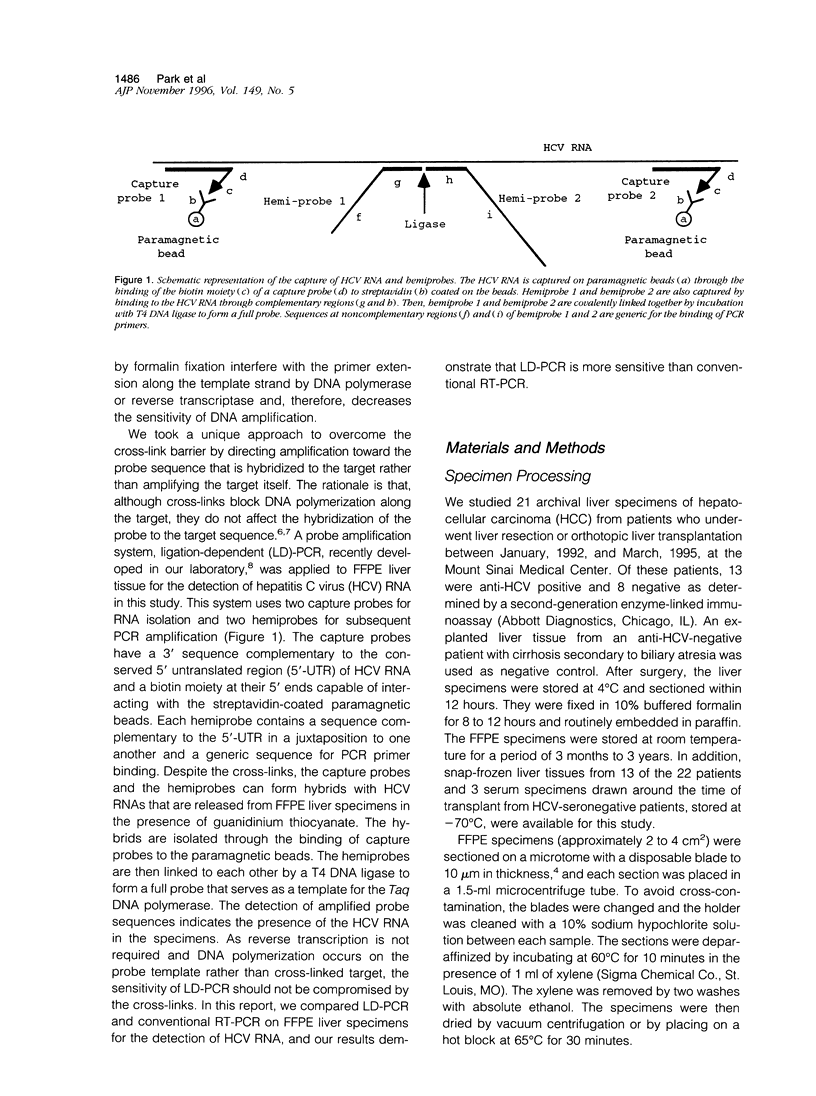
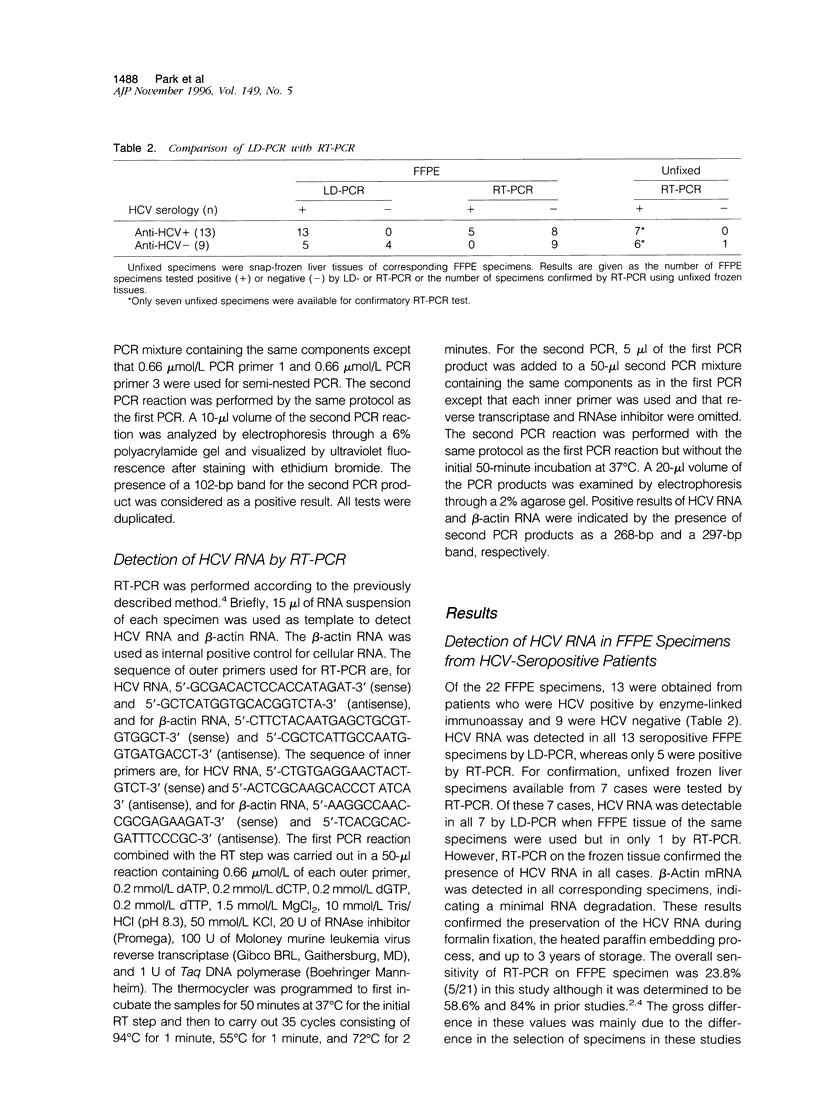
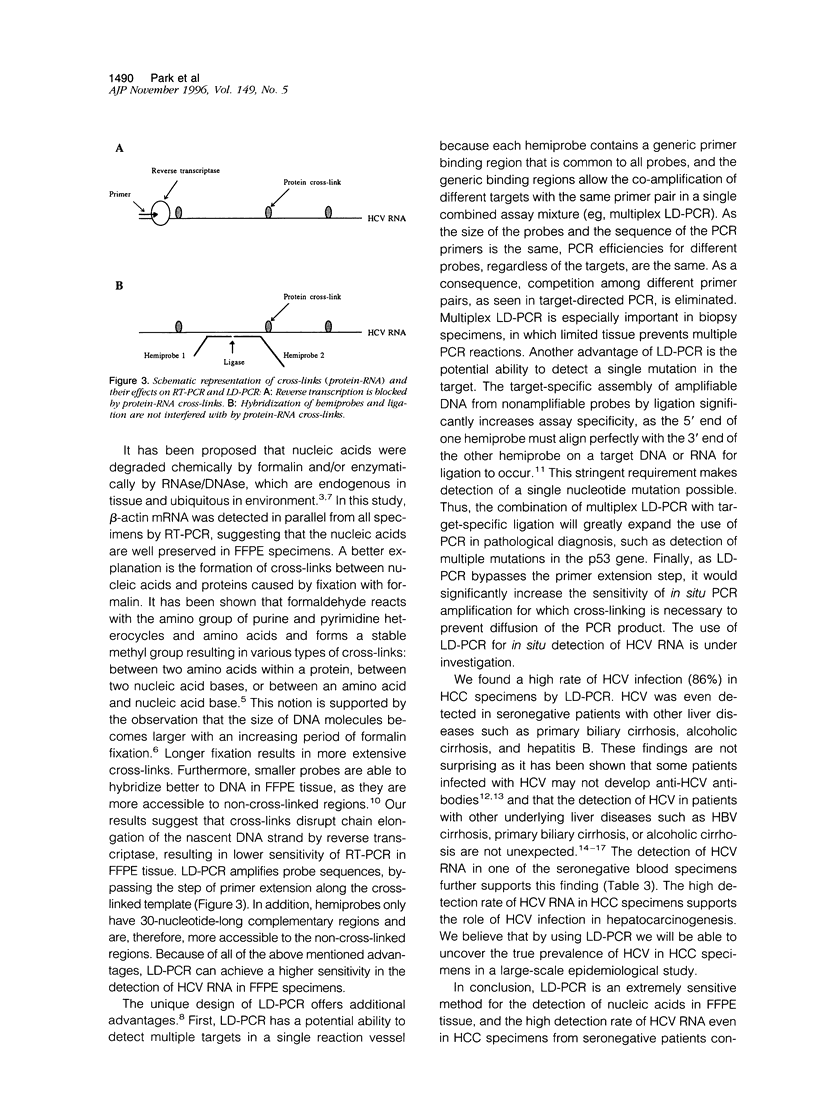
Abstract
Reverse transcription polymerase chain reaction (RT-PCR) has been used to detect hepatitis C virus (HCV) sequences in liver tissue. However, RT-PCR has a variable detection sensitivity, especially on routinely processed formalin-fixed, paraffin-embedded (FFPE) specimens. RNA-RNA and RNA-protein cross-links formed during formalin fixation is the major limiting factor preventing reverse trans criptase from extending the primers. To overcome this problem, we applied the ligation-dependent PCR (LD-PCR) for the detection of HCV RNA in FFPE liver tissue. This method uses two capture probes for RNA isolation and two hemiprobes for the subsequent PCR. Despite cross-links, the capture probes and the hemiprobes are able to form hybrids with HCV RNAs released from the FFPE tissue. The hybrids are isolated through binding of the capture probes to paramagnetic beads. The hemiprobes are then ligated by a T4 DNA ligase to form a full probe that serves as a template for the Taq DNA polymerase. A total of 22 FFPE liver specimens, 21 with hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) and 1 with biliary cirrhosis secondary to bile duct atresia were selected for this study, of which 13 patients were HCV seropositive and 9 seronegative. HCV RNA was detectable by ID-PCR from all 13 HCV-seropositive HCCs and from 5 of 8 HCV-seronegative HCCs but not from the HCV-seronegative liver with biliary atresia. By contrast, RT-PCR detected HCV sequences in only 5 of the HCV-sero-positive and in 1 of the HCV-seronegative HCCs. To resolve the discordance between the LD-PCR and RT-PCR results, RT-PCR was performed on frozen liver tissue of the discrepant specimens, which confirmed the LD-PCR positive results. In conclusion, LD-PCR is a more sensitive method than RT-PCR for the detection of HCV sequences in routinely processed liver tissues. A high rate of HCV infection (86%) is found in HCC specimens, indicating a previously underestimated role of HCV in HCC pathogenesis.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Abe K., Inchauspe G., Shikata T., Prince A. M. Three different patterns of hepatitis C virus infection in chimpanzees. Hepatology. 1992 Apr;15(4):690–695. doi: 10.1002/hep.1840150423. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Akyol G., Dash S., Shieh Y. S., Malter J. S., Gerber M. A. Detection of hepatitis C virus RNA sequences by polymerase chain reaction in fixed liver tissue. Mod Pathol. 1992 Sep;5(5):501–504. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Auerbach C., Moutschen-Dahmen M., Moutschen J. Genetic and cytogenetical effects of formaldehyde and related compounds. Mutat Res. 1977;39(3-4):317–361. doi: 10.1016/0165-1110(77)90011-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barnes R. E., Meyer R. A., Gordon S. C. Prevalence of anti-HCV in cryptogenic cirrhosis in a suburban Detroit community. Am J Gastroenterol. 1992 Aug;87(8):1001–1004. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bortolotti F., Vajro P., Cadrobbi P., Lepore L., Zancan L., Barbera C., Crivellaro C., Fontanella A., Alberti A., D'Addezio M. Cryptogenic chronic liver disease and hepatitis C virus infection in children. J Hepatol. 1992 May;15(1-2):73–76. doi: 10.1016/0168-8278(92)90014-g. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bresters D., Schipper M. E., Reesink H. W., Boeser-Nunnink B. D., Cuypers H. T. The duration of fixation influences the yield of HCV cDNA-PCR products from formalin-fixed, paraffin-embedded liver tissue. J Virol Methods. 1994 Jul;48(2-3):267–272. doi: 10.1016/0166-0934(94)90125-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cenac A., Pedroso M. L., Djibo A., Develoux M., Pichoud C., Lamothe F., Trepo C., Warter A. Hepatitis B, C, and D virus infections in patients with chronic hepatitis, cirrhosis, and hepatocellular carcinoma: a comparative study in Niger. Am J Trop Med Hyg. 1995 Apr;52(4):293–296. doi: 10.4269/ajtmh.1995.52.293. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chomczynski P., Sacchi N. Single-step method of RNA isolation by acid guanidinium thiocyanate-phenol-chloroform extraction. Anal Biochem. 1987 Apr;162(1):156–159. doi: 10.1006/abio.1987.9999. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dubeau L., Chandler L. A., Gralow J. R., Nichols P. W., Jones P. A. Southern blot analysis of DNA extracted from formalin-fixed pathology specimens. Cancer Res. 1986 Jun;46(6):2964–2969. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hsuih T. C., Park Y. N., Zaretsky C., Wu F., Tyagi S., Kramer F. R., Sperling R., Zhang D. Y. Novel, ligation-dependent PCR assay for detection of hepatitis C in serum. J Clin Microbiol. 1996 Mar;34(3):501–507. doi: 10.1128/jcm.34.3.501-507.1996. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Landegren U., Kaiser R., Sanders J., Hood L. A ligase-mediated gene detection technique. Science. 1988 Aug 26;241(4869):1077–1080. doi: 10.1126/science.3413476. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miyakawa H., Sato C., Izumi N., Tazawa J., Ebata A., Hattori K., Sakai H., Ikeda T., Hirata R., Sakai Y. Hepatitis C virus infection in alcoholic liver cirrhosis in Japan: its contribution to the development of hepatocellular carcinoma. Alcohol Alcohol Suppl. 1993;1A:85–90. doi: 10.1093/alcalc/28.supplement_1a.85. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moench T. R., Gendelman H. E., Clements J. E., Narayan O., Griffin D. E. Efficiency of in situ hybridization as a function of probe size and fixation technique. J Virol Methods. 1985 Jun;11(2):119–130. doi: 10.1016/0166-0934(85)90035-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nuovo G. J., Silverstein S. J. Comparison of formalin, buffered formalin, and Bouin's fixation on the detection of human papillomavirus deoxyribonucleic acid from genital lesions. Lab Invest. 1988 Nov;59(5):720–724. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Panigrahi A. K., Nanda S. K., Dixit R. K., Acharya S. K., Zuckerman A. J., Panda S. K. Diagnosis of hepatitis C virus-associated chronic liver disease in India: comparison of HCV antibody assay with a polymerase chain reaction for the 5' noncoding region. J Med Virol. 1994 Oct;44(2):176–179. doi: 10.1002/jmv.1890440211. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- el-Batanony M. H., Savage K., Jacobs R., el-Refaie A. O., Squadrito G. G., Brown D., Saleh S. M., Raouf A. A., Amer K. M., Dusheiko G. M. Hepatitis C virus-polymerase chain reaction of routinely processed liver biopsies. J Med Virol. 1994 Aug;43(4):380–385. doi: 10.1002/jmv.1890430411. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]