Abstract
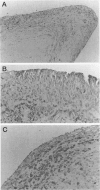
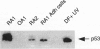
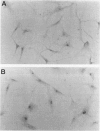
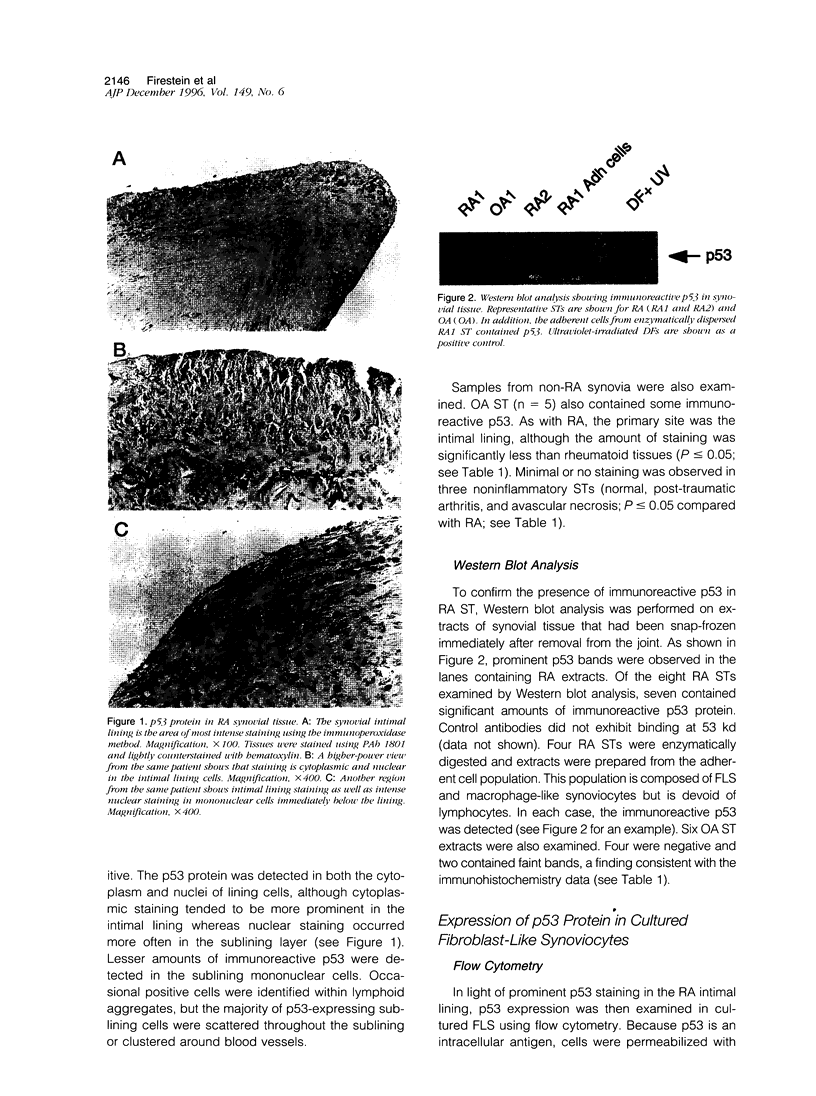
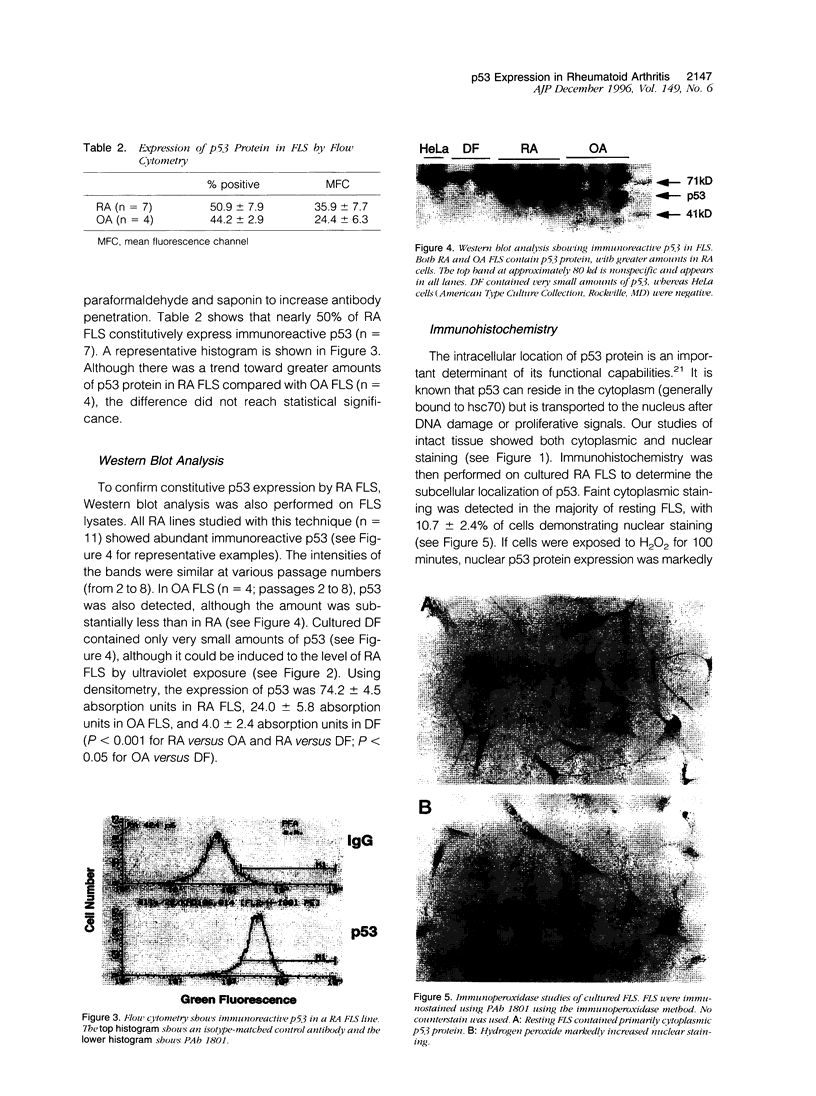
DNA damage induces p53 tumor suppressor gene expression and protein production, which in turn facilitates DNA repair or apoptosis. Wild-type p53 protein has a short half-life, so it is rarely detected in non-neoplastic tissue. Because DNA fragmentation is abundant in the intimal lining in rheumatoid arthritis (RA) synovial tissue (ST) using in situ end-labeling (Firestein GS, Yeo M, Zvaifler NJ: Apoptosis in rheumatoid arthritis synovium. J Clin Invest 1995, 96:1631-1638), we assessed ST p53 expression. Immunohistochemical analysis of fixed RA synovium using antibody PAb 1801 showed prominent p53 staining in the cytoplasm and nuclei of intimal lining cells. Noninflammatory and osteoarthritis (OA) ST had significantly less p53 in the lining. These data were confirmed by Western blot analysis of ST extracts, with abundant p53 found in RA compared with OA. p53 expression in cultured fibroblast-like synoviocytes (FLS) was then examined. Flow cytometry on permeabilized cells showed that RA FLS constitutively express p53 protein. Western blots showed that RA FLS expressed significantly more p53 than either OA FLS or dermal fibroblasts. Immunohistochemistry of FLS cultured in chamber slides localized the p53 to the cytoplasm of most resting FLS, with nuclear staining in only 10.7 +/- 2.4%. Exposure to hydrogen peroxide for increased nuclear staining to 70.7 +/- 12.8% after 8 hours (P = 0.003). These data indicate that p53 is overexpressed in RA ST in the intimal lining, which is the primary site of DNA damage, and is constitutively expressed by FLS.
Full text
PDF






Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Ajioka Y., Watanabe H., Matsuda K. Over-expression of p53 protein in neoplastic changes in ulcerative colitis: immunohistochemical study. J Gastroenterol. 1995 Nov;30 (Suppl 8):33–35. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Alvaro-Gracia J. M., Zvaifler N. J., Firestein G. S. Cytokines in chronic inflammatory arthritis. V. Mutual antagonism between interferon-gamma and tumor necrosis factor-alpha on HLA-DR expression, proliferation, collagenase production, and granulocyte macrophage colony-stimulating factor production by rheumatoid arthritis synoviocytes. J Clin Invest. 1990 Dec;86(6):1790–1798. doi: 10.1172/JCI114908. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Arnett F. C., Edworthy S. M., Bloch D. A., McShane D. J., Fries J. F., Cooper N. S., Healey L. A., Kaplan S. R., Liang M. H., Luthra H. S. The American Rheumatism Association 1987 revised criteria for the classification of rheumatoid arthritis. Arthritis Rheum. 1988 Mar;31(3):315–324. doi: 10.1002/art.1780310302. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Banks L., Matlashewski G., Crawford L. Isolation of human-p53-specific monoclonal antibodies and their use in the studies of human p53 expression. Eur J Biochem. 1986 Sep 15;159(3):529–534. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1986.tb09919.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barnes D. M., Hanby A. M., Gillett C. E., Mohammed S., Hodgson S., Bobrow L. G., Leigh I. M., Purkis T., MacGeoch C., Spurr N. K. Abnormal expression of wild type p53 protein in normal cells of a cancer family patient. Lancet. 1992 Aug 1;340(8814):259–263. doi: 10.1016/0140-6736(92)92354-i. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Buckbinder L., Talbott R., Seizinger B. R., Kley N. Gene regulation by temperature-sensitive p53 mutants: identification of p53 response genes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1994 Oct 25;91(22):10640–10644. doi: 10.1073/pnas.91.22.10640. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bártek J., Bártková J., Vojtesek B., Stasková Z., Lukás J., Rejthar A., Kovarík J., Midgley C. A., Gannon J. V., Lane D. P. Aberrant expression of the p53 oncoprotein is a common feature of a wide spectrum of human malignancies. Oncogene. 1991 Sep;6(9):1699–1703. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carrier F., Smith M. L., Bae I., Kilpatrick K. E., Lansing T. J., Chen C. Y., Engelstein M., Friend S. H., Henner W. D., Gilmer T. M. Characterization of human Gadd45, a p53-regulated protein. J Biol Chem. 1994 Dec 23;269(51):32672–32677. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Coates P. J., Save V., Ansari B., Hall P. A. Demonstration of DNA damage/repair in individual cells using in situ end labelling: association of p53 with sites of DNA damage. J Pathol. 1995 May;176(1):19–26. doi: 10.1002/path.1711760105. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davidoff A. M., Humphrey P. A., Iglehart J. D., Marks J. R. Genetic basis for p53 overexpression in human breast cancer. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Jun 1;88(11):5006–5010. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.11.5006. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Donehower L. A., Harvey M., Slagle B. L., McArthur M. J., Montgomery C. A., Jr, Butel J. S., Bradley A. Mice deficient for p53 are developmentally normal but susceptible to spontaneous tumours. Nature. 1992 Mar 19;356(6366):215–221. doi: 10.1038/356215a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Edwards J. C. The nature and origins of synovium: experimental approaches to the study of synoviocyte differentiation. J Anat. 1994 Jun;184(Pt 3):493–501. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fields S., Jang S. K. Presence of a potent transcription activating sequence in the p53 protein. Science. 1990 Aug 31;249(4972):1046–1049. doi: 10.1126/science.2144363. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Finlay C. A., Hinds P. W., Levine A. J. The p53 proto-oncogene can act as a suppressor of transformation. Cell. 1989 Jun 30;57(7):1083–1093. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90045-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Finlay C. A., Hinds P. W., Tan T. H., Eliyahu D., Oren M., Levine A. J. Activating mutations for transformation by p53 produce a gene product that forms an hsc70-p53 complex with an altered half-life. Mol Cell Biol. 1988 Feb;8(2):531–539. doi: 10.1128/mcb.8.2.531. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Finlay C. A., Hinds P. W., Tan T. H., Eliyahu D., Oren M., Levine A. J. Activating mutations for transformation by p53 produce a gene product that forms an hsc70-p53 complex with an altered half-life. Mol Cell Biol. 1988 Feb;8(2):531–539. doi: 10.1128/mcb.8.2.531. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Firestein G. S., Yeo M., Zvaifler N. J. Apoptosis in rheumatoid arthritis synovium. J Clin Invest. 1995 Sep;96(3):1631–1638. doi: 10.1172/JCI118202. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fritsche M., Haessler C., Brandner G. Induction of nuclear accumulation of the tumor-suppressor protein p53 by DNA-damaging agents. Oncogene. 1993 Feb;8(2):307–318. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gannon J. V., Greaves R., Iggo R., Lane D. P. Activating mutations in p53 produce a common conformational effect. A monoclonal antibody specific for the mutant form. EMBO J. 1990 May;9(5):1595–1602. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1990.tb08279.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Geiler T., Kriegsmann J., Keyszer G. M., Gay R. E., Gay S. A new model for rheumatoid arthritis generated by engraftment of rheumatoid synovial tissue and normal human cartilage into SCID mice. Arthritis Rheum. 1994 Nov;37(11):1664–1671. doi: 10.1002/art.1780371116. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gotlieb W. H., Watson J. M., Rezai A., Johnson M., Martínez-Maza O., Berek J. S. Cytokine-induced modulation of tumor suppressor gene expression in ovarian cancer cells: up-regulation of p53 gene expression and induction of apoptosis by tumor necrosis factor-alpha. Am J Obstet Gynecol. 1994 Apr;170(4):1121–1130. doi: 10.1016/s0002-9378(94)70106-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Graeber T. G., Osmanian C., Jacks T., Housman D. E., Koch C. J., Lowe S. W., Giaccia A. J. Hypoxia-mediated selection of cells with diminished apoptotic potential in solid tumours. Nature. 1996 Jan 4;379(6560):88–91. doi: 10.1038/379088a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hamelin R., Jego N., Laurent-Puig P., Vidaud M., Thomas G. Efficient screening of p53 mutations by denaturing gradient gel electrophoresis in colorectal tumors. Oncogene. 1993 Aug;8(8):2213–2220. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hansson M., Asea A., Ersson U., Hermodsson S., Hellstrand K. Induction of apoptosis in NK cells by monocyte-derived reactive oxygen metabolites. J Immunol. 1996 Jan 1;156(1):42–47. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harris A. L. Mutant p53--the commonest genetic abnormality in human cancer? J Pathol. 1990 Sep;162(1):5–6. doi: 10.1002/path.1711620103. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hermeking H., Eick D. Mediation of c-Myc-induced apoptosis by p53. Science. 1994 Sep 30;265(5181):2091–2093. doi: 10.1126/science.8091232. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hollstein M., Sidransky D., Vogelstein B., Harris C. C. p53 mutations in human cancers. Science. 1991 Jul 5;253(5015):49–53. doi: 10.1126/science.1905840. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kallakury B. V., Figge J., Ross J. S., Fisher H. A., Figge H. L., Jennings T. A. Association of p53 immunoreactivity with high gleason tumor grade in prostatic adenocarcinoma. Hum Pathol. 1994 Jan;25(1):92–97. doi: 10.1016/0046-8177(94)90177-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lafyatis R., Remmers E. F., Roberts A. B., Yocum D. E., Sporn M. B., Wilder R. L. Anchorage-independent growth of synoviocytes from arthritic and normal joints. Stimulation by exogenous platelet-derived growth factor and inhibition by transforming growth factor-beta and retinoids. J Clin Invest. 1989 Apr;83(4):1267–1276. doi: 10.1172/JCI114011. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lane D. P. Cancer. p53, guardian of the genome. Nature. 1992 Jul 2;358(6381):15–16. doi: 10.1038/358015a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lin D., Shields M. T., Ullrich S. J., Appella E., Mercer W. E. Growth arrest induced by wild-type p53 protein blocks cells prior to or near the restriction point in late G1 phase. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1992 Oct 1;89(19):9210–9214. doi: 10.1073/pnas.89.19.9210. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maltzman W., Czyzyk L. UV irradiation stimulates levels of p53 cellular tumor antigen in nontransformed mouse cells. Mol Cell Biol. 1984 Sep;4(9):1689–1694. doi: 10.1128/mcb.4.9.1689. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Martinez J., Georgoff I., Martinez J., Levine A. J. Cellular localization and cell cycle regulation by a temperature-sensitive p53 protein. Genes Dev. 1991 Feb;5(2):151–159. doi: 10.1101/gad.5.2.151. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McGahon A. J., Martin S. J., Bissonnette R. P., Mahboubi A., Shi Y., Mogil R. J., Nishioka W. K., Green D. R. The end of the (cell) line: methods for the study of apoptosis in vitro. Methods Cell Biol. 1995;46:153–185. doi: 10.1016/s0091-679x(08)61929-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Michalovitz D., Halevy O., Oren M. Conditional inhibition of transformation and of cell proliferation by a temperature-sensitive mutant of p53. Cell. 1990 Aug 24;62(4):671–680. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90113-s. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mietz J. A., Unger T., Huibregtse J. M., Howley P. M. The transcriptional transactivation function of wild-type p53 is inhibited by SV40 large T-antigen and by HPV-16 E6 oncoprotein. EMBO J. 1992 Dec;11(13):5013–5020. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1992.tb05608.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miller S. D., Farmer G., Prives C. p53 inhibits DNA replication in vitro in a DNA-binding-dependent manner. Mol Cell Biol. 1995 Dec;15(12):6554–6560. doi: 10.1128/mcb.15.12.6554. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morales-Ducret J., Wayner E., Elices M. J., Alvaro-Gracia J. M., Zvaifler N. J., Firestein G. S. Alpha 4/beta 1 integrin (VLA-4) ligands in arthritis. Vascular cell adhesion molecule-1 expression in synovium and on fibroblast-like synoviocytes. J Immunol. 1992 Aug 15;149(4):1424–1431. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Müller-Ladner U., Kriegsmann J., Franklin B. N., Matsumoto S., Geiler T., Gay R. E., Gay S. Synovial fibroblasts of patients with rheumatoid arthritis attach to and invade normal human cartilage when engrafted into SCID mice. Am J Pathol. 1996 Nov;149(5):1607–1615. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nakajima T., Aono H., Hasunuma T., Yamamoto K., Shirai T., Hirohata K., Nishioka K. Apoptosis and functional Fas antigen in rheumatoid arthritis synoviocytes. Arthritis Rheum. 1995 Apr;38(4):485–491. doi: 10.1002/art.1780380405. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pontén F., Berne B., Ren Z. P., Nistér M., Pontén J. Ultraviolet light induces expression of p53 and p21 in human skin: effect of sunscreen and constitutive p21 expression in skin appendages. J Invest Dermatol. 1995 Sep;105(3):402–406. doi: 10.1111/1523-1747.ep12321071. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Qu Z., Garcia C. H., O'Rourke L. M., Planck S. R., Kohli M., Rosenbaum J. T. Local proliferation of fibroblast-like synoviocytes contributes to synovial hyperplasia. Results of proliferating cell nuclear antigen/cyclin, c-myc, and nucleolar organizer region staining. Arthritis Rheum. 1994 Feb;37(2):212–220. doi: 10.1002/art.1780370210. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Raycroft L., Wu H. Y., Lozano G. Transcriptional activation by wild-type but not transforming mutants of the p53 anti-oncogene. Science. 1990 Aug 31;249(4972):1049–1051. doi: 10.1126/science.2144364. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reich N. C., Oren M., Levine A. J. Two distinct mechanisms regulate the levels of a cellular tumor antigen, p53. Mol Cell Biol. 1983 Dec;3(12):2143–2150. doi: 10.1128/mcb.3.12.2143. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rodrigues N. R., Rowan A., Smith M. E., Kerr I. B., Bodmer W. F., Gannon J. V., Lane D. P. p53 mutations in colorectal cancer. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Oct;87(19):7555–7559. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.19.7555. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sarkar G., Yoon H. S., Sommer S. S. Dideoxy fingerprinting (ddE): a rapid and efficient screen for the presence of mutations. Genomics. 1992 Jun;13(2):441–443. doi: 10.1016/0888-7543(92)90266-u. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith M. L., Chen I. T., Zhan Q., Bae I., Chen C. Y., Gilmer T. M., Kastan M. B., O'Connor P. M., Fornace A. J., Jr Interaction of the p53-regulated protein Gadd45 with proliferating cell nuclear antigen. Science. 1994 Nov 25;266(5189):1376–1380. doi: 10.1126/science.7973727. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tendler Y., Schwartz Y., Reshef R., Shasha S. M., Rotter V., Shkolnik T. Immunohistochemical detection of p53 protein expression in HPV-induced condyloma acuminatum. Acta Derm Venereol. 1995 May;75(3):177–179. doi: 10.2340/0001555575177179. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tsukada T., Tomooka Y., Takai S., Ueda Y., Nishikawa S., Yagi T., Tokunaga T., Takeda N., Suda Y., Abe S. Enhanced proliferative potential in culture of cells from p53-deficient mice. Oncogene. 1993 Dec;8(12):3313–3322. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ueda N., Shah S. V. Endonuclease-induced DNA damage and cell death in oxidant injury to renal tubular epithelial cells. J Clin Invest. 1992 Dec;90(6):2593–2597. doi: 10.1172/JCI116154. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Villuendas R., Piris M. A., Orradre J. L., Mollejo M., Algara P., Sanchez L., Martinez J. C., Martinez P. P53 protein expression in lymphomas and reactive lymphoid tissue. J Pathol. 1992 Mar;166(3):235–241. doi: 10.1002/path.1711660305. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vojtesek B., Bártek J., Midgley C. A., Lane D. P. An immunochemical analysis of the human nuclear phosphoprotein p53. New monoclonal antibodies and epitope mapping using recombinant p53. J Immunol Methods. 1992 Jul 6;151(1-2):237–244. doi: 10.1016/0022-1759(92)90122-a. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zhang W., Grasso L., McClain C. D., Gambel A. M., Cha Y., Travali S., Deisseroth A. B., Mercer W. E. p53-independent induction of WAF1/CIP1 in human leukemia cells is correlated with growth arrest accompanying monocyte/macrophage differentiation. Cancer Res. 1995 Feb 1;55(3):668–674. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ziegler A., Jonason A. S., Leffell D. J., Simon J. A., Sharma H. W., Kimmelman J., Remington L., Jacks T., Brash D. E. Sunburn and p53 in the onset of skin cancer. Nature. 1994 Dec 22;372(6508):773–776. doi: 10.1038/372773a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]