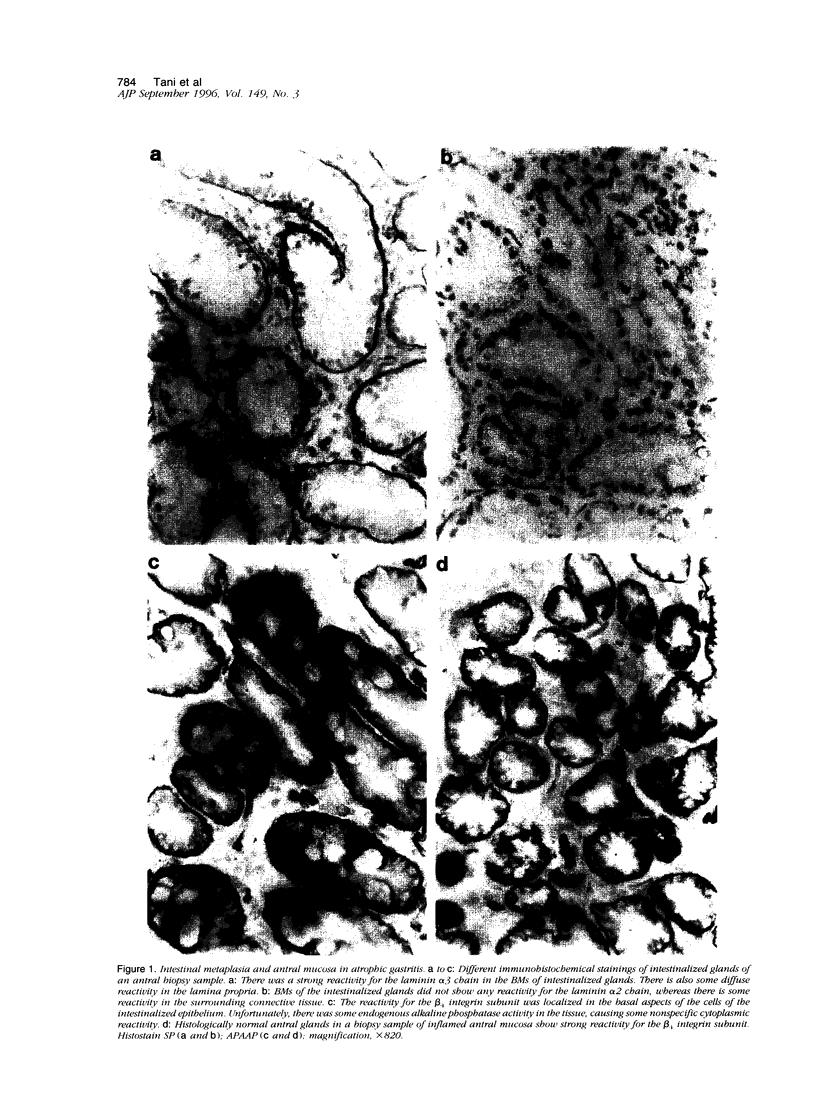
Abstract
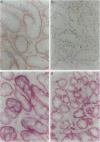
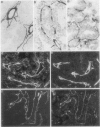
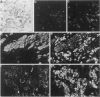
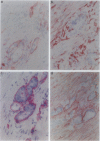
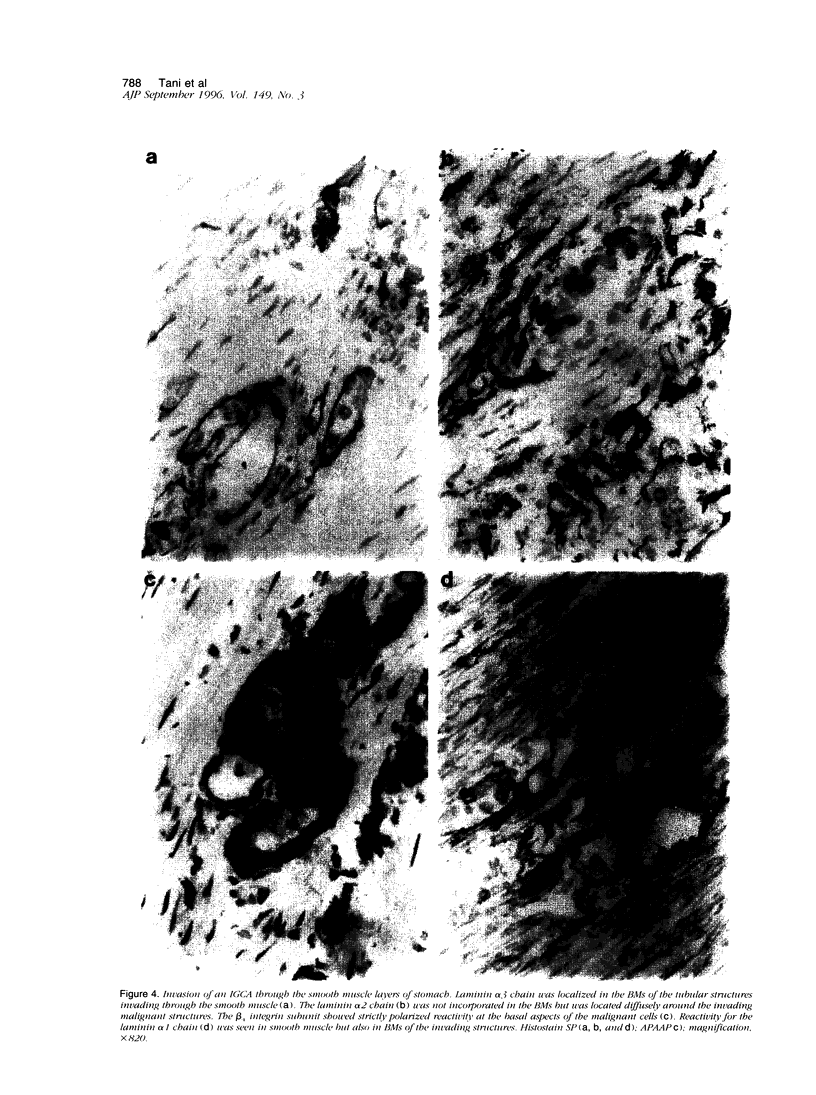
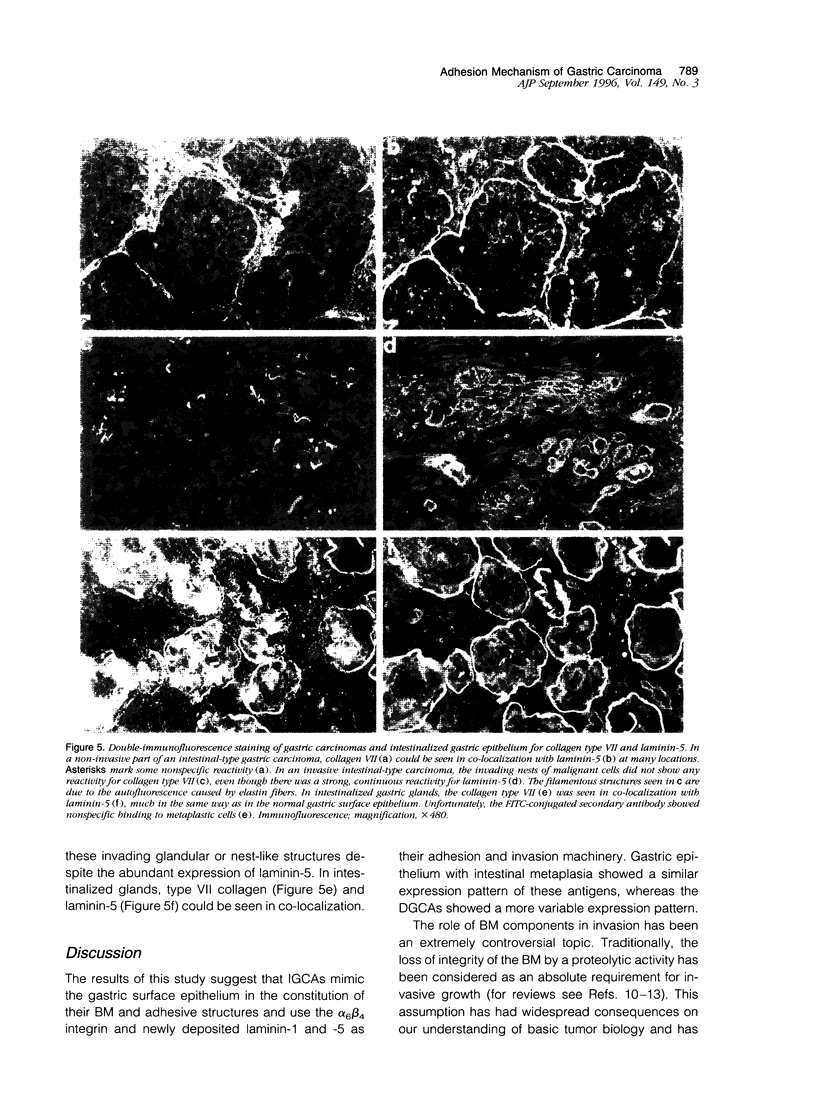
We studied the expression and distribution of different laminin chains, the alpha 6 beta 4 integrin and type VII collagen, i.e., components of the epithelial adhesion complex, in gastric carcinomas and in suggested preneoplastic stages of this malignancy. Intestinal-type gastric carcinomas showed strong reactivity for laminin alpha 1, alpha 3, beta 1, and beta 3 chains, the components of laminin-1 and -5, at the interface between malignant cells and tumor stroma. The reactivities were continuous throughout the carcinomas, even in structures invading through the smooth muscle layers of the gastric wall. The expression of different laminin chains was accompanied by strong polarized reactivity for the alpha 6 beta 4 integrin, which is a receptor for both laminin-1 and laminin-5. Collagen type VII was only occasionally present at sites showing reactivity for laminin-5 and was totally absent from the cell islands invading through the gastric wall. Intestinalized gastric epithelium showed a similar expression pattern of laminins and the alpha 6 beta 4 integrin as the gastric carcinomas. Our results suggest that gastric carcinomas use the alpha 6 beta 4 integrin and newly deposited laminin-1 and -5, accompanied by the disappearance of type VII collagen, as their mechanism of adhesion during the invasion through surrounding tissues. Unlike in previous studies, the reactivity for the laminin-5 protein was not restricted to the invading cells but surrounded the malignant glandular structures throughout the tumor. Our results also show that both intestinal-type gastric carcinoma, and intestinal metaplasia mimic the gastric surface epithelium in the expression pattern of laminins and the beta 4 integrin subunit. This supports previous studies proposing a pathogenetic sequence from intestinal metaplasia to gastric carcinoma.
Full text
PDF



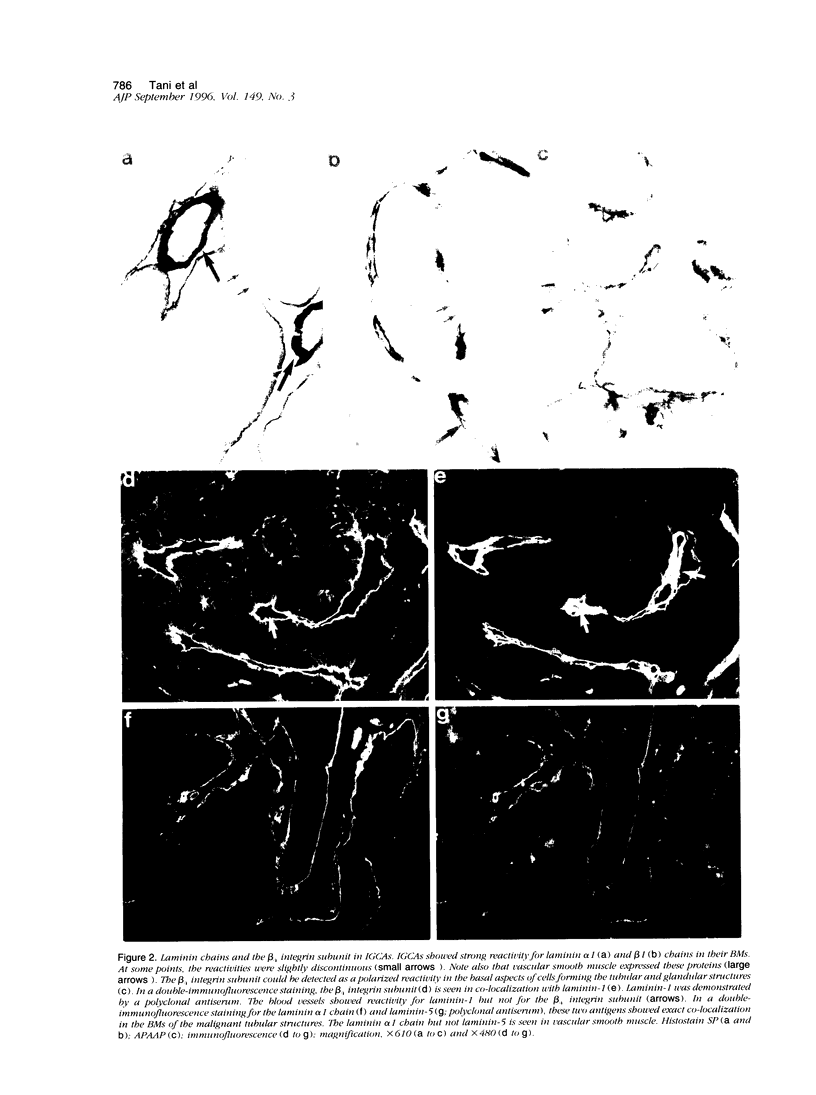
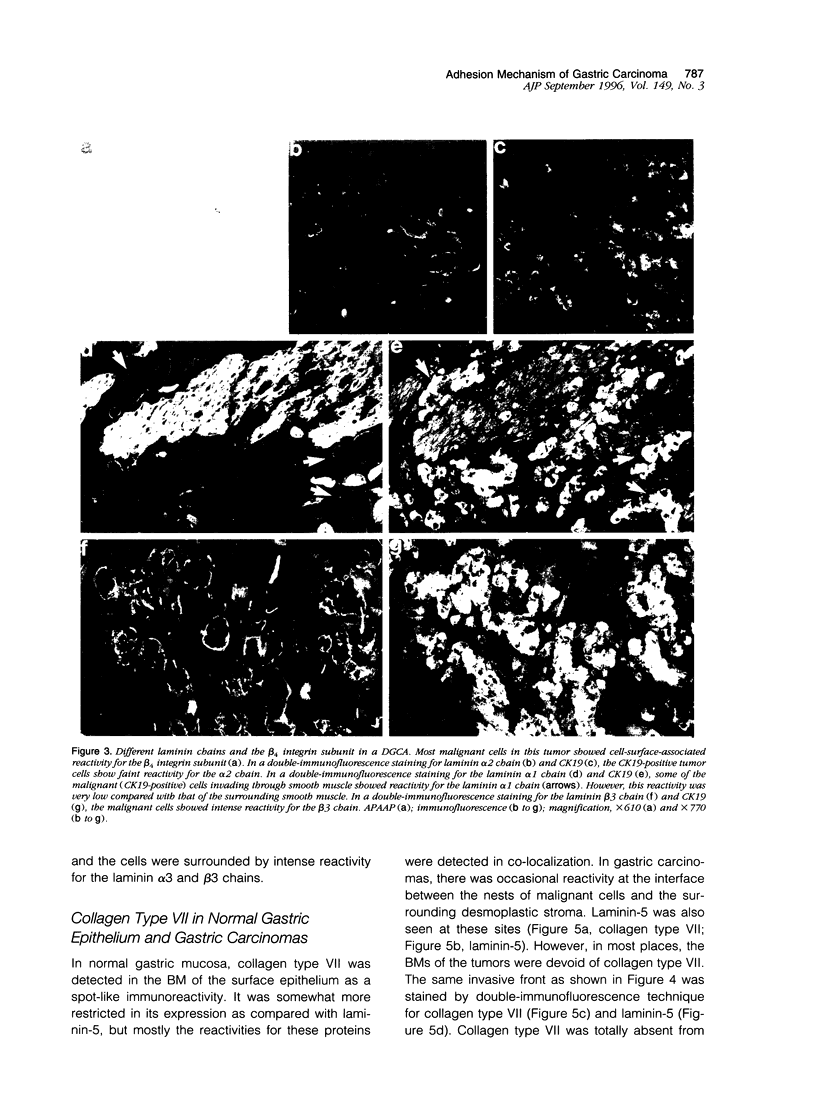




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Beaulieu J. F., Vachon P. H. Reciprocal expression of laminin A-chain isoforms along the crypt-villus axis in the human small intestine. Gastroenterology. 1994 Apr;106(4):829–839. doi: 10.1016/0016-5085(94)90740-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bernstein L. R., Liotta L. A. Molecular mediators of interactions with extracellular matrix components in metastasis and angiogenesis. Curr Opin Oncol. 1994 Jan;6(1):106–113. doi: 10.1097/00001622-199401000-00015. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bosman F. T. The borderline: basement membranes and the transition from premalignant to malignant neoplasia. Microsc Res Tech. 1994 Jun 15;28(3):216–225. doi: 10.1002/jemt.1070280306. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Correa P. Helicobacter pylori and gastric carcinogenesis. Am J Surg Pathol. 1995;19 (Suppl 1):S37–S43. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cress A. E., Rabinovitz I., Zhu W., Nagle R. B. The alpha 6 beta 1 and alpha 6 beta 4 integrins in human prostate cancer progression. Cancer Metastasis Rev. 1995 Sep;14(3):219–228. doi: 10.1007/BF00690293. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- David L., Nesland J. M., Holm R., Sobrinho-Simões M. Expression of laminin, collagen IV, fibronectin, and type IV collagenase in gastric carcinoma. An immunohistochemical study of 87 patients. Cancer. 1994 Feb 1;73(3):518–527. doi: 10.1002/1097-0142(19940201)73:3<518::aid-cncr2820730305>3.0.co;2-t. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Downer C. S., Watt F. M., Speight P. M. Loss of alpha 6 and beta 4 integrin subunits coincides with loss of basement membrane components in oral squamous cell carcinomas. J Pathol. 1993 Nov;171(3):183–190. doi: 10.1002/path.1711710306. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Engvall E., Davis G. E., Dickerson K., Ruoslahti E., Varon S., Manthorpe M. Mapping of domains in human laminin using monoclonal antibodies: localization of the neurite-promoting site. J Cell Biol. 1986 Dec;103(6 Pt 1):2457–2465. doi: 10.1083/jcb.103.6.2457. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Flug M., Köpf-Maier P. The basement membrane and its involvement in carcinoma cell invasion. Acta Anat (Basel) 1995;152(2):69–84. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Furcht L. T., Skubitz A. P., Fields G. B. Tumor cell invasion, matrix metalloproteinases, and the dogma. Lab Invest. 1994 Jun;70(6):781–783. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gusterson B. A., Warburton M. J., Mitchell D., Kraft N., Hancock W. W. Invading squamous cell carcinoma can retain a basal lamina. An immunohistochemical study using a monoclonal antibody to type IV collagen. Lab Invest. 1984 Jul;51(1):82–87. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hashimoto M., Tokunaga A., Nishi K., Wada M., Masumori K., Kumagae Y., Numajiri H., Matsukura N., Yoshiyasu M., Tanaka N. [3H]thymidine autoradiographic and alkaline phosphatase histochemical studies of intestinal metaplasia of the human stomach. Histochem J. 1983 Oct;15(10):953–959. doi: 10.1007/BF01002491. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hattori T., Fujita S. Tritiated thymidine autoradiographic study on histogenesis and spreading of intestinal metaplasia in human stomach. Pathol Res Pract. 1979 Jan;164(3):224–237. doi: 10.1016/S0344-0338(79)80045-X. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hessle H., Sakai L. Y., Hollister D. W., Burgeson R. E., Engvall E. Basement membrane diversity detected by monoclonal antibodies. Differentiation. 1984;26(1):49–54. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-0436.1984.tb01372.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hida J., Matsuda T., Kitaoka M., Machidera N., Kubo R., Yasutomi M. The role of basement membrane in colorectal cancer invasion and liver metastasis. Cancer. 1994 Jul 15;74(2):592–598. doi: 10.1002/1097-0142(19940715)74:2<592::aid-cncr2820740210>3.0.co;2-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jones J. C., Asmuth J., Baker S. E., Langhofer M., Roth S. I., Hopkinson S. B. Hemidesmosomes: extracellular matrix/intermediate filament connectors. Exp Cell Res. 1994 Jul;213(1):1–11. doi: 10.1006/excr.1994.1166. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jones J. C., Kurpakus M. A., Cooper H. M., Quaranta V. A function for the integrin alpha 6 beta 4 in the hemidesmosome. Cell Regul. 1991 Jun;2(6):427–438. doi: 10.1091/mbc.2.6.427. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Knox J. D., Cress A. E., Clark V., Manriquez L., Affinito K. S., Dalkin B. L., Nagle R. B. Differential expression of extracellular matrix molecules and the alpha 6-integrins in the normal and neoplastic prostate. Am J Pathol. 1994 Jul;145(1):167–174. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LAUREN P. THE TWO HISTOLOGICAL MAIN TYPES OF GASTRIC CARCINOMA: DIFFUSE AND SO-CALLED INTESTINAL-TYPE CARCINOMA. AN ATTEMPT AT A HISTO-CLINICAL CLASSIFICATION. Acta Pathol Microbiol Scand. 1965;64:31–49. doi: 10.1111/apm.1965.64.1.31. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leoncini P., Petracca R., Ruggiero P., Cintorino M., Syrjänen S., Mäntyjärvi R., Syrjänen K. Expression of cytokeratin No. 19 polypeptide in genital papillomavirus lesions. Gynecol Obstet Invest. 1990;29(1):59–66. doi: 10.1159/000293302. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Liebert M., Washington R., Wedemeyer G., Carey T. E., Grossman H. B. Loss of co-localization of alpha 6 beta 4 integrin and collagen VII in bladder cancer. Am J Pathol. 1994 Apr;144(4):787–795. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Liesi P., Dahl D., Vaheri A. Laminin is produced by early rat astrocytes in primary culture. J Cell Biol. 1983 Mar;96(3):920–924. doi: 10.1083/jcb.96.3.920. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MACDONALD W. C., TRIER J. S., EVERETT N. B. CELL PROLIFERATION AND MIGRATION IN THE STOMACH, DUODENUM, AND RECTUM OF MAN: RADIOAUTOGRAPHIC STUDIES. Gastroenterology. 1964 Apr;46:405–417. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marinkovich M. P., Keene D. R., Rimberg C. S., Burgeson R. E. Cellular origin of the dermal-epidermal basement membrane. Dev Dyn. 1993 Aug;197(4):255–267. doi: 10.1002/aja.1001970404. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marinkovich M. P., Lunstrum G. P., Burgeson R. E. The anchoring filament protein kalinin is synthesized and secreted as a high molecular weight precursor. J Biol Chem. 1992 Sep 5;267(25):17900–17906. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mercurio A. M. Laminin receptors: achieving specificity through cooperation. Trends Cell Biol. 1995 Nov;5(11):419–423. doi: 10.1016/s0962-8924(00)89100-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Merker H. J. Morphology of the basement membrane. Microsc Res Tech. 1994 Jun 1;28(2):95–124. doi: 10.1002/jemt.1070280203. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ming S. C. Gastric carcinoma. A pathobiological classification. Cancer. 1977 Jun;39(6):2475–2485. doi: 10.1002/1097-0142(197706)39:6<2475::aid-cncr2820390626>3.0.co;2-l. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Orita H., Korenaga D., Maehara Y., Baba H., Sugimachi K. Laminin distribution patterns are closely related to liver metastasis in gastric cancer. Cancer. 1993 Feb 15;71(4):1201–1206. doi: 10.1002/1097-0142(19930215)71:4<1201::aid-cncr2820710405>3.0.co;2-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pignatelli M., Cardillo M. R., Hanby A., Stamp G. W. Integrins and their accessory adhesion molecules in mammary carcinomas: loss of polarization in poorly differentiated tumors. Hum Pathol. 1992 Oct;23(10):1159–1166. doi: 10.1016/0046-8177(92)90034-z. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pyke C., Salo S., Ralfkiaer E., Rømer J., Danø K., Tryggvason K. Laminin-5 is a marker of invading cancer cells in some human carcinomas and is coexpressed with the receptor for urokinase plasminogen activator in budding cancer cells in colon adenocarcinomas. Cancer Res. 1995 Sep 15;55(18):4132–4139. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rossen K., Dahlstrøm K. K., Mercurio A. M., Wewer U. M. Expression of the alpha 6 beta 4 integrin by squamous cell carcinomas and basal cell carcinomas: possible relation to invasive potential? Acta Derm Venereol. 1994 Mar;74(2):101–105. doi: 10.2340/0001555574101105. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rousselle P., Lunstrum G. P., Keene D. R., Burgeson R. E. Kalinin: an epithelium-specific basement membrane adhesion molecule that is a component of anchoring filaments. J Cell Biol. 1991 Aug;114(3):567–576. doi: 10.1083/jcb.114.3.567. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ryan M. C., Tizard R., VanDevanter D. R., Carter W. G. Cloning of the LamA3 gene encoding the alpha 3 chain of the adhesive ligand epiligrin. Expression in wound repair. J Biol Chem. 1994 Sep 9;269(36):22779–22787. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sakai L. Y., Keene D. R., Morris N. P., Burgeson R. E. Type VII collagen is a major structural component of anchoring fibrils. J Cell Biol. 1986 Oct;103(4):1577–1586. doi: 10.1083/jcb.103.4.1577. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Savoia P., Cremona O., Trusolino L., Pepino E., Marchisio P. C. Integrins and basement membrane proteins in skin carcinomas. Pathol Res Pract. 1994 Oct;190(9-10):950–954. doi: 10.1016/s0344-0338(11)81001-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Simo P., Bouziges F., Lissitzky J. C., Sorokin L., Kedinger M., Simon-Assmann P. Dual and asynchronous deposition of laminin chains at the epithelial-mesenchymal interface in the gut. Gastroenterology. 1992 Jun;102(6):1835–1845. doi: 10.1016/0016-5085(92)90303-g. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Simon-Assmann P., Duclos B., Orian-Rousseau V., Arnold C., Mathelin C., Engvall E., Kedinger M. Differential expression of laminin isoforms and alpha 6-beta 4 integrin subunits in the developing human and mouse intestine. Dev Dyn. 1994 Sep;201(1):71–85. doi: 10.1002/aja.1002010108. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Simon-Assmann P., Kedinger M. Heterotypic cellular cooperation in gut morphogenesis and differentiation. Semin Cell Biol. 1993 Jun;4(3):221–230. doi: 10.1006/scel.1993.1026. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sipponen P., Seppälä K. Gastric carcinoma: failed adaptation to Helicobacter pylori. Scand J Gastroenterol Suppl. 1992;193:33–38. doi: 10.3109/00365529209096003. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sugihara H., Hattori T., Fujita S., Fukuda M. Distribution of fibronectin and laminin in early and advanced signet-ring-cell carcinomas of the stomach. Int J Cancer. 1989 Feb 15;43(2):263–269. doi: 10.1002/ijc.2910430217. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tamura R. N., Rozzo C., Starr L., Chambers J., Reichardt L. F., Cooper H. M., Quaranta V. Epithelial integrin alpha 6 beta 4: complete primary structure of alpha 6 and variant forms of beta 4. J Cell Biol. 1990 Oct;111(4):1593–1604. doi: 10.1083/jcb.111.4.1593. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Timpl R., Brown J. C. The laminins. Matrix Biol. 1994 Aug;14(4):275–281. doi: 10.1016/0945-053x(94)90192-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Virtanen I., Tani T., Bäck N., Häppölä O., Laitinen L., Kiviluoto T., Salo J., Burgeson R. E., Lehto V. P., Kivilaakso E. Differential expression of laminin chains and their integrin receptors in human gastric mucosa. Am J Pathol. 1995 Oct;147(4):1123–1132. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vuolteenaho R., Nissinen M., Sainio K., Byers M., Eddy R., Hirvonen H., Shows T. B., Sariola H., Engvall E., Tryggvason K. Human laminin M chain (merosin): complete primary structure, chromosomal assignment, and expression of the M and A chain in human fetal tissues. J Cell Biol. 1994 Feb;124(3):381–394. doi: 10.1083/jcb.124.3.381. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wetzels R. H., Robben H. C., Leigh I. M., Schaafsma H. E., Vooijs G. P., Ramaekers F. C. Distribution patterns of type VII collagen in normal and malignant human tissues. Am J Pathol. 1991 Aug;139(2):451–459. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]