Abstract
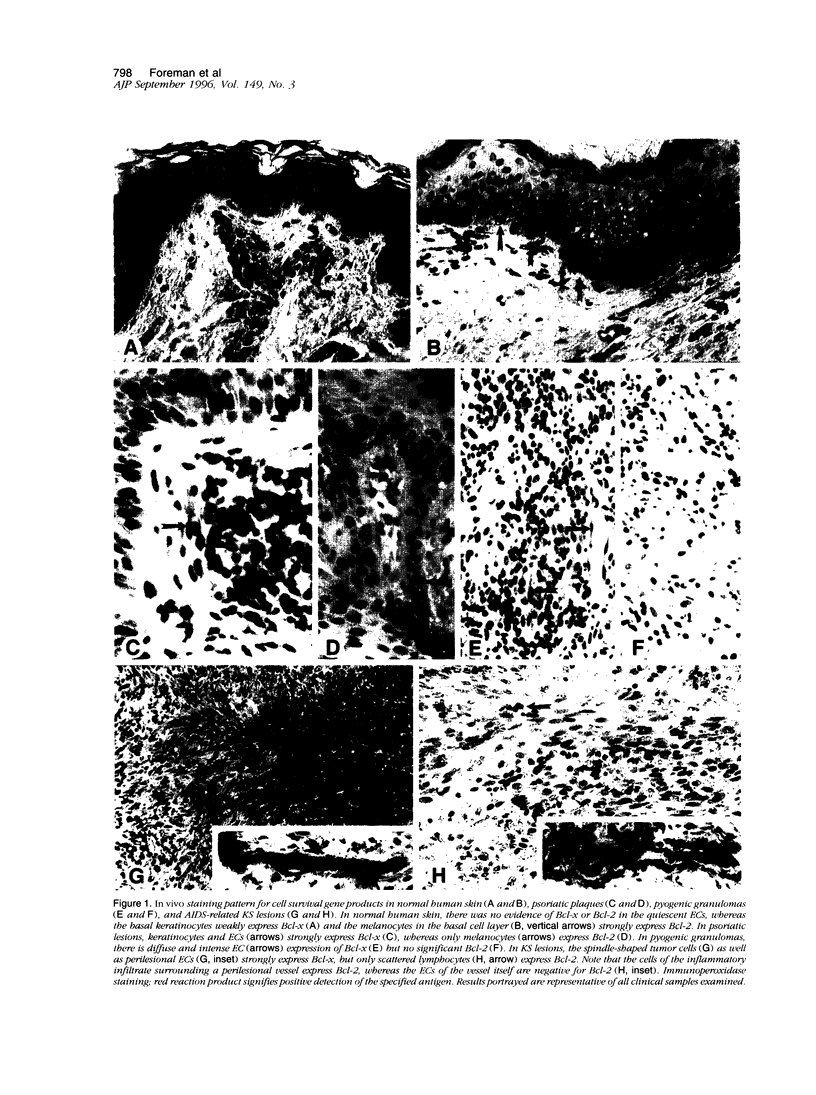
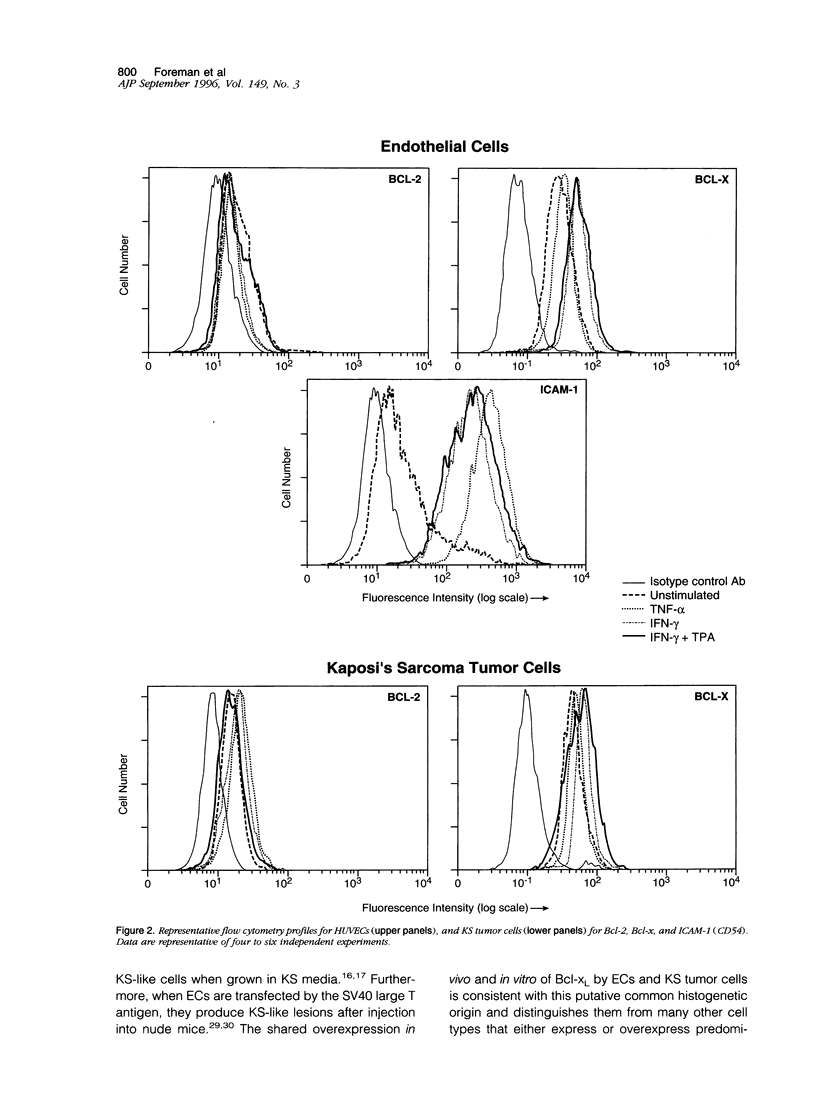
Several recently identified proteins such as Bcl-2 and Bcl-x have been found to regulate programmed cell death (i.e., apoptosis). In this report, we examined the levels of expression of proteins that can either prevent apoptosis (i.e., Bcl-2 or the long form of Bcl-x, designated Bcl-x1) or promote apoptosis (i.e., Bax or the short form of Bcl-x, designated Bcl-xs) in proliferating benign and malignant endothelial cells (ECs). In normal skin with quiescent ECs, no detection by immunohistochemical staining was observed for Bcl-xL, Bcl-xs, or Bcl-2. However, in diseased skin samples that feature a prominent angiogenic response such as in psoriasis or pyogenic granulomas, the proliferating ECs markedly overexpressed Bcl-xL, with little to no Bcl-2. In an acquired-immune-deficiency-syndrome-related neoplasm, Kaposi's sarcoma, the spindle-shaped tumor cells also overexpressed Bcl-xL compared with Bcl-2. These in vivo studies were extended in vitro using cultured ECs and Kaposi's sarcoma tumor cells that were examined by flow cytometry and immunoblot analysis. Both cultured ECs and Kaposi's sarcoma tumor cells express significantly higher levels of Bcl-xL than Bcl-2. Such overexpression of cell survival gene products may contribute to prolonging the longevity of EC-derived cells in several different benign and neoplastic skin disorders that are characterized by a prominent angiogenic tissue response.
Full text
PDF





Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Boise L. H., González-García M., Postema C. E., Ding L., Lindsten T., Turka L. A., Mao X., Nuñez G., Thompson C. B. bcl-x, a bcl-2-related gene that functions as a dominant regulator of apoptotic cell death. Cell. 1993 Aug 27;74(4):597–608. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(93)90508-n. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brooks J. J. Kaposi's sarcoma: a reversible hyperplasia. Lancet. 1986 Dec 6;2(8519):1309–1311. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(86)91436-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brooks P. C., Montgomery A. M., Rosenfeld M., Reisfeld R. A., Hu T., Klier G., Cheresh D. A. Integrin alpha v beta 3 antagonists promote tumor regression by inducing apoptosis of angiogenic blood vessels. Cell. 1994 Dec 30;79(7):1157–1164. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(94)90007-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Costa J., Rabson A. S. Generalised Kaposi's sarcoma is not a neoplasm. Lancet. 1983 Jan 1;1(8314-5):58–58. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(83)91583-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dole M. G., Jasty R., Cooper M. J., Thompson C. B., Nuñez G., Castle V. P. Bcl-xL is expressed in neuroblastoma cells and modulates chemotherapy-induced apoptosis. Cancer Res. 1995 Jun 15;55(12):2576–2582. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ensoli B., Barillari G., Gallo R. C. Pathogenesis of AIDS-associated Kaposi's sarcoma. Hematol Oncol Clin North Am. 1991 Apr;5(2):281–295. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Folkman J. Angiogenesis in psoriasis: therapeutic implications. J Invest Dermatol. 1972 Jul;59(1):40–43. doi: 10.1111/1523-1747.ep12625746. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Folkman J. The role of angiogenesis in tumor growth. Semin Cancer Biol. 1992 Apr;3(2):65–71. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- González-García M., Pérez-Ballestero R., Ding L., Duan L., Boise L. H., Thompson C. B., Núez G. bcl-XL is the major bcl-x mRNA form expressed during murine development and its product localizes to mitochondria. Development. 1994 Oct;120(10):3033–3042. doi: 10.1242/dev.120.10.3033. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gottschalk A. R., Boise L. H., Thompson C. B., Quintáns J. Identification of immunosuppressant-induced apoptosis in a murine B-cell line and its prevention by bcl-x but not bcl-2. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1994 Jul 19;91(15):7350–7354. doi: 10.1073/pnas.91.15.7350. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Haake A. R., Polakowska R. R. Cell death by apoptosis in epidermal biology. J Invest Dermatol. 1993 Aug;101(2):107–112. doi: 10.1111/1523-1747.ep12363594. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hengartner M. O. Programmed cell death. A rich harvest. Curr Biol. 1994 Oct 1;4(10):950–952. doi: 10.1016/s0960-9822(00)00216-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hockenbery D. M., Zutter M., Hickey W., Nahm M., Korsmeyer S. J. BCL2 protein is topographically restricted in tissues characterized by apoptotic cell death. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Aug 15;88(16):6961–6965. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.16.6961. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hockenbery D., Nuñez G., Milliman C., Schreiber R. D., Korsmeyer S. J. Bcl-2 is an inner mitochondrial membrane protein that blocks programmed cell death. Nature. 1990 Nov 22;348(6299):334–336. doi: 10.1038/348334a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Huang Y. Q., Friedman-Kien A. E., Li J. J., Nickoloff B. J. Cultured Kaposi's sarcoma cell lines express factor XIIIa, CD14, and VCAM-1, but not factor VIII or ELAM-1. Arch Dermatol. 1993 Oct;129(10):1291–1296. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Joensuu H., Pylkkänen L., Toikkanen S. Bcl-2 protein expression and long-term survival in breast cancer. Am J Pathol. 1994 Nov;145(5):1191–1198. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Krajewski S., Krajewska M., Shabaik A., Miyashita T., Wang H. G., Reed J. C. Immunohistochemical determination of in vivo distribution of Bax, a dominant inhibitor of Bcl-2. Am J Pathol. 1994 Dec;145(6):1323–1336. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Krajewski S., Krajewska M., Shabaik A., Wang H. G., Irie S., Fong L., Reed J. C. Immunohistochemical analysis of in vivo patterns of Bcl-X expression. Cancer Res. 1994 Nov 1;54(21):5501–5507. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lu Q. L., Poulsom R., Wong L., Hanby A. M. Bcl-2 expression in adult and embryonic non-haematopoietic tissues. J Pathol. 1993 Apr;169(4):431–437. doi: 10.1002/path.1711690408. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mansbridge J. N., Nickoloff B. J., Morhenn V. B. Induction of new proteins by gamma interferon in cultured human keratinocytes. J Invest Dermatol. 1987 May;88(5):602–610. doi: 10.1111/1523-1747.ep12470212. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Modlin R. L., Hofman F. M., Meyer P. R., Vaccaro S. A., Ammann A. J., Conant M. A., Rea T. H., Taylor C. R. Altered distribution of B and T lymphocytes in lymph-nodes from homosexual men with Kaposi's sarcoma. Lancet. 1983 Oct 1;2(8353):768–771. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(83)92300-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Naidu Y. M., Rosen E. M., Zitnick R., Goldberg I., Park M., Naujokas M., Polverini P. J., Nickoloff B. J. Role of scatter factor in the pathogenesis of AIDS-related Kaposi sarcoma. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1994 Jun 7;91(12):5281–5285. doi: 10.1073/pnas.91.12.5281. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nickoloff B. J., Foreman K. E. Charting a new course through the chaos of KS (Kaposi's sarcoma) Am J Pathol. 1996 May;148(5):1323–1329. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nickoloff B. J., Karabin G. D., Barker J. N., Griffiths C. E., Sarma V., Mitra R. S., Elder J. T., Kunkel S. L., Dixit V. M. Cellular localization of interleukin-8 and its inducer, tumor necrosis factor-alpha in psoriasis. Am J Pathol. 1991 Jan;138(1):129–140. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Núez G., Merino R., Grillot D., González-García M. Bcl-2 and Bcl-x: regulatory switches for lymphoid death and survival. Immunol Today. 1994 Dec;15(12):582–588. doi: 10.1016/0167-5699(94)90221-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- O'Connell K. A., Edidin M. A mouse lymphoid endothelial cell line immortalized by simian virus 40 binds lymphocytes and retains functional characteristics of normal endothelial cells. J Immunol. 1990 Jan 15;144(2):521–525. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- O'Connell K. A., Rudmann A. A. Cloned spindle and epithelioid cells from murine Kaposi's sarcoma-like tumors are of endothelial origin. J Invest Dermatol. 1993 Jun;100(6):742–745. doi: 10.1111/1523-1747.ep12475688. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Re F., Zanetti A., Sironi M., Polentarutti N., Lanfrancone L., Dejana E., Colotta F. Inhibition of anchorage-dependent cell spreading triggers apoptosis in cultured human endothelial cells. J Cell Biol. 1994 Oct;127(2):537–546. doi: 10.1083/jcb.127.2.537. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reed J. C. Bcl-2 and the regulation of programmed cell death. J Cell Biol. 1994 Jan;124(1-2):1–6. doi: 10.1083/jcb.124.1.1. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reed J. C., Meister L., Tanaka S., Cuddy M., Yum S., Geyer C., Pleasure D. Differential expression of bcl2 protooncogene in neuroblastoma and other human tumor cell lines of neural origin. Cancer Res. 1991 Dec 15;51(24):6529–6538. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reiners J. J., Jr, Rupp T., Colby A., Cantu A. R., Pavone A. Tumor copromoting activity of gamma-interferon in the murine skin multistage carcinogenesis model. Cancer Res. 1989 Mar 1;49(5):1202–1206. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rutgers J. L., Wieczorek R., Bonetti F., Kaplan K. L., Posnett D. N., Friedman-Kien A. E., Knowles D. M., 2nd The expression of endothelial cell surface antigens by AIDS-associated Kaposi's sarcoma. Evidence for a vascular endothelial cell origin. Am J Pathol. 1986 Mar;122(3):493–499. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thompson C. B. Apoptosis in the pathogenesis and treatment of disease. Science. 1995 Mar 10;267(5203):1456–1462. doi: 10.1126/science.7878464. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Veis D. J., Sorenson C. M., Shutter J. R., Korsmeyer S. J. Bcl-2-deficient mice demonstrate fulminant lymphoid apoptosis, polycystic kidneys, and hypopigmented hair. Cell. 1993 Oct 22;75(2):229–240. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(93)80065-m. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wrone-Smith T., Johnson T., Nelson B., Boise L. H., Thompson C. B., Núez G., Nickoloff B. J. Discordant expression of Bcl-x and Bcl-2 by keratinocytes in vitro and psoriatic keratinocytes in vivo. Am J Pathol. 1995 May;146(5):1079–1088. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]