Abstract
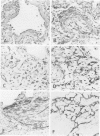
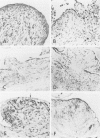
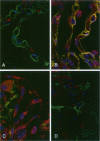
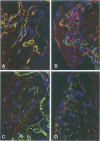
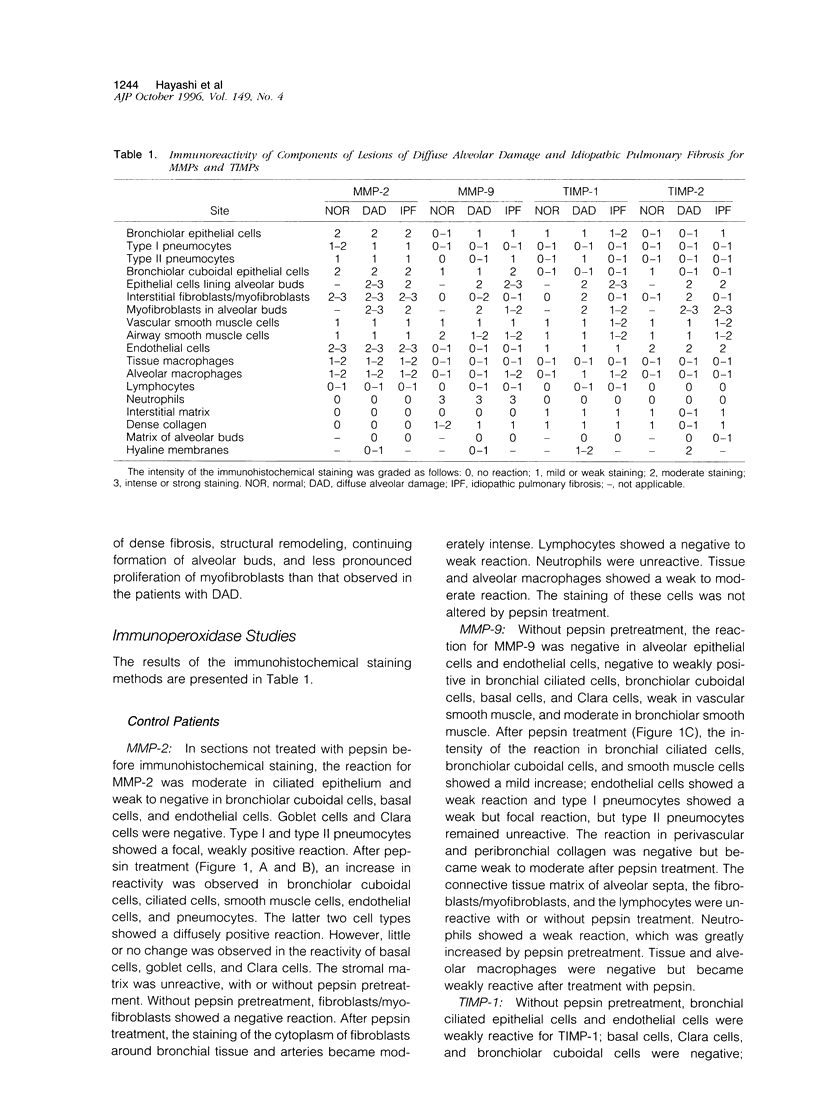
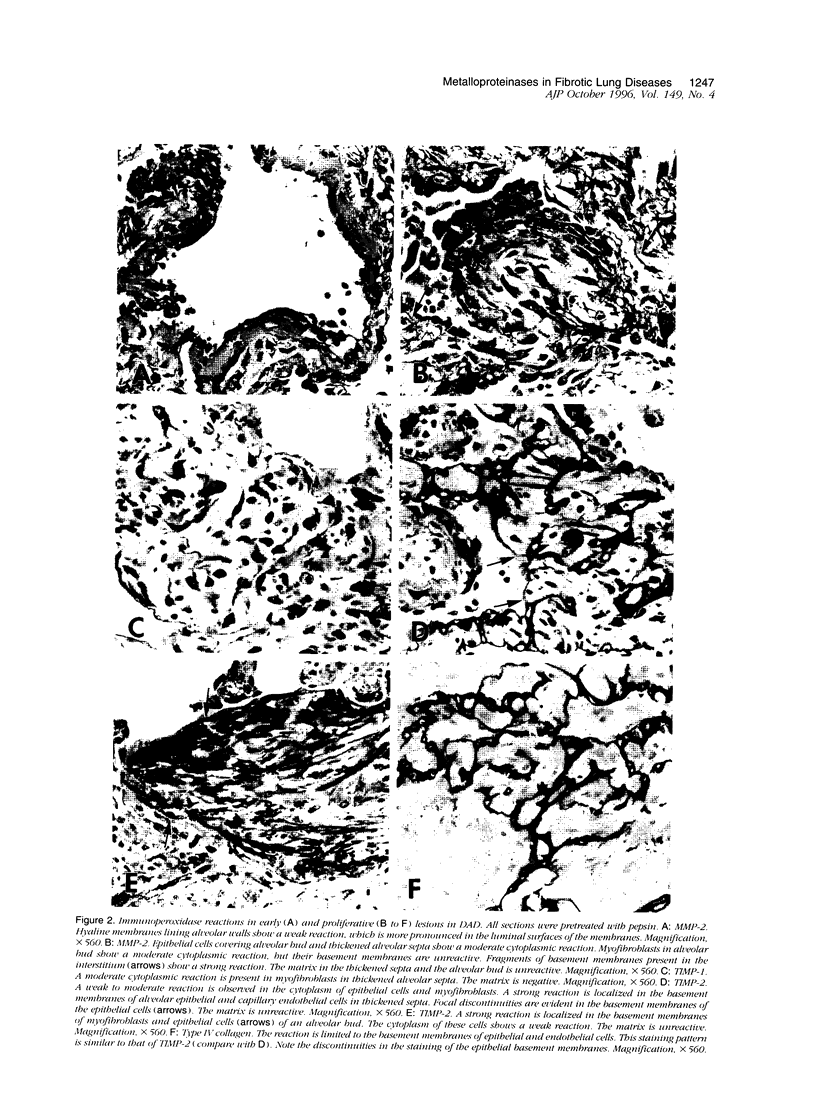
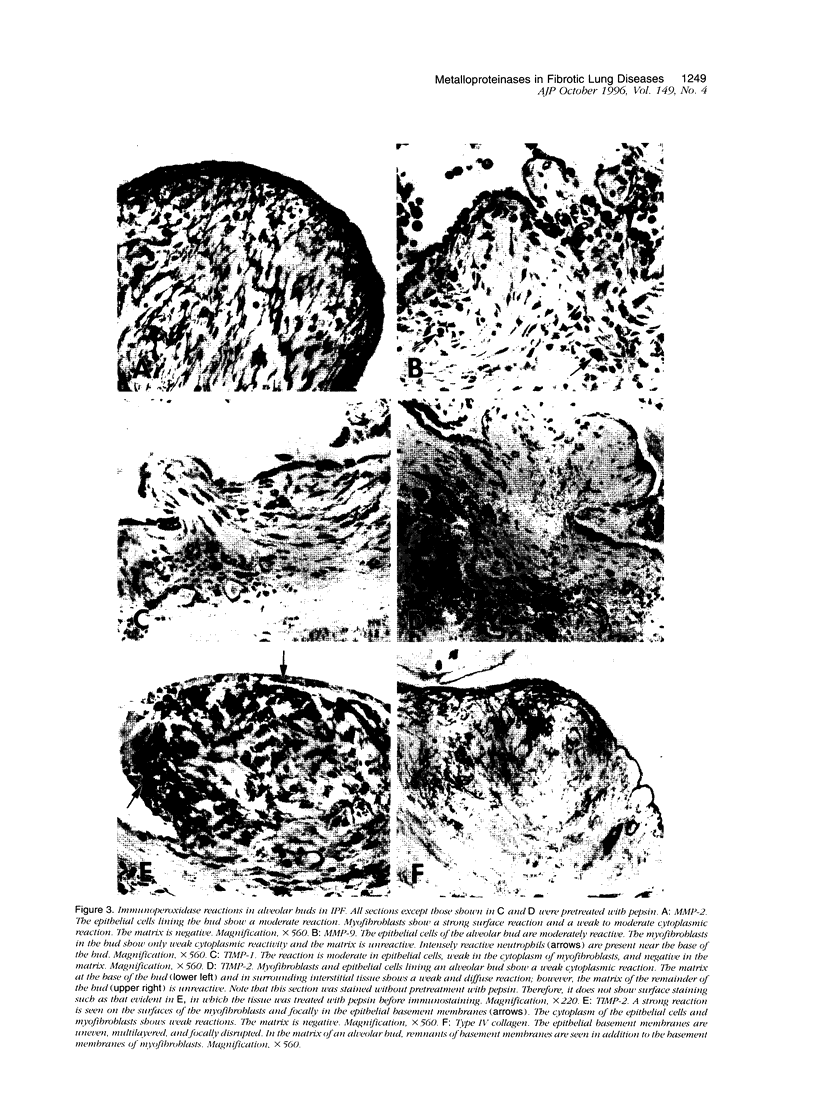
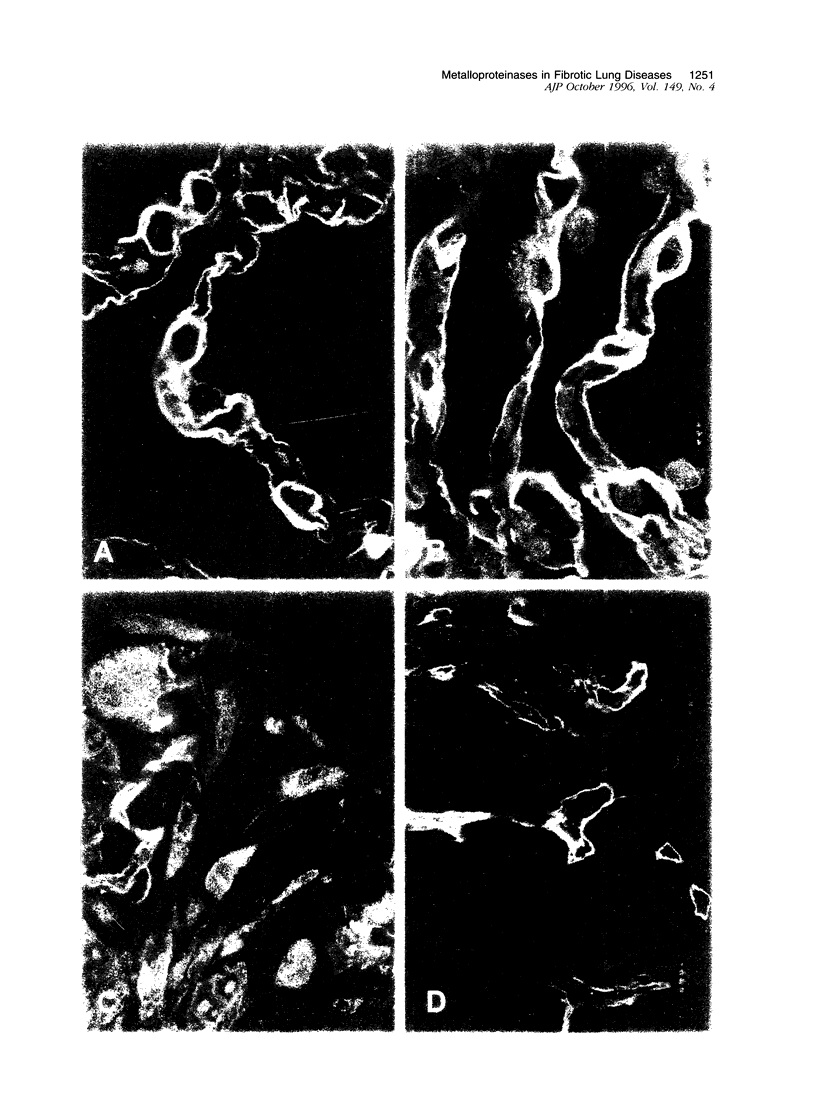
Immunohistochemical and confocal microscopic studies of the localization of matrix metalloproteinases (MMPs), their tissue inhibitors (TIMPs), and type IV collagen were made in lung tissues from patients with normal pulmonary histology (n = 3), diffuse alveolar damage (n = 14), and idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis (n = 12). Pretreatment with pepsin revealed otherwise undetectable MMP- and TIMP-immunoreactive sites. In normal lung, MMP-2, MMP-9, TIMP-1, and TIMP-2 were localized in ciliated cells, endothelial cells, pneumocytes, macrophages, and smooth muscle cells; fibroblasts showed a strong reaction only for MMP-2. Only TIMP-2 showed co-localization with type IV collagen. Myofibroblasts and epithelial cells expressed increased reactivity for MMPs and TIMPs in both disorders. The reactivities for MMPs and TIMPs were stronger in diffuse alveolar damage. MMP-2 showed focal co-localization in capillary endothelial and disrupted epithelial basement membranes, suggesting activation of collagenolysis. A protective effect against this lysis was suggested by the extensive co-localization of TIMP-2 with type IV collagen and fibrillar collagens. Alveolar buds showed increased reactivity for MMPs and TIMPs in their lining epithelial cells, myofibroblasts, and their basement membranes; however, their matrices were mostly unreactive. These findings emphasize the complexity of the roles of MMPs and TIMPs in collagen turnover in diffuse alvcolar damage and idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis.
Full text
PDF










Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Agostini C., Garbisa S., Trentin L., Zambello R., Fastelli G., Onisto M., Cipriani A., Festi G., Casara D., Semenzato G. Pulmonary alveolar macrophages from patients with active sarcoidosis express type IV collagenolytic proteinase. An enzymatic mechanism for influx of mononuclear phagocytes at sites of disease activity. J Clin Invest. 1989 Aug;84(2):605–612. doi: 10.1172/JCI114205. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Agren M. S. Gelatinase activity during wound healing. Br J Dermatol. 1994 Nov;131(5):634–640. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2133.1994.tb04974.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Basset F., Ferrans V. J., Soler P., Takemura T., Fukuda Y., Crystal R. G. Intraluminal fibrosis in interstitial lung disorders. Am J Pathol. 1986 Mar;122(3):443–461. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brown P. D., Levy A. T., Margulies I. M., Liotta L. A., Stetler-Stevenson W. G. Independent expression and cellular processing of Mr 72,000 type IV collagenase and interstitial collagenase in human tumorigenic cell lines. Cancer Res. 1990 Oct 1;50(19):6184–6191. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Canete-Soler R., Litzky L., Lubensky I., Muschel R. J. Localization of the 92 kd gelatinase mRNA in squamous cell and adenocarcinomas of the lung using in situ hybridization. Am J Pathol. 1994 Mar;144(3):518–527. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carmichael D. F., Sommer A., Thompson R. C., Anderson D. C., Smith C. G., Welgus H. G., Stricklin G. P. Primary structure and cDNA cloning of human fibroblast collagenase inhibitor. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Apr;83(8):2407–2411. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.8.2407. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cawston T. E., Galloway W. A., Mercer E., Murphy G., Reynolds J. J. Purification of rabbit bone inhibitor of collagenase. Biochem J. 1981 Apr 1;195(1):159–165. doi: 10.1042/bj1950159. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Collier I. E., Wilhelm S. M., Eisen A. Z., Marmer B. L., Grant G. A., Seltzer J. L., Kronberger A., He C. S., Bauer E. A., Goldberg G. I. H-ras oncogene-transformed human bronchial epithelial cells (TBE-1) secrete a single metalloprotease capable of degrading basement membrane collagen. J Biol Chem. 1988 May 15;263(14):6579–6587. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Corcoran M. L., Stetler-Stevenson W. G., Brown P. D., Wahl L. M. Interleukin 4 inhibition of prostaglandin E2 synthesis blocks interstitial collagenase and 92-kDa type IV collagenase/gelatinase production by human monocytes. J Biol Chem. 1992 Jan 5;267(1):515–519. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- D'Armiento J., Dalal S. S., Okada Y., Berg R. A., Chada K. Collagenase expression in the lungs of transgenic mice causes pulmonary emphysema. Cell. 1992 Dec 11;71(6):955–961. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(92)90391-o. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Denholm E. M., Rollins S. M. Alveolar macrophage secretion of a 92-kDa gelatinase in response to bleomycin. Am J Physiol. 1993 Dec;265(6 Pt 1):L581–L585. doi: 10.1152/ajplung.1993.265.6.L581. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fosang A. J., Last K., Knäuper V., Neame P. J., Murphy G., Hardingham T. E., Tschesche H., Hamilton J. A. Fibroblast and neutrophil collagenases cleave at two sites in the cartilage aggrecan interglobular domain. Biochem J. 1993 Oct 1;295(Pt 1):273–276. doi: 10.1042/bj2950273. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ganser G. L., Stricklin G. P., Matrisian L. M. EGF and TGF alpha influence in vitro lung development by the induction of matrix-degrading metalloproteinases. Int J Dev Biol. 1991 Dec;35(4):453–461. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goldberg G. I., Collier I. E., Eisen A. Z., Grant G. A., Marmer B. L., Wilhelm S. M. Mosaic structure of the secreted ECM metalloproteases and interaction of the type IV collagenases with inhibitors. Matrix Suppl. 1992;1:25–30. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goldberg G. I., Marmer B. L., Grant G. A., Eisen A. Z., Wilhelm S., He C. S. Human 72-kilodalton type IV collagenase forms a complex with a tissue inhibitor of metalloproteases designated TIMP-2. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Nov;86(21):8207–8211. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.21.8207. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hembry R. M., Murphy G., Reynolds J. J. Immunolocalization of tissue inhibitor of metalloproteinases (TIMP) in human cells. Characterization and use of a specific antiserum. J Cell Sci. 1985 Feb;73:105–119. doi: 10.1242/jcs.73.1.105. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hurewitz A. N., Zucker S., Mancuso P., Wu C. L., Dimassimo B., Lysik R. M., Moutsiakis D. Human pleural effusions are rich in matrix metalloproteinases. Chest. 1992 Dec;102(6):1808–1814. doi: 10.1378/chest.102.6.1808. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Matsubara M., Girard M. T., Kublin C. L., Cintron C., Fini M. E. Differential roles for two gelatinolytic enzymes of the matrix metalloproteinase family in the remodelling cornea. Dev Biol. 1991 Oct;147(2):425–439. doi: 10.1016/0012-1606(91)90300-r. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Matsubara M., Zieske J. D., Fini M. E. Mechanism of basement membrane dissolution preceding corneal ulceration. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 1991 Dec;32(13):3221–3237. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McGowan S. E. Extracellular matrix and the regulation of lung development and repair. FASEB J. 1992 Aug;6(11):2895–2904. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Minoo P., Penn R., deLemos D. M., Coalson J. J., deLemos R. A. Tissue inhibitor of metalloproteinase-1 mRNA is specifically induced in lung tissue after birth. Pediatr Res. 1993 Dec;34(6):729–734. doi: 10.1203/00006450-199312000-00007. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moloney D., O'Connor C. M., Fitzgerald M. X. Bronchoalveolar lavage collagenase and collagenase inhibitory capacity in interstitial lung disease. Biochem Soc Trans. 1992 Feb;20(1):79S–79S. doi: 10.1042/bst020079s. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Montaño M., Ramos C., González G., Vadillo F., Pardo A., Selman M. Lung collagenase inhibitors and spontaneous and latent collagenase activity in idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis and hypersensitivity pneumonitis. Chest. 1989 Nov;96(5):1115–1119. doi: 10.1378/chest.96.5.1115. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Murphy A. N., Unsworth E. J., Stetler-Stevenson W. G. Tissue inhibitor of metalloproteinases-2 inhibits bFGF-induced human microvascular endothelial cell proliferation. J Cell Physiol. 1993 Nov;157(2):351–358. doi: 10.1002/jcp.1041570219. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ohori N. P., Yousem S. A., Griffin J., Stanis K., Stetler-Stevenson W. G., Colby T. V., Sonmez-Alpan E. Comparison of extracellular matrix antigens in subtypes of bronchioloalveolar carcinoma and conventional pulmonary adenocarcinoma. An immunohistochemical study. Am J Surg Pathol. 1992 Jul;16(7):675–686. doi: 10.1097/00000478-199207000-00006. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oikarinen A., Kylmäniemi M., Autio-Harmainen H., Autio P., Salo T. Demonstration of 72-kDa and 92-kDa forms of type IV collagenase in human skin: variable expression in various blistering diseases, induction during re-epithelialization, and decrease by topical glucocorticoids. J Invest Dermatol. 1993 Aug;101(2):205–210. doi: 10.1111/1523-1747.ep12363823. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pardo A., Selman M. Decreased collagenase production by fibroblasts derived from idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis. Matrix Suppl. 1992;1:417–418. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pardo A., Selman M., Ramírez R., Ramos C., Montaño M., Stricklin G., Raghu G. Production of collagenase and tissue inhibitor of metalloproteinases by fibroblasts derived from normal and fibrotic human lungs. Chest. 1992 Oct;102(4):1085–1089. doi: 10.1378/chest.102.4.1085. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Piedboeuf B., Johnston C. J., Watkins R. H., Hudak B. B., Lazo J. S., Cherian M. G., Horowitz S. Increased expression of tissue inhibitor of metalloproteinases (TIMP-I) and metallothionein in murine lungs after hyperoxic exposure. Am J Respir Cell Mol Biol. 1994 Feb;10(2):123–132. doi: 10.1165/ajrcmb.10.2.8110467. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ray J. M., Stetler-Stevenson W. G. The role of matrix metalloproteases and their inhibitors in tumour invasion, metastasis and angiogenesis. Eur Respir J. 1994 Nov;7(11):2062–2072. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Salo T., Mäkelä M., Kylmäniemi M., Autio-Harmainen H., Larjava H. Expression of matrix metalloproteinase-2 and -9 during early human wound healing. Lab Invest. 1994 Feb;70(2):176–182. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schnaper H. W., Grant D. S., Stetler-Stevenson W. G., Fridman R., D'Orazi G., Murphy A. N., Bird R. E., Hoythya M., Fuerst T. R., French D. L. Type IV collagenase(s) and TIMPs modulate endothelial cell morphogenesis in vitro. J Cell Physiol. 1993 Aug;156(2):235–246. doi: 10.1002/jcp.1041560204. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sepper R., Konttinen Y. T., Sorsa T., Koski H. Gelatinolytic and type IV collagenolytic activity in bronchiectasis. Chest. 1994 Oct;106(4):1129–1133. doi: 10.1378/chest.106.4.1129. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shapiro S. D., Kobayashi D. K., Welgus H. G. Identification of TIMP-2 in human alveolar macrophages. Regulation of biosynthesis is opposite to that of metalloproteinases and TIMP-1. J Biol Chem. 1992 Jul 15;267(20):13890–13894. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Soini Y., Päkkö P., Autio-Harmainen H. Genes of laminin B1 chain, alpha 1 (IV) chain of type IV collagen, and 72-kd type IV collagenase are mainly expressed by the stromal cells of lung carcinomas. Am J Pathol. 1993 May;142(5):1622–1630. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stetler-Stevenson W. G., Aznavoorian S., Liotta L. A. Tumor cell interactions with the extracellular matrix during invasion and metastasis. Annu Rev Cell Biol. 1993;9:541–573. doi: 10.1146/annurev.cb.09.110193.002545. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stetler-Stevenson W. G., Brown P. D., Onisto M., Levy A. T., Liotta L. A. Tissue inhibitor of metalloproteinases-2 (TIMP-2) mRNA expression in tumor cell lines and human tumor tissues. J Biol Chem. 1990 Aug 15;265(23):13933–13938. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stetler-Stevenson W. G., Krutzsch H. C., Liotta L. A. Tissue inhibitor of metalloproteinase (TIMP-2). A new member of the metalloproteinase inhibitor family. J Biol Chem. 1989 Oct 15;264(29):17374–17378. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stricklin G. P., Li L., Jancic V., Wenczak B. A., Nanney L. B. Localization of mRNAs representing collagenase and TIMP in sections of healing human burn wounds. Am J Pathol. 1993 Dec;143(6):1657–1666. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stricklin G. P., Li L., Nanney L. B. Localization of mRNAs representing interstitial collagenase, 72-kda gelatinase, and TIMP in healing porcine burn wounds. J Invest Dermatol. 1994 Sep;103(3):352–358. doi: 10.1111/1523-1747.ep12394926. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stricklin G. P., Nanney L. B. Immunolocalization of collagenase and TIMP in healing human burn wounds. J Invest Dermatol. 1994 Oct;103(4):488–492. doi: 10.1111/1523-1747.ep12395601. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Strongin A. Y., Collier I., Bannikov G., Marmer B. L., Grant G. A., Goldberg G. I. Mechanism of cell surface activation of 72-kDa type IV collagenase. Isolation of the activated form of the membrane metalloprotease. J Biol Chem. 1995 Mar 10;270(10):5331–5338. doi: 10.1074/jbc.270.10.5331. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ståhle-Bäckdahl M., Parks W. C. 92-kd gelatinase is actively expressed by eosinophils and stored by neutrophils in squamous cell carcinoma. Am J Pathol. 1993 Apr;142(4):995–1000. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Swanson P. E., Hagen K. A., Wick M. R. Avidin-biotin-peroxidase-antiperoxidase (ABPAP) complex. An immunocytochemical method with enhanced sensitivity. Am J Clin Pathol. 1987 Aug;88(2):162–176. doi: 10.1093/ajcp/88.2.162. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Urbanski S. J., Edwards D. R., Maitland A., Leco K. J., Watson A., Kossakowska A. E. Expression of metalloproteinases and their inhibitors in primary pulmonary carcinomas. Br J Cancer. 1992 Dec;66(6):1188–1194. doi: 10.1038/bjc.1992.434. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weiland J. E., Garcia J. G., Davis W. B., Gadek J. E. Neutrophil collagenase in rheumatoid interstitial lung disease. J Appl Physiol (1985) 1987 Feb;62(2):628–633. doi: 10.1152/jappl.1987.62.2.628. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Welgus H. G., Stricklin G. P. Human skin fibroblast collagenase inhibitor. Comparative studies in human connective tissues, serum, and amniotic fluid. J Biol Chem. 1983 Oct 25;258(20):12259–12264. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wilhelm S. M., Collier I. E., Marmer B. L., Eisen A. Z., Grant G. A., Goldberg G. I. SV40-transformed human lung fibroblasts secrete a 92-kDa type IV collagenase which is identical to that secreted by normal human macrophages. J Biol Chem. 1989 Oct 15;264(29):17213–17221. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zucker S., Lysik R. M., Malik M., Bauer B. A., Caamano J., Klein-Szanto A. J. Secretion of gelatinases and tissue inhibitors of metalloproteinases by human lung cancer cell lines and revertant cell lines: not an invariant correlation with metastasis. Int J Cancer. 1992 Sep 30;52(3):366–371. doi: 10.1002/ijc.2910520307. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zucker S., Wieman J., Lysik R. M., Imhof B., Nagase H., Ramamurthy N., Liotta L. A., Golub L. M. Gelatin-degrading type IV collagenase isolated from human small cell lung cancer. Invasion Metastasis. 1989;9(3):167–181. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]