frogs, dissected, and defolliculated as described previously (23,24). One day after defolliculation, oocytes were injected with 46 nl of water containing mRNA (0.25 μg/μl) to obtain maximal protein expression. Oocytes were maintained in Barth's solution (in mM: 90 NaCl, 3 KCl, 0.82 MgSO4, 0.41 CaCl2, 0.33 Ca(NO3)2, 5 Hepes, pH 7.6) supplemented with 5% horse serum, 2.5 mM Na+ pyruvate, 100 units/ml penicillin, and 0.1 mg/ml streptomycin for 4–7 days before electrophysiological and fluorescence experimentation.
Molecular biology
Preparation of the constructs C255A and C511A have been described elsewhere (21).
Electrophysiology
The saline solution normally used in our electrophysiological experiments is composed of (in mM): 90 NaCl, 3 KCl, 0.82 MgCl2, 0.74 CaCl2, 10 Hepes, and the pH was adjusted to 7.6 with NaOH. α-Methyl-glucose (αMG, a nonmetabolizable glucose analog) or Pz (200 μM) were added to this solution where indicated. The 0 mM Na+ solution was obtained by replacing 90 mM Na+ with 90 mM N-methyl-d-glucamine (NMDG) and buffering with Tris rather than NaOH. Use of the two-electrode voltage-clamp apparatus has been described previously (21). In this series of experiments, voltage pulses ranged from −175 to +75 mV (with 25 mV steps) with 150 ms pulse duration.
Fluorescence
A Nikon Diaphot inverted microscope was employed with a 40× oil immersion objective (numerical aperture 1.30, Nikon, Tokyo, Japan). Dichroic mirrors with discrimination wavelengths of 505 or 570 nm (505DCXR or 570DCXR; The Optikon Corporation, Kitchener, Ontario, Canada) were used for Alexa Fluor 488 C5 maleimide (Alexa488) and fluorescein-5-maleimide (FM), or TMR5M or TMR6M dyes (Molecular Probes, Eugene, OR), respectively. See Fig. 1 A for the probe structures of TMR5M and TMR6M. A 30-W halogen lamp (GE Lighting, Cleveland, OH) was used to illuminate oocytes; the optimal excitation wavelengths were obtained by using excitation filters (10 nm bandpass) centered at 488 nm for Alexa488 and FM and at 550 nm for TMR5M and TMR6M dyes (Omega Optical, Brattleboro, VT). Fluorescence intensity was read from the oocyte animal pole, through 10 nm bandpass filters centered at 535 or 600 nm (Omega Optical) for Alexa488 and FM, or TMR5M and TMR6M dyes, respectively, with a PIN-020A photodiode (UDT Sensors, Hawthorne, CA). Oocytes were preincubated for 5–10 min on ice before the dye was added to the bathing solution to minimize dye internalization. A 10-min labeling period was performed on ice at the oocytes resting potential using 20 μM dye in the 90 mM Na+ containing solution. The fluorescence and electrophysiological signals were acquired using a Digidata 1322A digitizer and Clampex 8.2 software (Axon Instruments, Union City, CA).
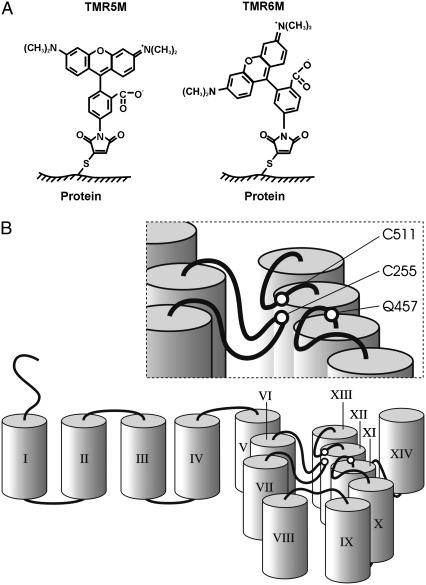
FIGURE 1.
SGLT1 membrane topology and probe structures. (A) Chemical structures of tetramethylrhodamine-5-maleimide (TMR5M) and tetramethylrhodamine-6-maleimide (TMR6M) attached to a sulfur atom of a cysteine residue. (B) Cartoon illustrating a pseudo-three-dimensional membrane topology and the transmembrane segments around the disulfide bridge C255–C511 in SGLT1. TMS were schematically represented by cylinders and are identified by Roman numerals. The position of the disulfide bridge C255–C511 close to the membrane is shown as is the nearby residue Q457.
Voltage-clamped fluorescence experiments
In simultaneous electrophysiology-fluorescence experiments, the oocytes were clamped at a membrane potential of −50 mV and five or 10 repetitions of membrane potential steps (five repetitions for C255A mutant and 10 repetitions for C511A mutant) were applied. A mechanical shutter was opened 100 ms before and closed 150 ms after the membrane potential pulse to reduce photobleaching. Under these conditions, photobleaching was typically 1% after 5–10 series of voltage pulses. The mean fluorescence recorded for each individual voltage pulse was normalized by the value recorded at −50 mV to correct for photobleaching. Data were obtained with a sampling frequency of 5 kHz, without filtering, and the repetitions were averaged for each experiment. Data were reduced by averaging 35 consecutive data points. Steady-state fluorescence was taken as the mean of normalized fluorescence values recorded between 120 and 145 ms after the initiation of the voltage pulse. In absolute value, the fluorescence level of labeled oocytes was observed to remain essentially constant (taking into consideration the photobleaching effect) at extreme depolarizing potentials (+75 mV) in the presence of different Na+ or αMG concentrations. We thus baselined the steady-state fluorescence values to equal 0 at +75 mV. Time constants for fluorescence changes were measured by fitting a single exponential to the fluorescence measurements using Clampfit 8.2 program (Axon Instruments).
Statistics
Experiments were performed on at least three oocytes obtained from a minimum of three different donors. Data are reported as mean ± SE and are compared using unpaired Student's t-test; statistical significance was set at p < 0.05.
RESULTS
Before using thiol-targeted probes to examine the fluorescence of SGLT1 mutants where one cysteine in the disulfide bridge has been mutated, the effects of Vm on the background fluorescence level of oocytes expressing either wt SGLT1, or the double mutant C255A/C511A, after labeling, was tested. The level of fluorescence observed was comparable to that seen with noninjected oocytes that had been similarly labeled, which was approximately three to four times smaller than the fluorescence level of TMR5M-labeled mutants C255A and C511A (21). As expected, no voltage-dependent changes in the background fluorescence (ΔF) could be observed in oocytes expressing wt SGLT1 or the double mutant C255A/C511A. The effect of voltage was within the noise level, which averaged 0.5%.
The effect of Vm was then investigated on the fluorescence generated by the two hydrophilic probes, Alexa488 and FM, and the two slightly hydrophobic probes, TMR5M and TMR6M, when attached to either C255 or C511. The positions of the labeled cysteines are shown in Fig. 1 B on a cartoon of a SGLT1 topology that accounts for the presence of a C255–C511 disulfide bridge.
Fluorescence labeling of C255
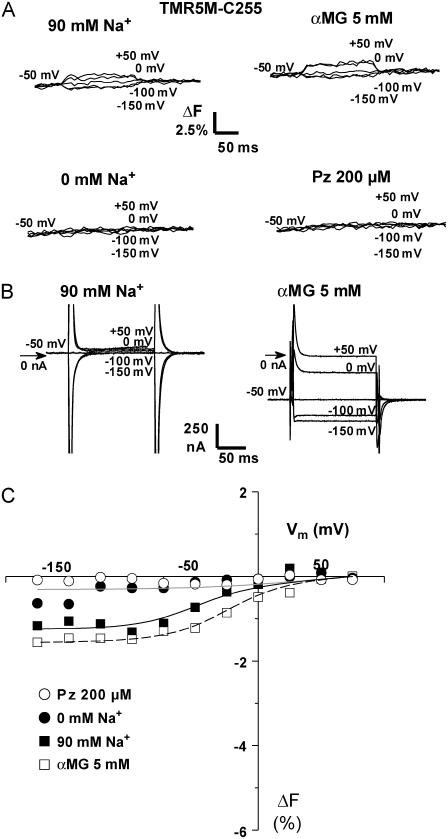
The accessibility of C255 to TMR6M, Alexa488, and FM is weak, i.e., the fluorescence intensity was comparable to the level obtained with oocytes expressing wt SGLT1 that were submitted to the same labeling procedures. However, labeling this cysteine residue with TMR5M produced a measurable ΔF in the presence of Na+ and in the presence of Na+ and αMG (see Fig. 2 A). Once corrected for photobleaching, to maintain a constant F value at −50 mV (see Materials and Methods), the ΔF from +75 to −175 mV was −1.5% in the presence of 90 mM Na+. The presence of αMG slightly enhanced the total amplitude of ΔF. No ΔF could be observed in the absence of Na+, except at extremely hyperpolarizing potentials, where the ΔF is ∼0.5% less than the fluorescence value at +75 mV. As expected, the presence of Pz, a specific inhibitor of SGLT1, completely inhibited this ΔF at all values of Vm. The labeling of C255 with TMR5M had no effect on the mutant's electrophysiological characteristics. SGLT1 specific currents in the absence and in the presence of αMG are shown on Fig. 2 B for a typical TMR5M-C255 expressing oocyte. The αMG cotransport currents were approximately −700 nA at −150 mV and the amount of charge transferred during pre-steady-state currents did not show any significant difference from that previously published (the V1/2 being ∼−30 mV and ∼+5 mV in the absence and in the presence of αMG, respectively) (22).
FIGURE 2.
Substrate and voltage effects on the fluorescence of TMR5M attached to C255. (A) Results from typical TMR5M-labeled C255-expressing oocytes are shown. Fluorescence changes (ΔF) in the presence of 90 mM Na+ (upper left), 0 mM Na+ (lower left), 5 mM αMG (upper right), and 200 μM Pz (lower right) at different voltages, as indicated. (B) SGLT1 specific current in the absence of αMG (left) or in its presence (right) for the oocyte presented in panel A. This illustrates the pre-steady-state currents, i.e., the Pz-sensitive current, in the absence and in the presence of αMG for the labeled mutant. (C) Mean steady-state ΔF versus Vm curves (n = 3). The fluorescence values were corrected for photobleaching and normalized to have the same fluorescence values at +75 mV (see Materials and Methods). The smooth lines are from the fluorescence model (see Table 2 and Discussion for details). Errors bars were omitted when smaller than symbols.
The normalized steady-state levels of fluorescence and their modulation by Vm (ΔF-Vm) are shown in Fig. 2 C. The fluorescence values were baseline to 0 at +75 mV (see Materials and Methods). Globally, the effects of glucose on ΔF-Vm are to slightly increase the amplitude of ΔF and to shift the midpoint of the ΔF-V curve toward more positive Vm (from −36 ± 5 mV in its absence to −13 ± 8 mV in its presence).
Fluorescence labeling of C511
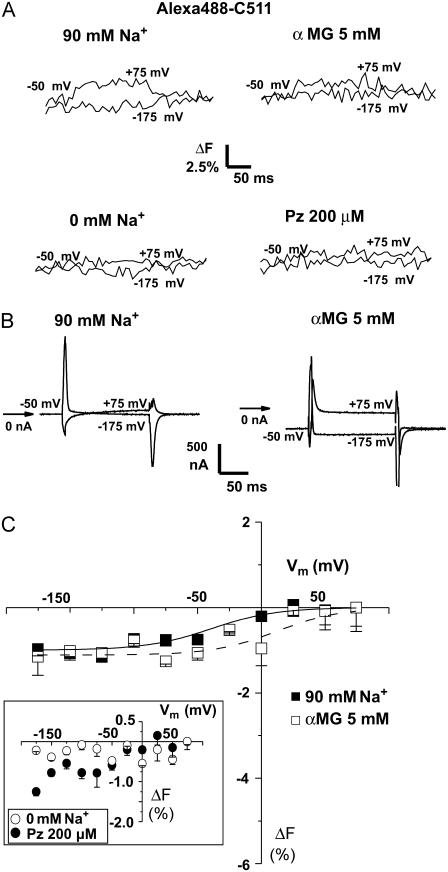
When C511 was labeled with Alexa488, small ΔF was observed with steps in Vm, particularly at positive Vm in the 90 mM Na+ solution as illustrated in Fig. 3 A for a typical oocyte. Under these conditions, the maximal ΔF was −1% for a voltage pulse from +75 to −175 mV, whether or not 5 mM αMG mM was present. This ΔF required the presence of Na+ and was completely inhibited when the transporter was blocked with Pz (in 90 mM Na+ solution). The SGLT1 specific currents from this oocyte, which were recorded simultaneously with the fluorescence signal, are shown in Fig. 3 B. Labeling with Alexa488 had no influence on the pre-steady-state currents characteristics of mutant C255A. Average ΔF-Vm curves are shown in Fig. 3 C. Similarly, FM attached to C511 produced weak but measurable ΔF (data not shown).
FIGURE 3.
Substrate and voltage effects on the fluorescence of Alexa488 attached to C511. (A) ΔF for +75 and −175 mV, in various conditions, as indicated, from typical Alexa488-labeled C511-expressing oocytes is shown. (B) Pre-steady-state current traces for the oocyte presented in panel A with (right) or without αMG (left). (C) Mean steady-state ΔF-Vm curve (n = 3). The inset shows the mean steady-state ΔF-Vm curve in the absence of Na+ and in the presence of Pz. The curves represent Boltzmann relations fitted to the points. Mean ± SE are shown.
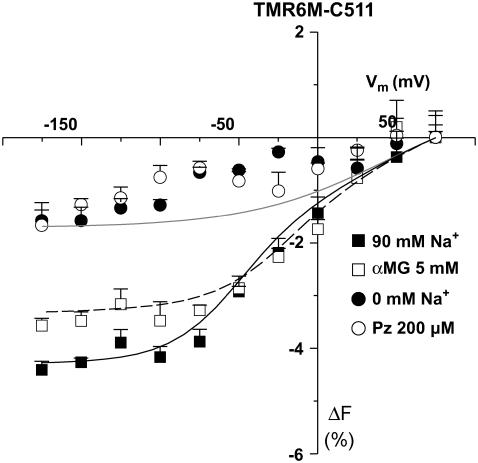
Both TMR5M and TMR6M could be bound to C511 without affecting the protein's electrophysiological characteristics (not shown). Fig. 4 illustrates the average ΔF-Vm curves with TMR6M attached to C511 in the presence of 90 mM Na+, 0 mM Na+, 5 mM αMG, and 200 μM Pz for different Vm values. First, in the presence of 90 mM Na+, a pulse from +75 to −175 mV produced a change in fluorescence of −4%. Both the absence of Na+ and the presence of Pz significantly inhibited the voltage dependency of TMR6M fluorescence. Glucose causes a shift of the ΔF-Vm curve midpoint by ∼20 mV toward more positive Vm (from −21 ± 6 mV in its absence to −2 ± 6 mV in its presence) and a modest reduction (0.6%) in the total amplitude of ΔF. Because the amplitude of the voltage-dependent fluorescent changes were sufficiently large, the time constants of the fluorescence (τF) could be established. The τF values were voltage independent, were the same in the presence or absence of glucose, and were always between 5 and 10 ms.
FIGURE 4.
Substrate and voltage effects on the fluorescence of TMR6M attached to C511. Mean steady-state ΔF-Vm curve are shown (n = 3). The smooth lines are from the fluorescence model (see Table 2 and Discussion for details). Mean ± SE are shown.
TMR5M-C511 fluorescence increased by 1–2% when hyperpolarizing from +75 to −75 mV before reaching a quasiplateau at hyperpolarizing Vm in the absence of Na+ (NMDG+ replacement) (n = 4, data not shown). Replacing 90 mM Na+ by 90 mM NMDG+ or Li+ produced the same effect, indicating that Vm could slightly influence the fluorescence intensity in the presence of these cations (n = 4, data not shown).
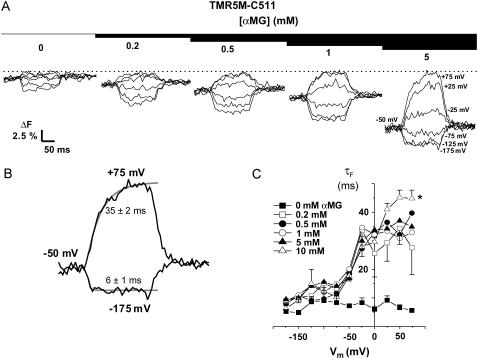
TMR5M-C511 oocytes were observed to be extremely sensitive to the presence of αMG in the bathing solution, as shown in Fig. 5 for a typical oocyte and in Fig. 6 A for a mean of eight oocytes. Increases in αMG concentration progressively enhanced the total amplitude of the ΔF and shifted the voltage sensitivity toward more positive potentials (see Figs. 5 A and 6 A). At 0 mV, there was almost no change in fluorescence in the presence of 1 mM αMG (as compared to the 90 mM Na+ solution) whereas at 10 mM αMG, fluorescence was already 4% lower than that measured at +75 mV (F+75mV) (Fig. 6 A). At hyperpolarizing Vm, the amplitude of the ΔF progressively increased with increasing [αMG] until reaching a plateau value at 5–10 mM αMG of ∼10% lower than F+75mV (Fig. 6 A). As shown in Fig. 5 C, the τF values exhibited a clear voltage dependence in the presence of αMG. Fig. 5 B illustrates the accuracy of a monoexponential fit to the experimental data from the oocytes shown on Fig. 5 A, at 5 mM αMG. Time constants were significantly slower when αMG was increased (reaching ∼45 ms at depolarizing Vm in the presence of 10 mM αMG) whereas, in the absence of αMG, it was voltage independent and was measured in the 5–10-ms range (see Fig. 5 C). At +75 mV, an increase in [αMG] increases τF value (p = 0.04, 0.2 mM against 5 mM αMG). These data allowed us to estimate an apparent affinity for αMG (KmFαMG) based on the effects of the substrate on the observed ΔF at the different Vm values. We found that the KmFαMG was voltage independent below −75 mV but voltage dependent at voltages higher than −50 mV (Fig. 6 C), as was found from the steady-state αMG-dependent current analysis (this work and Gagnon et al. (21)). The KmFαMG value was 1.0 ± 0.2 mM at −150 mV, and the KmIαMG, calculated from the steady-state currents (illustrated on Fig. 6 B) measured simultaneously with the fluorescence intensities, gave a value of 1.6 ± 0.3 mM, as shown on Fig. 6 C.
FIGURE 5.
Effect of αMG on fluorescence of TMR5M attached to C511. (A) The typical ΔF for different αMG concentrations for Vm going from +75 to −175 mV, by 50-mV increment, are shown. A dotted line indicates the +75-mV level. (B) A monoexponential fit (gray line) is represented over the fluorescence traces (black line) for +75 and −175 mV to illustrate the accuracy of the fit. The corresponding time constants are indicated. (C) Mean time constants τF for fluorescence in the presence and absence of various αMG concentrations (n = 8). *, p ≤ 0.05. Mean ± SE are shown.
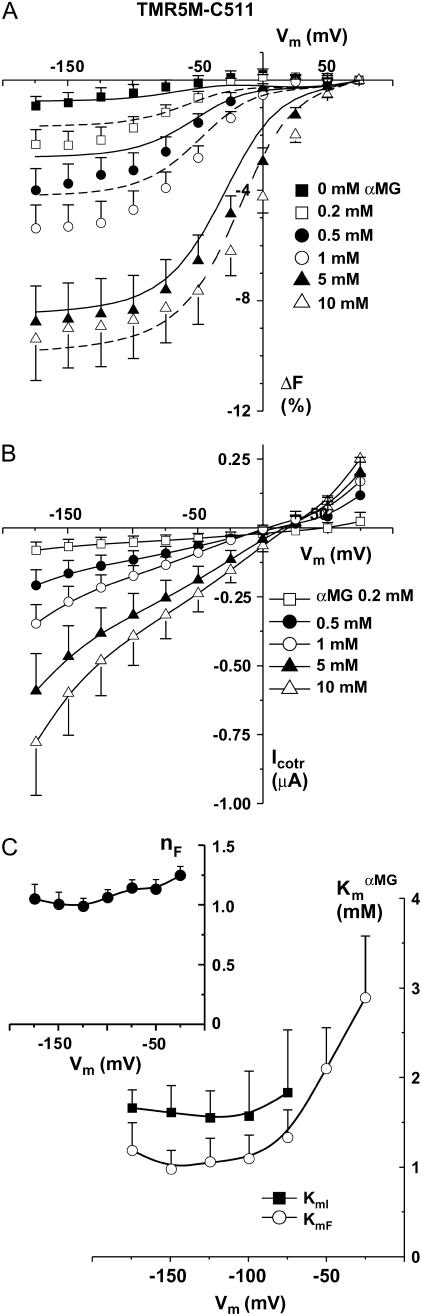
FIGURE 6.
Estimates of the apparent affinity values. (A) Mean steady-state ΔF-Vm curve for different αMG concentrations (n = 8). (B) Mean Icotr (αMG cotransport current), simultaneously measured with fluorescence changes (n = 8). (C) Estimates of the apparent affinity values as a function of Vm coming from the simultaneous fluorescence (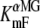 , open circles) and currents (
, open circles) and currents (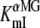 , solid squares) measurements. The fluorescence data were fitted using a Hill equation and the nH parameter is represented in the inset. The Icotr versus [αMG] at a given Vm were fitted using a Michaelis-Menten equation. Mean ± SE are shown.
, solid squares) measurements. The fluorescence data were fitted using a Hill equation and the nH parameter is represented in the inset. The Icotr versus [αMG] at a given Vm were fitted using a Michaelis-Menten equation. Mean ± SE are shown.
Table 1 summarizes the ΔF observed for the different dyes attached to either of the two available cysteine residues in the SGLT1 mutants.
TABLE 1.
Summary of the experimental maximal ΔF (from +75 to −175 mV) observed for the different dyes attached to C255 and C511
| Dye | C255 | C511 |
|---|---|---|
| Alexa488 | Not accessible | 90 Na+ −1% |
| 0 Na+ none | ||
| αMG −1% | ||
| Pz none | ||
| FM | Not accessible | weak ΔF |
| TMR5M | 90 Na+ −1.3% | 90 Na+ −4% |
| 0 Na+ −0.5% | 0 Na+ 1.5% | |
| αMG −1.5% | αMG −10–12% | |
| Pz none | Pz −4% (as 90 Na+) | |
| TMR6M | Not accessible | 90 Na+ −4.5% |
| 0 Na+ −1% | ||
| αMG −3.5% | ||
| Pz −1% |
DISCUSSION
VCF can indicate changes in the immediate environment of a dye attached to a specific residue of a transporter during the protein's turnover at different membrane potentials. Local ionic strength, pH, and hydrophobicity in the vicinity of the label can all influence its fluorescence level. For example, TMRM experiences a 33% decrease in fluorescence and a shift in maximum absorption wavelength from 567 to 575 nm when going from a hydrophobic (ethanol) to a polar (water) environment (10). Even if the precise environment (i.e., nearby amino acids) of a labeled cysteine is impossible to establish in the absence of a crystal structure, movement of the protein during its transport cycle may directly affect this microenvironment and the concomitant fluorescence changes can be used to monitor the transport cycle. However, it must be borne in mind that these changes in fluorescence reflect only the conformational changes that alter that specific microdomain of the protein.
The extreme sensitivity of dye to changes in their microenvironment can be seen by examining the results in this article. The fully functional SGLT1 mutants C255A and C511A allow labeling of C511 or C255, which are located close together as they normally form a disulfide bridge in wt SGLT1. Although four dyes were used (FM, Alexa488, TMR5M, and TMR6M) only two were experiencing significant changes in their immediate environment, detecting voltage- and ligand-sensitive conformational changes. The observation that voltage-dependent ΔF was obtained with several dyes at position C511 but only with one fluorophore at position C255 indicates that the specific three-dimensional structure of a fluorophore is also important in reporting a conformational change. In this study, hydrophobic probes such as TMR were better suited for measuring substrate- and Vm-dependent conformational changes in our mutant transporters.
Effects of Na+ on voltage-dependent ΔF
A ΔF was measured with TMR5M-C511, with TMR5M-C255 and Alexa488-C511, though only at hyperpolarizing Vm, in the absence of Na+, though it was not measurable with TMR6M-C511. The fact that conformational changes can be detected with TMR5M at these two positions in the absence of Na+ is in agreement with the past observations of pre-steady-state currents in this condition as well as with the models recently proposed for SGLT1 that require the presence of three different Na+-independent states to account for pre-steady-state current measurements (see below) (18,25). The ΔF voltage dependence in the presence of Na+ correlated well with what had been previously observed when measuring the transferred charge (22). The V1/2 values obtained from analysis of fluorescence were −36 and −21 mV for TMR5M-C255 and TMR6M-C511 in the absence of glucose whereas the V1/2 constants for both mutants, when calculated using the charges transferred in the absence of glucose, were of ∼−30 mV.
High sensitivity of TMR5M-C511 to αMG binding
The presence of αMG shifted the midpoint of the ΔF-Vm relation of TMR(5 or 6)M (attached to C255 or C511) toward more positive Vm. The same shift occurred for the pre-steady-state currents of these proteins in the presence of different αMG concentrations (22). For TMR5M-C255 and TMR6M-C511, the presence of glucose shifted the ΔF-Vm curve by ∼20 mV. For transferred charges, the TMR5M-C511 shift in V1/2 is ∼40 mV when adding 5 mM αMG (22). In addition to a positive shift in the ΔF-Vm curve, αMG addition increased the ΔF amplitude for TMR5M-C511 (Figs. 5 and 6) but not for TMR5M-C255 (Fig. 2) and TMR6M-C511 (Fig. 4). These different behaviors, as well the absence of effect of αMG on several other TMR5M-labeled cysteine mutants (20), rule out the possibility of a direct quenching effect of αMG on TMR fluorescence.
αMG has also an influence on the τF for TMR5M-C511, which is much slower at depolarizing Vm than at hyperpolarizing Vm, where τF reaches the 5–10-ms level typically observed for this mutant in the absence of αMG. Although this behavior was also observed for the pre-steady-state currents recorded in these mutants in the presence of the same amount of αMG, the absolute values for the current time constant (τI) at positive Vm was between 4.5 and 5.5 ms, i.e., almost 10× faster than the observed τF (22). The discrepancy between the time constant values (τF and τI) could originate from many sources and has also been reported for SGLT1 and NaPi-IIb (16,17,19). It suggests that changes in fluorescence report a transporter conformational change with some “delay”, compared to the pre-steady-state currents. This could occur if a slow relaxation in the environment of the fluorescent dye, without being a part of the transport cycle, was a consequence of a relatively fast conformational change of the transporter.
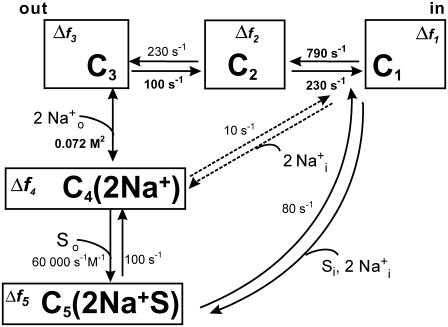
Kinetic model based on SGLT1 fluorescence data
We have used a linear fluorescence model based on a five-state kinetic model of the SGLT1 mutants C255A and C511A (22) (see Fig. 7). The rate constants originally derived exclusively from the pre-steady-state electrophysiological data were maintained (22) and the kij0 values are given in Fig. 7. The experimental ΔF, normalized using the fluorescence levels observed at +75 mV, were reproduced within the kinetic model by attributing a certain Δfi to each of the model's five states. Using the voltage-dependent probabilities (Ci) of finding the transporter in a given state i, the total ΔF was calculated as follows:
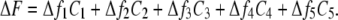 |
(1) |
FIGURE 7.
Kinetic model of the cotransport mechanism used to simulate conformation-dependent fluorescence variations. The model was established in a previous study to account for the mutants (C255A and C511A) pre-steady-state currents (22). Each box represents a state for which a change in fluorescence value (Δfi) was attributed with respect to the total fluorescence intensity recorded when the transporter is facing a Vm of +75 mV. The rate constants (kij) between state “i” and “j = i + 1” are calculated as 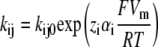 and
and 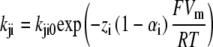 were kept as previously determined (22). The kij0, representing the values of kij at 0 mV, are indicated in small characters and those that are voltage dependent are in bold. The values of zi used for the equivalent charge moving across the entire membrane electrical field in the step between state “i” and “i + 1” were −0.38, −0.52, and −1.1 for i varying from 1 to 3, respectively. The values for αi describing the asymmetry of the energy barrier were 0.3 and 0 for i of 1 and 2, respectively. The Na+ binding step is assumed to be in rapid equilibrium. The constants k14 (in M−2s−1) and k15 (in M−3s−1) were calculated to respect microreversibility. See Table 2 for the Δfi values for the different dyes and Discussion for further details.
were kept as previously determined (22). The kij0, representing the values of kij at 0 mV, are indicated in small characters and those that are voltage dependent are in bold. The values of zi used for the equivalent charge moving across the entire membrane electrical field in the step between state “i” and “i + 1” were −0.38, −0.52, and −1.1 for i varying from 1 to 3, respectively. The values for αi describing the asymmetry of the energy barrier were 0.3 and 0 for i of 1 and 2, respectively. The Na+ binding step is assumed to be in rapid equilibrium. The constants k14 (in M−2s−1) and k15 (in M−3s−1) were calculated to respect microreversibility. See Table 2 for the Δfi values for the different dyes and Discussion for further details.
The model was applied to the data for TMR5M-C255, TMR6M-C511, and TMR5M-C511, and the Δfi values were determined as follows. First, we established the Δf1, Δf2, and Δf3 values (for states where Na+ is absent) to account for the voltage dependence of the fluorescence in the absence of Na+. Under these conditions, C1 is dominant at positive Vm and C3 is dominant at negative Vm, providing strong constraints on the Δfi values that can be used. We kept these values fixed when adjusting Δf4 to reproduce the ΔF-Vm curve in the presence of Na+. Finally, the Δf5 value was determined in the presence of αMG while keeping the other Δfi values fixed. The continuous lines presented in Figs. 2 C, 4, and 6 A were derived from this fluorescence model, using the fluorescence measurements obtained for each probe/mutant combination. The steady-state changes of fluorescence under different conditions for TMR5M-C255 and for both TMR dyes bound to C511 are fairly well reproduced.
The Δfi values used for simulations of the different ΔF-Vm curves for the various probes and SGLT1 positions are shown in Table 2. It is not surprising that the value of Δf1 is similar for all cases presented (1.8 or 1.5) in Table 2 because ∼35% of the mutant transporters are in state C1 at +75 mV, which was attributed a normalized fluorescence level of 100%. The Δf2 value is negative for TMR5M-C511 (−2.5) but positive for the other two cases (1.3 for TMR5M-C255 and 0.5 for TMR6M-C511); Δf3 was almost the same for TMR5M for the two mutants but changed its sign for TMR6M-C511. The sign had to be changed because of the reduction in the amplitude of ΔF in the presence of αMG compared with that in its absence (see Fig. 4); Δf3 also influences the Vm at which half of the ΔF occurs.
TABLE 2.
Change in fluorescence values (Δfi) attributed to each state (Ci) in the kinetic model
| Cysteine | Dye | Δf1 | Δf2 | Δf3 | Δf4 | Δf5 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| C255 | TMR5M | 1.8 | 1.3 | 1.2 | 0 | −0.9 |
| C511 | TMR5M | 1.8 | −2.5 | 1 | −1.1 | −16.5 |
| TMR6M | 1.5 | 0.5 | −1.2 | −4 | −3.6 |
These values, given in percentage of the fluorescence level recorded at +75 mV, were used to simulate the steady-state fluorescence (ΔF) as a function of membrane potential (Vm).
The Δf4 and Δf5 parameters are primarily responsible for the results observed in the presence of Na+ and αMG. In the case of the two mutants used, the state C4(2Na+) dominates at low αMG concentrations whereas the state C5(2Na+S) dominates at high αMG concentrations (22). Thus, for TMR5M-C511 in the presence of various αMG concentrations, it was found that Δf4 plays an important role in explaining the fluorescence level observed at low αMG concentrations whereas the effect of Δf5 becomes dominant for the higher αMG concentrations. Examining the values of Δf4 and Δf5 in Table 2 is interesting because in two cases (TMR5M-C255 and TMR5M-C511), the value of Δf5 is larger and more negative than the one of Δf4. In the case of TMR5M-C255, the values of Δf4 and Δf5 were, respectively, of 0 and −0.9 whereas those for TMR5M-C511 were −1.1 and −16.5. This explains why adding αMG produces a larger decrease in fluorescence for TMR5M-C511 (Fig. 6 A) than for TMR5M-C255 (Fig. 2 C). However, for TMR6M-C511, the value of Δf5 (−3.6) was slightly smaller than Δf4 (−4), which explains the small decrease in the maximal ΔF due to the addition of αMG (Fig. 4). A possible explanation of the large effect of αMG on the fluorescence of TMR5M-C511 (Fig. 6 A) would be that the conformational change triggered by the binding of αMG produced an increase in the polarity in the immediate environment of TMR5M when it is attached to C511 (10).
C255 and C511 are positioned in a “hot spot” in the SGLT1 structure
Previously, only residues Q457C and D454C have been shown to produce ΔF that are sensitive to different Vm and substrate conditions in SGLT1 (11,17–19). However, the functional relevance of these observations is questionable because the transport kinetics of Q457C are highly perturbed compared to wt SGLT1, and substrate cotransport (though not substrate binding) was abolished by the fluorescent labeling itself in both of these mutants. Some other residues located in loop XIII–XIV were labeled with TMR5M without any evident, state-dependent ΔF (20). In this study, we have identified two other amino acid residues, located adjacent in the intact protein, where ΔF could be observed with more than one dye. In addition, our mutant transporters were fully functional when labeled with the dyes. Four different combinations of cysteine residue and fluorescent dye were found to be sensitive to the voltage-dependent conformational change of the cotransporter. Interestingly, even though C255 and C511 are positioned close together, they behave differently when labeled with the same dye, a stark confirmation of the fact that protein conformational changes are measurable by sensing the physicochemical environment of the fluorophore at a very small scale.
CONCLUSIONS
Fluorescence changes observed with four different fluorescent dyes attached to two nearby cysteine residues in fully functional mutants of SGLT1 have been reported. The two more hydrophobic probes (TMR5M and TMR6M) were particularly useful for detecting voltage-dependent conformational changes. The fact that the fluorescence intensities measured as a function of voltage, Na+, and αMG concentrations are fully compatible with the occupation probabilities predicted by the five-state kinetic model previously proposed (22) provides an additional and independent support for the validity of this model.
Acknowledgments
We acknowledge Rikard Blunck and Mike Coady for valuable discussions and for comments on the manuscript, Michel Brunette for technical assistance, and Claude Gauthier for art work.
This work was supported by the Canadian Institutes of Health Research (grant No. MOP-10580). D.G.G. is a Natural sciences and engineering research council of Canada and Fonds de la recherche en santé du Québec postgraduate scholar.
Abbreviations used: Alexa488, Alexa Fluor 488 C5 maleimide; αMG: α-methyl-glucose; TMR5M-C255, C255 labeled by TMR5M; FM, fluorescein-5-maleimide; ΔF-Vm, fluorescence change versus membrane potential; hSGLT1, human isoform of SGLT1; I-V, current versus membrane potential; Icotr, αMG-induced cotransport current (IαMG-I90Na); 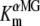 , apparent affinity for αMG; Pz, phlorizin; Q-V, transferred charge versus membrane potential; SGLT1, high affinity Na+/glucose cotransporter; TMS, transmembrane segment; TMR5M or TMR6M, tetramethylrhodamine-5(or 6)-maleimide; VCF, voltage-clamp fluorometry; Vm, membrane potential; wt, wild-type.
, apparent affinity for αMG; Pz, phlorizin; Q-V, transferred charge versus membrane potential; SGLT1, high affinity Na+/glucose cotransporter; TMS, transmembrane segment; TMR5M or TMR6M, tetramethylrhodamine-5(or 6)-maleimide; VCF, voltage-clamp fluorometry; Vm, membrane potential; wt, wild-type.
References
- 1.Hazama, A., D. D. Loo, and E. M. Wright. 1997. Presteady-state currents of the rabbit Na+/glucose cotransporter (SGLT1). J. Membr. Biol. 155:175–186. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 2.Tseeb, V. E., V. I. Geletiuk, and V. N. Kazachenko. 1991. Temperature dependence of the conductivity of individual potential-dependent K+-channels in mollusk neurons. Biofizika. 36:810–821. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3.Hille, B. 2001. Ion Channels of Excitable Membranes. Sinauer Associates, Sunderland, MA.
- 4.Hogg, R. C., B. Buisson, and D. Bertrand. 2005. Allosteric modulation of ligand-gated ion channels. Biochem. Pharmacol. 70:1267–1276. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5.Keramidas, A., A. J. Moorhouse, P. R. Schofield, and P. H. Barry. 2004. Ligand-gated ion channels: mechanisms underlying ion selectivity. Prog. Biophys. Mol. Biol. 86:161–204. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6.Bezanilla, F. 2000. The voltage sensor in voltage-dependent ion channels. Physiol. Rev. 80:555–592. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 7.Accardi, A., and C. Miller. 2004. Secondary active transport mediated by a prokaryotic homologue of ClC Cl− channels. Nature. 427:803–807. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 8.Artigas, P., and D. C. Gadsby. 2002. Ion channel-like properties of the Na+/K+ Pump. Ann. N. Y. Acad. Sci. 976:31–40. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 9.Cha, A., and F. Bezanilla. 1997. Characterizing voltage-dependent conformational changes in the Shaker K+ channel with fluorescence. Neuron. 19:1127–1140. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 10.Mannuzzu, L. M., M. M. Moronne, and E. Y. Isacoff. 1996. Direct physical measure of conformational rearrangement underlying potassium channel gating. Science. 271:213–216. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 11.Loo, D. D., B. A. Hirayama, E. M. Gallardo, J. T. Lam, E. Turk, and E. M. Wright. 1998. Conformational changes couple Na+ and glucose transport. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA. 95:7789–7794. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 12.Wright, E. M., and E. Turk. 2004. The sodium/glucose cotransport family SLC5. Pflugers Arch. 447:510–518. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 13.Li, M., R. A. Farley, and H. A. Lester. 2000. An intermediate state of the gamma-aminobutyric acid transporter GAT1 revealed by simultaneous voltage clamp and fluorescence. J. Gen. Physiol. 115:491–508. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 14.Li, M., and H. A. Lester. 2002. Early fluorescence signals detect transitions at mammalian serotonin transporters. Biophys. J. 83:206–218. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 15.Larsson, H. P., A. V. Tzingounis, H. P. Koch, and M. P. Kavanaugh. 2004. Fluorometric measurements of conformational changes in glutamate transporters. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA. 101:3951–3956. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 16.Virkki, L. V., I. C. Forster, J. Biber, and H. Murer. 2005. Substrate interactions in the human type IIa sodium-phosphate cotransporter (NaPi-IIa). Am. J. Physiol. Renal Physiol. 288:F969–F981. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 17.Diez-Sampedro, A., D. D. Loo, E. M. Wright, G. A. Zampighi, and B. A. Hirayama. 2004. Coupled sodium/glucose cotransport by SGLT1 requires a negative charge at position 454. Biochemistry. 43:13175–13184. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 18.Loo, D. D., B. A. Hirayama, A. Cha, F. Bezanilla, and E. M. Wright. 2005. Perturbation analysis of the voltage-sensitive conformational changes of the Na+/glucose cotransporter. J. Gen. Physiol. 125:13–36. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 19.Meinild, A. K., B. A. Hirayama, E. M. Wright, and D. D. Loo. 2002. Fluorescence studies of ligand-induced conformational changes of the Na(+)/glucose cotransporter. Biochemistry. 41:1250–1258. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 20.Gagnon, D. G., A. Holt, F. Bourgeois, B. Wallendorff, M. J. Coady, and J. Y. Lapointe. 2005. Membrane topology of loop 13–14 of the Na(+)/glucose cotransporter (SGLT1): a SCAM and fluorescent labelling study. Biochim. Biophys. Acta. 1712:173–184. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 21.Gagnon, D. G., P. Bissonnette, and J. Y. Lapointe. 2006. Identification of a disulfide bridge linking the fourth and the seventh extracellular loops of the Na+/glucose cotransporter. J. Gen. Physiol. 127:145–158. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 22.Gagnon, D.G., C. Frindel, and J.-Y. Lapointe. 2006. Effect of substrate on the pre-steady-state kinetics of the Na+/glucose cotransporter. Biophys. J. 92:461–472. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 23.Gagnon, M. P., P. Bissonnette, L. M. Deslandes, B. Wallendorff, and J. Y. Lapointe. 2004. Glucose accumulation can account for the initial water flux triggered by Na+/glucose cotransport. Biophys. J. 86:125–133. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 24.Bissonnette, P., J. Noel, M. J. Coady, and J. Y. Lapointe. 1999. Functional expression of tagged human Na+-glucose cotransporter in Xenopus laevis oocytes. J. Physiol. 520:359–371. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 25.Chen, X. Z., M. J. Coady, and J. Y. Lapointe. 1996. Fast voltage clamp discloses a new component of pre-steady-state currents from the Na(+)-glucose cotransporter. Biophys. J. 71:2544–2552. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]