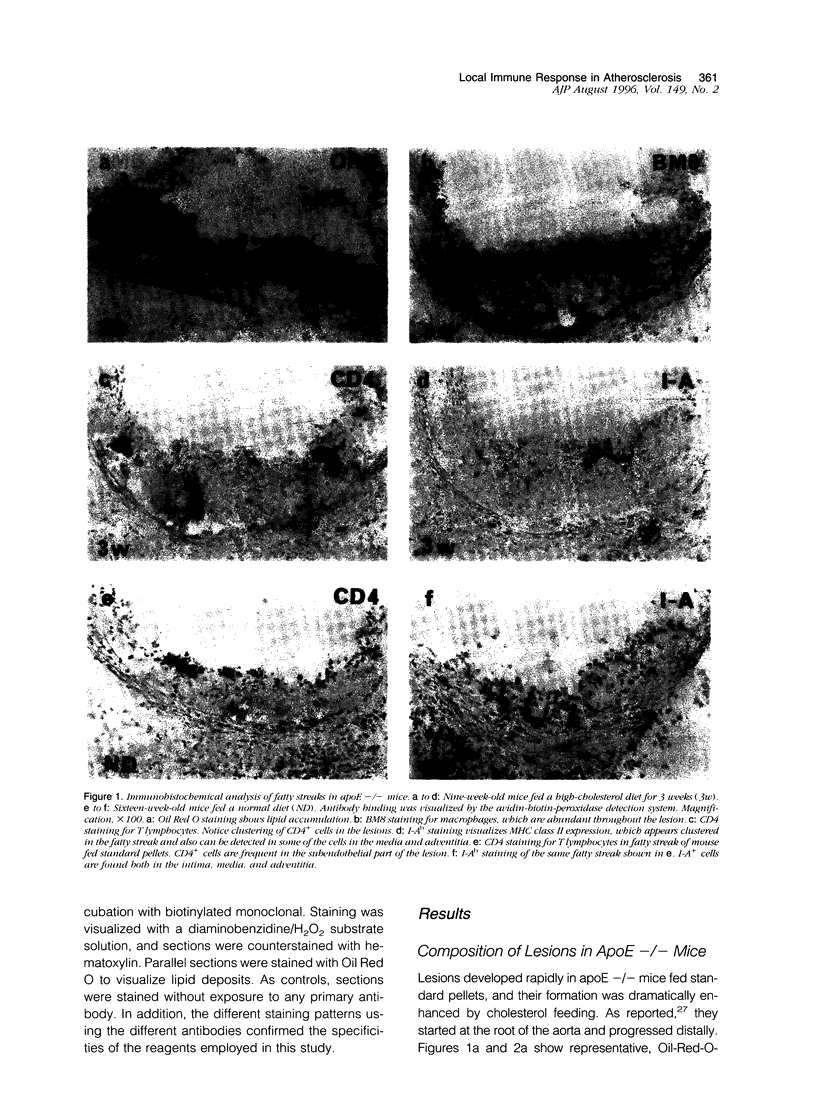
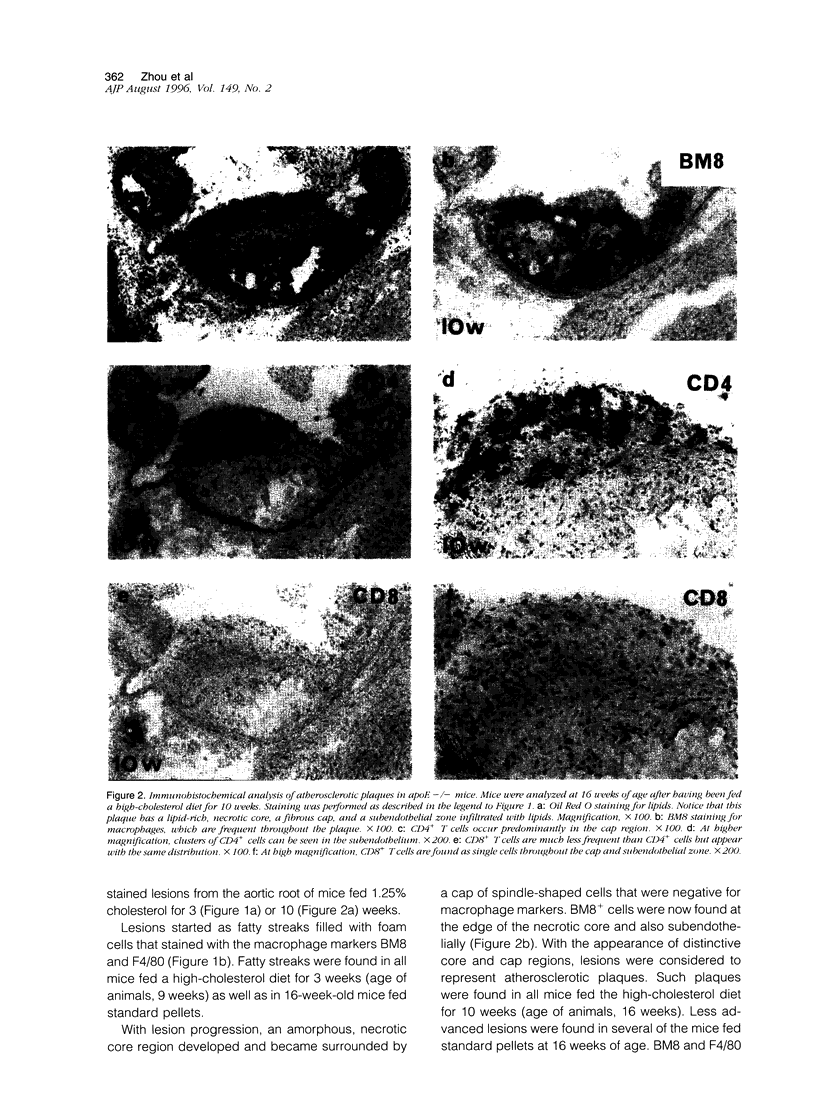
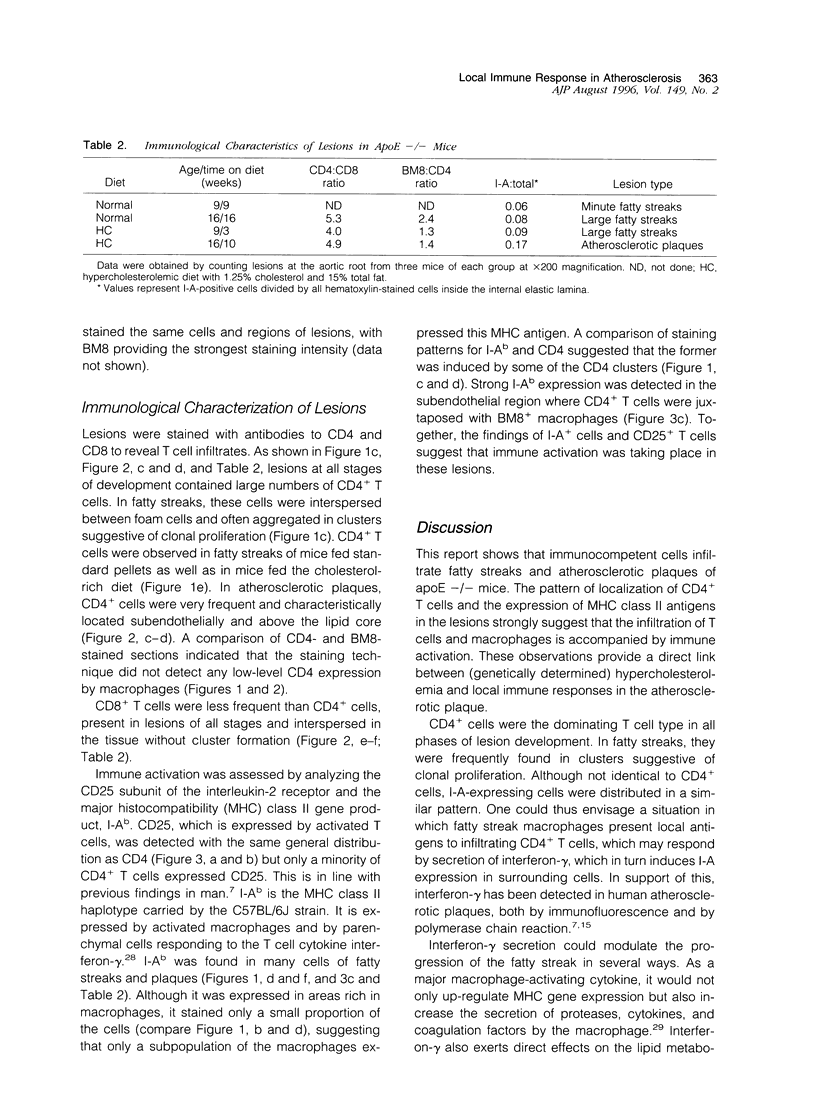
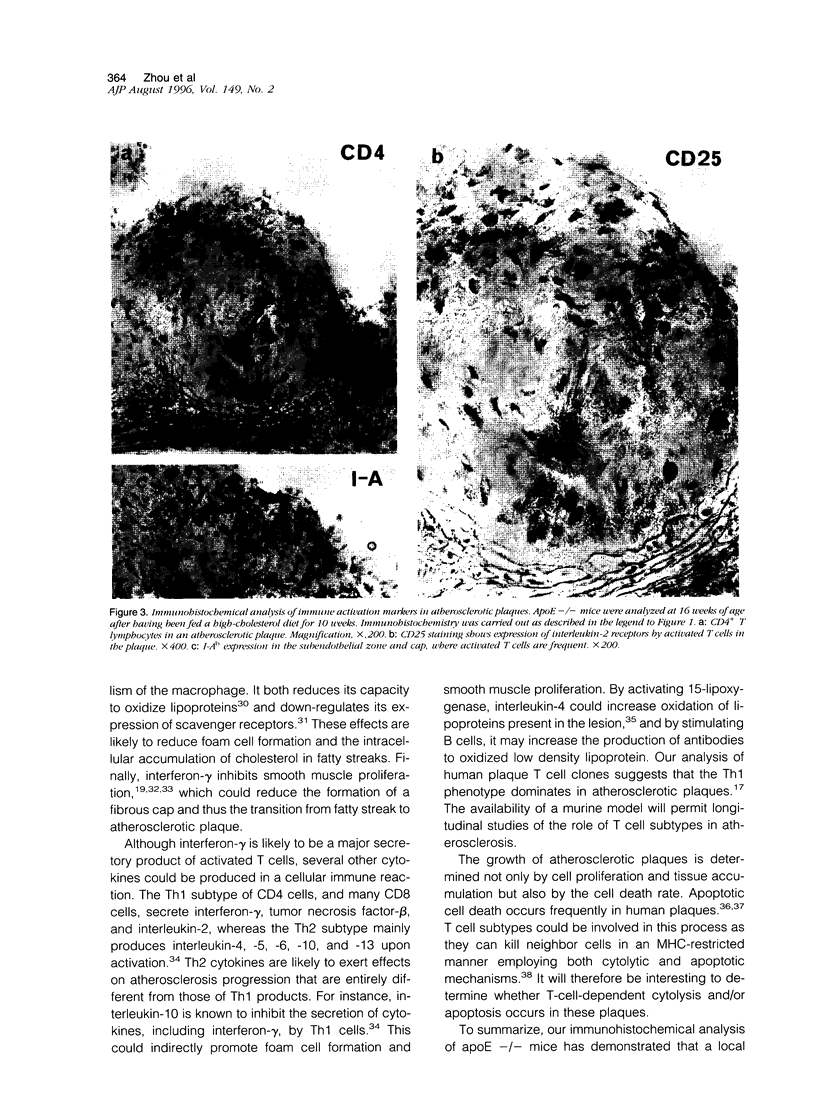
Abstract
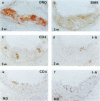
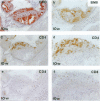
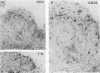
It has been suggested that immune responses are involved in the development of atherosclerosis. We have evaluated this possibility by analyzing immunocompetent cells in a murine model of the disease. Apolipoprotein E knockout (apoE -/-) mice are genetically hypercholesterolemic due to targeted disruption of the apolipoprotein E gene and develop severe atherosclerosis. Such mice were fed either standard pellets or a diet containing 1.25% cholesterol. Lesions were analyzed from mice at 9 and 16 weeks of age. Immunohistochemical staining of fatty streaks showed that CD4+ T cells were frequent, both in clusters and as single cells. In advanced atherosclerotic plaques, CD4+ T cells were prominent in the fibrous cap and subendotbelially, whereas CD8+ T cells were sparse. The CD25 subunit of the interleukin-2 receptor, which is a marker for activated T cells, was expressed in CD4-rich areas and the major histocompatibility complex class II antigen, I-A(b), which is induced by cytokines released from activated T cells, was also found in the lesions. These data indicate that CD4+ T cells participate in the formation of atherosclerotic lesions in genetically hypercholesterolemic apoE -/- mice. They suggest that immune activation is part of the disease process, and we speculate that a direct link may exist between cholesterol accumulation and T cell activation, possibly by autoimmune responses to modified lipoproteins.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Barath P., Fishbein M. C., Cao J., Berenson J., Helfant R. H., Forrester J. S. Tumor necrosis factor gene expression in human vascular intimal smooth muscle cells detected by in situ hybridization. Am J Pathol. 1990 Sep;137(3):503–509. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Berke G. The binding and lysis of target cells by cytotoxic lymphocytes: molecular and cellular aspects. Annu Rev Immunol. 1994;12:735–773. doi: 10.1146/annurev.iy.12.040194.003511. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Christen S., Thomas S. R., Garner B., Stocker R. Inhibition by interferon-gamma of human mononuclear cell-mediated low density lipoprotein oxidation. Participation of tryptophan metabolism along the kynurenine pathway. J Clin Invest. 1994 May;93(5):2149–2158. doi: 10.1172/JCI117211. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Drew A. F., Tipping P. G. Cyclosporine treatment reduces early atherosclerosis in the cholesterol-fed rabbit. Atherosclerosis. 1995 Aug;116(2):181–189. doi: 10.1016/0021-9150(95)05539-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Emeson E. E., Robertson A. L., Jr T lymphocytes in aortic and coronary intimas. Their potential role in atherogenesis. Am J Pathol. 1988 Feb;130(2):369–376. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Emeson E. E., Shen M. L. Accelerated atherosclerosis in hyperlipidemic C57BL/6 mice treated with cyclosporin A. Am J Pathol. 1993 Jun;142(6):1906–1915. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Farrar M. A., Schreiber R. D. The molecular cell biology of interferon-gamma and its receptor. Annu Rev Immunol. 1993;11:571–611. doi: 10.1146/annurev.iy.11.040193.003035. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fyfe A. I., Qiao J. H., Lusis A. J. Immune-deficient mice develop typical atherosclerotic fatty streaks when fed an atherogenic diet. J Clin Invest. 1994 Dec;94(6):2516–2520. doi: 10.1172/JCI117622. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Geng Y. J., Hansson G. K. Interferon-gamma inhibits scavenger receptor expression and foam cell formation in human monocyte-derived macrophages. J Clin Invest. 1992 Apr;89(4):1322–1330. doi: 10.1172/JCI115718. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Geng Y. J., Holm J., Nygren S., Bruzelius M., Stemme S., Hansson G. K. Expression of the macrophage scavenger receptor in atheroma. Relationship to immune activation and the T-cell cytokine interferon-gamma. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol. 1995 Nov;15(11):1995–2002. doi: 10.1161/01.atv.15.11.1995. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Geng Y. J., Libby P. Evidence for apoptosis in advanced human atheroma. Colocalization with interleukin-1 beta-converting enzyme. Am J Pathol. 1995 Aug;147(2):251–266. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Glimcher L. H., Kara C. J. Sequences and factors: a guide to MHC class-II transcription. Annu Rev Immunol. 1992;10:13–49. doi: 10.1146/annurev.iy.10.040192.000305. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Han D. K., Haudenschild C. C., Hong M. K., Tinkle B. T., Leon M. B., Liau G. Evidence for apoptosis in human atherogenesis and in a rat vascular injury model. Am J Pathol. 1995 Aug;147(2):267–277. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hancock W. W., Adams D. H., Wyner L. R., Sayegh M. H., Karnovsky M. J. CD4+ mononuclear cells induce cytokine expression, vascular smooth muscle cell proliferation, and arterial occlusion after endothelial injury. Am J Pathol. 1994 Nov;145(5):1008–1014. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hansson G. K., Hellstrand M., Rymo L., Rubbia L., Gabbiani G. Interferon gamma inhibits both proliferation and expression of differentiation-specific alpha-smooth muscle actin in arterial smooth muscle cells. J Exp Med. 1989 Nov 1;170(5):1595–1608. doi: 10.1084/jem.170.5.1595. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hansson G. K., Holm J., Holm S., Fotev Z., Hedrich H. J., Fingerle J. T lymphocytes inhibit the vascular response to injury. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Dec 1;88(23):10530–10534. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.23.10530. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hansson G. K., Holm J. Interferon-gamma inhibits arterial stenosis after injury. Circulation. 1991 Sep;84(3):1266–1272. doi: 10.1161/01.cir.84.3.1266. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hansson G. K., Holm J., Jonasson L. Detection of activated T lymphocytes in the human atherosclerotic plaque. Am J Pathol. 1989 Jul;135(1):169–175. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hansson G. K. Immune and inflammatory mechanisms in the development of atherosclerosis. Br Heart J. 1993 Jan;69(1 Suppl):S38–S41. doi: 10.1136/hrt.69.1_suppl.s38. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hansson G. K., Jonasson L., Seifert P. S., Stemme S. Immune mechanisms in atherosclerosis. Arteriosclerosis. 1989 Sep-Oct;9(5):567–578. doi: 10.1161/01.atv.9.5.567. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jonasson L., Holm J., Skalli O., Bondjers G., Hansson G. K. Regional accumulations of T cells, macrophages, and smooth muscle cells in the human atherosclerotic plaque. Arteriosclerosis. 1986 Mar-Apr;6(2):131–138. doi: 10.1161/01.atv.6.2.131. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jonasson L., Holm J., Skalli O., Gabbiani G., Hansson G. K. Expression of class II transplantation antigen on vascular smooth muscle cells in human atherosclerosis. J Clin Invest. 1985 Jul;76(1):125–131. doi: 10.1172/JCI111934. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Libby P., Hansson G. K. Involvement of the immune system in human atherogenesis: current knowledge and unanswered questions. Lab Invest. 1991 Jan;64(1):5–15. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moyer C. F., Sajuthi D., Tulli H., Williams J. K. Synthesis of IL-1 alpha and IL-1 beta by arterial cells in atherosclerosis. Am J Pathol. 1991 Apr;138(4):951–960. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Munro J. M., van der Walt J. D., Munro C. S., Chalmers J. A., Cox E. L. An immunohistochemical analysis of human aortic fatty streaks. Hum Pathol. 1987 Apr;18(4):375–380. doi: 10.1016/s0046-8177(87)80168-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nakashima Y., Plump A. S., Raines E. W., Breslow J. L., Ross R. ApoE-deficient mice develop lesions of all phases of atherosclerosis throughout the arterial tree. Arterioscler Thromb. 1994 Jan;14(1):133–140. doi: 10.1161/01.atv.14.1.133. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Piedrahita J. A., Zhang S. H., Hagaman J. R., Oliver P. M., Maeda N. Generation of mice carrying a mutant apolipoprotein E gene inactivated by gene targeting in embryonic stem cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1992 May 15;89(10):4471–4475. doi: 10.1073/pnas.89.10.4471. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Romagnani S. Lymphokine production by human T cells in disease states. Annu Rev Immunol. 1994;12:227–257. doi: 10.1146/annurev.iy.12.040194.001303. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roselaar S. E., Schonfeld G., Daugherty A. Enhanced development of atherosclerosis in cholesterol-fed rabbits by suppression of cell-mediated immunity. J Clin Invest. 1995 Sep;96(3):1389–1394. doi: 10.1172/JCI118174. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ross R. The pathogenesis of atherosclerosis: a perspective for the 1990s. Nature. 1993 Apr 29;362(6423):801–809. doi: 10.1038/362801a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Steinberg D., Parthasarathy S., Carew T. E., Khoo J. C., Witztum J. L. Beyond cholesterol. Modifications of low-density lipoprotein that increase its atherogenicity. N Engl J Med. 1989 Apr 6;320(14):915–924. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198904063201407. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stemme S., Faber B., Holm J., Wiklund O., Witztum J. L., Hansson G. K. T lymphocytes from human atherosclerotic plaques recognize oxidized low density lipoprotein. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1995 Apr 25;92(9):3893–3897. doi: 10.1073/pnas.92.9.3893. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stemme S., Hansson G. K. Immune mechanisms in atherosclerosis. Coron Artery Dis. 1994 Mar;5(3):216–222. doi: 10.1097/00019501-199403000-00006. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stemme S., Holm J., Hansson G. K. T lymphocytes in human atherosclerotic plaques are memory cells expressing CD45RO and the integrin VLA-1. Arterioscler Thromb. 1992 Feb;12(2):206–211. doi: 10.1161/01.atv.12.2.206. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Xu Q., Kleindienst R., Waitz W., Dietrich H., Wick G. Increased expression of heat shock protein 65 coincides with a population of infiltrating T lymphocytes in atherosclerotic lesions of rabbits specifically responding to heat shock protein 65. J Clin Invest. 1993 Jun;91(6):2693–2702. doi: 10.1172/JCI116508. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ylä-Herttuala S., Rosenfeld M. E., Parthasarathy S., Sigal E., Särkioja T., Witztum J. L., Steinberg D. Gene expression in macrophage-rich human atherosclerotic lesions. 15-lipoxygenase and acetyl low density lipoprotein receptor messenger RNA colocalize with oxidation specific lipid-protein adducts. J Clin Invest. 1991 Apr;87(4):1146–1152. doi: 10.1172/JCI115111. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van der Wal A. C., Das P. K., Bentz van de Berg D., van der Loos C. M., Becker A. E. Atherosclerotic lesions in humans. In situ immunophenotypic analysis suggesting an immune mediated response. Lab Invest. 1989 Aug;61(2):166–170. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]