Abstract
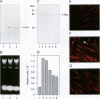
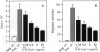
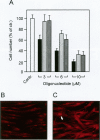
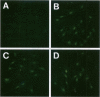
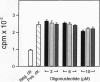
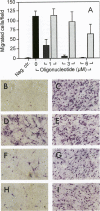
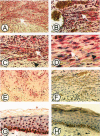
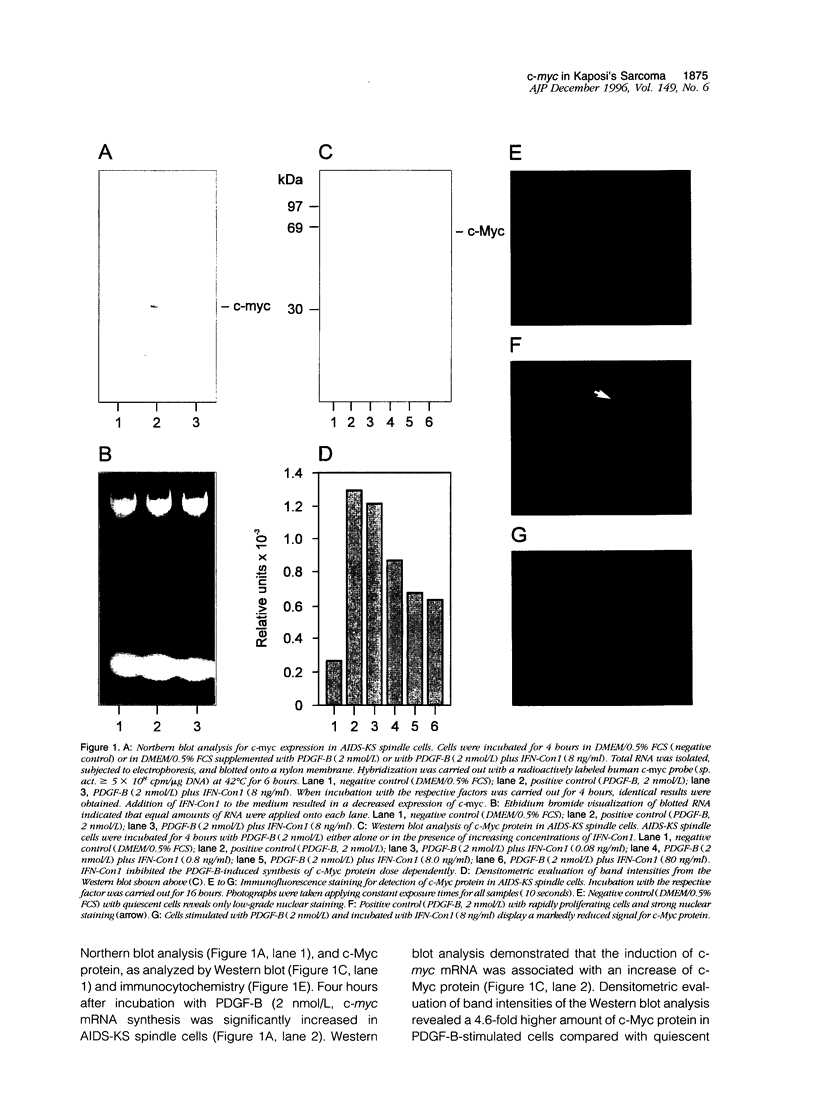
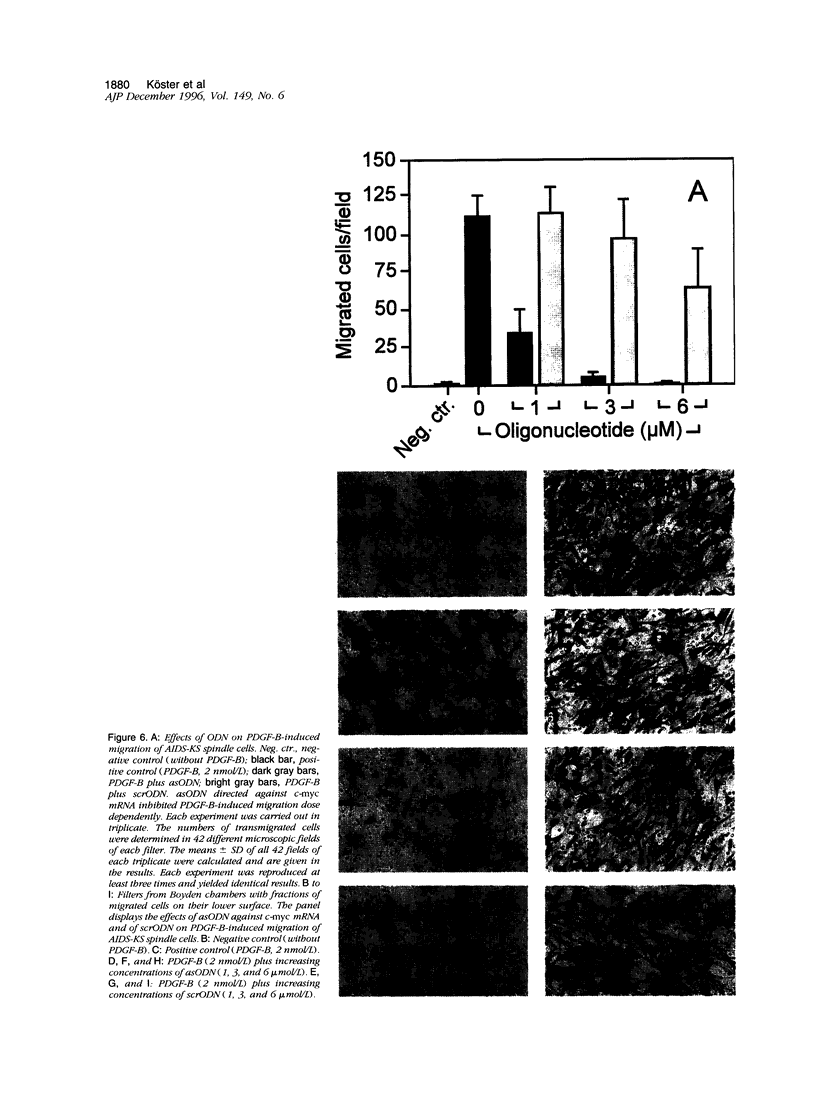
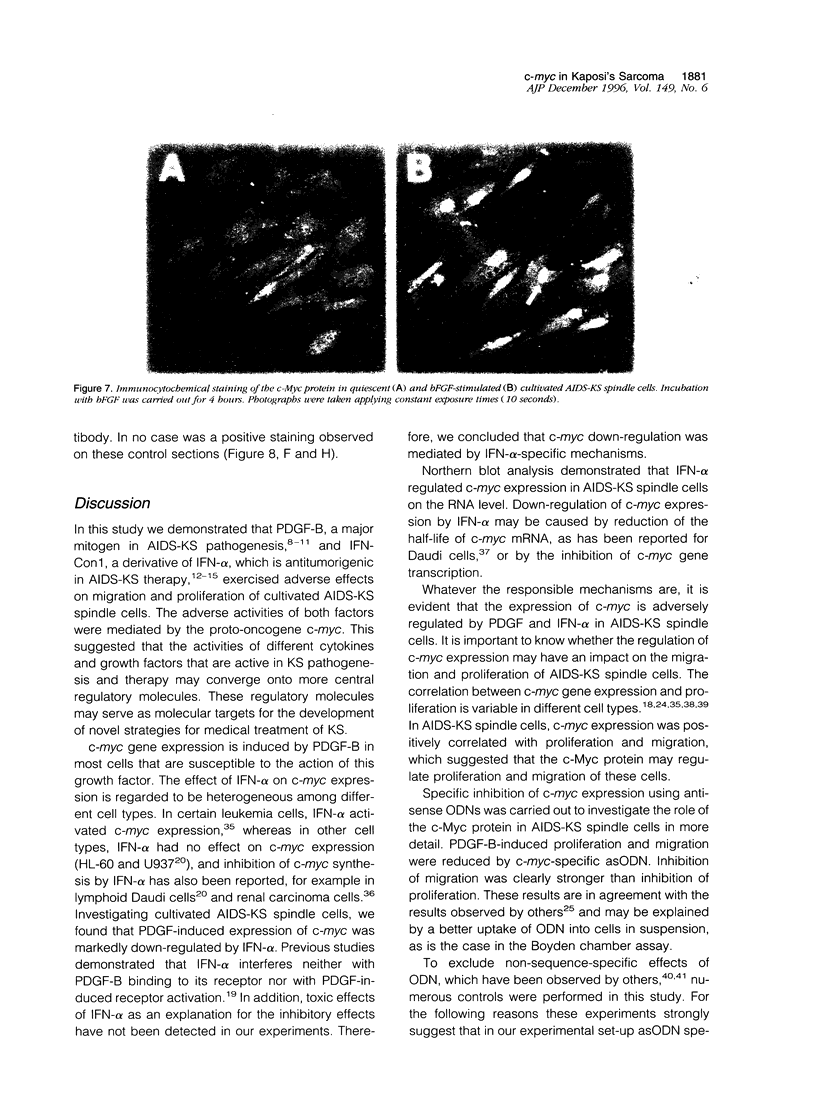
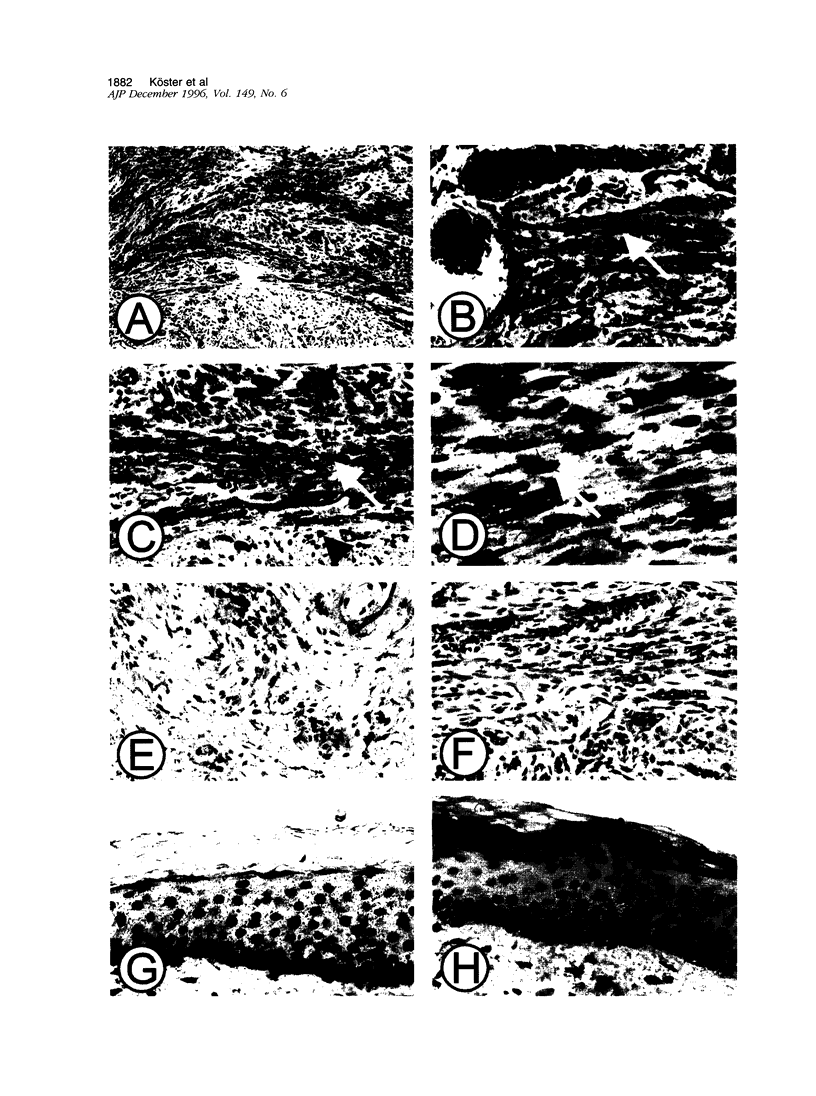
Platelet-derived growth factor-B (PDGF-B) is a potent paracrine-acting mitogen in Kaposi's sarcoma (KS) lesions. Interferon-alpha is widely used for clinical treatment of KS. Here we show that platelet-derived growth factor-B activates proliferation and migration of cultivated AIDS-KS spindle cells whereas interferon-alpha acts as an inhibitor. At the molecular level, these opposite activities of platelet-derived growth factor-B and interferon-alpha converged onto the adverse regulation of the c-myc gene expression. Platelet-derived growth factor-B induced c-myc mRNA and protein synthesis in cultivated AIDS-KS spindle cells whereas interferon-alpha inhibited these processes. Using c-myc-specific phoshothioate antisense oligodeoxynucleotides, we demonstrated that down-regulation of c-myc expression is sufficient to inhibit proliferation and migration of KS spindle cells in vitro. This indicated that c-Myc protein may be an important regulatory molecule of KS spindle cell proliferation and migration. High amounts of the c-Myc protein were detected in the nuclei of KS spindle cells in histological sections of AIDS-KS biopsies. This suggested that the c-myc gene may also regulate proliferation and migration of AIDS-KS spindle cells in vivo. In this case, c-myc may play an important role in the focus of major pathogenic and therapeutic pathways of KS.
Full text
PDF






Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Albini A., Fontanini G., Masiello L., Tacchetti C., Bigini D., Luzzi P., Noonan D. M., Stetler-Stevenson W. G. Angiogenic potential in vivo by Kaposi's sarcoma cell-free supernatants and HIV-1 tat product: inhibition of KS-like lesions by tissue inhibitor of metalloproteinase-2. AIDS. 1994 Sep;8(9):1237–1244. doi: 10.1097/00002030-199409000-00004. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Armelin H. A., Armelin M. C., Kelly K., Stewart T., Leder P., Cochran B. H., Stiles C. D. Functional role for c-myc in mitogenic response to platelet-derived growth factor. Nature. 1984 Aug 23;310(5979):655–660. doi: 10.1038/310655a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BOYDEN S. The chemotactic effect of mixtures of antibody and antigen on polymorphonuclear leucocytes. J Exp Med. 1962 Mar 1;115:453–466. doi: 10.1084/jem.115.3.453. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bennett M. R., Anglin S., McEwan J. R., Jagoe R., Newby A. C., Evan G. I. Inhibition of vascular smooth muscle cell proliferation in vitro and in vivo by c-myc antisense oligodeoxynucleotides. J Clin Invest. 1994 Feb;93(2):820–828. doi: 10.1172/JCI117036. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Biro S., Fu Y. M., Yu Z. X., Epstein S. E. Inhibitory effects of antisense oligodeoxynucleotides targeting c-myc mRNA on smooth muscle cell proliferation and migration. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1993 Jan 15;90(2):654–658. doi: 10.1073/pnas.90.2.654. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burgess T. L., Fisher E. F., Ross S. L., Bready J. V., Qian Y. X., Bayewitch L. A., Cohen A. M., Herrera C. J., Hu S. S., Kramer T. B. The antiproliferative activity of c-myb and c-myc antisense oligonucleotides in smooth muscle cells is caused by a nonantisense mechanism. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1995 Apr 25;92(9):4051–4055. doi: 10.1073/pnas.92.9.4051. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chang Y., Cesarman E., Pessin M. S., Lee F., Culpepper J., Knowles D. M., Moore P. S. Identification of herpesvirus-like DNA sequences in AIDS-associated Kaposi's sarcoma. Science. 1994 Dec 16;266(5192):1865–1869. doi: 10.1126/science.7997879. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chaouchi N., Wallon C., Taieb J., Auffredou M. T., Tertian G., Lemoine F. M., Delfraissy J. F., Vazquez A. Interferon-alpha-mediated prevention of in vitro apoptosis of chronic lymphocytic leukemia B cells: role of bcl-2 and c-myc. Clin Immunol Immunopathol. 1994 Nov;73(2):197–204. doi: 10.1006/clin.1994.1188. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cornali E., Zietz C., Benelli R., Weninger W., Masiello L., Breier G., Tschachler E., Albini A., Stürzl M. Vascular endothelial growth factor regulates angiogenesis and vascular permeability in Kaposi's sarcoma. Am J Pathol. 1996 Dec;149(6):1851–1869. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dani C., Mechti N., Piechaczyk M., Lebleu B., Jeanteur P., Blanchard J. M. Increased rate of degradation of c-myc mRNA in interferon-treated Daudi cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Aug;82(15):4896–4899. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.15.4896. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Einat M., Resnitzky D., Kimchi A. Close link between reduction of c-myc expression by interferon and, G0/G1 arrest. Nature. 1985 Feb 14;313(6003):597–600. doi: 10.1038/313597a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Einat M., Resnitzky D., Kimchi A. Inhibitory effects of interferon on the expression of genes regulated by platelet-derived growth factor. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Nov;82(22):7608–7612. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.22.7608. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ensoli B., Barillari G., Gallo R. C. Pathogenesis of AIDS-associated Kaposi's sarcoma. Hematol Oncol Clin North Am. 1991 Apr;5(2):281–295. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ensoli B., Gendelman R., Markham P., Fiorelli V., Colombini S., Raffeld M., Cafaro A., Chang H. K., Brady J. N., Gallo R. C. Synergy between basic fibroblast growth factor and HIV-1 Tat protein in induction of Kaposi's sarcoma. Nature. 1994 Oct 20;371(6499):674–680. doi: 10.1038/371674a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Friedman-Kien A. E. Disseminated Kaposi's sarcoma syndrome in young homosexual men. J Am Acad Dermatol. 1981 Oct;5(4):468–471. doi: 10.1016/s0190-9622(81)80010-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heikkila R., Schwab G., Wickstrom E., Loke S. L., Pluznik D. H., Watt R., Neckers L. M. A c-myc antisense oligodeoxynucleotide inhibits entry into S phase but not progress from G0 to G1. 1987 Jul 30-Aug 5Nature. 328(6129):445–449. doi: 10.1038/328445a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Holt J. T., Redner R. L., Nienhuis A. W. An oligomer complementary to c-myc mRNA inhibits proliferation of HL-60 promyelocytic cells and induces differentiation. Mol Cell Biol. 1988 Feb;8(2):963–973. doi: 10.1128/mcb.8.2.963. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ikegaki N., Kennett R. H. Molecular genetic characterization of epitope-specific monoclonal antibodies against the myc family proteins. Oncogene. 1990 Mar;5(3):397–403. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kelly K., Cochran B. H., Stiles C. D., Leder P. Cell-specific regulation of the c-myc gene by lymphocyte mitogens and platelet-derived growth factor. Cell. 1983 Dec;35(3 Pt 2):603–610. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(83)90092-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klein M. L., Bartley T. D., Lai P. H., Lu H. S. Structural characterization of recombinant consensus interferon-alpha. J Chromatogr. 1988 Nov 11;454:205–215. doi: 10.1016/s0021-9673(00)88614-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lilenbaum R. C., Ratner L. Systemic treatment of Kaposi's sarcoma: current status and future directions. AIDS. 1994 Feb;8(2):141–151. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marcu K. B., Bossone S. A., Patel A. J. myc function and regulation. Annu Rev Biochem. 1992;61:809–860. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.61.070192.004113. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ninomiya-Tsuji J., Torti F. M., Ringold G. M. Tumor necrosis factor-induced c-myc expression in the absence of mitogenesis is associated with inhibition of adipocyte differentiation. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1993 Oct 15;90(20):9611–9615. doi: 10.1073/pnas.90.20.9611. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ozes O. N., Reiter Z., Klein S., Blatt L. M., Taylor M. W. A comparison of interferon-Con1 with natural recombinant interferons-alpha: antiviral, antiproliferative, and natural killer-inducing activities. J Interferon Res. 1992 Feb;12(1):55–59. doi: 10.1089/jir.1992.12.55. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Persson H., Hennighausen L., Taub R., DeGrado W., Leder P. Antibodies to human c-myc oncogene product: evidence of an evolutionarily conserved protein induced during cell proliferation. Science. 1984 Aug 17;225(4663):687–693. doi: 10.1126/science.6431612. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reiter Z., Ozés O. N., Blatt L. M., Sturzl M., Taylor M. W. A possible role for interferon-alpha and activated natural killer cells in remission of AIDS-related Kaposi's sarcoma: in vitro studies. J Acquir Immune Defic Syndr. 1992;5(5):469–476. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roth W. K., Brandstetter H., Stürzl M. Cellular and molecular features of HIV-associated Kaposi's sarcoma. AIDS. 1992 Sep;6(9):895–913. doi: 10.1097/00002030-199209000-00001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roth W. K., Werner S., Risau W., Remberger K., Hofschneider P. H. Cultured, AIDS-related Kaposi's sarcoma cells express endothelial cell markers and are weakly malignant in vitro. Int J Cancer. 1988 Nov 15;42(5):767–773. doi: 10.1002/ijc.2910420523. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roth W. K., Werner S., Schirren C. G., Hofschneider P. H. Depletion of PDGF from serum inhibits growth of AIDS-related and sporadic Kaposi's sarcoma cells in culture. Oncogene. 1989 Apr;4(4):483–487. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Safai B., Johnson K. G., Myskowski P. L., Koziner B., Yang S. Y., Cunningham-Rundles S., Godbold J. H., Dupont B. The natural history of Kaposi's sarcoma in the acquired immunodeficiency syndrome. Ann Intern Med. 1985 Nov;103(5):744–750. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-103-5-744. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Singh R. K., Gutman M., Bucana C. D., Sanchez R., Llansa N., Fidler I. J. Interferons alpha and beta down-regulate the expression of basic fibroblast growth factor in human carcinomas. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1995 May 9;92(10):4562–4566. doi: 10.1073/pnas.92.10.4562. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stickler M. C., Friedman-Kien A. E. Kaposi's sarcoma. Clin Dermatol. 1991 Jan-Mar;9(1):39–47. doi: 10.1016/0738-081x(91)90113-y. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stürzl M., Brandstetter H., Roth W. K. Kaposi's sarcoma: a review of gene expression and ultrastructure of KS spindle cells in vivo. AIDS Res Hum Retroviruses. 1992 Oct;8(10):1753–1763. doi: 10.1089/aid.1992.8.1753. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stürzl M., Brandstetter H., Zietz C., Eisenburg B., Raivich G., Gearing D. P., Brockmeyer N. H., Hofschneider P. H. Identification of interleukin-1 and platelet-derived growth factor-B as major mitogens for the spindle cells of Kaposi's sarcoma: a combined in vitro and in vivo analysis. Oncogene. 1995 May 18;10(10):2007–2016. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stürzl M., Roth W. K., Brockmeyer N. H., Zietz C., Speiser B., Hofschneider P. H. Expression of platelet-derived growth factor and its receptor in AIDS-related Kaposi sarcoma in vivo suggests paracrine and autocrine mechanisms of tumor maintenance. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1992 Aug 1;89(15):7046–7050. doi: 10.1073/pnas.89.15.7046. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wagner R. W. Gene inhibition using antisense oligodeoxynucleotides. Nature. 1994 Nov 24;372(6504):333–335. doi: 10.1038/372333a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Werner S., Hofschneider P. H., Heldin C. H., Ostman A., Roth W. K. Cultured Kaposi's sarcoma-derived cells express functional PDGF A-type and B-type receptors. Exp Cell Res. 1990 Mar;187(1):98–103. doi: 10.1016/0014-4827(90)90122-q. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wickstrom E. L., Bacon T. A., Gonzalez A., Freeman D. L., Lyman G. H., Wickstrom E. Human promyelocytic leukemia HL-60 cell proliferation and c-myc protein expression are inhibited by an antisense pentadecadeoxynucleotide targeted against c-myc mRNA. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Feb;85(4):1028–1032. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.4.1028. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Womer R. B., Frick K., Mitchell C. D., Ross A. H., Bishayee S., Scher C. D. PDGF induces c-myc mRNA expression in MG-63 human osteosarcoma cells but does not stimulate cell replication. J Cell Physiol. 1987 Jul;132(1):65–72. doi: 10.1002/jcp.1041320109. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]