Abstract
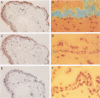
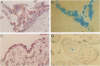
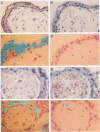
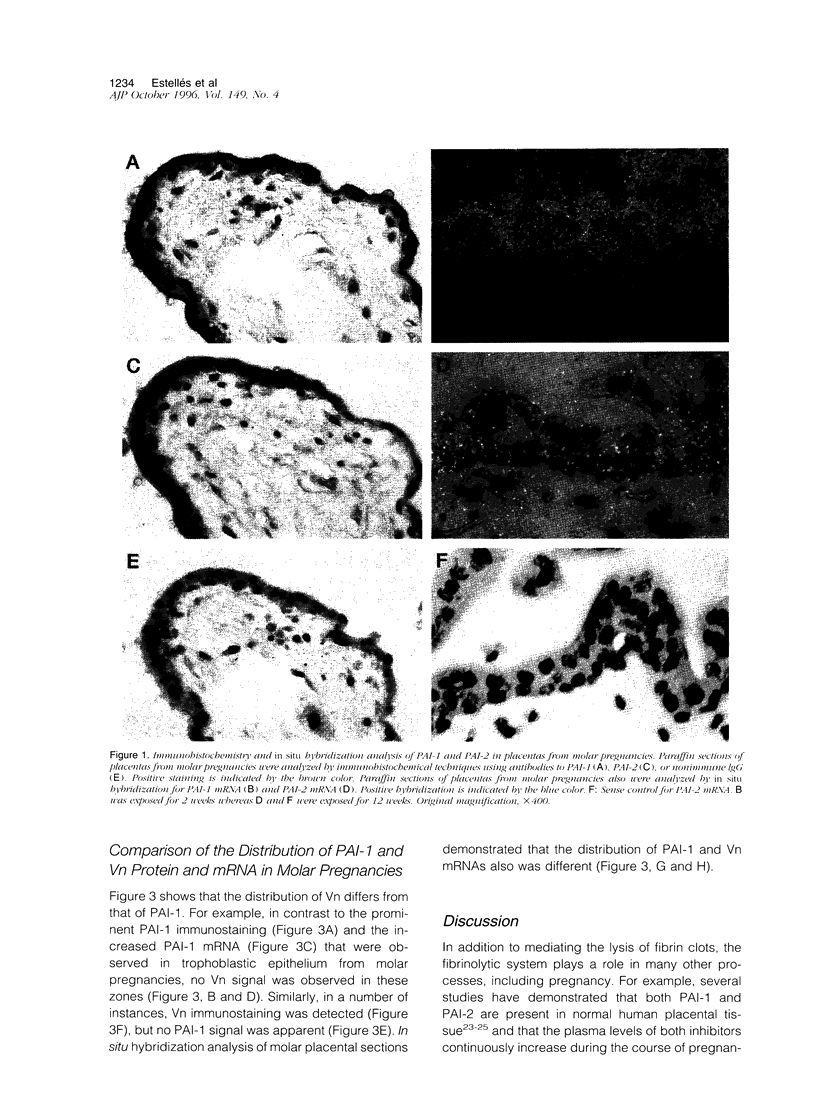
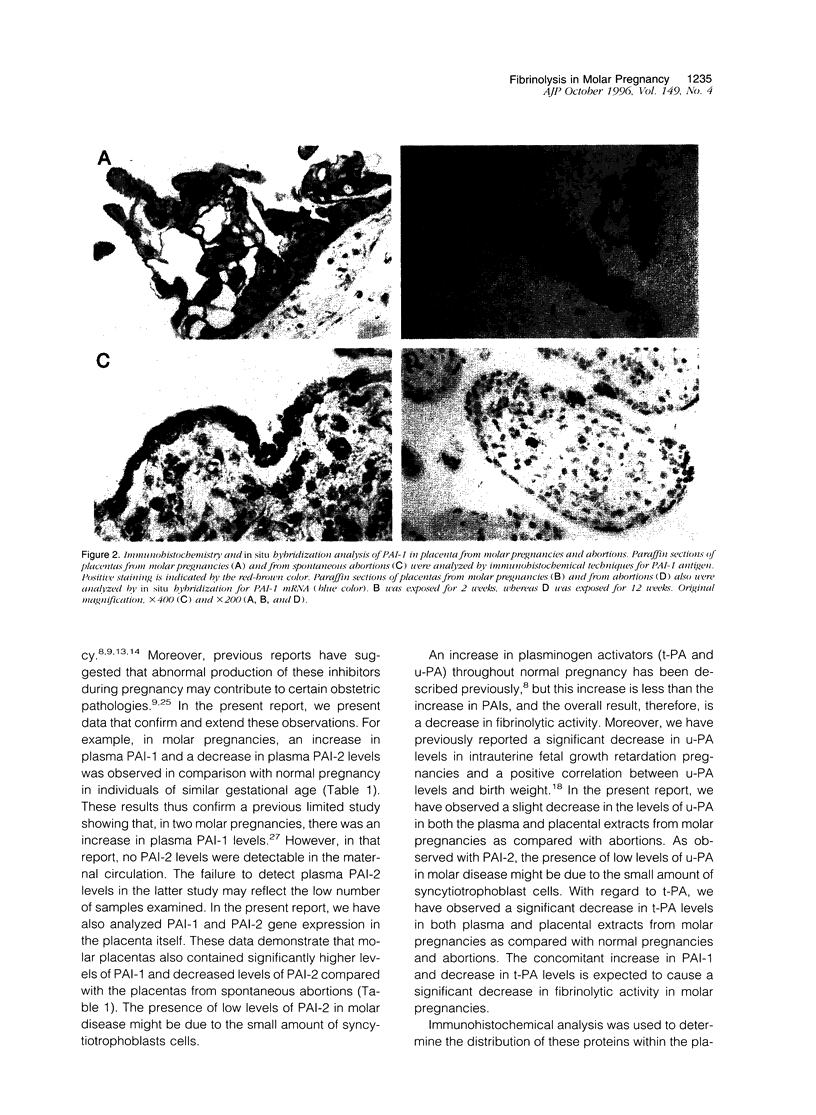
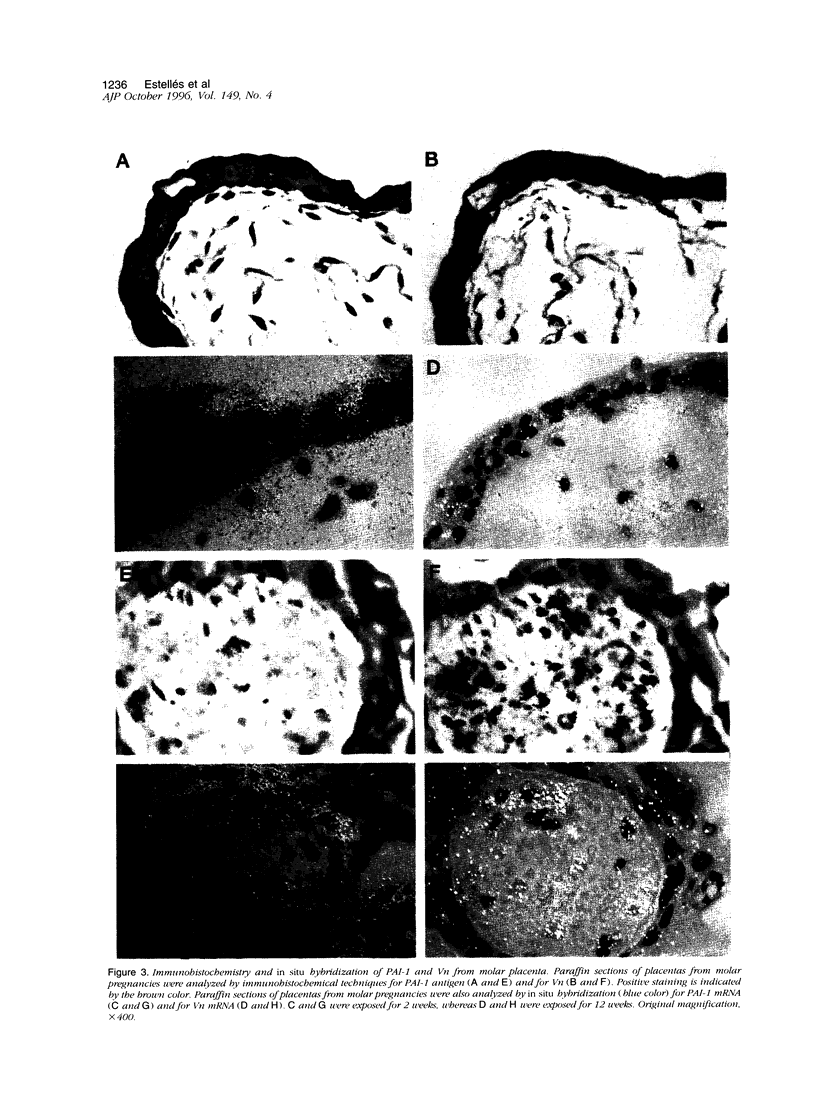
We previously reported significantly elevated levels of plasminogen activator inhibitor type 1 (PAI-1) in plasma and placenta from pregnant women with severe pre-eclampsia, and pre-eclampsia is a frequent problem in molar pregnancies. As increases in PAI-1 may contribute to the placental alterations that occur in pre-eclampsia, we have begun to investigate changes in PAI-1 as well as PAI-2 and several other components of the fibrinolytic system in patients with trophoblastic disease. Significant increases in plasma PAI-1 and decreases in plasma PAI-2 levels were observed in molar pregnancies when compared with the levels in normal pregnant women of similar gestational age. PAI-1 antigen levels also were increased, and PAI-2 levels were decreased in placenta from women with molar pregnancies compared with placenta obtained by spontaneous abortion. Immunohistochemical analysis revealed strong positive and specific staining of PAI-1 in trophoblastic epithelium in molar pregnancies and relatively weak staining of PAI-2. No association between the distribution of PAI-1 and vitronectin was found, and no specific signal for tissue type PA, urokinase type PA, tumor necrosis factor-alpha, or interleukin-1 was detected. In situ hybridization revealed an increase in PAI-1 but not PAI-2 mRNAs in placenta from molar pregnancies in comparison with placenta from abortions. These results demonstrate increased PAI-1 protein and mRNA in trophoblastic disease and suggest that localized elevated levels of PAI-1 may contribute to the hemostatic problems associated with this disorder.
Full text
PDF






Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- ALBRECHTSEN O. K. The fibrinolytic activity of the human endometrium. Acta Endocrinol (Copenh) 1956 Oct;23(2):207–218. doi: 10.1530/acta.0.0230207. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Arkwright P. D., Rademacher T. W., Dwek R. A., Redman C. W. Pre-eclampsia is associated with an increase in trophoblast glycogen content and glycogen synthase activity, similar to that found in hydatidiform moles. J Clin Invest. 1993 Jun;91(6):2744–2753. doi: 10.1172/JCI116515. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Astedt B., Hägerstrand I., Lecander I. Cellular localisation in placenta of placental type plasminogen activator inhibitor. Thromb Haemost. 1986 Aug 20;56(1):63–65. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Aznar J., Gilabert J., Estellés A., España F. Fibrinolytic activity and protein C in preeclampsia. Thromb Haemost. 1986 Jun 30;55(3):314–317. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bachmann F. The enigma PAI-2. Gene expression, evolutionary and functional aspects. Thromb Haemost. 1995 Jul;74(1):172–179. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ballegeer V., Spitz B., Kieckens L., Moreau H., Van Assche A., Collen D. Predictive value of increased plasma levels of fibronectin in gestational hypertension. Am J Obstet Gynecol. 1989 Aug;161(2):432–436. doi: 10.1016/0002-9378(89)90537-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chen H. L., Yang Y. P., Hu X. L., Yelavarthi K. K., Fishback J. L., Hunt J. S. Tumor necrosis factor alpha mRNA and protein are present in human placental and uterine cells at early and late stages of gestation. Am J Pathol. 1991 Aug;139(2):327–335. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Declerck P. J., De Mol M., Alessi M. C., Baudner S., Pâques E. P., Preissner K. T., Müller-Berghaus G., Collen D. Purification and characterization of a plasminogen activator inhibitor 1 binding protein from human plasma. Identification as a multimeric form of S protein (vitronectin). J Biol Chem. 1988 Oct 25;263(30):15454–15461. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Estellés A., Gilabert J., Aznar J., Loskutoff D. J., Schleef R. R. Changes in the plasma levels of type 1 and type 2 plasminogen activator inhibitors in normal pregnancy and in patients with severe preeclampsia. Blood. 1989 Sep;74(4):1332–1338. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Estellés A., Gilabert J., España F., Aznar J., Galbis M. Fibrinolytic parameters in normotensive pregnancy with intrauterine fetal growth retardation and in severe preeclampsia. Am J Obstet Gynecol. 1991 Jul;165(1):138–142. doi: 10.1016/0002-9378(91)90242-j. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Estellés A., Gilabert J., Keeton M., Eguchi Y., Aznar J., Grancha S., Espña F., Loskutoff D. J., Schleef R. R. Altered expression of plasminogen activator inhibitor type 1 in placentas from pregnant women with preeclampsia and/or intrauterine fetal growth retardation. Blood. 1994 Jul 1;84(1):143–150. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Feinberg R. F., Kao L. C., Haimowitz J. E., Queenan J. T., Jr, Wun T. C., Strauss J. F., 3rd, Kliman H. J. Plasminogen activator inhibitor types 1 and 2 in human trophoblasts. PAI-1 is an immunocytochemical marker of invading trophoblasts. Lab Invest. 1989 Jul;61(1):20–26. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gilabert J., Estellés A., Ayuso M. J., España F., Chirivella M., Grancha S., Micó J. M., Aznar J. Evaluation of plasminogen activators and plasminogen activator inhibitors in plasma and amniotic fluid in pregnancies complicated with intrauterine fetal growth retardation. Gynecol Obstet Invest. 1994;38(3):157–162. doi: 10.1159/000292470. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gilabert J., Estellés A., Aznar J., España F., Andrés C., Santos T., Vallés J. Contribution of platelets to increased plasminogen activator inhibitor type 1 in severe preeclampsia. Thromb Haemost. 1990 Jun 28;63(3):361–366. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Graeff H., von Hugo R., Schröck R. Recent aspects of hemostasis, hematology and hemorheology in preeclampsia-eclampsia. Eur J Obstet Gynecol Reprod Biol. 1984 May;17(2-3):91–102. doi: 10.1016/0028-2243(84)90133-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hamilton J. A., Whitty G. A., Wojta J., Gallichio M., McGrath K., Ianches G. Regulation of plasminogen activator inhibitor-1 levels in human monocytes. Cell Immunol. 1993 Nov;152(1):7–17. doi: 10.1006/cimm.1993.1263. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hamilton J. A., Wojta J., Gallichio M., McGrath K., Filonzi E. L. Contrasting effects of transforming growth factor-beta and IL-1 on the regulation of plasminogen activator inhibitors in human synovial fibroblasts. J Immunol. 1993 Nov 15;151(10):5154–5161. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Inglis T. C., Stuart J., George A. J., Davies A. J. Haemostatic and rheological changes in normal pregnancy and pre-eclampsia. Br J Haematol. 1982 Mar;50(3):461–465. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2141.1982.tb01941.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jenne D., Stanley K. K. Molecular cloning of S-protein, a link between complement, coagulation and cell-substrate adhesion. EMBO J. 1985 Dec 1;4(12):3153–3157. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1985.tb04058.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jättelä M., Kuusela P., Saksela E. Demonstration of tumor necrosis factor in human amniotic fluids and supernatants of placental and decidual tissues. Lab Invest. 1988 Jan;58(1):48–52. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kauma S., Matt D., Strom S., Eierman D., Turner T. Interleukin-1 beta, human leukocyte antigen HLA-DR alpha, and transforming growth factor-beta expression in endometrium, placenta, and placental membranes. Am J Obstet Gynecol. 1990 Nov;163(5 Pt 1):1430–1437. doi: 10.1016/0002-9378(90)90601-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Keeton M., Eguchi Y., Sawdey M., Ahn C., Loskutoff D. J. Cellular localization of type 1 plasminogen activator inhibitor messenger RNA and protein in murine renal tissue. Am J Pathol. 1993 Jan;142(1):59–70. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kruithof E. K., Tran-Thang C., Gudinchet A., Hauert J., Nicoloso G., Genton C., Welti H., Bachmann F. Fibrinolysis in pregnancy: a study of plasminogen activator inhibitors. Blood. 1987 Feb;69(2):460–466. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Loskutoff D. J., Sawdey M., Mimuro J. Type 1 plasminogen activator inhibitor. Prog Hemost Thromb. 1989;9:87–115. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Medcalf R. L., Kruithof E. K., Schleuning W. D. Plasminogen activator inhibitor 1 and 2 are tumor necrosis factor/cachectin-responsive genes. J Exp Med. 1988 Aug 1;168(2):751–759. doi: 10.1084/jem.168.2.751. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mimuro J., Loskutoff D. J. Purification of a protein from bovine plasma that binds to type 1 plasminogen activator inhibitor and prevents its interaction with extracellular matrix. Evidence that the protein is vitronectin. J Biol Chem. 1989 Jan 15;264(2):936–939. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Radtke K. P., Wenz K. H., Heimburger N. Isolation of plasminogen activator inhibitor-2 (PAI-2) from human placenta. Evidence for vitronectin/PAI-2 complexes in human placenta extract. Biol Chem Hoppe Seyler. 1990 Dec;371(12):1119–1127. doi: 10.1515/bchm3.1990.371.2.1119. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reith A., Booth N. A., Moore N. R., Cruickshank D. J., Bennett B. Plasminogen activator inhibitors (PAI-1 and PAI-2) in normal pregnancies, pre-eclampsia and hydatidiform mole. Br J Obstet Gynaecol. 1993 Apr;100(4):370–374. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-0528.1993.tb12982.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schleef R. R., Podor T. J., Dunne E., Mimuro J., Loskutoff D. J. The majority of type 1 plasminogen activator inhibitor associated with cultured human endothelial cells is located under the cells and is accessible to solution-phase tissue-type plasminogen activator. J Cell Biol. 1990 Jan;110(1):155–163. doi: 10.1083/jcb.110.1.155. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Seiffert D., Ciambrone G., Wagner N. V., Binder B. R., Loskutoff D. J. The somatomedin B domain of vitronectin. Structural requirements for the binding and stabilization of active type 1 plasminogen activator inhibitor. J Biol Chem. 1994 Jan 28;269(4):2659–2666. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sprengers E. D., Kluft C. Plasminogen activator inhibitors. Blood. 1987 Feb;69(2):381–387. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Taniguchi T., Matsuzaki N., Kameda T., Shimoya K., Jo T., Saji F., Tanizawa O. The enhanced production of placental interleukin-1 during labor and intrauterine infection. Am J Obstet Gynecol. 1991 Jul;165(1):131–137. doi: 10.1016/0002-9378(91)90241-i. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tsakok F. H., Koh S., Ratnam S. S. Coagulation and fibrinolysis in intact hydatidiform molar pregnancy. Br Med J. 1976 Dec 18;2(6050):1481–1484. doi: 10.1136/bmj.2.6050.1481. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Watanabe T., Araki M., Mimuro J., Tamada T., Sakata Y. Fibrinolytic components in fetal membranes and amniotic fluid. Am J Obstet Gynecol. 1993 Apr;168(4):1283–1289. doi: 10.1016/0002-9378(93)90381-r. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wolf H. K., Zarnegar R., Oliver L., Michalopoulos G. K. Hepatocyte growth factor in human placenta and trophoblastic disease. Am J Pathol. 1991 Apr;138(4):1035–1043. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ye R. D., Wun T. C., Sadler J. E. cDNA cloning and expression in Escherichia coli of a plasminogen activator inhibitor from human placenta. J Biol Chem. 1987 Mar 15;262(8):3718–3725. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- de Boer K., Lecander I., ten Cate J. W., Borm J. J., Treffers P. E. Placental-type plasminogen activator inhibitor in preeclampsia. Am J Obstet Gynecol. 1988 Mar;158(3 Pt 1):518–522. doi: 10.1016/0002-9378(88)90016-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]