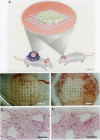
Abstract
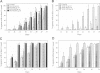
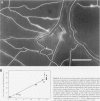
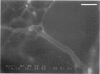
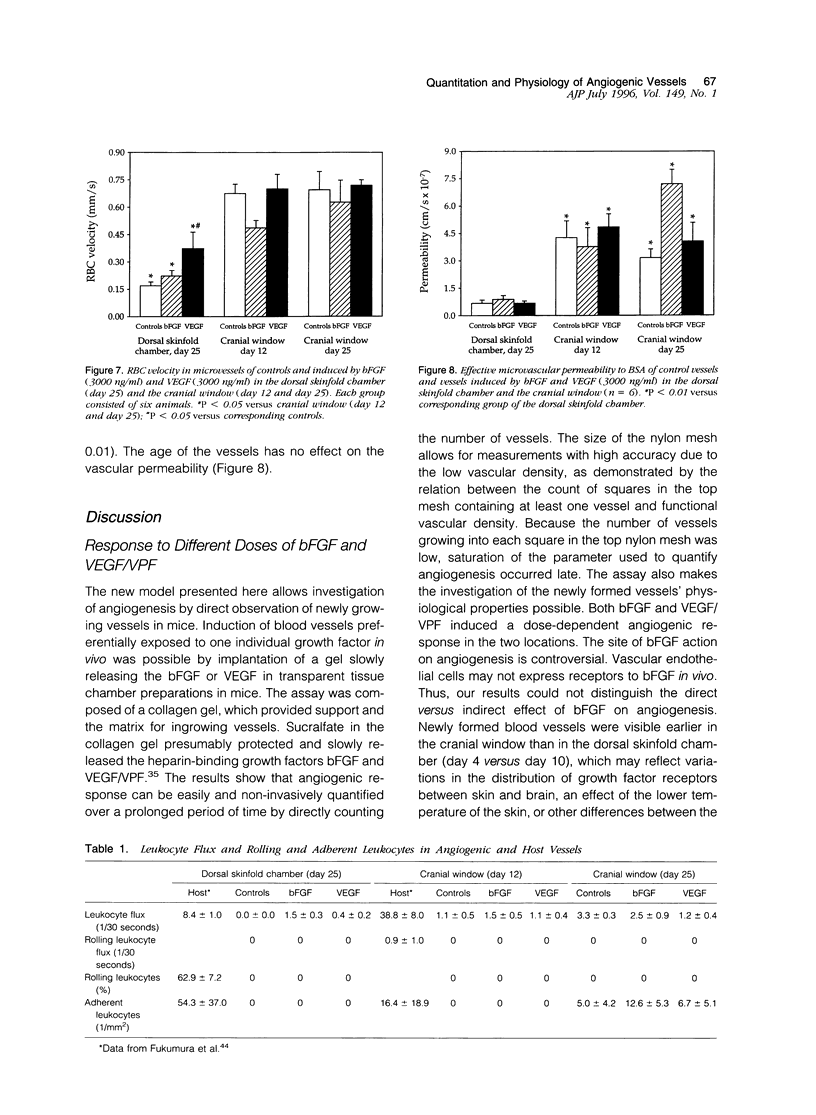
A prerequisite for the development of novel angiogenic and anti-angiogenic agents is the availability of routine in vivo assays that permit 1) repeated, long-term quantitation of angiogenesis and 2) physiological characterization of angiogenic vessels. We report here the development of such an assay in mice. Using this assay, we tested the hypothesis that the physiological properties of angiogenic vessels governed by the microenvironment and vessel origin rather than the initial angiogenic stimulus. Gels containing basic fibroblast growth factor (bFGF) or vascular endothelial growth (VEGF) were implanted in transparent windows in the dorsal skin or cranium of mice. Vessels could be continuously and non-invasively monitored and easily quantified for more than 5 weeks after gel implantation. Newly formed vessels were first visible on day 4 in the cranial window and day 10 in the dorsal skinfold chamber, respectively. The number of vessels was dependent on the dose of bFGF and VEGF. At 3000 ng/ml, bFGF- and VEGF-induced blood vessels had similar diameters, red blood cell velocities, and microvascular permeability to albumin. However, red blood cell velocities and microvascular permeability to albumin were higher in the cranial window than in the dorsal skinfold chamber. Leukocyte-endothelial interaction was nearly zero in both sites. Thus, newly grown microvessels resembled vessels of granulation and neoplastic tissue in many aspects. Their physiological properties were mainly determined by the microenvironment, whereas the initial angiogenic response was stimulated by growth factors.
Full text
PDF

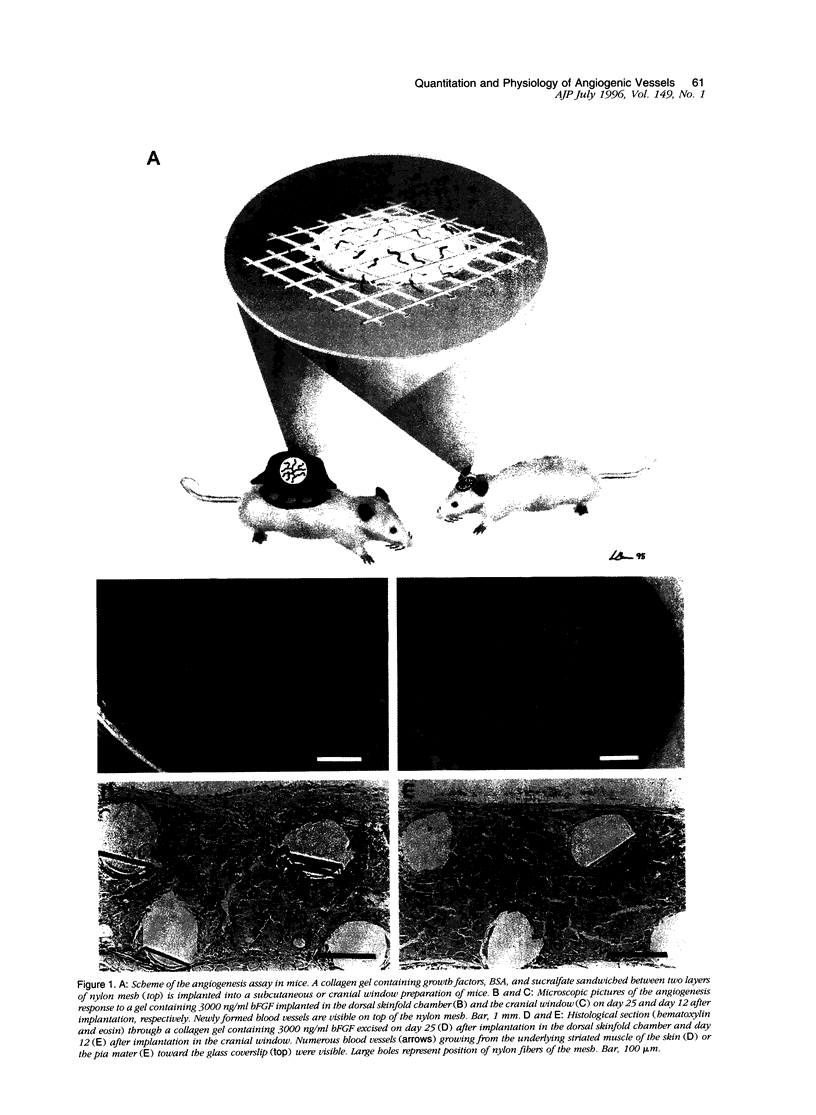


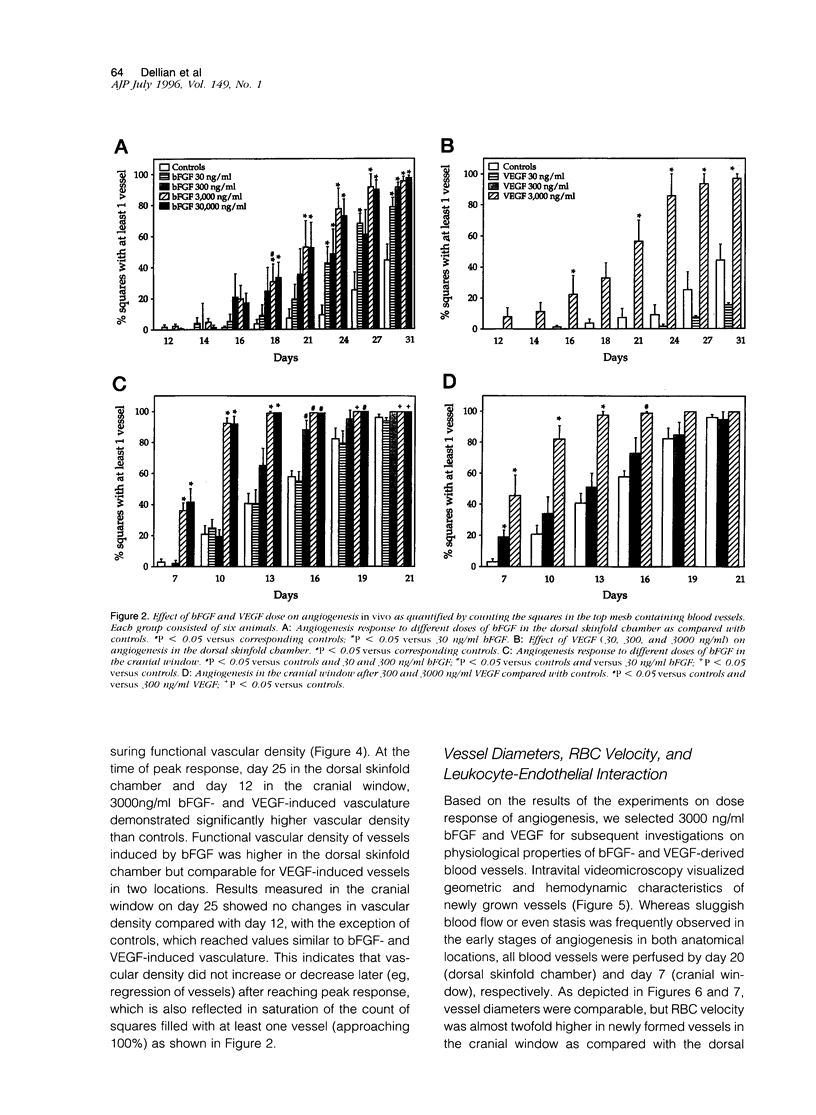
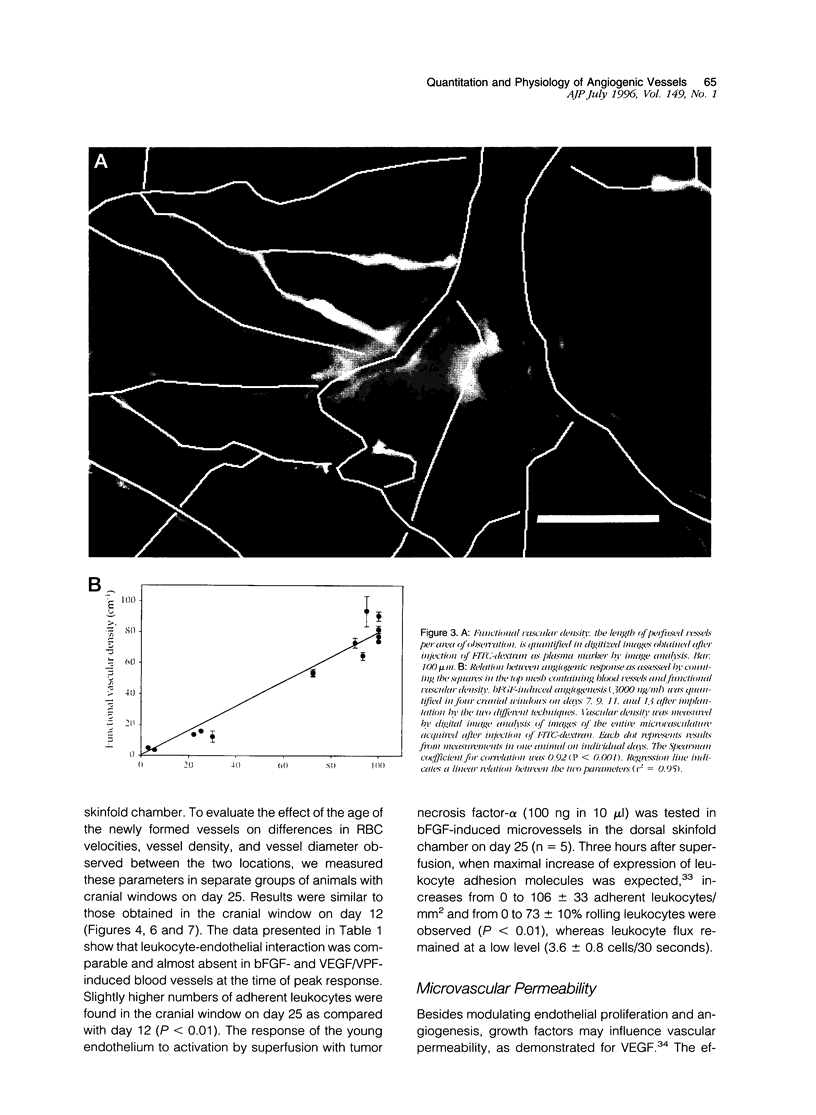
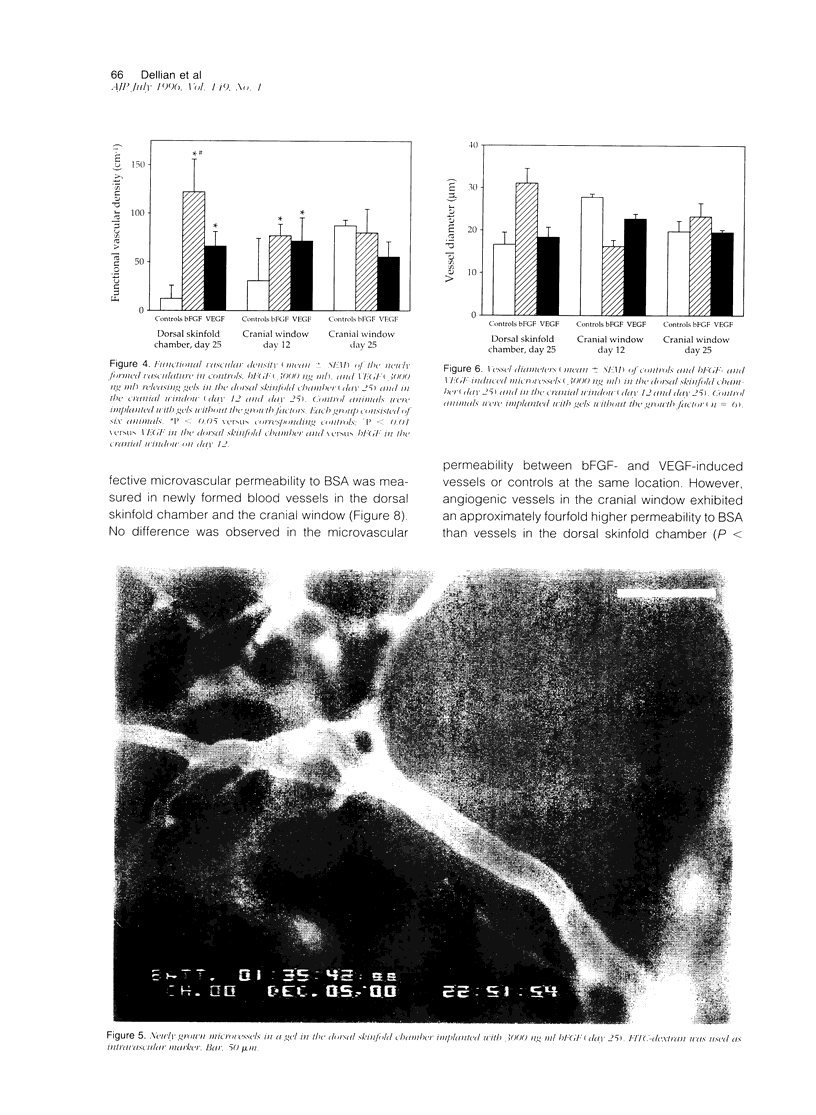




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Andrade S. P., Fan T. P., Lewis G. P. Quantitative in-vivo studies on angiogenesis in a rat sponge model. Br J Exp Pathol. 1987 Dec;68(6):755–766. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Atherton A., Born G. V. Quantitative investigations of the adhesiveness of circulating polymorphonuclear leucocytes to blood vessel walls. J Physiol. 1972 Apr;222(2):447–474. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1972.sp009808. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Auerbach R., Auerbach W., Polakowski I. Assays for angiogenesis: a review. Pharmacol Ther. 1991;51(1):1–11. doi: 10.1016/0163-7258(91)90038-n. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Axelsson K., Ljung B. M., Moore D. H., 2nd, Thor A. D., Chew K. L., Edgerton S. M., Smith H. S., Mayall B. H. Tumor angiogenesis as a prognostic assay for invasive ductal breast carcinoma. J Natl Cancer Inst. 1995 Jul 5;87(13):997–1008. doi: 10.1093/jnci/87.13.997. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Broadwell R. D., Baker B. J., Ebert P. S., Hickey W. F. Allografts of CNS tissue possess a blood-brain barrier: III. Neuropathological, methodological, and immunological considerations. Microsc Res Tech. 1994 Apr 15;27(6):471–494. doi: 10.1002/jemt.1070270603. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brogi E., Wu T., Namiki A., Isner J. M. Indirect angiogenic cytokines upregulate VEGF and bFGF gene expression in vascular smooth muscle cells, whereas hypoxia upregulates VEGF expression only. Circulation. 1994 Aug;90(2):649–652. doi: 10.1161/01.cir.90.2.649. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brooks P. C., Clark R. A., Cheresh D. A. Requirement of vascular integrin alpha v beta 3 for angiogenesis. Science. 1994 Apr 22;264(5158):569–571. doi: 10.1126/science.7512751. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Collins P. D., Connolly D. T., Williams T. J. Characterization of the increase in vascular permeability induced by vascular permeability factor in vivo. Br J Pharmacol. 1993 May;109(1):195–199. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1993.tb13553.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dellian M., Abels C., Kuhnle G. E., Goetz A. E. Effects of photodynamic therapy on leucocyte-endothelium interaction: differences between normal and tumour tissue. Br J Cancer. 1995 Nov;72(5):1125–1130. doi: 10.1038/bjc.1995.475. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dewhirst M. W., Tso C. Y., Oliver R., Gustafson C. S., Secomb T. W., Gross J. F. Morphologic and hemodynamic comparison of tumor and healing normal tissue microvasculature. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. 1989 Jul;17(1):91–99. doi: 10.1016/0360-3016(89)90375-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dudar T. E., Jain R. K. Microcirculatory flow changes during tissue growth. Microvasc Res. 1983 Jan;25(1):1–21. doi: 10.1016/0026-2862(83)90040-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dvorak H. F. Tumors: wounds that do not heal. Similarities between tumor stroma generation and wound healing. N Engl J Med. 1986 Dec 25;315(26):1650–1659. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198612253152606. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Endrich B., Hammersen F., Götz A., Messmer K. Microcirculatory blood flow, capillary morphology and local oxygen pressure of the hamster amelanotic melanoma A-Mel-3. J Natl Cancer Inst. 1982 Mar;68(3):475–485. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Endrich B., Intaglietta M., Reinhold H. S., Gross J. F. Hemodynamic characteristics in microcirculatory blood channels during early tumor growth. Cancer Res. 1979 Jan;39(1):17–23. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Endrich B., Reinhold H. S., Gross J. F., Intaglietta M. Tissue perfusion inhomogeneity during early tumor growth in rats. J Natl Cancer Inst. 1979 Feb;62(2):387–395. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fidler I. J., Ellis L. M. The implications of angiogenesis for the biology and therapy of cancer metastasis. Cell. 1994 Oct 21;79(2):185–188. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(94)90187-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fidler I. J. Modulation of the organ microenvironment for treatment of cancer metastasis. J Natl Cancer Inst. 1995 Nov 1;87(21):1588–1592. doi: 10.1093/jnci/87.21.1588. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Folkman J. Angiogenesis in cancer, vascular, rheumatoid and other disease. Nat Med. 1995 Jan;1(1):27–31. doi: 10.1038/nm0195-27. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fukumura D., Salehi H. A., Witwer B., Tuma R. F., Melder R. J., Jain R. K. Tumor necrosis factor alpha-induced leukocyte adhesion in normal and tumor vessels: effect of tumor type, transplantation site, and host strain. Cancer Res. 1995 Nov 1;55(21):4824–4829. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gerlowski L. E., Jain R. K. Microvascular permeability of normal and neoplastic tissues. Microvasc Res. 1986 May;31(3):288–305. doi: 10.1016/0026-2862(86)90018-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hu D. E., Fan T. P. Suppression of VEGF-induced angiogenesis by the protein tyrosine kinase inhibitor, lavendustin A. Br J Pharmacol. 1995 Jan;114(2):262–268. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1995.tb13221.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hynes R. O. Integrins: versatility, modulation, and signaling in cell adhesion. Cell. 1992 Apr 3;69(1):11–25. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(92)90115-s. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kandel J., Bossy-Wetzel E., Radvanyi F., Klagsbrun M., Folkman J., Hanahan D. Neovascularization is associated with a switch to the export of bFGF in the multistep development of fibrosarcoma. Cell. 1991 Sep 20;66(6):1095–1104. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(91)90033-u. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kim K. J., Li B., Winer J., Armanini M., Gillett N., Phillips H. S., Ferrara N. Inhibition of vascular endothelial growth factor-induced angiogenesis suppresses tumour growth in vivo. Nature. 1993 Apr 29;362(6423):841–844. doi: 10.1038/362841a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Koch A. E., Halloran M. M., Haskell C. J., Shah M. R., Polverini P. J. Angiogenesis mediated by soluble forms of E-selectin and vascular cell adhesion molecule-1. Nature. 1995 Aug 10;376(6540):517–519. doi: 10.1038/376517a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leibovich S. J., Polverini P. J., Shepard H. M., Wiseman D. M., Shively V., Nuseir N. Macrophage-induced angiogenesis is mediated by tumour necrosis factor-alpha. Nature. 1987 Oct 15;329(6140):630–632. doi: 10.1038/329630a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leung D. W., Cachianes G., Kuang W. J., Goeddel D. V., Ferrara N. Vascular endothelial growth factor is a secreted angiogenic mitogen. Science. 1989 Dec 8;246(4935):1306–1309. doi: 10.1126/science.2479986. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leunig M., Yuan F., Menger M. D., Boucher Y., Goetz A. E., Messmer K., Jain R. K. Angiogenesis, microvascular architecture, microhemodynamics, and interstitial fluid pressure during early growth of human adenocarcinoma LS174T in SCID mice. Cancer Res. 1992 Dec 1;52(23):6553–6560. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Loftus J. C., Smith J. W., Ginsberg M. H. Integrin-mediated cell adhesion: the extracellular face. J Biol Chem. 1994 Oct 14;269(41):25235–25238. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Melder R. J., Munn L. L., Yamada S., Ohkubo C., Jain R. K. Selectin- and integrin-mediated T-lymphocyte rolling and arrest on TNF-alpha-activated endothelium: augmentation by erythrocytes. Biophys J. 1995 Nov;69(5):2131–2138. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(95)80087-1. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miller J. W., Adamis A. P., Shima D. T., D'Amore P. A., Moulton R. S., O'Reilly M. S., Folkman J., Dvorak H. F., Brown L. F., Berse B. Vascular endothelial growth factor/vascular permeability factor is temporally and spatially correlated with ocular angiogenesis in a primate model. Am J Pathol. 1994 Sep;145(3):574–584. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nguyen M., Shing Y., Folkman J. Quantitation of angiogenesis and antiangiogenesis in the chick embryo chorioallantoic membrane. Microvasc Res. 1994 Jan;47(1):31–40. doi: 10.1006/mvre.1994.1003. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nguyen M., Strubel N. A., Bischoff J. A role for sialyl Lewis-X/A glycoconjugates in capillary morphogenesis. Nature. 1993 Sep 16;365(6443):267–269. doi: 10.1038/365267a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nolte D., Hecht R., Schmid P., Botzlar A., Menger M. D., Neumueller C., Sinowatz F., Vestweber D., Messmer K. Role of Mac-1 and ICAM-1 in ischemia-reperfusion injury in a microcirculation model of BALB/C mice. Am J Physiol. 1994 Oct;267(4 Pt 2):H1320–H1328. doi: 10.1152/ajpheart.1994.267.4.H1320. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- O'Brien T., Cranston D., Fuggle S., Bicknell R., Harris A. L. Different angiogenic pathways characterize superficial and invasive bladder cancer. Cancer Res. 1995 Feb 1;55(3):510–513. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ohkubo C., Bigos D., Jain R. K. Interleukin 2 induced leukocyte adhesion to the normal and tumor microvascular endothelium in vivo and its inhibition by dextran sulfate: implications for vascular leak syndrome. Cancer Res. 1991 Mar 1;51(5):1561–1563. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Passaniti A., Taylor R. M., Pili R., Guo Y., Long P. V., Haney J. A., Pauly R. R., Grant D. S., Martin G. R. A simple, quantitative method for assessing angiogenesis and antiangiogenic agents using reconstituted basement membrane, heparin, and fibroblast growth factor. Lab Invest. 1992 Oct;67(4):519–528. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Plate K. H., Breier G., Millauer B., Ullrich A., Risau W. Up-regulation of vascular endothelial growth factor and its cognate receptors in a rat glioma model of tumor angiogenesis. Cancer Res. 1993 Dec 1;53(23):5822–5827. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Plate K. H., Breier G., Weich H. A., Risau W. Vascular endothelial growth factor is a potential tumour angiogenesis factor in human gliomas in vivo. Nature. 1992 Oct 29;359(6398):845–848. doi: 10.1038/359845a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pötgens A. J., Lubsen N. H., van Altena M. C., Schoenmakers J. G., Ruiter D. J., de Waal R. M. Vascular permeability factor expression influences tumor angiogenesis in human melanoma lines xenografted to nude mice. Am J Pathol. 1995 Jan;146(1):197–209. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roberts W. G., Palade G. E. Increased microvascular permeability and endothelial fenestration induced by vascular endothelial growth factor. J Cell Sci. 1995 Jun;108(Pt 6):2369–2379. doi: 10.1242/jcs.108.6.2369. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schmid-Schoenbein G. W., Zweifach B. W., Kovalcheck S. The application of stereological principles to morphometry of the microcirculation in different tissues. Microvasc Res. 1977 Nov;14(3):303–317. doi: 10.1016/0026-2862(77)90028-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Senger D. R., Galli S. J., Dvorak A. M., Perruzzi C. A., Harvey V. S., Dvorak H. F. Tumor cells secrete a vascular permeability factor that promotes accumulation of ascites fluid. Science. 1983 Feb 25;219(4587):983–985. doi: 10.1126/science.6823562. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Singh R. K., Bucana C. D., Gutman M., Fan D., Wilson M. R., Fidler I. J. Organ site-dependent expression of basic fibroblast growth factor in human renal cell carcinoma cells. Am J Pathol. 1994 Aug;145(2):365–374. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sprugel K. H., McPherson J. M., Clowes A. W., Ross R. Effects of growth factors in vivo. I. Cell ingrowth into porous subcutaneous chambers. Am J Pathol. 1987 Dec;129(3):601–613. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tuder R. M., Flook B. E., Voelkel N. F. Increased gene expression for VEGF and the VEGF receptors KDR/Flk and Flt in lungs exposed to acute or to chronic hypoxia. Modulation of gene expression by nitric oxide. J Clin Invest. 1995 Apr;95(4):1798–1807. doi: 10.1172/JCI117858. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Warren R. S., Yuan H., Matli M. R., Gillett N. A., Ferrara N. Regulation by vascular endothelial growth factor of human colon cancer tumorigenesis in a mouse model of experimental liver metastasis. J Clin Invest. 1995 Apr;95(4):1789–1797. doi: 10.1172/JCI117857. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weidner N., Semple J. P., Welch W. R., Folkman J. Tumor angiogenesis and metastasis--correlation in invasive breast carcinoma. N Engl J Med. 1991 Jan 3;324(1):1–8. doi: 10.1056/NEJM199101033240101. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wilting J., Christ B., Bokeloh M., Weich H. A. In vivo effects of vascular endothelial growth factor on the chicken chorioallantoic membrane. Cell Tissue Res. 1993 Oct;274(1):163–172. doi: 10.1007/BF00327997. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wu N. Z., Klitzman B., Dodge R., Dewhirst M. W. Diminished leukocyte-endothelium interaction in tumor microvessels. Cancer Res. 1992 Aug 1;52(15):4265–4268. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yuan F., Dellian M., Fukumura D., Leunig M., Berk D. A., Torchilin V. P., Jain R. K. Vascular permeability in a human tumor xenograft: molecular size dependence and cutoff size. Cancer Res. 1995 Sep 1;55(17):3752–3756. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yuan F., Salehi H. A., Boucher Y., Vasthare U. S., Tuma R. F., Jain R. K. Vascular permeability and microcirculation of gliomas and mammary carcinomas transplanted in rat and mouse cranial windows. Cancer Res. 1994 Sep 1;54(17):4564–4568. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yuan X. Q., Smith T. L., Prough D. S., De Witt D. S., Dusseau J. W., Lynch C. D., Fulton J. M., Hutchins P. M. Long-term effects of nimodipine on pial microvasculature and systemic circulation in conscious rats. Am J Physiol. 1990 May;258(5 Pt 2):H1395–H1401. doi: 10.1152/ajpheart.1990.258.5.H1395. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ziche M., Morbidelli L., Alessandri G., Gullino P. M. Angiogenesis can be stimulated or repressed in vivo by a change in GM3:GD3 ganglioside ratio. Lab Invest. 1992 Dec;67(6):711–715. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]