Abstract
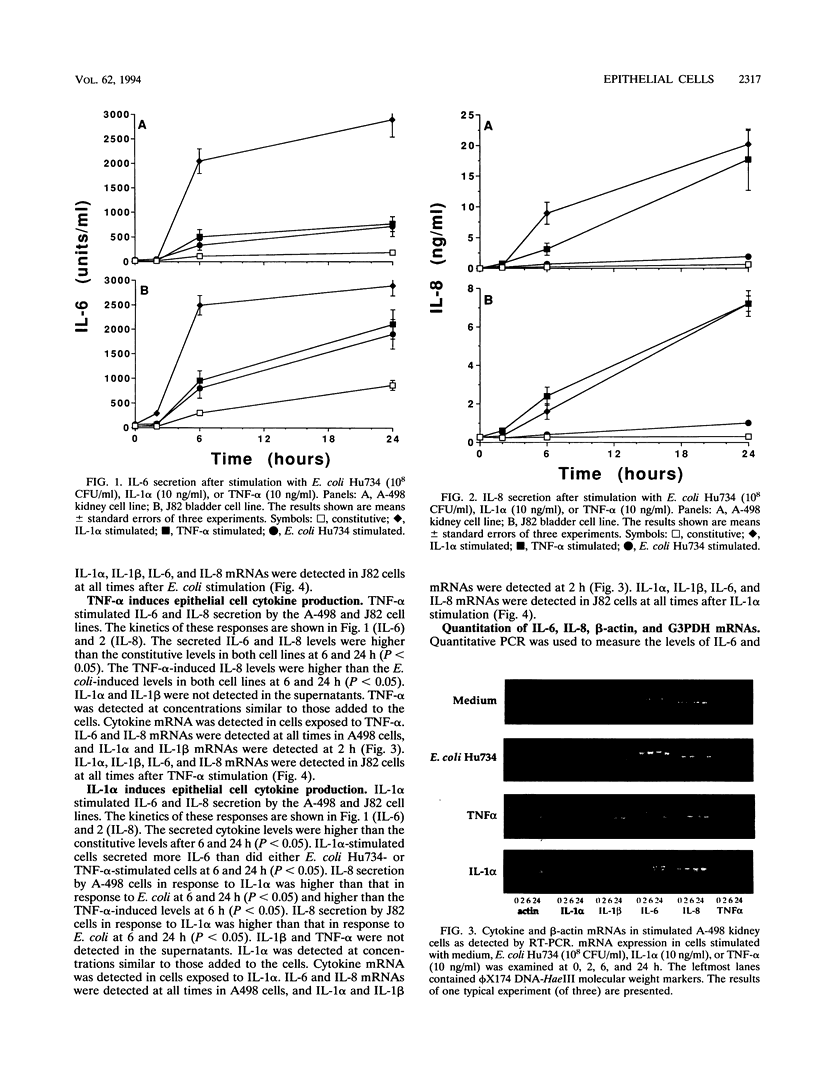
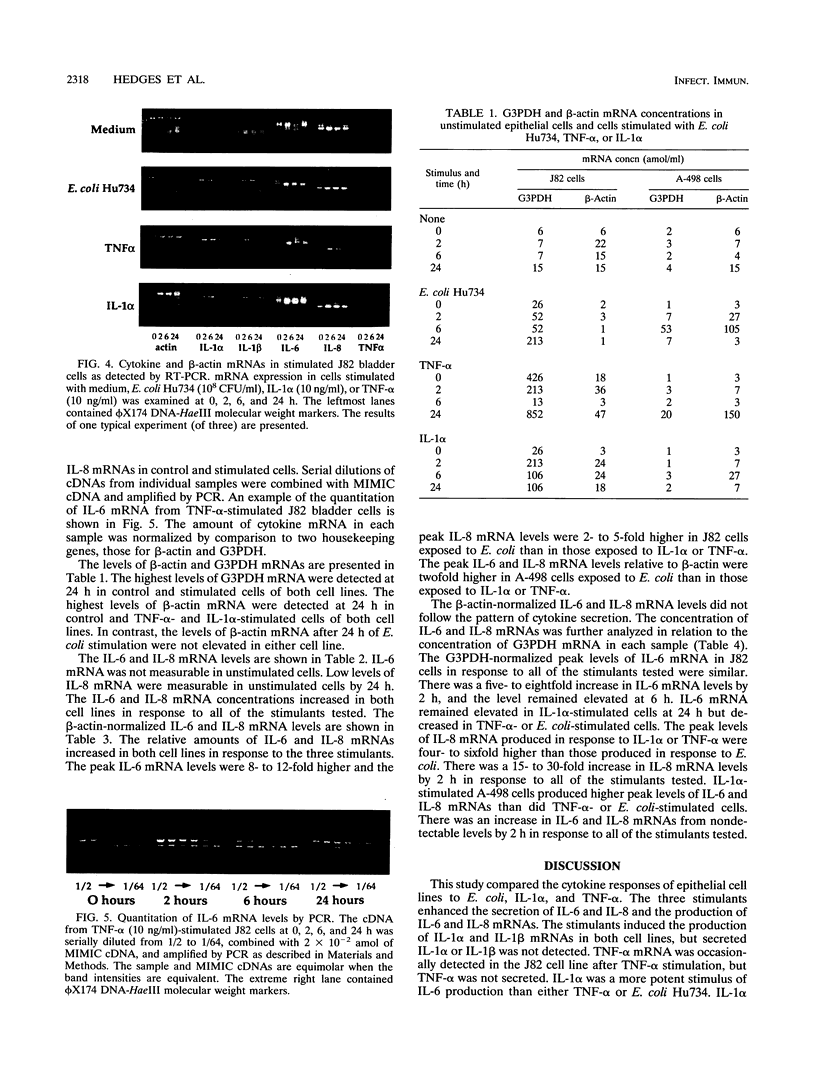
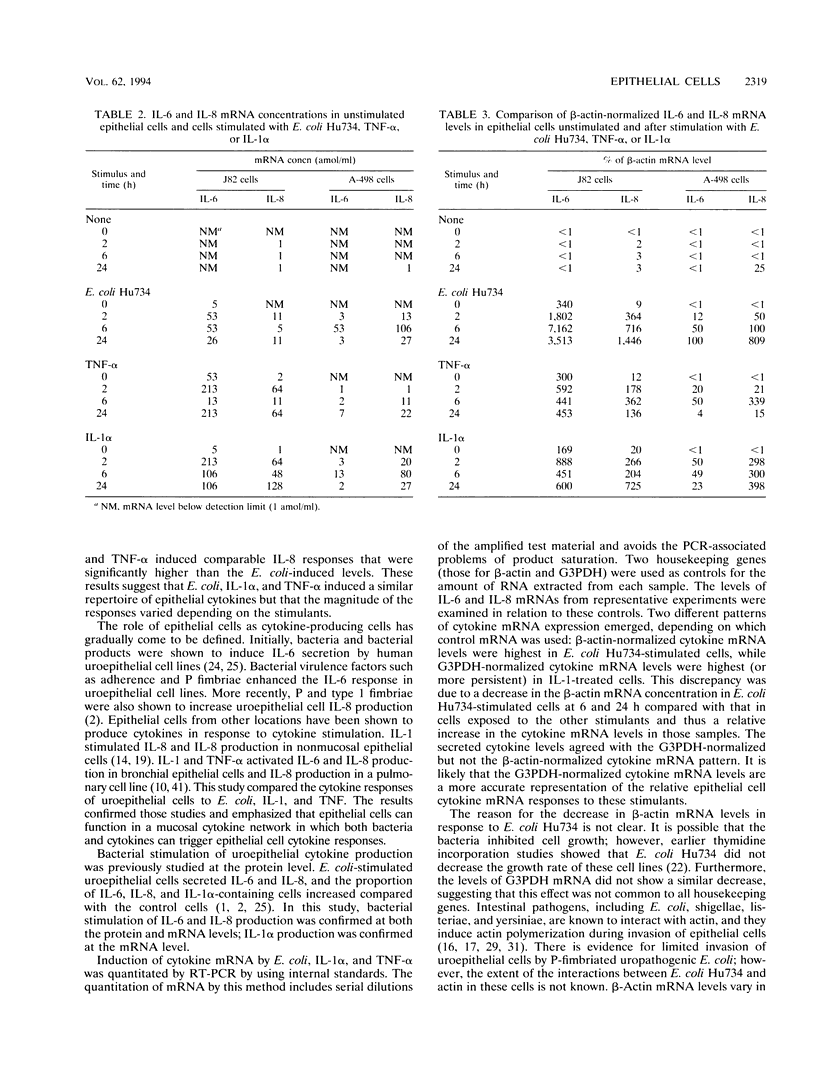
This study compared the cytokine production of uroepithelial cell lines in response to gram-negative bacteria and inflammatory cytokines. Human kidney (A498) and bladder (J82) epithelial cell lines were stimulated with either Escherichia coli Hu734, interleukin 1 alpha (IL-1 alpha), or tumor necrosis factor alpha (TNF-alpha). Supernatant samples were removed, and the RNA was extracted from cells at 0, 2, 6, and 24 h. The secreted cytokine levels were determined by bioassay or immunoassay; mRNA was examined by reverse transcription-PCR. The two cell lines secreted IL-6 and IL-8 constitutively. IL-6 and IL-8 mRNA were constitutively produced in both cell lines; IL-1 beta mRNA was detected in J82 cells. IL-1 alpha induced significantly higher levels of IL-6 secretion than did E. coli Hu734 or TNF-alpha. IL-1 alpha and TNF-alpha induced significantly higher levels of IL-8 secretion than did E. coli Hu734. Secreted IL-1 beta was not detected; IL-1 alpha and TNF-alpha were not detected above the levels used for stimulation. IL-1 alpha, IL-1 beta, IL-6, and IL-8 mRNAs were detected in both cell lines after exposure to the stimulants. TNF-alpha mRNA was occasionally detected in the J82 cell line after TNF-alpha stimulation. Cytokine (IL-6 and IL-8) and control (glyceraldehyde 3-phosphate dehydrogenase [G3PDH] and beta-actin) mRNA concentrations were quantitated with internal PCR standards. Cytokine mRNA levels relative to beta-actin mRNA levels were the highest in E. coli-stimulated cells. In comparison, the cytokine mRNA levels relative to G3PDH mRNA levels were the highest in IL-1 alpha-stimulated cells. beta-Actin mRNA levels decreased after bacterial stimulation but not after cytokine stimulation, while G3PDH mRNA levels increased in response to all of the stimulants tested. These results suggested that E. coli Hu734 lowered the beta-actin mRNA levels in uroepithelial cells, thus distorting the IL-6 and IL-8 mRNA levels relative to this control. In summary, E. coli IL-1 alpha and TNF-alpha were found to activate the de novo synthesis and secretion of IL-6 and IL-8 in uroepithelial cells. These results emphasize the role of epithelial cells in cytokine-mediated responses during the early stages of infection.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Agace W. W., Hedges S. R., Ceska M., Svanborg C. Interleukin-8 and the neutrophil response to mucosal gram-negative infection. J Clin Invest. 1993 Aug;92(2):780–785. doi: 10.1172/JCI116650. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Agace W., Hedges S., Andersson U., Andersson J., Ceska M., Svanborg C. Selective cytokine production by epithelial cells following exposure to Escherichia coli. Infect Immun. 1993 Feb;61(2):602–609. doi: 10.1128/iai.61.2.602-609.1993. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Andersson J., Nagy S., Groth C. G., Andersson U. Effects of FK506 and cyclosporin A on cytokine production studied in vitro at a single-cell level. Immunology. 1992 Jan;75(1):136–142. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Arnold R., Scheffer J., König B., König W. Effects of Listeria monocytogenes and Yersinia enterocolitica on cytokine gene expression and release from human polymorphonuclear granulocytes and epithelial (HEp-2) cells. Infect Immun. 1993 Jun;61(6):2545–2552. doi: 10.1128/iai.61.6.2545-2552.1993. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bakouche O., Moreau J. L., Lachman L. B. Secretion of IL-1: role of protein kinase C. J Immunol. 1992 Jan 1;148(1):84–91. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bazzoni F., Cassatella M. A., Rossi F., Ceska M., Dewald B., Baggiolini M. Phagocytosing neutrophils produce and release high amounts of the neutrophil-activating peptide 1/interleukin 8. J Exp Med. 1991 Mar 1;173(3):771–774. doi: 10.1084/jem.173.3.771. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Beagley K. W., Eldridge J. H., Lee F., Kiyono H., Everson M. P., Koopman W. J., Hirano T., Kishimoto T., McGhee J. R. Interleukins and IgA synthesis. Human and murine interleukin 6 induce high rate IgA secretion in IgA-committed B cells. J Exp Med. 1989 Jun 1;169(6):2133–2148. doi: 10.1084/jem.169.6.2133. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brenner C. A., Tam A. W., Nelson P. A., Engleman E. G., Suzuki N., Fry K. E., Larrick J. W. Message amplification phenotyping (MAPPing): a technique to simultaneously measure multiple mRNAs from small numbers of cells. Biotechniques. 1989 Nov-Dec;7(10):1096–1103. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chin J., Kostura M. J. Dissociation of IL-1 beta synthesis and secretion in human blood monocytes stimulated with bacterial cell wall products. J Immunol. 1993 Nov 15;151(10):5574–5585. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chirgwin J. M., Przybyla A. E., MacDonald R. J., Rutter W. J. Isolation of biologically active ribonucleic acid from sources enriched in ribonuclease. Biochemistry. 1979 Nov 27;18(24):5294–5299. doi: 10.1021/bi00591a005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cromwell O., Hamid Q., Corrigan C. J., Barkans J., Meng Q., Collins P. D., Kay A. B. Expression and generation of interleukin-8, IL-6 and granulocyte-macrophage colony-stimulating factor by bronchial epithelial cells and enhancement by IL-1 beta and tumour necrosis factor-alpha. Immunology. 1992 Nov;77(3):330–337. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dinarello C. A., Cannon J. G., Wolff S. M., Bernheim H. A., Beutler B., Cerami A., Figari I. S., Palladino M. A., Jr, O'Connor J. V. Tumor necrosis factor (cachectin) is an endogenous pyrogen and induces production of interleukin 1. J Exp Med. 1986 Jun 1;163(6):1433–1450. doi: 10.1084/jem.163.6.1433. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eckmann L., Kagnoff M. F., Fierer J. Epithelial cells secrete the chemokine interleukin-8 in response to bacterial entry. Infect Immun. 1993 Nov;61(11):4569–4574. doi: 10.1128/iai.61.11.4569-4574.1993. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Edén C. S., Freter R., Hagberg L., Hull R., Hull S., Leffler H., Schoolnik G. Inhibition of experimental ascending urinary tract infection by an epithelial cell-surface receptor analogue. Nature. 1982 Aug 5;298(5874):560–562. doi: 10.1038/298560a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Elner V. M., Strieter R. M., Elner S. G., Baggiolini M., Lindley I., Kunkel S. L. Neutrophil chemotactic factor (IL-8) gene expression by cytokine-treated retinal pigment epithelial cells. Am J Pathol. 1990 Apr;136(4):745–750. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Espevik T., Nissen-Meyer J. A highly sensitive cell line, WEHI 164 clone 13, for measuring cytotoxic factor/tumor necrosis factor from human monocytes. J Immunol Methods. 1986 Dec 4;95(1):99–105. doi: 10.1016/0022-1759(86)90322-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Finlay B. B., Falkow S. Comparison of the invasion strategies used by Salmonella cholerae-suis, Shigella flexneri and Yersinia enterocolitica to enter cultured animal cells: endosome acidification is not required for bacterial invasion or intracellular replication. Biochimie. 1988 Aug;70(8):1089–1099. doi: 10.1016/0300-9084(88)90271-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Finlay B. B., Rosenshine I., Donnenberg M. S., Kaper J. B. Cytoskeletal composition of attaching and effacing lesions associated with enteropathogenic Escherichia coli adherence to HeLa cells. Infect Immun. 1992 Jun;60(6):2541–2543. doi: 10.1128/iai.60.6.2541-2543.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fong Y., Tracey K. J., Moldawer L. L., Hesse D. G., Manogue K. B., Kenney J. S., Lee A. T., Kuo G. C., Allison A. C., Lowry S. F. Antibodies to cachectin/tumor necrosis factor reduce interleukin 1 beta and interleukin 6 appearance during lethal bacteremia. J Exp Med. 1989 Nov 1;170(5):1627–1633. doi: 10.1084/jem.170.5.1627. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Galy A. H., Spits H. IL-1, IL-4, and IFN-gamma differentially regulate cytokine production and cell surface molecule expression in cultured human thymic epithelial cells. J Immunol. 1991 Dec 1;147(11):3823–3830. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hansson G. K., Hellstrand M., Rymo L., Rubbia L., Gabbiani G. Interferon gamma inhibits both proliferation and expression of differentiation-specific alpha-smooth muscle actin in arterial smooth muscle cells. J Exp Med. 1989 Nov 1;170(5):1595–1608. doi: 10.1084/jem.170.5.1595. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Havell E. A., Sehgal P. B. Tumor necrosis factor-independent IL-6 production during murine listeriosis. J Immunol. 1991 Jan 15;146(2):756–761. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hedges S., Agace W., Svensson M., Svanborg C. Cyclosporin A does not inhibit IL-1 alpha-induced epithelial cell IL-6 secretion. Scand J Immunol. 1993 May;37(5):581–586. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-3083.1993.tb02575.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hedges S., Anderson P., Lidin-Janson G., de Man P., Svanborg C. Interleukin-6 response to deliberate colonization of the human urinary tract with gram-negative bacteria. Infect Immun. 1991 Jan;59(1):421–427. doi: 10.1128/iai.59.1.421-427.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hedges S., Svensson M., Svanborg C. Interleukin-6 response of epithelial cell lines to bacterial stimulation in vitro. Infect Immun. 1992 Apr;60(4):1295–1301. doi: 10.1128/iai.60.4.1295-1301.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Helle M., Brakenhoff J. P., De Groot E. R., Aarden L. A. Interleukin 6 is involved in interleukin 1-induced activities. Eur J Immunol. 1988 Jun;18(6):957–959. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830180619. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jablons D. M., Mulé J. J., McIntosh J. K., Sehgal P. B., May L. T., Huang C. M., Rosenberg S. A., Lotze M. T. IL-6/IFN-beta-2 as a circulating hormone. Induction by cytokine administration in humans. J Immunol. 1989 Mar 1;142(5):1542–1547. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kalb T. H., Chuang M. T., Marom Z., Mayer L. Evidence for accessory cell function by class II MHC antigen-expressing airway epithelial cells. Am J Respir Cell Mol Biol. 1991 Apr;4(4):320–329. doi: 10.1165/ajrcmb/4.4.320. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Knutton S., Baldwin T., Williams P. H., McNeish A. S. Actin accumulation at sites of bacterial adhesion to tissue culture cells: basis of a new diagnostic test for enteropathogenic and enterohemorrhagic Escherichia coli. Infect Immun. 1989 Apr;57(4):1290–1298. doi: 10.1128/iai.57.4.1290-1298.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kreft B., Bohnet S., Carstensen O., Hacker J., Marre R. Differential expression of interleukin-6, intracellular adhesion molecule 1, and major histocompatibility complex class II molecules in renal carcinoma cells stimulated with S fimbriae of uropathogenic Escherichia coli. Infect Immun. 1993 Jul;61(7):3060–3063. doi: 10.1128/iai.61.7.3060-3063.1993. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Manjarrez-Hernandez H. A., Baldwin T. J., Aitken A., Knutton S., Williams P. H. Intestinal epithelial cell protein phosphorylation in enteropathogenic Escherichia coli diarrhoea. Lancet. 1992 Feb 29;339(8792):521–523. doi: 10.1016/0140-6736(92)90340-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mathison J. C., Wolfson E., Ulevitch R. J. Participation of tumor necrosis factor in the mediation of gram negative bacterial lipopolysaccharide-induced injury in rabbits. J Clin Invest. 1988 Jun;81(6):1925–1937. doi: 10.1172/JCI113540. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mayer L., Eisenhardt D., Salomon P., Bauer W., Plous R., Piccinini L. Expression of class II molecules on intestinal epithelial cells in humans. Differences between normal and inflammatory bowel disease. Gastroenterology. 1991 Jan;100(1):3–12. doi: 10.1016/0016-5085(91)90575-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McGee D. W., Beagley K. W., Aicher W. K., McGhee J. R. Transforming growth factor-beta enhances interleukin-6 secretion by intestinal epithelial cells. Immunology. 1992 Sep;77(1):7–12. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McGhee J. R., Mestecky J., Elson C. O., Kiyono H. Regulation of IgA synthesis and immune response by T cells and interleukins. J Clin Immunol. 1989 May;9(3):175–199. doi: 10.1007/BF00916814. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mizutani H., Black R., Kupper T. S. Human keratinocytes produce but do not process pro-interleukin-1 (IL-1) beta. Different strategies of IL-1 production and processing in monocytes and keratinocytes. J Clin Invest. 1991 Mar;87(3):1066–1071. doi: 10.1172/JCI115067. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Perregaux D., Barberia J., Lanzetti A. J., Geoghegan K. F., Carty T. J., Gabel C. A. IL-1 beta maturation: evidence that mature cytokine formation can be induced specifically by nigericin. J Immunol. 1992 Aug 15;149(4):1294–1303. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Siebert P. D., Fukuda M. Induction of cytoskeletal vimentin and actin gene expression by a tumor-promoting phorbol ester in the human leukemic cell line K562. J Biol Chem. 1985 Mar 25;260(6):3868–3874. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Siebert P. D., Larrick J. W. PCR MIMICS: competitive DNA fragments for use as internal standards in quantitative PCR. Biotechniques. 1993 Feb;14(2):244–249. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Standiford T. J., Kunkel S. L., Basha M. A., Chensue S. W., Lynch J. P., 3rd, Toews G. B., Westwick J., Strieter R. M. Interleukin-8 gene expression by a pulmonary epithelial cell line. A model for cytokine networks in the lung. J Clin Invest. 1990 Dec;86(6):1945–1953. doi: 10.1172/JCI114928. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Svanborg C., Agace W., Hedges S., Linder H., Svensson M. Bacterial adherence and epithelial cell cytokine production. Zentralbl Bakteriol. 1993 Apr;278(2-3):359–364. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Van Damme J., Opdenakker G., Simpson R. J., Rubira M. R., Cayphas S., Vink A., Billiau A., Van Snick J. Identification of the human 26-kD protein, interferon beta 2 (IFN-beta 2), as a B cell hybridoma/plasmacytoma growth factor induced by interleukin 1 and tumor necrosis factor. J Exp Med. 1987 Mar 1;165(3):914–919. doi: 10.1084/jem.165.3.914. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Waage A., Brandtzaeg P., Halstensen A., Kierulf P., Espevik T. The complex pattern of cytokines in serum from patients with meningococcal septic shock. Association between interleukin 6, interleukin 1, and fatal outcome. J Exp Med. 1989 Jan 1;169(1):333–338. doi: 10.1084/jem.169.1.333. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Waage A. Production and clearance of tumor necrosis factor in rats exposed to endotoxin and dexamethasone. Clin Immunol Immunopathol. 1987 Dec;45(3):348–355. doi: 10.1016/0090-1229(87)90087-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zanetti G., Heumann D., Gérain J., Kohler J., Abbet P., Barras C., Lucas R., Glauser M. P., Baumgartner J. D. Cytokine production after intravenous or peritoneal gram-negative bacterial challenge in mice. Comparative protective efficacy of antibodies to tumor necrosis factor-alpha and to lipopolysaccharide. J Immunol. 1992 Mar 15;148(6):1890–1897. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- de Man P., van Kooten C., Aarden L., Engberg I., Linder H., Svanborg Edén C. Interleukin-6 induced at mucosal surfaces by gram-negative bacterial infection. Infect Immun. 1989 Nov;57(11):3383–3388. doi: 10.1128/iai.57.11.3383-3388.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]