Abstract
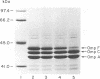
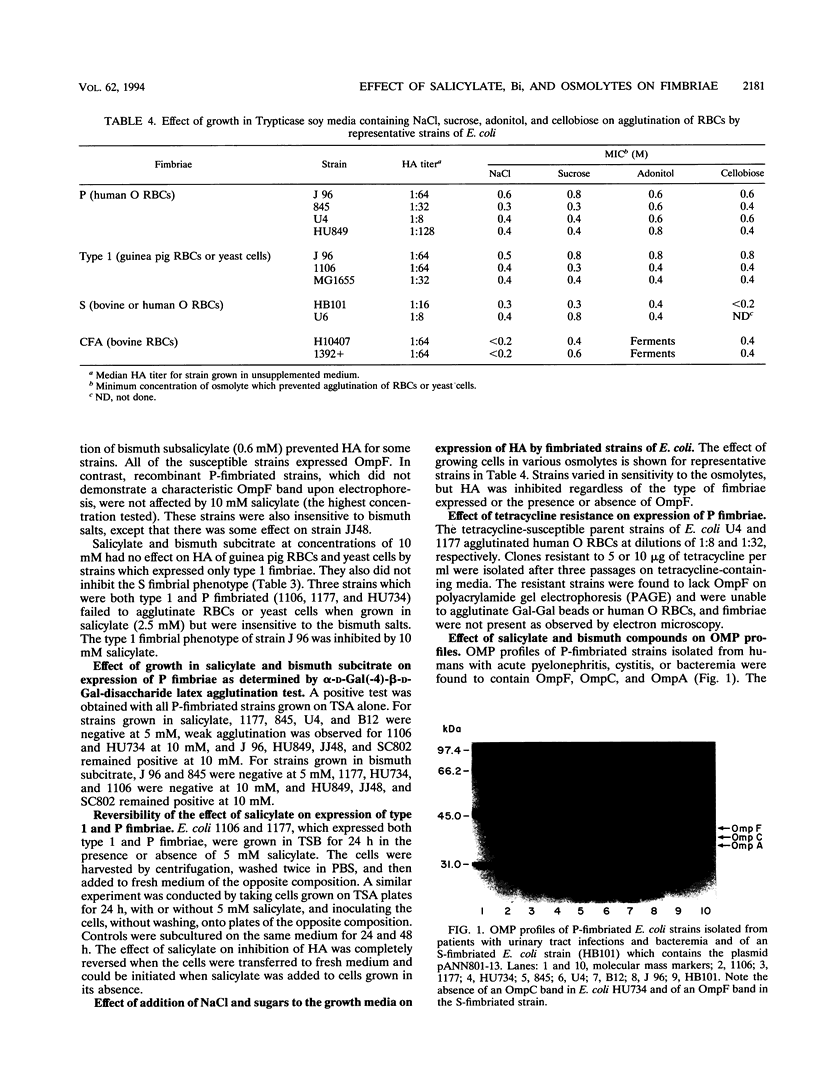
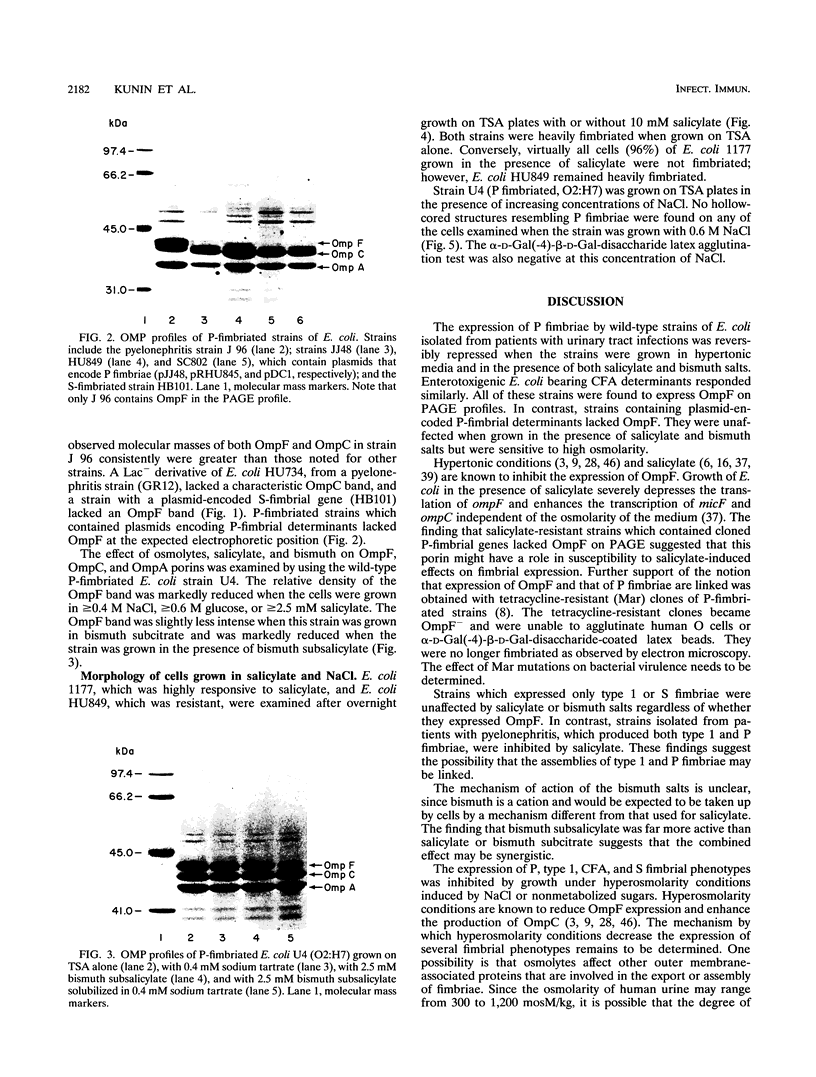
Adherence of Escherichia coli is facilitated by fimbriae and several outer membrane proteins (OMPs). Hypertonic conditions, salicylate, and Mar mutations are known to reduce OmpF expression. We speculated that OMPs involved in export or assembly of fimbrial subunits might be similarly affected. To explore this hypothesis, E. coli expressing P, type 1, S, colonization factor antigen I (CFA/I), or CFA/II fimbriae was grown in the presence of salicylate, bismuth salts, NaCl, and nonfermented sugars. Tetracycline-resistant clones were derived from several P-fimbriated strains. The bacteria were tested for the ability to agglutinate erythrocytes, yeast cells, and alpha-D-Gal(-4)-beta-D-Gal-bonded latex (Gal-Gal) beads and were examined for fimbriae by electron microscopy. Hyperosmolar conditions decreased fimbrial expression for all strains. Expression of P fimbriae by pyelonephritic strains, all of which were OmpF+, was reversibly repressed by salicylate and bismuth salts. CFA strains were similarly affected. Tetracycline-resistant P-fimbriated strains were OmpF deficient, were unable to agglutinate erythrocytes and Gal-Gal beads, and lacked fimbriae as observed by electron microscopy. Strains with plasmid-encoded P-fimbrial genes did not demonstrate OmpF on polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis profiles and were not affected by salicylate. The type 1-fimbriated phenotype was not affected by salicylate or bismuth unless the strains also expressed P fimbriae. S-fimbriated strains were not affected. The mechanism by which salicylates, bismuth salts, and tetracycline resistance inhibit or modulate the expression of P fimbriae may be mediated through OmpF and other OMPs.
Full text
PDF


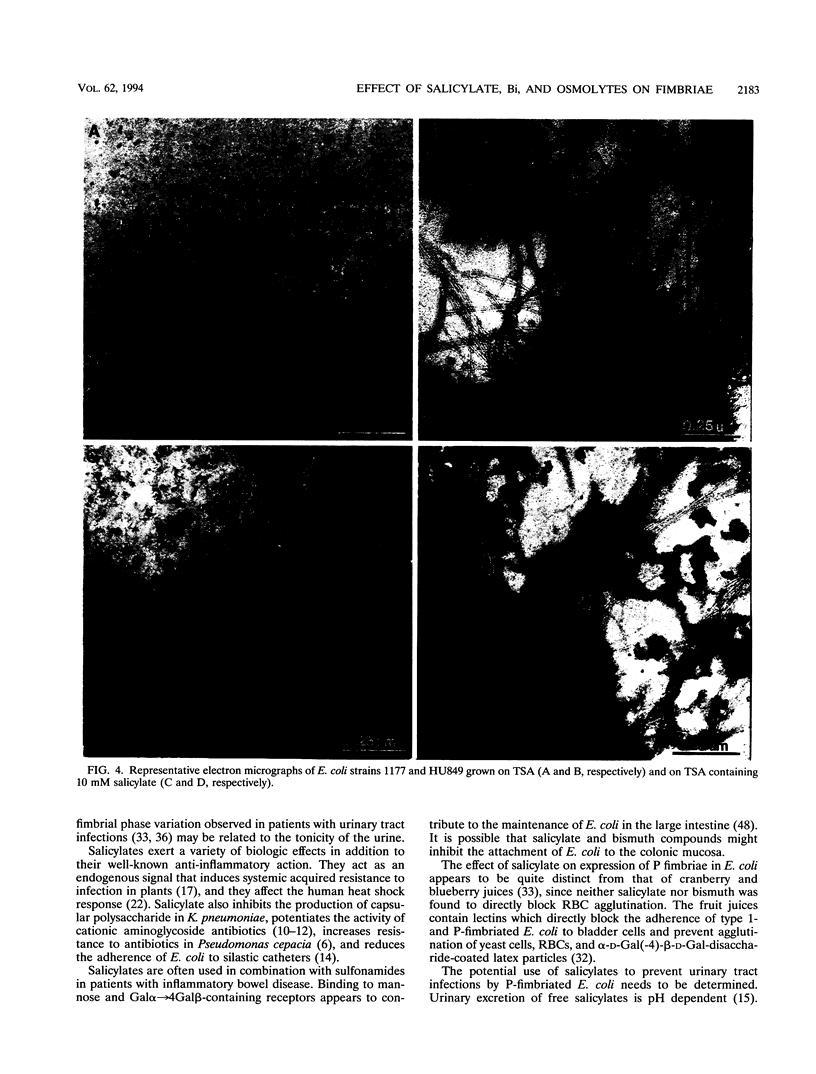



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Alphen W. V., Lugtenberg B. Influence of osmolarity of the growth medium on the outer membrane protein pattern of Escherichia coli. J Bacteriol. 1977 Aug;131(2):623–630. doi: 10.1128/jb.131.2.623-630.1977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bakaletz L. O., Tallan B. M., Hoepf T., DeMaria T. F., Birck H. G., Lim D. J. Frequency of fimbriation of nontypable Haemophilus influenzae and its ability to adhere to chinchilla and human respiratory epithelium. Infect Immun. 1988 Feb;56(2):331–335. doi: 10.1128/iai.56.2.331-335.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bakken J. S., Sanders C. C., Thomson K. S. Selective ceftazidime resistance in Escherichia coli: association with changes in outer membrane protein. J Infect Dis. 1987 Jun;155(6):1220–1225. doi: 10.1093/infdis/155.6.1220. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barron A., May G., Bremer E., Villarejo M. Regulation of envelope protein composition during adaptation to osmotic stress in Escherichia coli. J Bacteriol. 1986 Aug;167(2):433–438. doi: 10.1128/jb.167.2.433-438.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bernardini M. L., Sanna M. G., Fontaine A., Sansonetti P. J. OmpC is involved in invasion of epithelial cells by Shigella flexneri. Infect Immun. 1993 Sep;61(9):3625–3635. doi: 10.1128/iai.61.9.3625-3635.1993. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blomfield I. C., McClain M. S., Princ J. A., Calie P. J., Eisenstein B. I. Type 1 fimbriation and fimE mutants of Escherichia coli K-12. J Bacteriol. 1991 Sep;173(17):5298–5307. doi: 10.1128/jb.173.17.5298-5307.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burns J. L., Clark D. K. Salicylate-inducible antibiotic resistance in Pseudomonas cepacia associated with absence of a pore-forming outer membrane protein. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1992 Oct;36(10):2280–2285. doi: 10.1128/aac.36.10.2280. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clegg S. Cloning of genes determining the production of mannose-resistant fimbriae in a uropathogenic strain of Escherichia coli belonging to serogroup O6. Infect Immun. 1982 Nov;38(2):739–744. doi: 10.1128/iai.38.2.739-744.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cohen S. P., McMurry L. M., Levy S. B. marA locus causes decreased expression of OmpF porin in multiple-antibiotic-resistant (Mar) mutants of Escherichia coli. J Bacteriol. 1988 Dec;170(12):5416–5422. doi: 10.1128/jb.170.12.5416-5422.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Csonka L. N., Hanson A. D. Prokaryotic osmoregulation: genetics and physiology. Annu Rev Microbiol. 1991;45:569–606. doi: 10.1146/annurev.mi.45.100191.003033. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Domenico P., Salo R. J., Straus D. C., Hutson J. C., Cunha B. A. Salicylate or bismuth salts enhance opsonophagocytosis of Klebsiella pneumoniae. Infection. 1992 Mar-Apr;20(2):66–72. doi: 10.1007/BF01711065. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Domenico P., Schwartz S., Cunha B. A. Reduction of capsular polysaccharide production in Klebsiella pneumoniae by sodium salicylate. Infect Immun. 1989 Dec;57(12):3778–3782. doi: 10.1128/iai.57.12.3778-3782.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Domenico P., Straus D. C., Woods D. E., Cunha B. A. Salicylate potentiates amikacin therapy in rodent models of Klebsiella pneumoniae infection. J Infect Dis. 1993 Sep;168(3):766–769. doi: 10.1093/infdis/168.3.766. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Edén C. S., Hansson H. A. Escherichia coli pili as possible mediators of attachment to human urinary tract epithelial cells. Infect Immun. 1978 Jul;21(1):229–237. doi: 10.1128/iai.21.1.229-237.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Evans D. G., Evans D. J., Jr, Tjoa W. Hemagglutination of human group A erythrocytes by enterotoxigenic Escherichia coli isolated from adults with diarrhea: correlation with colonization factor. Infect Immun. 1977 Nov;18(2):330–337. doi: 10.1128/iai.18.2.330-337.1977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Farber B. F., Wolff A. G. The use of salicylic acid to prevent the adherence of Escherichia coli to silastic catheters. J Urol. 1993 Mar;149(3):667–670. doi: 10.1016/s0022-5347(17)36176-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Foulds J., Murray D. M., Chai T., Rosner J. L. Decreased permeation of cephalosporins through the outer membrane of Escherichia coli grown in salicylates. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1989 Apr;33(4):412–417. doi: 10.1128/aac.33.4.412. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gaffney T., Friedrich L., Vernooij B., Negrotto D., Nye G., Uknes S., Ward E., Kessmann H., Ryals J. Requirement of salicylic Acid for the induction of systemic acquired resistance. Science. 1993 Aug 6;261(5122):754–756. doi: 10.1126/science.261.5122.754. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johnson J. R., Swanson J. L., Neill M. A. Avian P1 antigens inhibit agglutination mediated by P fimbriae of uropathogenic Escherichia coli. Infect Immun. 1992 Feb;60(2):578–583. doi: 10.1128/iai.60.2.578-583.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johnson J. R. Virulence factors in Escherichia coli urinary tract infection. Clin Microbiol Rev. 1991 Jan;4(1):80–128. doi: 10.1128/cmr.4.1.80. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jurivich D. A., Sistonen L., Kroes R. A., Morimoto R. I. Effect of sodium salicylate on the human heat shock response. Science. 1992 Mar 6;255(5049):1243–1245. doi: 10.1126/science.1546322. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Korhonen T. K., Väisänen-Rhen V., Rhen M., Pere A., Parkkinen J., Finne J. Escherichia coli fimbriae recognizing sialyl galactosides. J Bacteriol. 1984 Aug;159(2):762–766. doi: 10.1128/jb.159.2.762-766.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Krogfelt K. A. Bacterial adhesion: genetics, biogenesis, and role in pathogenesis of fimbrial adhesins of Escherichia coli. Rev Infect Dis. 1991 Jul-Aug;13(4):721–735. doi: 10.1093/clinids/13.4.721. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kunin C. M., Hua T. H., Krishnan C., Van Arsdale White L., Hacker J. Isolation of a nicotinamide-requiring clone of Escherichia coli O18:K1:H7 from women with acute cystitis: resemblance to strains found in neonatal meningitis. Clin Infect Dis. 1993 Mar;16(3):412–416. doi: 10.1093/clind/16.3.412. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Le Rudulier D., Strom A. R., Dandekar A. M., Smith L. T., Valentine R. C. Molecular biology of osmoregulation. Science. 1984 Jun 8;224(4653):1064–1068. doi: 10.1126/science.224.4653.1064. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lugtenberg B., Peters R., Bernheimer H., Berendsen W. Influence of cultural conditions and mutations on the composition of the outer membrane proteins of Escherichia coli. Mol Gen Genet. 1976 Sep 23;147(3):251–262. doi: 10.1007/BF00582876. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McClain M. S., Blomfield I. C., Eberhardt K. J., Eisenstein B. I. Inversion-independent phase variation of type 1 fimbriae in Escherichia coli. J Bacteriol. 1993 Jul;175(14):4335–4344. doi: 10.1128/jb.175.14.4335-4344.1993. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mårild S., Jodal U., Orskov I., Orskov F., Svanborg Edén C. Special virulence of the Escherichia coli O1:K1:H7 clone in acute pyelonephritis. J Pediatr. 1989 Jul;115(1):40–45. doi: 10.1016/s0022-3476(89)80326-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Normark S., Lark D., Hull R., Norgren M., Båga M., O'Hanley P., Schoolnik G., Falkow S. Genetics of digalactoside-binding adhesin from a uropathogenic Escherichia coli strain. Infect Immun. 1983 Sep;41(3):942–949. doi: 10.1128/iai.41.3.942-949.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- O'Hanley P., Lark D., Falkow S., Schoolnik G. Molecular basis of Escherichia coli colonization of the upper urinary tract in BALB/c mice. Gal-Gal pili immunization prevents Escherichia coli pyelonephritis in the BALB/c mouse model of human pyelonephritis. J Clin Invest. 1985 Feb;75(2):347–360. doi: 10.1172/JCI111707. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ofek I., Goldhar J., Zafriri D., Lis H., Adar R., Sharon N. Anti-Escherichia coli adhesin activity of cranberry and blueberry juices. N Engl J Med. 1991 May 30;324(22):1599–1599. doi: 10.1056/NEJM199105303242214. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Parkkinen J., Finne J., Achtman M., Väisänen V., Korhonen T. K. Escherichia coli strains binding neuraminyl alpha 2-3 galactosides. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1983 Mar 16;111(2):456–461. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(83)90328-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pere A., Nowicki B., Saxén H., Siitonen A., Korhonen T. K. Expression of P, type-1, and type-1C fimbriae of Escherichia coli in the urine of patients with acute urinary tract infection. J Infect Dis. 1987 Oct;156(4):567–574. doi: 10.1093/infdis/156.4.567. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rosner J. L., Chai T. J., Foulds J. Regulation of ompF porin expression by salicylate in Escherichia coli. J Bacteriol. 1991 Sep;173(18):5631–5638. doi: 10.1128/jb.173.18.5631-5638.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Saukkonen K. M., Nowicki B., Leinonen M. Role of type 1 and S fimbriae in the pathogenesis of Escherichia coli O18:K1 bacteremia and meningitis in the infant rat. Infect Immun. 1988 Apr;56(4):892–897. doi: 10.1128/iai.56.4.892-897.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schlager T. A., Wanke C. A., Guerrant R. L. Net fluid secretion and impaired villous function induced by colonization of the small intestine by nontoxigenic colonizing Escherichia coli. Infect Immun. 1990 May;58(5):1337–1343. doi: 10.1128/iai.58.5.1337-1343.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sherman P., Cockerill F., 3rd, Soni R., Brunton J. Outer membranes are competitive inhibitors of Escherichia coli O157:H7 adherence to epithelial cells. Infect Immun. 1991 Mar;59(3):890–899. doi: 10.1128/iai.59.3.890-899.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sox T. E., Olson C. A. Binding and killing of bacteria by bismuth subsalicylate. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1989 Dec;33(12):2075–2082. doi: 10.1128/aac.33.12.2075. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Svanborg Edén C., Gotschlich E. C., Korhonen T. K., Leffler H., Schoolnik G. Aspects on structure and function of pili on uropathogenic Escherichia coli. Prog Allergy. 1983;33:189–202. doi: 10.1159/000318330. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tartera C., Metcalf E. S. Osmolarity and growth phase overlap in regulation of Salmonella typhi adherence to and invasion of human intestinal cells. Infect Immun. 1993 Jul;61(7):3084–3089. doi: 10.1128/iai.61.7.3084-3089.1993. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vuopio-Varkila J., Schoolnik G. K. Localized adherence by enteropathogenic Escherichia coli is an inducible phenotype associated with the expression of new outer membrane proteins. J Exp Med. 1991 Nov 1;174(5):1167–1177. doi: 10.1084/jem.174.5.1167. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wold A. E., Thorssén M., Hull S., Edén C. S. Attachment of Escherichia coli via mannose- or Gal alpha 1----4Gal beta-containing receptors to human colonic epithelial cells. Infect Immun. 1988 Oct;56(10):2531–2537. doi: 10.1128/iai.56.10.2531-2537.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]