Abstract
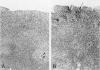
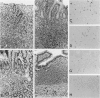
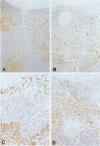
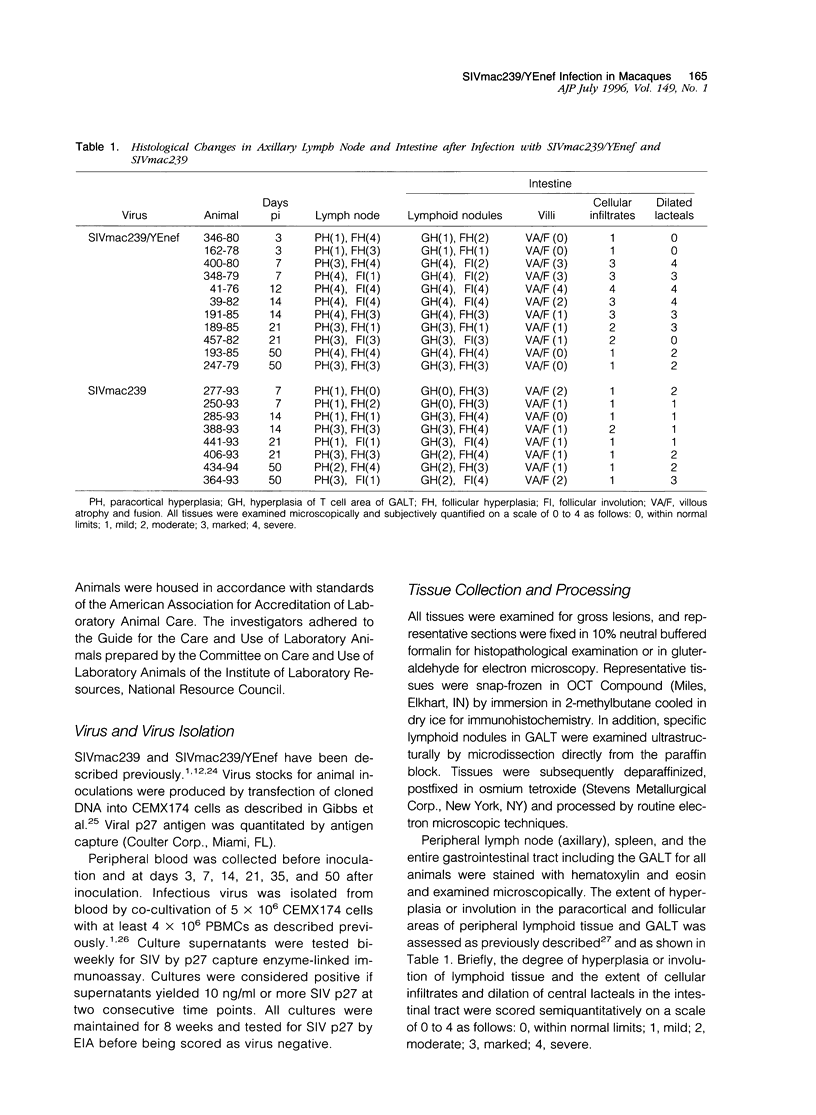
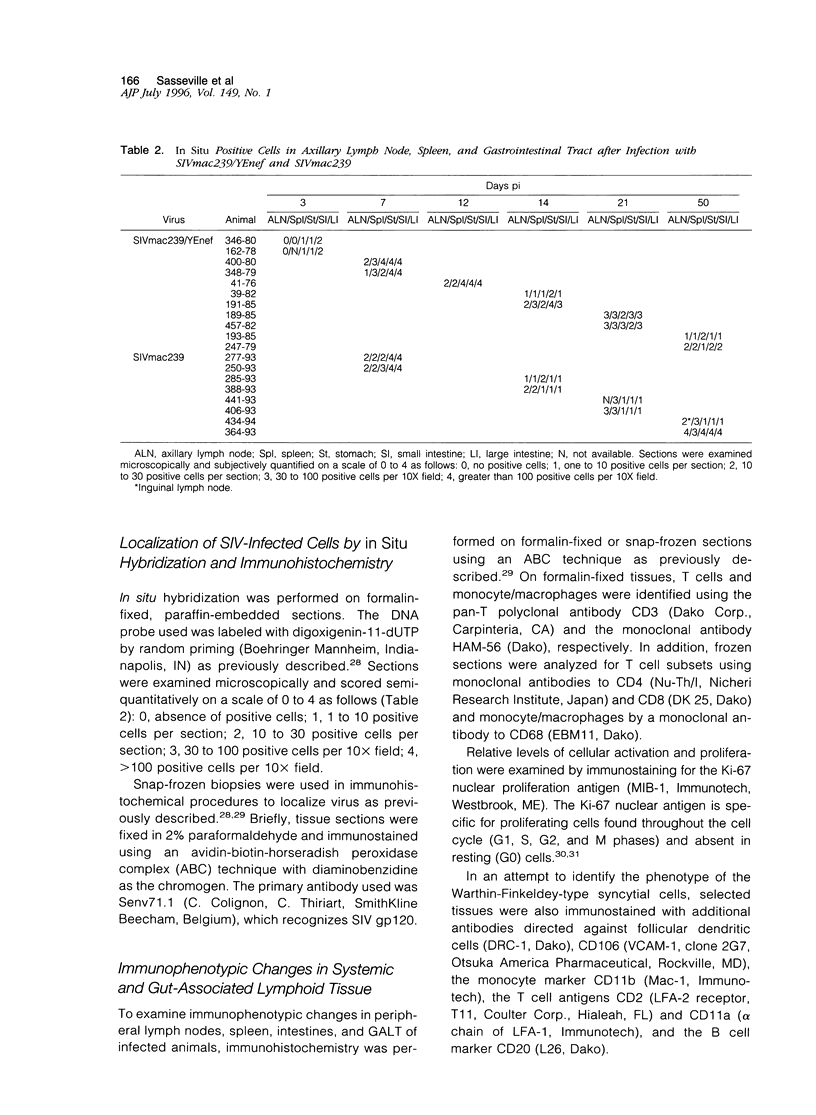
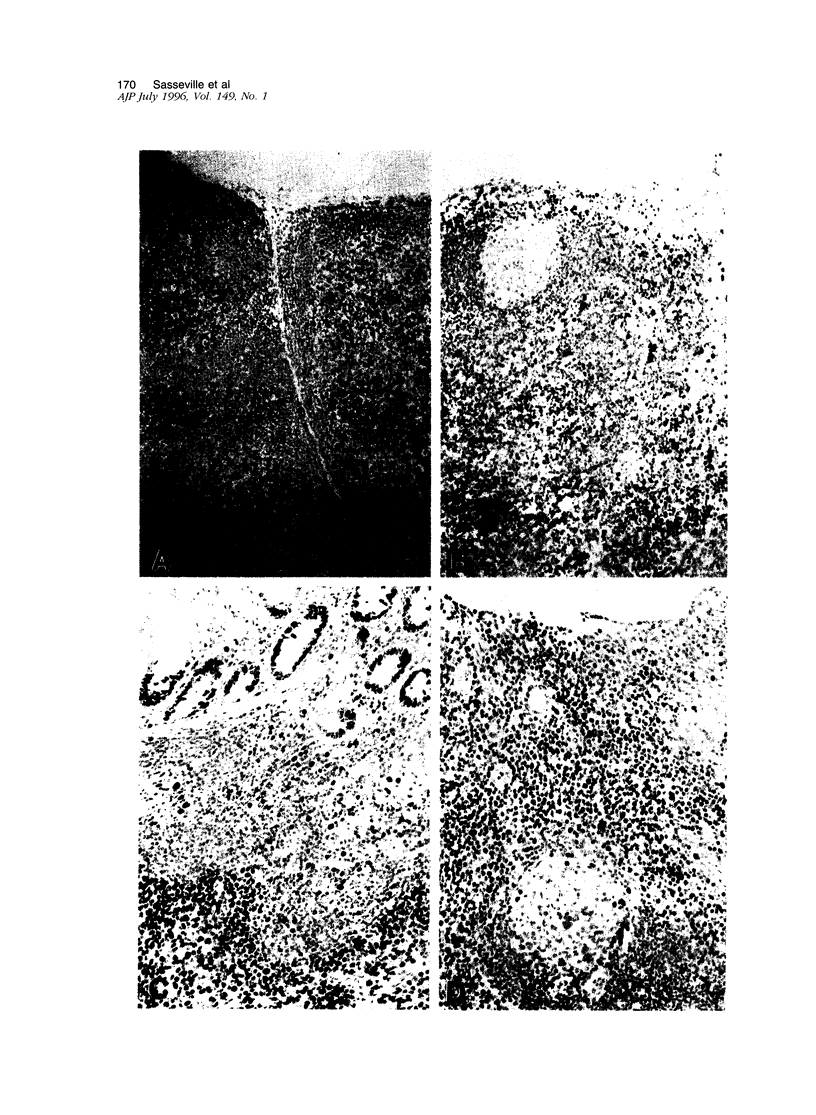
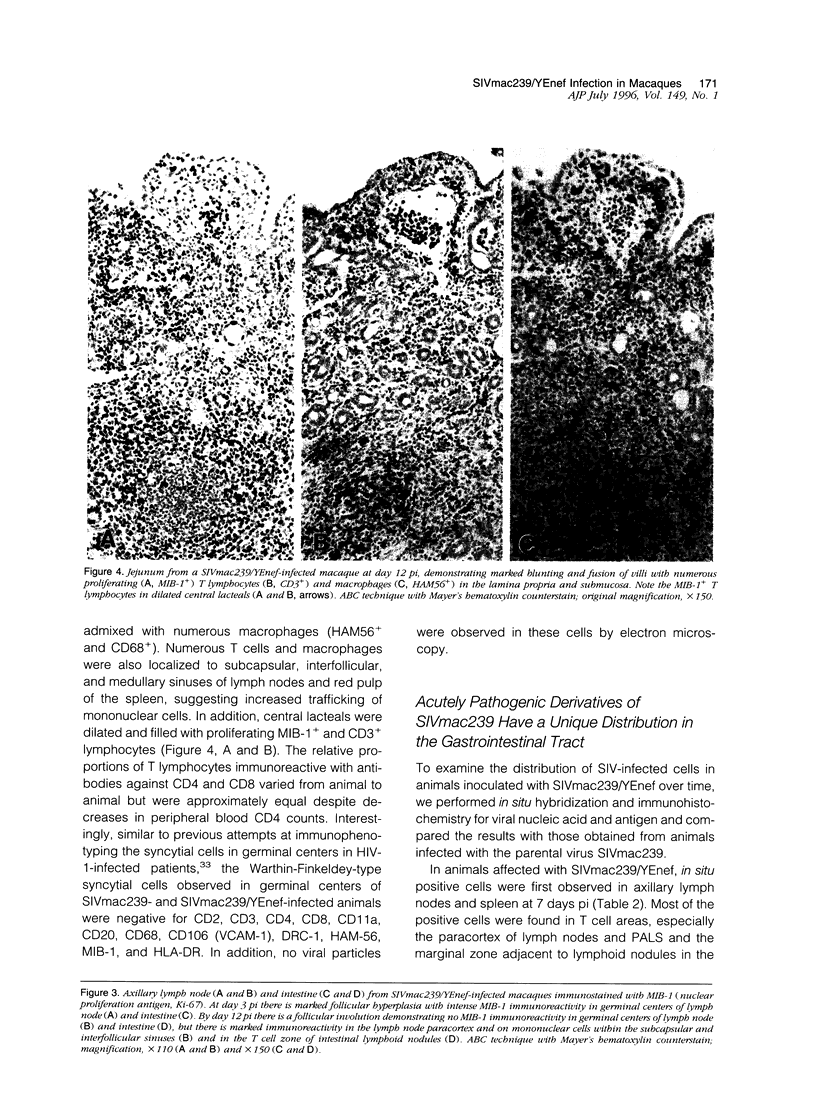
The molecularly cloned virus known as SIVmac239/YEnef causes extensive lymphocyte activation in unstimulated peripheral mononuclear cell cultures and induces an acute disease syndrome in macaque monkeys. Here we describe the histopathological and immunophenotypic changes and viral localization in peripheral lymph nodes, spleen, and gastrointestinal tract (including the gut-associated lymphoid tissue (GALT) in rhesus monkeys inoculated with SIVmac239/YEnet beginning at day 3 postinoculation (pi). The findings are compared with those of rhesus monkeys inoculated with the same dose of parental SIVmac239. Histopathological examination of peripheral lymphoid tissue and GALT demonstrated marked hyperplasia of T-cell-dependent regions and involution of germinal centers as early as day 7 pi. The most striking lesions were multifocal areas of lymphohistiocytic gastroenteritis and colitis. Cellular infiltrates peaked between day 7 and 14 pi and were composed primarily of CD3+ T lymphocytes and HAM-56+ monocyte/macrophages. Many of these inflammatory cells were also strongly immunoreactive for teh nuclear proliferation antigen Ki-67. Despite the presence of severe gastrointestinal pathology by day 7 pi, no significant difference in the numbers of virus-positive cells in the gastrointestinal tract was observed between these animals and SIVmac239-infected animals examined at the same time point. However, the distribution of virus in the gastrointestinal tract was markedly different, with virus localized to lymphoid nodules of GALT in SIVmac239-infected animals and restricted to areas of lymphohistiocytic gastroenteritis and colitis in animals infected with SIVmac239/YEnef. Our data indicate that the acute disease syndrome induced by SIVmac239/YEnef is not simply related to increased viral replication in the gastrointestinal tract but is likely due to inappropriate virus-induced T lymphocyte activation and proliferation in GALT and subsequent mucosal destruction.
Full text
PDF









Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Barbareschi M., Girlando S., Mauri F. M., Forti S., Eccher C., Mauri F. A., Togni R., Dalla Palma P., Doglioni C. Quantitative growth fraction evaluation with MIB1 and Ki67 antibodies in breast carcinomas. Am J Clin Pathol. 1994 Aug;102(2):171–175. doi: 10.1093/ajcp/102.2.171. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Berlin C., Berg E. L., Briskin M. J., Andrew D. P., Kilshaw P. J., Holzmann B., Weissman I. L., Hamann A., Butcher E. C. Alpha 4 beta 7 integrin mediates lymphocyte binding to the mucosal vascular addressin MAdCAM-1. Cell. 1993 Jul 16;74(1):185–195. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(93)90305-a. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Birx D. L., Lewis M. G., Vahey M., Tencer K., Zack P. M., Brown C. R., Jahrling P. B., Tosato G., Burke D., Redfield R. Association of interleukin-6 in the pathogenesis of acutely fatal SIVsmm/PBj-14 in pigtailed macaques. AIDS Res Hum Retroviruses. 1993 Nov;9(11):1123–1129. doi: 10.1089/aid.1993.9.1123. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burke A. P., Anderson D., Benson W., Turnicky R., Mannan P., Liang Y. H., Smialek J., Virmani R. Localization of human immunodeficiency virus 1 RNA in thymic tissues from asymptomatic drug addicts. Arch Pathol Lab Med. 1995 Jan;119(1):36–41. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burke A. P., Anderson D., Mannan P., Ribas J. L., Liang Y. H., Smialek J., Virmani R. Systemic lymphadenopathic histology in human immunodeficiency virus-1-seropositive drug addicts without apparent acquired immunodeficiency syndrome. Hum Pathol. 1994 Mar;25(3):248–256. doi: 10.1016/0046-8177(94)90196-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cepek K. L., Parker C. M., Madara J. L., Brenner M. B. Integrin alpha E beta 7 mediates adhesion of T lymphocytes to epithelial cells. J Immunol. 1993 Apr 15;150(8 Pt 1):3459–3470. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chakrabarti L., Isola P., Cumont M. C., Claessens-Maire M. A., Hurtrel M., Montagnier L., Hurtrel B. Early stages of simian immunodeficiency virus infection in lymph nodes. Evidence for high viral load and successive populations of target cells. Am J Pathol. 1994 Jun;144(6):1226–1237. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Daniel M. D., Letvin N. L., Sehgal P. K., Hunsmann G., Schmidt D. K., King N. W., Desrosiers R. C. Long-term persistent infection of macaque monkeys with the simian immunodeficiency virus. J Gen Virol. 1987 Dec;68(Pt 12):3183–3189. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-68-12-3183. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Desrosiers R. C., Hansen-Moosa A., Mori K., Bouvier D. P., King N. W., Daniel M. D., Ringler D. J. Macrophage-tropic variants of SIV are associated with specific AIDS-related lesions but are not essential for the development of AIDS. Am J Pathol. 1991 Jul;139(1):29–35. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Desrosiers R. C. The simian immunodeficiency viruses. Annu Rev Immunol. 1990;8:557–578. doi: 10.1146/annurev.iy.08.040190.003013. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Desrosiers R. C., Wyand M. S., Kodama T., Ringler D. J., Arthur L. O., Sehgal P. K., Letvin N. L., King N. W., Daniel M. D. Vaccine protection against simian immunodeficiency virus infection. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Aug;86(16):6353–6357. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.16.6353. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dewhurst S., Embretson J. E., Anderson D. C., Mullins J. I., Fultz P. N. Sequence analysis and acute pathogenicity of molecularly cloned SIVSMM-PBj14. Nature. 1990 Jun 14;345(6276):636–640. doi: 10.1038/345636a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dewhurst S., Embretson J. E., Fultz P. N., Mullins J. I. Molecular clones from a non-acutely pathogenic derivative of SIVsmmPBj14: characterization and comparison to acutely pathogenic clones. AIDS Res Hum Retroviruses. 1992 Jun;8(6):1179–1187. doi: 10.1089/aid.1992.8.1179. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dittmar M. T., Cichutek K., Fultz P. N., Kurth R. The U3 promoter region of the acutely lethal simian immunodeficiency virus clone smmPBj1.9 confers related biological activity on the apathogenic clone agm3mc. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1995 Feb 28;92(5):1362–1366. doi: 10.1073/pnas.92.5.1362. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dollard S. C., Gummuluru S., Tsang S., Fultz P. N., Dewhurst S. Enhanced responsiveness to nuclear factor kappa B contributes to the unique phenotype of simian immunodeficiency virus variant SIVsmmPBj14. J Virol. 1994 Dec;68(12):7800–7809. doi: 10.1128/jvi.68.12.7800-7809.1994. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Du Z., Lang S. M., Sasseville V. G., Lackner A. A., Ilyinskii P. O., Daniel M. D., Jung J. U., Desrosiers R. C. Identification of a nef allele that causes lymphocyte activation and acute disease in macaque monkeys. Cell. 1995 Aug 25;82(4):665–674. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(95)90038-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ewing E. P., Jr, Chandler F. W., Spira T. J., Brynes R. K., Chan W. C. Primary lymph node pathology in AIDS and AIDS-related lymphadenopathy. Arch Pathol Lab Med. 1985 Nov;109(11):977–981. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fultz P. N., McClure H. M., Anderson D. C., Switzer W. M. Identification and biologic characterization of an acutely lethal variant of simian immunodeficiency virus from sooty mangabeys (SIV/SMM). AIDS Res Hum Retroviruses. 1989 Aug;5(4):397–409. doi: 10.1089/aid.1989.5.397. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fultz P. N., Zack P. M. Unique lentivirus--host interactions: SIVsmmPBj14 infection of macaques. Virus Res. 1994 May;32(2):205–225. doi: 10.1016/0168-1702(94)90042-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gardner M. B., Luciw P. A. Simian immunodeficiency viruses and their relationship to the human immunodeficiency viruses. AIDS. 1988;2 (Suppl 1):S3–10. doi: 10.1097/00002030-198800001-00002. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gibbs J. S., Regier D. A., Desrosiers R. C. Construction and in vitro properties of HIV-1 mutants with deletions in "nonessential" genes. AIDS Res Hum Retroviruses. 1994 Apr;10(4):343–350. doi: 10.1089/aid.1994.10.343. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gummuluru S., Novembre F. J., Seshi B., Dewhurst S. SIVsmmPBj14 induces expression of a mucosal integrin on macaque lymphocytes. Virology. 1996 Jan 1;215(1):97–100. doi: 10.1006/viro.1996.0010. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hamann A., Andrew D. P., Jablonski-Westrich D., Holzmann B., Butcher E. C. Role of alpha 4-integrins in lymphocyte homing to mucosal tissues in vivo. J Immunol. 1994 Apr 1;152(7):3282–3293. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heise C., Miller C. J., Lackner A., Dandekar S. Primary acute simian immunodeficiency virus infection of intestinal lymphoid tissue is associated with gastrointestinal dysfunction. J Infect Dis. 1994 May;169(5):1116–1120. doi: 10.1093/infdis/169.5.1116. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heise C., Vogel P., Miller C. J., Halsted C. H., Dandekar S. Simian immunodeficiency virus infection of the gastrointestinal tract of rhesus macaques. Functional, pathological, and morphological changes. Am J Pathol. 1993 Jun;142(6):1759–1771. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Horvath C. J., Desrosiers R. C., Sehgal P. K., King N. W., Ringler D. J. Effect of simian immunodeficiency virus infection on tumor necrosis factor-alpha production by alveolar macrophages. Lab Invest. 1991 Sep;65(3):280–286. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Horvath C. J., Hunt R. D., Simon M. A., Sehgal P. K., Ringler D. J. An immunohistologic study of granulomatous inflammation in SIV-infected rhesus monkeys. J Leukoc Biol. 1993 May;53(5):532–540. doi: 10.1002/jlb.53.5.532. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kamel O. W., LeBrun D. P., Berry G. J., Dorfman R. F., Warnke R. A. Warthin-Finkeldey polykaryocytes demonstrate a T-cell immunophenotype. Am J Clin Pathol. 1992 Feb;97(2):179–183. doi: 10.1093/ajcp/97.2.179. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kestler H. W., 3rd, Ringler D. J., Mori K., Panicali D. L., Sehgal P. K., Daniel M. D., Desrosiers R. C. Importance of the nef gene for maintenance of high virus loads and for development of AIDS. Cell. 1991 May 17;65(4):651–662. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(91)90097-i. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kjeldsberg C. R., Kim H. Polykaryocytes resembling Warthin-Finkeldey giant cells in reactive and neoplastic lymphoid disorders. Hum Pathol. 1981 Mar;12(3):267–272. doi: 10.1016/s0046-8177(81)80128-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kodama T., Mori K., Kawahara T., Ringler D. J., Desrosiers R. C. Analysis of simian immunodeficiency virus sequence variation in tissues of rhesus macaques with simian AIDS. J Virol. 1993 Nov;67(11):6522–6534. doi: 10.1128/jvi.67.11.6522-6534.1993. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kraal G., Schornagel K., Streeter P. R., Holzmann B., Butcher E. C. Expression of the mucosal vascular addressin, MAdCAM-1, on sinus-lining cells in the spleen. Am J Pathol. 1995 Sep;147(3):763–771. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lackner A. A. Pathology of simian immunodeficiency virus induced disease. Curr Top Microbiol Immunol. 1994;188:35–64. doi: 10.1007/978-3-642-78536-8_3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lackner A. A., Vogel P., Ramos R. A., Kluge J. D., Marthas M. Early events in tissues during infection with pathogenic (SIVmac239) and nonpathogenic (SIVmac1A11) molecular clones of simian immunodeficiency virus. Am J Pathol. 1994 Aug;145(2):428–439. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Landberg G., Tan E. M., Roos G. Flow cytometric multiparameter analysis of proliferating cell nuclear antigen/cyclin and Ki-67 antigen: a new view of the cell cycle. Exp Cell Res. 1990 Mar;187(1):111–118. doi: 10.1016/0014-4827(90)90124-s. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lewis M. G., Zack P. M., Elkins W. R., Jahrling P. B. Infection of rhesus and cynomolgus macaques with a rapidly fatal SIV (SIVSMM/PBj) isolate from sooty mangabeys. AIDS Res Hum Retroviruses. 1992 Sep;8(9):1631–1639. doi: 10.1089/aid.1992.8.1631. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lionetti P., Breese E., Braegger C. P., Murch S. H., Taylor J., MacDonald T. T. T-cell activation can induce either mucosal destruction or adaptation in cultured human fetal small intestine. Gastroenterology. 1993 Aug;105(2):373–381. doi: 10.1016/0016-5085(93)90710-t. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MacDonald T. T., Spencer J. Cell-mediated immune injury in the intestine. Gastroenterol Clin North Am. 1992 Jun;21(2):367–386. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MacDonald T. T., Spencer J. Evidence that activated mucosal T cells play a role in the pathogenesis of enteropathy in human small intestine. J Exp Med. 1988 Apr 1;167(4):1341–1349. doi: 10.1084/jem.167.4.1341. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mori K., Ringler D. J., Desrosiers R. C. Restricted replication of simian immunodeficiency virus strain 239 in macrophages is determined by env but is not due to restricted entry. J Virol. 1993 May;67(5):2807–2814. doi: 10.1128/jvi.67.5.2807-2814.1993. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mori K., Ringler D. J., Kodama T., Desrosiers R. C. Complex determinants of macrophage tropism in env of simian immunodeficiency virus. J Virol. 1992 Apr;66(4):2067–2075. doi: 10.1128/jvi.66.4.2067-2075.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Naidu Y. M., Kestler H. W., 3rd, Li Y., Butler C. V., Silva D. P., Schmidt D. K., Troup C. D., Sehgal P. K., Sonigo P., Daniel M. D. Characterization of infectious molecular clones of simian immunodeficiency virus (SIVmac) and human immunodeficiency virus type 2: persistent infection of rhesus monkeys with molecularly cloned SIVmac. J Virol. 1988 Dec;62(12):4691–4696. doi: 10.1128/jvi.62.12.4691-4696.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Novembre F. J., Johnson P. R., Lewis M. G., Anderson D. C., Klumpp S., McClure H. M., Hirsch V. M. Multiple viral determinants contribute to pathogenicity of the acutely lethal simian immunodeficiency virus SIVsmmPBj variant. J Virol. 1993 May;67(5):2466–2474. doi: 10.1128/jvi.67.5.2466-2474.1993. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pawson T. Protein modules and signalling networks. Nature. 1995 Feb 16;373(6515):573–580. doi: 10.1038/373573a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Piguet P. F., Grau G. E., Allet B., Vassalli P. Tumor necrosis factor/cachectin is an effector of skin and gut lesions of the acute phase of graft-vs.-host disease. J Exp Med. 1987 Nov 1;166(5):1280–1289. doi: 10.1084/jem.166.5.1280. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Regier D. A., Desrosiers R. C. The complete nucleotide sequence of a pathogenic molecular clone of simian immunodeficiency virus. AIDS Res Hum Retroviruses. 1990 Nov;6(11):1221–1231. doi: 10.1089/aid.1990.6.1221. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ringler D. J., Hancock W. W., King N. W., Letvin N. L., Daniel M. D., Desrosiers R. C., Murphy G. F. Immunophenotypic characterization of the cutaneous exanthem of SIV-infected rhesus monkeys. Apposition of degenerative Langerhans cells and cytotoxic lymphocytes during the development of acquired immunodeficiency syndrome. Am J Pathol. 1987 Feb;126(2):199–207. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ringler D. J., Murphy G. F., King N. W., Jr An erythematous maculopapular eruption in macaques infected with an HTLV-III-like virus (STLV-III). J Invest Dermatol. 1986 Nov;87(5):674–677. doi: 10.1111/1523-1747.ep12456437. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ringler D. J., Wyand M. S., Walsh D. G., MacKey J. J., Chalifoux L. V., Popovic M., Minassian A. A., Sehgal P. K., Daniel M. D., Desrosiers R. C. Cellular localization of simian immunodeficiency virus in lymphoid tissues. I. Immunohistochemistry and electron microscopy. Am J Pathol. 1989 Feb;134(2):373–383. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sartor R. B. Cytokines in intestinal inflammation: pathophysiological and clinical considerations. Gastroenterology. 1994 Feb;106(2):533–539. doi: 10.1016/0016-5085(94)90614-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Streeter P. R., Berg E. L., Rouse B. T., Bargatze R. F., Butcher E. C. A tissue-specific endothelial cell molecule involved in lymphocyte homing. Nature. 1988 Jan 7;331(6151):41–46. doi: 10.1038/331041a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wyand M. S., Ringler D. J., Naidu Y. M., Mattmuller M., Chalifoux L. V., Sehgal P. K., Daniel M. D., Desrosiers R. C., King N. W. Cellular localization of simian immunodeficiency virus in lymphoid tissues. II. In situ hybridization. Am J Pathol. 1989 Feb;134(2):385–393. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]