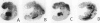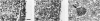Abstract
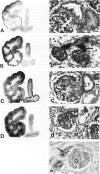
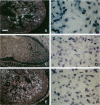
Increasing evidence suggests that the renin-angiotensin system (RAS) is not only a potent regulator of blood pressure and fluid and electrolyte homeostasis, but that it also plays an important role in growth and differentiation in development as well as in pathological states. We, therefore, investigated the expression of all components of the RAS in the human embryo and fetus by in situ hybridization or immunohistochemistry. This study is the first to demonstrate the presence of all components of the RAS in very early human development (30-35 days of gestation). Angiotensinogen mRNA is expressed in very high amounts in the yolk sac, liver, and kidney, whereas renin mRNA and angiotensin-converting enzyme are expressed in the chorion, kidney, and heart, thus allowing fetal production of angiotensin II. This effector molecule of the RAS mediates its effects through binding to specific receptor types, AT1 and AT2. Both of these receptors are also expressed very early in development (24 days of gestation), suggesting a role for angiotensin II in organogenesis. Based on the expression pattern of these receptors, angiotensin II likely plays a role in the growth and differentiation of the kidney, adrenal gland, heart, and liver, all organs that are of major importance for the regulation of blood pressure later in life.
Full text
PDF









Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Balla T., Baukal A. J., Eng S., Catt K. J. Angiotensin II receptor subtypes and biological responses in the adrenal cortex and medulla. Mol Pharmacol. 1991 Sep;40(3):401–406. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Beinlich C. J., White G. J., Baker K. M., Morgan H. E. Angiotensin II and left ventricular growth in newborn pig heart. J Mol Cell Cardiol. 1991 Sep;23(9):1031–1038. doi: 10.1016/0022-2828(91)91638-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bernstein J., Barajas L. Renal tubular dysgenesis: evidence of abnormality in the renin-angiotensin system. J Am Soc Nephrol. 1994 Aug;5(2):224–227. doi: 10.1681/ASN.V52224. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Celio M. R., Groscurth P., Inagami T. Ontogeny of renin immunoreactive cells in the human kidney. Anat Embryol (Berl) 1985;173(2):149–155. doi: 10.1007/BF00316297. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Charbit M., Déchaux M., Blazy I., Vargas R., Laouari D., Brocart D., Lacoste M., Gubler M. C., Sachs C. Deleterious effects of inhibition of the renin-angiotensin system in neonatal rats. Pediatr Nephrol. 1995 Jun;9(3):303–308. doi: 10.1007/BF02254192. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Falkenhahn M., Franke F., Bohle R. M., Zhu Y. C., Stauss H. M., Bachmann S., Danilov S., Unger T. Cellular distribution of angiotensin-converting enzyme after myocardial infarction. Hypertension. 1995 Feb;25(2):219–226. doi: 10.1161/01.hyp.25.2.219. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Friberg P., Sundelin B., Bohman S. O., Bobik A., Nilsson H., Wickman A., Gustafsson H., Petersen J., Adams M. A. Renin-angiotensin system in neonatal rats: induction of a renal abnormality in response to ACE inhibition or angiotensin II antagonism. Kidney Int. 1994 Feb;45(2):485–492. doi: 10.1038/ki.1994.63. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gaillard I., Clauser E., Corvol P. Structure of human angiotensinogen gene. DNA. 1989 Mar;8(2):87–99. doi: 10.1089/dna.1.1989.8.87. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gasc J. M., Monnot C., Clauser E., Corvol P. Co-expression of type 1 angiotensin II receptor (AT1R) and renin mRNAs in juxtaglomerular cells of the rat kidney. Endocrinology. 1993 Jun;132(6):2723–2725. doi: 10.1210/endo.132.6.8504772. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gershon M. D. Neural crest development. Do developing enteric neurons need endothelins? Curr Biol. 1995 Jun 1;5(6):601–604. doi: 10.1016/s0960-9822(95)00120-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gilbert B. W. ACE inhibitors and regression of left ventricular hypertrophy. Clin Cardiol. 1992 Oct;15(10):711–714. doi: 10.1002/clc.4960151027. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gomez R. A., Cassis L., Lynch K. R., Chevalier R. L., Wilfong N., Carey R. M., Peach M. J. Fetal expression of the angiotensinogen gene. Endocrinology. 1988 Nov;123(5):2298–2302. doi: 10.1210/endo-123-5-2298. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gomez R. A., Norwood V. F. Developmental consequences of the renin-angiotensin system. Am J Kidney Dis. 1995 Sep;26(3):409–431. doi: 10.1016/0272-6386(95)90487-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gomez R. A., Pupilli C., Everett A. D. Molecular and cellular aspects of renin during kidney ontogeny. Pediatr Nephrol. 1991 Jan;5(1):80–87. doi: 10.1007/BF00852854. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grady E. F., Sechi L. A., Griffin C. A., Schambelan M., Kalinyak J. E. Expression of AT2 receptors in the developing rat fetus. J Clin Invest. 1991 Sep;88(3):921–933. doi: 10.1172/JCI115395. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Graham P. C., Kingdom J. C., Raweily E. A., Gibson A. A., Lindop G. B. Distribution of renin-containing cells in the developing human kidney: an immunocytochemical study. Br J Obstet Gynaecol. 1992 Sep;99(9):765–769. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-0528.1992.tb13881.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gupta P., Franco-Saenz R., Mulrow P. J. Locally generated angiotensin II in the adrenal gland regulates basal, corticotropin-, and potassium-stimulated aldosterone secretion. Hypertension. 1995 Mar;25(3):443–448. doi: 10.1161/01.hyp.25.3.443. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harewood W. J., Phippard A. F., Duggin G. G., Horvath J. S., Tiller D. J. Fetotoxicity of angiotensin-converting enzyme inhibition in primate pregnancy: a prospective, placebo-controlled study in baboons (Papio hamadryas). Am J Obstet Gynecol. 1994 Sep;171(3):633–642. doi: 10.1016/0002-9378(94)90075-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hein L., Barsh G. S., Pratt R. E., Dzau V. J., Kobilka B. K. Behavioural and cardiovascular effects of disrupting the angiotensin II type-2 receptor in mice. Nature. 1995 Oct 26;377(6551):744–747. doi: 10.1038/377744a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hirsch A. T., Talsness C. E., Schunkert H., Paul M., Dzau V. J. Tissue-specific activation of cardiac angiotensin converting enzyme in experimental heart failure. Circ Res. 1991 Aug;69(2):475–482. doi: 10.1161/01.res.69.2.475. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Huckle W. R., Earp H. S. Regulation of cell proliferation and growth by angiotensin II. Prog Growth Factor Res. 1994;5(2):177–194. doi: 10.1016/0955-2235(94)90004-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ichiki T., Labosky P. A., Shiota C., Okuyama S., Imagawa Y., Fogo A., Niimura F., Ichikawa I., Hogan B. L., Inagami T. Effects on blood pressure and exploratory behaviour of mice lacking angiotensin II type-2 receptor. Nature. 1995 Oct 26;377(6551):748–750. doi: 10.1038/377748a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kim H. S., Krege J. H., Kluckman K. D., Hagaman J. R., Hodgin J. B., Best C. F., Jennette J. C., Coffman T. M., Maeda N., Smithies O. Genetic control of blood pressure and the angiotensinogen locus. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1995 Mar 28;92(7):2735–2739. doi: 10.1073/pnas.92.7.2735. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Krege J. H., John S. W., Langenbach L. L., Hodgin J. B., Hagaman J. R., Bachman E. S., Jennette J. C., O'Brien D. A., Smithies O. Male-female differences in fertility and blood pressure in ACE-deficient mice. Nature. 1995 May 11;375(6527):146–148. doi: 10.1038/375146a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miyata S., Haneda T. Hypertrophic growth of cultured neonatal rat heart cells mediated by type 1 angiotensin II receptor. Am J Physiol. 1994 Jun;266(6 Pt 2):H2443–H2451. doi: 10.1152/ajpheart.1994.266.6.H2443. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mounier F., Hinglais N., Sich M., Gros F., Lacoste M., Deris Y., Alhenc-Gelas F., Gubler M. C. Ontogenesis of angiotensin-I converting enzyme in human kidney. Kidney Int. 1987 Nov;32(5):684–690. doi: 10.1038/ki.1987.261. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nakajima M., Hutchinson H. G., Fujinaga M., Hayashida W., Morishita R., Zhang L., Horiuchi M., Pratt R. E., Dzau V. J. The angiotensin II type 2 (AT2) receptor antagonizes the growth effects of the AT1 receptor: gain-of-function study using gene transfer. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1995 Nov 7;92(23):10663–10667. doi: 10.1073/pnas.92.23.10663. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nio Y., Matsubara H., Murasawa S., Kanasaki M., Inada M. Regulation of gene transcription of angiotensin II receptor subtypes in myocardial infarction. J Clin Invest. 1995 Jan;95(1):46–54. doi: 10.1172/JCI117675. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ray P. E., Bruggeman L. A., Horikoshi S., Aguilera G., Klotman P. E. Angiotensin II stimulates human fetal mesangial cell proliferation and fibronectin biosynthesis by binding to AT1 receptors. Kidney Int. 1994 Jan;45(1):177–184. doi: 10.1038/ki.1994.21. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sadoshima J., Izumo S. Molecular characterization of angiotensin II--induced hypertrophy of cardiac myocytes and hyperplasia of cardiac fibroblasts. Critical role of the AT1 receptor subtype. Circ Res. 1993 Sep;73(3):413–423. doi: 10.1161/01.res.73.3.413. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shanmugam S., Corvol P., Gasc J. M. Ontogeny of the two angiotensin II type 1 receptor subtypes in rats. Am J Physiol. 1994 Dec;267(6 Pt 1):E828–E836. doi: 10.1152/ajpendo.1994.267.6.E828. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shanmugam S., Lenkei Z. G., Gasc J. M., Corvol P. L., Llorens-Cortes C. M. Ontogeny of angiotensin II type 2 (AT2) receptor mRNA in the rat. Kidney Int. 1995 Apr;47(4):1095–1100. doi: 10.1038/ki.1995.156. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shanmugam S., Llorens-Cortes C., Clauser E., Corvol P., Gasc J. M. Expression of angiotensin II AT2 receptor mRNA during development of rat kidney and adrenal gland. Am J Physiol. 1995 May;268(5 Pt 2):F922–F930. doi: 10.1152/ajprenal.1995.268.5.F922. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shanmugam S., Monnot C., Corvol P., Gasc J. M. Distribution of type 1 angiotensin II receptor subtype messenger RNAs in the rat fetus. Hypertension. 1994 Jan;23(1):137–141. doi: 10.1161/01.hyp.23.1.137. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shotan A., Widerhorn J., Hurst A., Elkayam U. Risks of angiotensin-converting enzyme inhibition during pregnancy: experimental and clinical evidence, potential mechanisms, and recommendations for use. Am J Med. 1994 May;96(5):451–456. doi: 10.1016/0002-9343(94)90172-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sibony M., Commo F., Callard P., Gasc J. M. Enhancement of mRNA in situ hybridization signal by microwave heating. Lab Invest. 1995 Oct;73(4):586–591. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Soubrier F., Panthier J. J., Corvol P., Rougeon F. Molecular cloning and nucleotide sequence of a human renin cDNA fragment. Nucleic Acids Res. 1983 Oct 25;11(20):7181–7190. doi: 10.1093/nar/11.20.7181. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stoll M., Steckelings U. M., Paul M., Bottari S. P., Metzger R., Unger T. The angiotensin AT2-receptor mediates inhibition of cell proliferation in coronary endothelial cells. J Clin Invest. 1995 Feb;95(2):651–657. doi: 10.1172/JCI117710. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sugaya T., Nishimatsu S., Tanimoto K., Takimoto E., Yamagishi T., Imamura K., Goto S., Imaizumi K., Hisada Y., Otsuka A. Angiotensin II type 1a receptor-deficient mice with hypotension and hyperreninemia. J Biol Chem. 1995 Aug 11;270(32):18719–18722. doi: 10.1074/jbc.270.32.18719. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tanimoto K., Sugiyama F., Goto Y., Ishida J., Takimoto E., Yagami K., Fukamizu A., Murakami K. Angiotensinogen-deficient mice with hypotension. J Biol Chem. 1994 Dec 16;269(50):31334–31337. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tian Y., Balla T., Baukal A. J., Catt K. J. Growth responses to angiotensin II in bovine adrenal glomerulosa cells. Am J Physiol. 1995 Jan;268(1 Pt 1):E135–E144. doi: 10.1152/ajpendo.1995.268.1.E135. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tsuzuki S., Ichiki T., Nakakubo H., Kitami Y., Guo D. F., Shirai H., Inagami T. Molecular cloning and expression of the gene encoding human angiotensin II type 2 receptor. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1994 May 16;200(3):1449–1454. doi: 10.1006/bbrc.1994.1613. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zemel S., Millan M. A., Feuillan P., Aguilera G. Characterization and distribution of angiotensin-II receptors in the primate fetus. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 1990 Oct;71(4):1003–1007. doi: 10.1210/jcem-71-4-1003. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]