Abstract
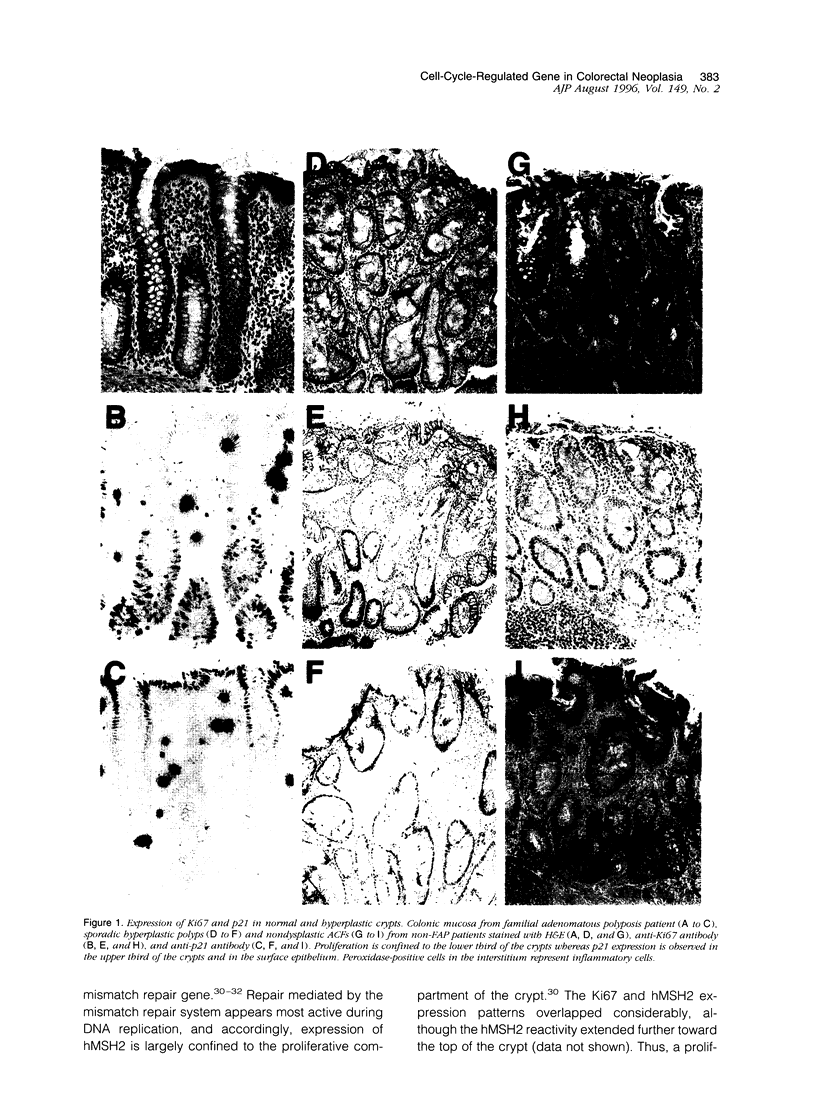
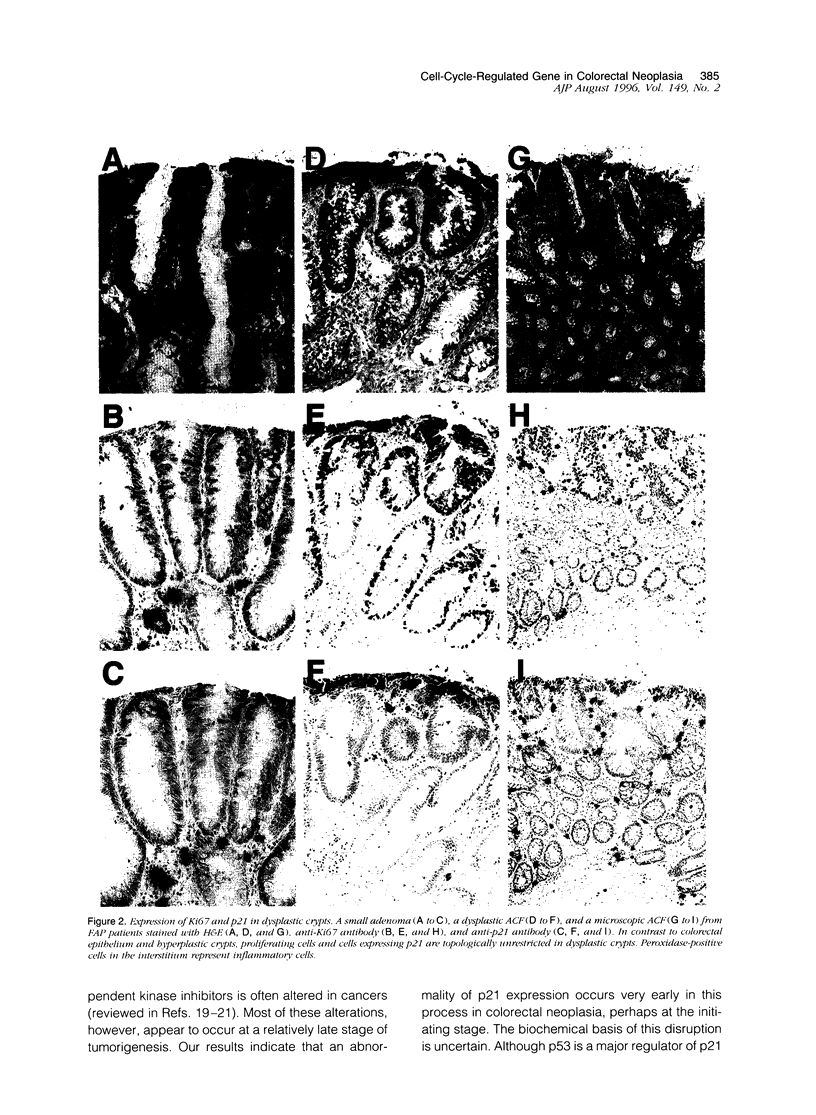
Aberrant crypt foci with dysplasia are thought to be the first detectable lesions of colorectal neoplasia. Because cell cycle disruption appears crucial for tumorigenesis, we analyzed the immunohistochemical expression patterns of the prototype cyclin-dependent kinase inhibitor p21 WAF1/CIP1 and the proliferation marker Ki67 in the early stages of colorectal tumorigenesis. In colorectal epithelium, p21 WAF1/CIP1 expression was undetectable in the lower third of the crypts, where Ki67 was expressed, but then sharply increased as cells passed out of the proliferating zone and migrated toward the humen. Hyperplastic polyps retained this normal compartmentalized pattern. In contrast, markedly decreased p21 WAF1/CIP1 immunostaining was observed in dysplastic aberrant crypt foci as well as in small adenomas. Moreover, the compartmentalization of Ki67 and p21 WAF1/CIP1 was lost, as Ki67 expression extended into the small p21-expressing zone at the top of the crypts. These data suggest that the dysregulated expression of cell-cycle-controlling genes and the consequent release from normal cell cycle controls may represent an essential early step in colorectal neoplasia.
Full text
PDF




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Baker S. J., Preisinger A. C., Jessup J. M., Paraskeva C., Markowitz S., Willson J. K., Hamilton S., Vogelstein B. p53 gene mutations occur in combination with 17p allelic deletions as late events in colorectal tumorigenesis. Cancer Res. 1990 Dec 1;50(23):7717–7722. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barrow B. J., O'Riordan M. A., Stellato T. A., Calkins B. M., Pretlow T. P. Enzyme-altered foci in colons of carcinogen-treated rats. Cancer Res. 1990 Mar 15;50(6):1911–1916. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bird R. P. Observation and quantification of aberrant crypts in the murine colon treated with a colon carcinogen: preliminary findings. Cancer Lett. 1987 Oct 30;37(2):147–151. doi: 10.1016/0304-3835(87)90157-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bos J. L., Fearon E. R., Hamilton S. R., Verlaan-de Vries M., van Boom J. H., van der Eb A. J., Vogelstein B. Prevalence of ras gene mutations in human colorectal cancers. 1987 May 28-Jun 3Nature. 327(6120):293–297. doi: 10.1038/327293a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- D'Urso G., Nurse P. Checkpoints in the cell cycle of fission yeast. Curr Opin Genet Dev. 1995 Feb;5(1):12–16. doi: 10.1016/s0959-437x(95)90047-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Elledge S. J., Harper J. W. Cdk inhibitors: on the threshold of checkpoints and development. Curr Opin Cell Biol. 1994 Dec;6(6):847–852. doi: 10.1016/0955-0674(94)90055-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fearon E. R., Vogelstein B. A genetic model for colorectal tumorigenesis. Cell. 1990 Jun 1;61(5):759–767. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90186-i. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Forrester K., Almoguera C., Han K., Grizzle W. E., Perucho M. Detection of high incidence of K-ras oncogenes during human colon tumorigenesis. 1987 May 28-Jun 3Nature. 327(6120):298–303. doi: 10.1038/327298a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gerdes J., Lemke H., Baisch H., Wacker H. H., Schwab U., Stein H. Cell cycle analysis of a cell proliferation-associated human nuclear antigen defined by the monoclonal antibody Ki-67. J Immunol. 1984 Oct;133(4):1710–1715. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Groden J., Thliveris A., Samowitz W., Carlson M., Gelbert L., Albertsen H., Joslyn G., Stevens J., Spirio L., Robertson M. Identification and characterization of the familial adenomatous polyposis coli gene. Cell. 1991 Aug 9;66(3):589–600. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(81)90021-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hamilton S. R. Pathogenesis of polyps (adenomas). Dis Colon Rectum. 1983 Jun;26(6):413–414. doi: 10.1007/BF02553387. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hamilton S. R. The adenoma-adenocarcinoma sequence in the large bowel: variations on a theme. J Cell Biochem Suppl. 1992;16G:41–46. doi: 10.1002/jcb.240501108. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harper J. W., Adami G. R., Wei N., Keyomarsi K., Elledge S. J. The p21 Cdk-interacting protein Cip1 is a potent inhibitor of G1 cyclin-dependent kinases. Cell. 1993 Nov 19;75(4):805–816. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(93)90499-g. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hartwell L. H., Kastan M. B. Cell cycle control and cancer. Science. 1994 Dec 16;266(5192):1821–1828. doi: 10.1126/science.7997877. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hunter T., Pines J. Cyclins and cancer. II: Cyclin D and CDK inhibitors come of age. Cell. 1994 Nov 18;79(4):573–582. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(94)90543-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jen J., Powell S. M., Papadopoulos N., Smith K. J., Hamilton S. R., Vogelstein B., Kinzler K. W. Molecular determinants of dysplasia in colorectal lesions. Cancer Res. 1994 Nov 1;54(21):5523–5526. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Joslyn G., Carlson M., Thliveris A., Albertsen H., Gelbert L., Samowitz W., Groden J., Stevens J., Spirio L., Robertson M. Identification of deletion mutations and three new genes at the familial polyposis locus. Cell. 1991 Aug 9;66(3):601–613. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(81)90022-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kinzler K. W., Nilbert M. C., Su L. K., Vogelstein B., Bryan T. M., Levy D. B., Smith K. J., Preisinger A. C., Hedge P., McKechnie D. Identification of FAP locus genes from chromosome 5q21. Science. 1991 Aug 9;253(5020):661–665. doi: 10.1126/science.1651562. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kobayashi M., Watanabe H., Ajioka Y., Maeo S. PCNA-positive cell distribution in depressed types of early carcinoma and adenoma of the large intestine. Gastroenterol Jpn. 1992 Oct;27(5):684–684. doi: 10.1007/BF02774987. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kolodner R. D. Mismatch repair: mechanisms and relationship to cancer susceptibility. Trends Biochem Sci. 1995 Oct;20(10):397–401. doi: 10.1016/s0968-0004(00)89087-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leach F. S., Nicolaides N. C., Papadopoulos N., Liu B., Jen J., Parsons R., Peltomäki P., Sistonen P., Aaltonen L. A., Nyström-Lahti M. Mutations of a mutS homolog in hereditary nonpolyposis colorectal cancer. Cell. 1993 Dec 17;75(6):1215–1225. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(93)90330-s. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leach F. S., Polyak K., Burrell M., Johnson K. A., Hill D., Dunlop M. G., Wyllie A. H., Peltomaki P., de la Chapelle A., Hamilton S. R. Expression of the human mismatch repair gene hMSH2 in normal and neoplastic tissues. Cancer Res. 1996 Jan 15;56(2):235–240. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McLellan E. A., Bird R. P. Aberrant crypts: potential preneoplastic lesions in the murine colon. Cancer Res. 1988 Nov 1;48(21):6187–6192. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miyoshi Y., Nagase H., Ando H., Horii A., Ichii S., Nakatsuru S., Aoki T., Miki Y., Mori T., Nakamura Y. Somatic mutations of the APC gene in colorectal tumors: mutation cluster region in the APC gene. Hum Mol Genet. 1992 Jul;1(4):229–233. doi: 10.1093/hmg/1.4.229. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nishisho I., Nakamura Y., Miyoshi Y., Miki Y., Ando H., Horii A., Koyama K., Utsunomiya J., Baba S., Hedge P. Mutations of chromosome 5q21 genes in FAP and colorectal cancer patients. Science. 1991 Aug 9;253(5020):665–669. doi: 10.1126/science.1651563. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Noda A., Ning Y., Venable S. F., Pereira-Smith O. M., Smith J. R. Cloning of senescent cell-derived inhibitors of DNA synthesis using an expression screen. Exp Cell Res. 1994 Mar;211(1):90–98. doi: 10.1006/excr.1994.1063. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Parker S. B., Eichele G., Zhang P., Rawls A., Sands A. T., Bradley A., Olson E. N., Harper J. W., Elledge S. J. p53-independent expression of p21Cip1 in muscle and other terminally differentiating cells. Science. 1995 Feb 17;267(5200):1024–1027. doi: 10.1126/science.7863329. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Powell S. M., Zilz N., Beazer-Barclay Y., Bryan T. M., Hamilton S. R., Thibodeau S. N., Vogelstein B., Kinzler K. W. APC mutations occur early during colorectal tumorigenesis. Nature. 1992 Sep 17;359(6392):235–237. doi: 10.1038/359235a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pretlow T. P., Barrow B. J., Ashton W. S., O'Riordan M. A., Pretlow T. G., Jurcisek J. A., Stellato T. A. Aberrant crypts: putative preneoplastic foci in human colonic mucosa. Cancer Res. 1991 Mar 1;51(5):1564–1567. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pretlow T. P., Brasitus T. A., Fulton N. C., Cheyer C., Kaplan E. L. K-ras mutations in putative preneoplastic lesions in human colon. J Natl Cancer Inst. 1993 Dec 15;85(24):2004–2007. doi: 10.1093/jnci/85.24.2004. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roncucci L., Stamp D., Medline A., Cullen J. B., Bruce W. R. Identification and quantification of aberrant crypt foci and microadenomas in the human colon. Hum Pathol. 1991 Mar;22(3):287–294. doi: 10.1016/0046-8177(91)90163-j. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sawhney N., Hall P. A. Ki67--structure, function, and new antibodies. J Pathol. 1992 Oct;168(2):161–162. doi: 10.1002/path.1711680202. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sherr C. J. G1 phase progression: cycling on cue. Cell. 1994 Nov 18;79(4):551–555. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(94)90540-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shibata D., Schaeffer J., Li Z. H., Capella G., Perucho M. Genetic heterogeneity of the c-K-ras locus in colorectal adenomas but not in adenocarcinomas. J Natl Cancer Inst. 1993 Jul 7;85(13):1058–1063. doi: 10.1093/jnci/85.13.1058. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith A. J., Stern H. S., Penner M., Hay K., Mitri A., Bapat B. V., Gallinger S. Somatic APC and K-ras codon 12 mutations in aberrant crypt foci from human colons. Cancer Res. 1994 Nov 1;54(21):5527–5530. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wargovich M. J., Harris C., Chen C. D., Palmer C., Steele V. E., Kelloff G. J. Growth kinetics and chemoprevention of aberrant crypts in the rat colon. J Cell Biochem Suppl. 1992;16G:51–54. doi: 10.1002/jcb.240501110. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Xiong Y., Hannon G. J., Zhang H., Casso D., Kobayashi R., Beach D. p21 is a universal inhibitor of cyclin kinases. Nature. 1993 Dec 16;366(6456):701–704. doi: 10.1038/366701a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- el-Deiry W. S., Tokino T., Velculescu V. E., Levy D. B., Parsons R., Trent J. M., Lin D., Mercer W. E., Kinzler K. W., Vogelstein B. WAF1, a potential mediator of p53 tumor suppression. Cell. 1993 Nov 19;75(4):817–825. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(93)90500-p. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- el-Deiry W. S., Tokino T., Waldman T., Oliner J. D., Velculescu V. E., Burrell M., Hill D. E., Healy E., Rees J. L., Hamilton S. R. Topological control of p21WAF1/CIP1 expression in normal and neoplastic tissues. Cancer Res. 1995 Jul 1;55(13):2910–2919. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]




