Abstract
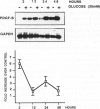
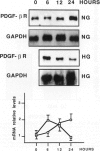
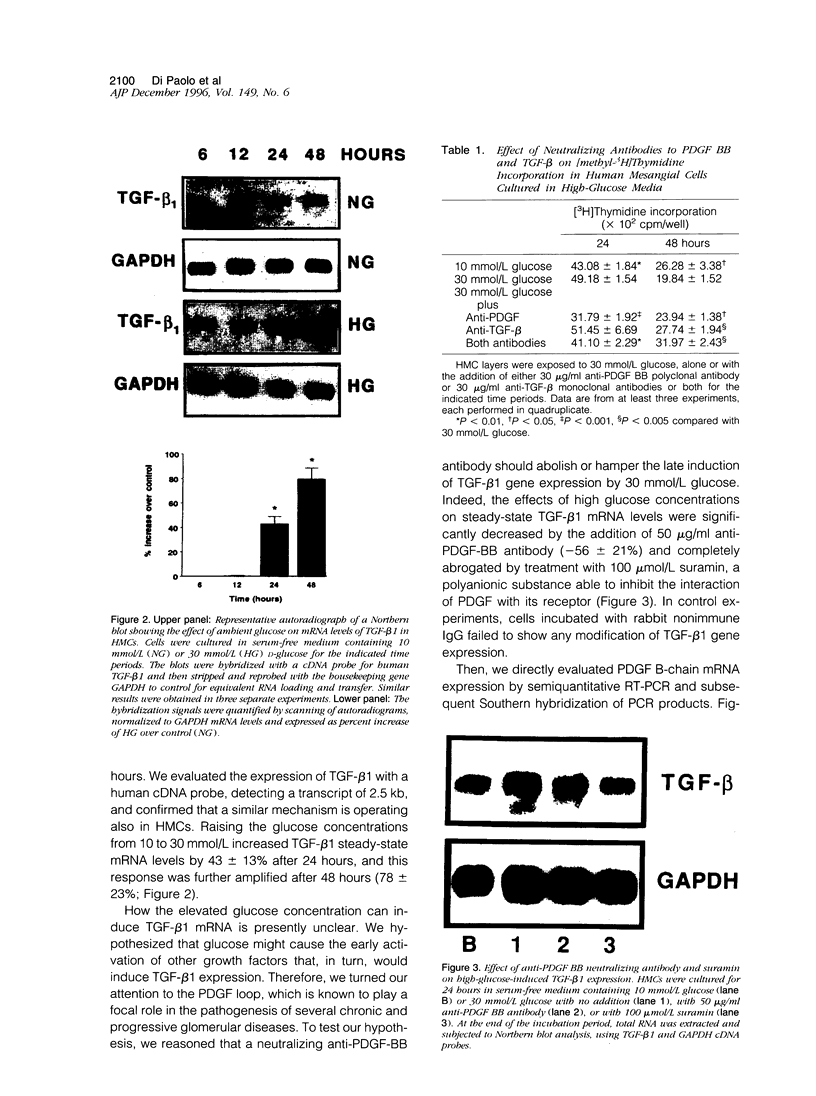
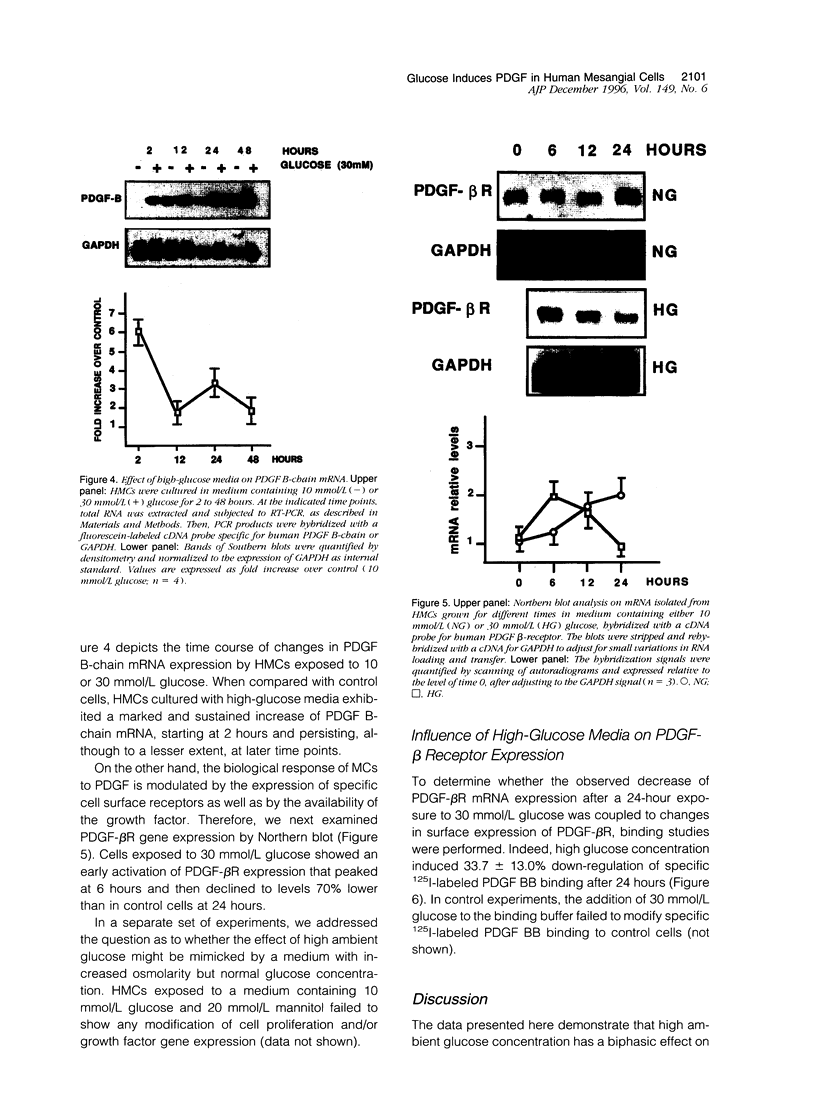
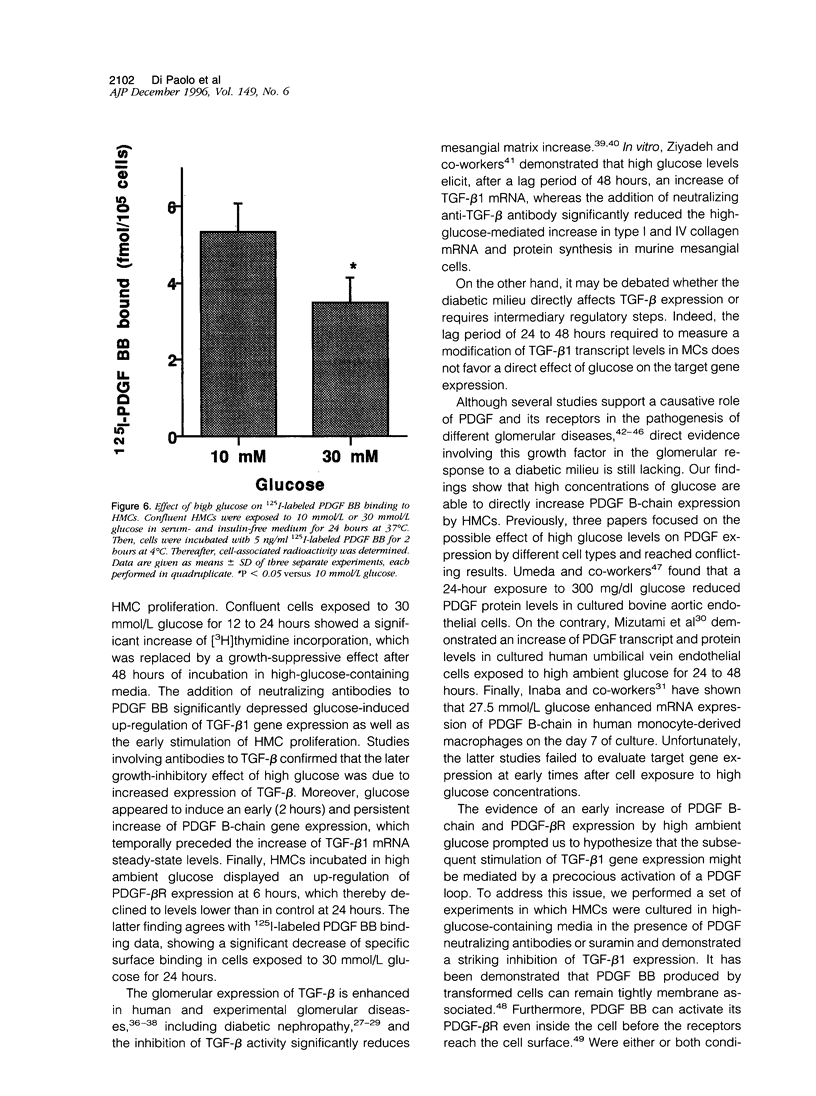
High glucose concentration has been shown to induce the overexpression of transforming growth factor (TGF)-beta 1 mRNA and protein in different cell types, including murine mesangial cells, thus possibly accounting for the expansion of mesangial extracellular matrix observed in diabetic glomerulopathy. In the present study, we evaluated platelet-derived growth factor (PDGF) B-chain and PDGF-beta receptor gene expression in human mesangial cells (HMCs) exposed to different concentrations of glucose and then sought a possible relationship between a PDGF loop and the modulation of TGF-beta 1 expression. HMC [3H]thymidine incorporation was upregulated by 30 mmol/L glucose (HG) up to 24 hours, whereas it was significantly inhibited at later time points. Neutralizing antibodies to PDGF BB abolished the biphasic response to HG, whereas anti-TGF-beta antibodies reversed only the late inhibitory effect of hyperglycemic medium. HG induced an early and persistent increase of PDGF B-chain gene expression, as evaluated by reverse transcriptase polymerase chain reaction, whereas PDGF-beta receptor mRNA increased by twofold after 6 hours, thereafter declining at levels 70% lower than in controls after 24 hours. 125I-Labeled PDGF BB binding studies in HMCs exposed to HG for 24 hours confirmed the decrease of PDGF-beta receptor expression. TGF-beta 1-specific transcripts showed 43 and 78% increases after 24 and 48 hours of incubation in HG, respectively, which was markedly diminished by anti-PDGF BB neutralizing antibodies or suramin. We conclude that HG induces an early activation of a PDGF loop that, in turn, causes an increase of TGF-beta 1 gene expression, thus modulating both HMC proliferation and mesangial matrix production.
Full text
PDF








Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Abboud H. E. Growth factors in glomerulonephritis. Kidney Int. 1993 Jan;43(1):252–267. doi: 10.1038/ki.1993.39. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Battegay E. J., Raines E. W., Seifert R. A., Bowen-Pope D. F., Ross R. TGF-beta induces bimodal proliferation of connective tissue cells via complex control of an autocrine PDGF loop. Cell. 1990 Nov 2;63(3):515–524. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90448-n. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bilous R. W., Mauer S. M., Sutherland D. E., Najarian J. S., Goetz F. C., Steffes M. W. The effects of pancreas transplantation on the glomerular structure of renal allografts in patients with insulin-dependent diabetes. N Engl J Med. 1989 Jul 13;321(2):80–85. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198907133210204. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Border W. A., Noble N. A. From serum sickness to cytokines: advances in understanding the molecular pathogenesis of kidney disease. Lab Invest. 1993 Feb;68(2):125–128. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Border W. A., Okuda S., Languino L. R., Ruoslahti E. Transforming growth factor-beta regulates production of proteoglycans by mesangial cells. Kidney Int. 1990 Feb;37(2):689–695. doi: 10.1038/ki.1990.35. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Border W. A., Okuda S., Languino L. R., Sporn M. B., Ruoslahti E. Suppression of experimental glomerulonephritis by antiserum against transforming growth factor beta 1. Nature. 1990 Jul 26;346(6282):371–374. doi: 10.1038/346371a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chomczynski P., Sacchi N. Single-step method of RNA isolation by acid guanidinium thiocyanate-phenol-chloroform extraction. Anal Biochem. 1987 Apr;162(1):156–159. doi: 10.1006/abio.1987.9999. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Coimbra T., Wiggins R., Noh J. W., Merritt S., Phan S. H. Transforming growth factor-beta production in anti-glomerular basement membrane disease in the rabbit. Am J Pathol. 1991 Jan;138(1):223–234. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cosio F. G. Effects of high glucose concentrations on human mesangial cell proliferation. J Am Soc Nephrol. 1995 Feb;5(8):1600–1609. doi: 10.1681/ASN.V581600. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Doi T., Vlassara H., Kirstein M., Yamada Y., Striker G. E., Striker L. J. Receptor-specific increase in extracellular matrix production in mouse mesangial cells by advanced glycosylation end products is mediated via platelet-derived growth factor. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1992 Apr 1;89(7):2873–2877. doi: 10.1073/pnas.89.7.2873. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eriksson A., Nistér M., Leveen P., Westermark B., Heldin C. H., Claesson-Welsh L. Induction of platelet-derived growth factor alpha- and beta-receptor mRNA and protein by platelet-derived growth factor BB. J Biol Chem. 1991 Nov 5;266(31):21138–21144. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Floege J., Eng E., Young B. A., Alpers C. E., Barrett T. B., Bowen-Pope D. F., Johnson R. J. Infusion of platelet-derived growth factor or basic fibroblast growth factor induces selective glomerular mesangial cell proliferation and matrix accumulation in rats. J Clin Invest. 1993 Dec;92(6):2952–2962. doi: 10.1172/JCI116918. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Floege J., Eng E., Young B. A., Johnson R. J. Factors involved in the regulation of mesangial cell proliferation in vitro and in vivo. Kidney Int Suppl. 1993 Jan;39:S47–S54. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fukui M., Nakamura T., Ebihara I., Nagaoka I., Tomino Y., Koide H. Low-protein diet attenuates increased gene expression of platelet-derived growth factor and transforming growth factor-beta in experimental glomerular sclerosis. J Lab Clin Med. 1993 Feb;121(2):224–234. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gesualdo L., Di Paolo S., Milani S., Pinzani M., Grappone C., Ranieri E., Pannarale G., Schena F. P. Expression of platelet-derived growth factor receptors in normal and diseased human kidney. An immunohistochemistry and in situ hybridization study. J Clin Invest. 1994 Jul;94(1):50–58. doi: 10.1172/JCI117348. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gesualdo L., Di Paolo S., Ranieri E., Schena F. P. Trapidil inhibits human mesangial cell proliferation: effect on PDGF beta-receptor binding and expression. Kidney Int. 1994 Oct;46(4):1002–1009. doi: 10.1038/ki.1994.360. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gesualdo L., Pinzani M., Floriano J. J., Hassan M. O., Nagy N. U., Schena F. P., Emancipator S. N., Abboud H. E. Platelet-derived growth factor expression in mesangial proliferative glomerulonephritis. Lab Invest. 1991 Aug;65(2):160–167. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grandaliano G., Biswas P., Choudhury G. G., Abboud H. E. Simvastatin inhibits PDGF-induced DNA synthesis in human glomerular mesangial cells. Kidney Int. 1993 Sep;44(3):503–508. doi: 10.1038/ki.1993.274. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gronwald R. G., Seifert R. A., Bowen-Pope D. F. Differential regulation of expression of two platelet-derived growth factor receptor subunits by transforming growth factor-beta. J Biol Chem. 1989 May 15;264(14):8120–8125. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Haberstroh U., Zahner G., Disser M., Thaiss F., Wolf G., Stahl R. A. TGF-beta stimulates rat mesangial cell proliferation in culture: role of PDGF beta-receptor expression. Am J Physiol. 1993 Feb;264(2 Pt 2):F199–F205. doi: 10.1152/ajprenal.1993.264.2.F199. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Iida H., Seifert R., Alpers C. E., Gronwald R. G., Phillips P. E., Pritzl P., Gordon K., Gown A. M., Ross R., Bowen-Pope D. F. Platelet-derived growth factor (PDGF) and PDGF receptor are induced in mesangial proliferative nephritis in the rat. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Aug 1;88(15):6560–6564. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.15.6560. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Inaba T., Ishibashi S., Gotoda T., Kawamura M., Morino N., Nojima Y., Kawakami M., Yazaki Y., Yamada N. Enhanced expression of platelet-derived growth factor-beta receptor by high glucose. Involvement of platelet-derived growth factor in diabetic angiopathy. Diabetes. 1996 Apr;45(4):507–512. doi: 10.2337/diab.45.4.507. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jaffer F., Saunders C., Shultz P., Throckmorton D., Weinshell E., Abboud H. E. Regulation of mesangial cell growth by polypeptide mitogens. Inhibitory role of transforming growth factor beta. Am J Pathol. 1989 Aug;135(2):261–269. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johnson R. J. Cytokine networks and the pathogenesis of glomerulonephritis. J Lab Clin Med. 1993 Feb;121(2):190–192. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johnson R. J., Raines E. W., Floege J., Yoshimura A., Pritzl P., Alpers C., Ross R. Inhibition of mesangial cell proliferation and matrix expansion in glomerulonephritis in the rat by antibody to platelet-derived growth factor. J Exp Med. 1992 May 1;175(5):1413–1416. doi: 10.1084/jem.175.5.1413. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Keating M. T., Williams L. T. Autocrine stimulation of intracellular PDGF receptors in v-sis-transformed cells. Science. 1988 Feb 19;239(4842):914–916. doi: 10.1126/science.2829358. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Knecht A., Fine L. G., Kleinman K. S., Rodemann H. P., Müller G. A., Woo D. D., Norman J. T. Fibroblasts of rabbit kidney in culture. II. Paracrine stimulation of papillary fibroblasts by PDGF. Am J Physiol. 1991 Aug;261(2 Pt 2):F292–F299. doi: 10.1152/ajprenal.1991.261.2.F292. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MacKay K., Striker L. J., Stauffer J. W., Doi T., Agodoa L. Y., Striker G. E. Transforming growth factor-beta. Murine glomerular receptors and responses of isolated glomerular cells. J Clin Invest. 1989 Apr;83(4):1160–1167. doi: 10.1172/JCI113996. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Massagué J. The transforming growth factor-beta family. Annu Rev Cell Biol. 1990;6:597–641. doi: 10.1146/annurev.cb.06.110190.003121. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mauer S. M., Steffes M. W., Ellis E. N., Sutherland D. E., Brown D. M., Goetz F. C. Structural-functional relationships in diabetic nephropathy. J Clin Invest. 1984 Oct;74(4):1143–1155. doi: 10.1172/JCI111523. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mizutani M., Okuda Y., Yamaoka T., Tsukahara K., Isaka M., Bannai C., Yamashita K. High glucose and hyperosmolarity increase platelet-derived growth factor mRNA levels in cultured human vascular endothelial cells. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1992 Sep 16;187(2):664–669. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(92)91246-m. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nakamura T., Fukui M., Ebihara I., Osada S., Nagaoka I., Tomino Y., Koide H. mRNA expression of growth factors in glomeruli from diabetic rats. Diabetes. 1993 Mar;42(3):450–456. doi: 10.2337/diab.42.3.450. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nathan D. M. Long-term complications of diabetes mellitus. N Engl J Med. 1993 Jun 10;328(23):1676–1685. doi: 10.1056/NEJM199306103282306. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Okuda S., Languino L. R., Ruoslahti E., Border W. A. Elevated expression of transforming growth factor-beta and proteoglycan production in experimental glomerulonephritis. Possible role in expansion of the mesangial extracellular matrix. J Clin Invest. 1990 Aug;86(2):453–462. doi: 10.1172/JCI114731. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pankewycz O. G., Guan J. X., Bolton W. K., Gomez A., Benedict J. F. Renal TGF-beta regulation in spontaneously diabetic NOD mice with correlations in mesangial cells. Kidney Int. 1994 Sep;46(3):748–758. doi: 10.1038/ki.1994.330. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Paulsson Y., Karlsson C., Heldin C. H., Westermark B. Density-dependent inhibitory effect of transforming growth factor-beta 1 on human fibroblasts involves the down-regulation of platelet-derived growth factor alpha-receptors. J Cell Physiol. 1993 Oct;157(1):97–103. doi: 10.1002/jcp.1041570113. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Phillips A. O., Steadman R., Topley N., Williams J. D. Elevated D-glucose concentrations modulate TGF-beta 1 synthesis by human cultured renal proximal tubular cells. The permissive role of platelet-derived growth factor. Am J Pathol. 1995 Aug;147(2):362–374. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Robbins K. C., Leal F., Pierce J. H., Aaronson S. A. The v-sis/PDGF-2 transforming gene product localizes to cell membranes but is not a secretory protein. EMBO J. 1985 Jul;4(7):1783–1792. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1985.tb03851.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rocco M. V., Chen Y., Goldfarb S., Ziyadeh F. N. Elevated glucose stimulates TGF-beta gene expression and bioactivity in proximal tubule. Kidney Int. 1992 Jan;41(1):107–114. doi: 10.1038/ki.1992.14. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shultz P. J., DiCorleto P. E., Silver B. J., Abboud H. E. Mesangial cells express PDGF mRNAs and proliferate in response to PDGF. Am J Physiol. 1988 Oct;255(4 Pt 2):F674–F684. doi: 10.1152/ajprenal.1988.255.4.F674. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Steffes M. W., Bilous R. W., Sutherland D. E., Mauer S. M. Cell and matrix components of the glomerular mesangium in type I diabetes. Diabetes. 1992 Jun;41(6):679–684. doi: 10.2337/diab.41.6.679. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Steffes M. W., Osterby R., Chavers B., Mauer S. M. Mesangial expansion as a central mechanism for loss of kidney function in diabetic patients. Diabetes. 1989 Sep;38(9):1077–1081. doi: 10.2337/diab.38.9.1077. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Striker L. J., Peten E. P., Elliot S. J., Doi T., Striker G. E. Mesangial cell turnover: effect of heparin and peptide growth factors. Lab Invest. 1991 Apr;64(4):446–456. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Throckmorton D. C., Brogden A. P., Min B., Rasmussen H., Kashgarian M. PDGF and TGF-beta mediate collagen production by mesangial cells exposed to advanced glycosylation end products. Kidney Int. 1995 Jul;48(1):111–117. doi: 10.1038/ki.1995.274. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Van Obberghen-Schilling E., Roche N. S., Flanders K. C., Sporn M. B., Roberts A. B. Transforming growth factor beta 1 positively regulates its own expression in normal and transformed cells. J Biol Chem. 1988 Jun 5;263(16):7741–7746. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wang P. H., Lau J., Chalmers T. C. Meta-analysis of effects of intensive blood-glucose control on late complications of type I diabetes. Lancet. 1993 May 22;341(8856):1306–1309. doi: 10.1016/0140-6736(93)90816-y. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wolf G., Sharma K., Chen Y., Ericksen M., Ziyadeh F. N. High glucose-induced proliferation in mesangial cells is reversed by autocrine TGF-beta. Kidney Int. 1992 Sep;42(3):647–656. doi: 10.1038/ki.1992.330. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yamamoto T., Nakamura T., Noble N. A., Ruoslahti E., Border W. A. Expression of transforming growth factor beta is elevated in human and experimental diabetic nephropathy. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1993 Mar 1;90(5):1814–1818. doi: 10.1073/pnas.90.5.1814. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yoshimura A., Gordon K., Alpers C. E., Floege J., Pritzl P., Ross R., Couser W. G., Bowen-Pope D. F., Johnson R. J. Demonstration of PDGF B-chain mRNA in glomeruli in mesangial proliferative nephritis by in situ hybridization. Kidney Int. 1991 Sep;40(3):470–476. doi: 10.1038/ki.1991.234. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yoshioka K., Takemura T., Murakami K., Okada M., Hino S., Miyamoto H., Maki S. Transforming growth factor-beta protein and mRNA in glomeruli in normal and diseased human kidneys. Lab Invest. 1993 Feb;68(2):154–163. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ziyadeh F. N., Sharma K., Ericksen M., Wolf G. Stimulation of collagen gene expression and protein synthesis in murine mesangial cells by high glucose is mediated by autocrine activation of transforming growth factor-beta. J Clin Invest. 1994 Feb;93(2):536–542. doi: 10.1172/JCI117004. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]