Abstract
An experimental vaccine that was based on secreted proteins of Mycobacterium tuberculosis was investigated in a mouse model of tuberculosis. I used a short-term culture filtrate (ST-CF) containing proteins secreted from actively replicating bacteria grown under defined culture conditions. The immunogenicity of the ST-CF was investigated in combination with different adjuvants, and peak proliferative responses were observed when ST-CF was administered with the surface-active agent dimethyldioctadecylammonium chloride. The immunity induced by this vaccine was dose dependent, and, in the optimal concentration, the vaccine induced a potent T-helper 1 response which efficiently protected the animals against a subsequent challenge with virulent M. tuberculosis. Antigenic targets for the T cells generated were mapped by employing narrow-molecular-weight fractions of ST-CF. The experimental vaccine primed a broadly defined T-cell repertoire directed to multiple secreted antigens present in ST-CF. A vaccination with viable Mycobacterium bovis bacillus Calmette-Guérin (BCG), in contrast, induced a restricted T-cell reactivity directed to two secreted protein fractions with molecular masses of 5 to 12 and 25 to 35 kDa. The protective efficacy of the ST-CF vaccine was compared with that of a BCG standard vaccine, and both induced a highly significant protection of equal magnitude. The vaccination with ST-CF gave rise to a population of long-lived CD4 cells which could be isolated 22 weeks after the vaccination and could adoptively transfer acquired resistance to T-cell-deficient recipients. My results confirm the hypothesis that M. tuberculosis cells release protective antigens during growth. The high efficacy of a subunit vaccine observed in the present study is discussed as a possible alternative to a live recombinant vaccine carrier.
Full text
PDF

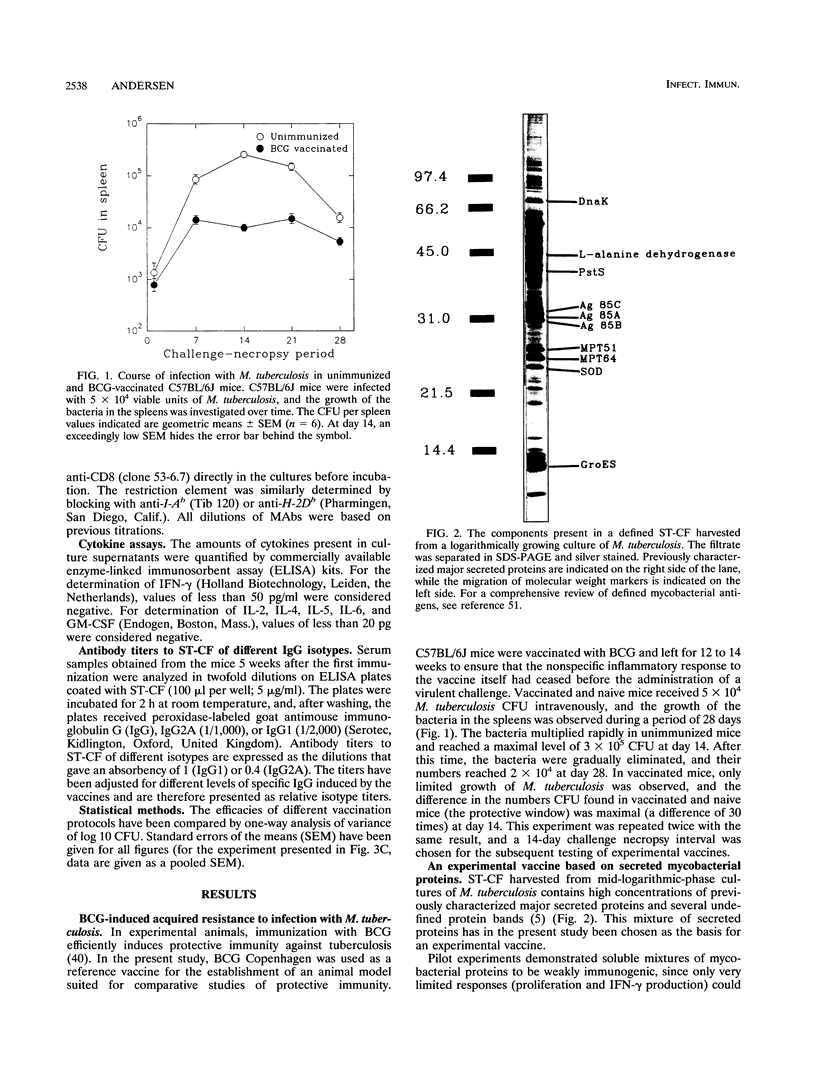
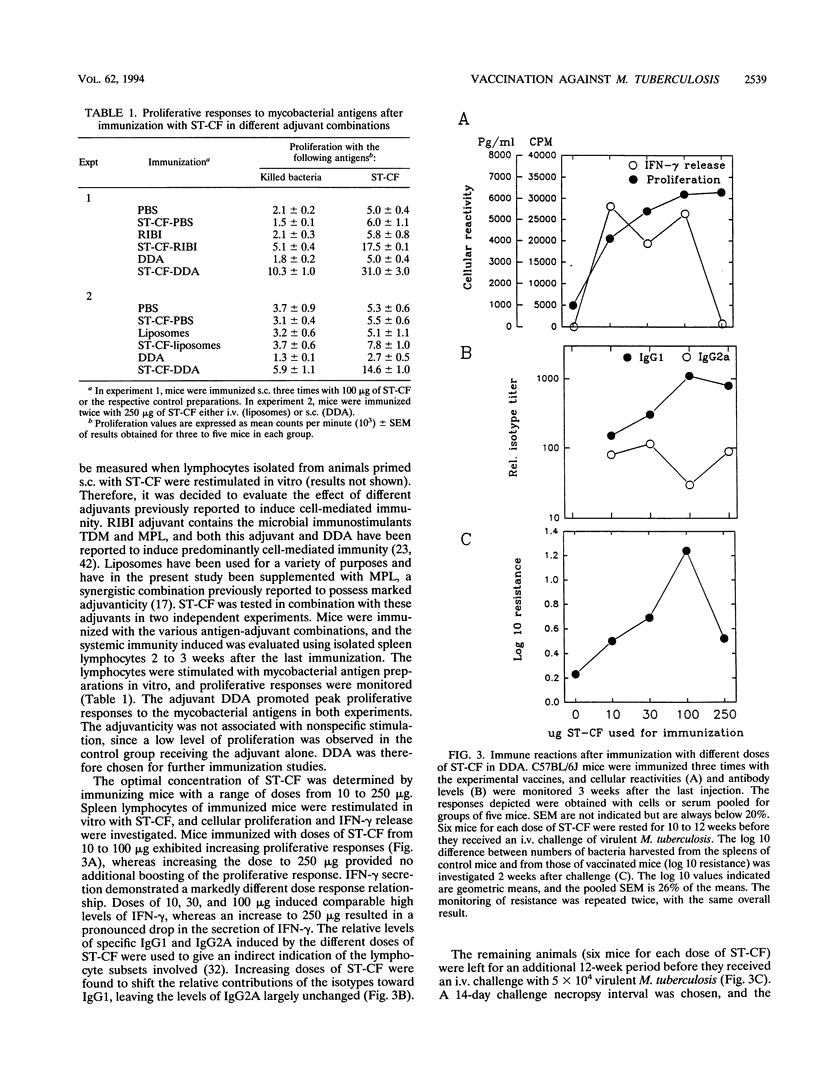

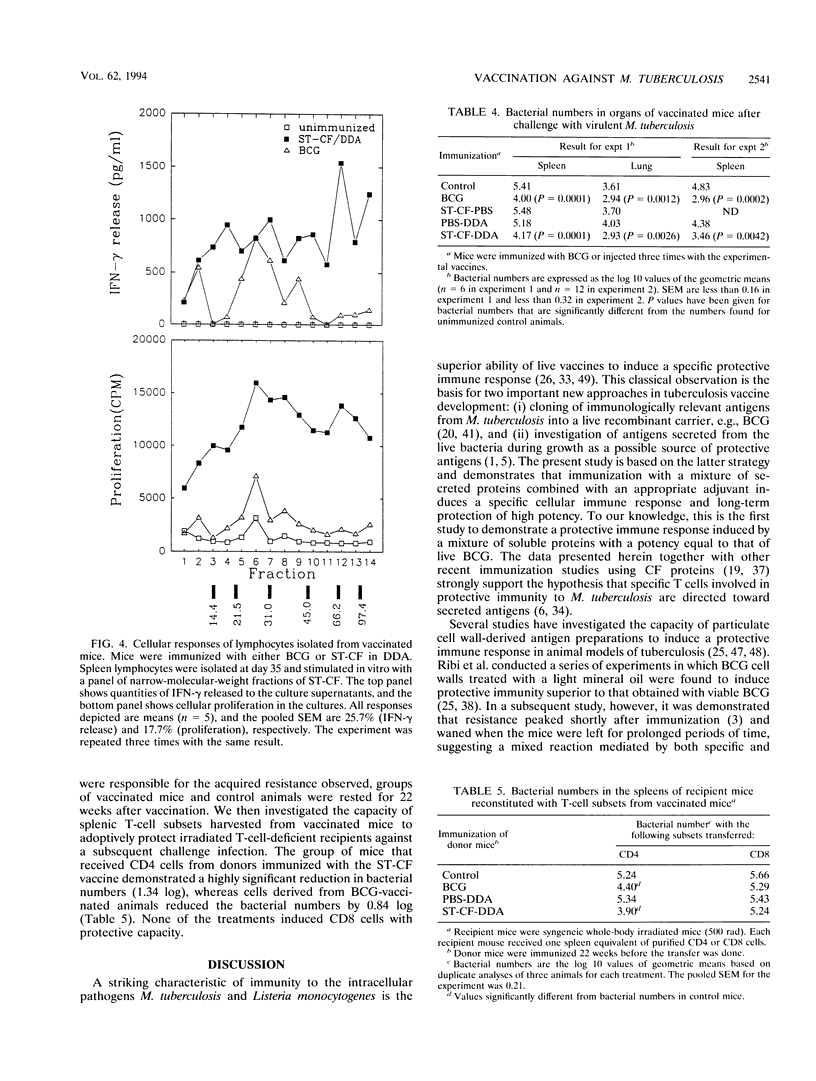



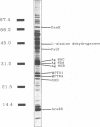
Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Abou-Zeid C., Smith I., Grange J. M., Ratliff T. L., Steele J., Rook G. A. The secreted antigens of Mycobacterium tuberculosis and their relationship to those recognized by the available antibodies. J Gen Microbiol. 1988 Feb;134(2):531–538. doi: 10.1099/00221287-134-2-531. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Abrahams E. W. Protection by BCG vaccination--a review of Australian epidemiology. Dev Biol Stand. 1986;58(Pt A):231–235. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Anacker R. L., Barclay W. R., Brehmer W., Larson C. L., Ribi E. Duration of immunity to tuberculosis in mice vaccinated intravenously with oil-treated cell walls of Mycobacterium bovis strain BCG. J Immunol. 1967 Jun;98(6):1265–1273. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Andersen P., Askgaard D., Gottschau A., Bennedsen J., Nagai S., Heron I. Identification of immunodominant antigens during infection with Mycobacterium tuberculosis. Scand J Immunol. 1992 Dec;36(6):823–831. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-3083.1992.tb03144.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Andersen P., Askgaard D., Ljungqvist L., Bennedsen J., Heron I. Proteins released from Mycobacterium tuberculosis during growth. Infect Immun. 1991 Jun;59(6):1905–1910. doi: 10.1128/iai.59.6.1905-1910.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Andersen P., Askgaard D., Ljungqvist L., Bentzon M. W., Heron I. T-cell proliferative response to antigens secreted by Mycobacterium tuberculosis. Infect Immun. 1991 Apr;59(4):1558–1563. doi: 10.1128/iai.59.4.1558-1563.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Andersen P., Heron I. Simultaneous electroelution of whole SDS-polyacrylamide gels for the direct cellular analysis of complex protein mixtures. J Immunol Methods. 1993 May 5;161(1):29–39. doi: 10.1016/0022-1759(93)90195-d. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Andersen P., Heron I. Specificity of a protective memory immune response against Mycobacterium tuberculosis. Infect Immun. 1993 Mar;61(3):844–851. doi: 10.1128/iai.61.3.844-851.1993. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Berche P., Gaillard J. L., Sansonetti P. J. Intracellular growth of Listeria monocytogenes as a prerequisite for in vivo induction of T cell-mediated immunity. J Immunol. 1987 Apr 1;138(7):2266–2271. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bomford R., Stapleton M., Winsor S., McKnight A., Andronova T. The control of the antibody isotype response to recombinant human immunodeficiency virus gp120 antigen by adjuvants. AIDS Res Hum Retroviruses. 1992 Oct;8(10):1765–1771. doi: 10.1089/aid.1992.8.1765. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bomford R. The comparative selectivity of adjuvants for humoral and cell-mediated immunity. I. Effect on the antibody response to bovine serum albumin and sheep red blood cells of Freund's incomplete and complete adjuvants, alhydrogel, Corynebacterium parvum, Bordetella pertussis, muramyl dipeptide and saponin. Clin Exp Immunol. 1980 Feb;39(2):426–434. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bomford R. The comparative selectivity of adjuvants for humoral and cell-mediated immunity. II. Effect on delayed-type hypersensitivity in the mouse and guinea pig, and cell-mediated immunity to tumour antigens in the mouse of Freund's incomplete and complete adjuvants, alhydrogel, Corynebacterium parvum, Bordetella pertussis, muramyl dipeptide and saponin. Clin Exp Immunol. 1980 Feb;39(2):435–441. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bretscher P. A. A strategy to improve the efficacy of vaccination against tuberculosis and leprosy. Immunol Today. 1992 Sep;13(9):342–345. doi: 10.1016/0167-5699(92)90168-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bretscher P. A., Wei G., Menon J. N., Bielefeldt-Ohmann H. Establishment of stable, cell-mediated immunity that makes "susceptible" mice resistant to Leishmania major. Science. 1992 Jul 24;257(5069):539–542. doi: 10.1126/science.1636090. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Forget A., Skamene E., Gros P., Miailhe A. C., Turcotte R. Differences in response among inbred mouse strains to infection with small doses of Mycobacterium bovis BCG. Infect Immun. 1981 Apr;32(1):42–47. doi: 10.1128/iai.32.1.42-47.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gregoriadis G. Immunological adjuvants: a role for liposomes. Immunol Today. 1990 Mar;11(3):89–97. doi: 10.1016/0167-5699(90)90034-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Havlir D. V., Wallis R. S., Boom W. H., Daniel T. M., Chervenak K., Ellner J. J. Human immune response to Mycobacterium tuberculosis antigens. Infect Immun. 1991 Feb;59(2):665–670. doi: 10.1128/iai.59.2.665-670.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hubbard R. D., Flory C. M., Collins F. M. Immunization of mice with mycobacterial culture filtrate proteins. Clin Exp Immunol. 1992 Jan;87(1):94–98. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2249.1992.tb06419.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jacobs W. R., Jr, Tuckman M., Bloom B. R. Introduction of foreign DNA into mycobacteria using a shuttle phasmid. Nature. 1987 Jun 11;327(6122):532–535. doi: 10.1038/327532a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kahl L. P., Scott C. A., Lelchuk R., Gregoriadis G., Liew F. Y. Vaccination against murine cutaneous leishmaniasis by using Leishmania major antigen/liposomes. Optimization and assessment of the requirement for intravenous immunization. J Immunol. 1989 Jun 15;142(12):4441–4449. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kalish M. L., Check I. J., Hunter R. L. Murine IgG isotype responses to the Plasmodium cynomolgi circumsporozoite peptide (NAGG)5. I. Effects of carrier, copolymer adjuvants, and lipopolysaccharide on isotype selection. J Immunol. 1991 May 15;146(10):3583–3590. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaufmann S. H., Väth U., Thole J. E., Van Embden J. D., Emmrich F. Enumeration of T cells reactive with Mycobacterium tuberculosis organisms and specific for the recombinant mycobacterial 64-kDa protein. Eur J Immunol. 1987 Mar;17(3):351–357. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830170308. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MACKANESS G. B. Cellular resistance to infection. J Exp Med. 1962 Sep 1;116:381–406. doi: 10.1084/jem.116.3.381. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mackay C. R. T-cell memory: the connection between function, phenotype and migration pathways. Immunol Today. 1991 Jun;12(6):189–192. doi: 10.1016/0167-5699(91)90051-T. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Masihi K. N., Brehmer W., Azuma I., Lange W., Müller S. Stimulation of chemiluminescence and resistance against aerogenic influenza virus infection by synthetic muramyl dipeptide combined with trehalose dimycolate. Infect Immun. 1984 Jan;43(1):233–237. doi: 10.1128/iai.43.1.233-237.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Milstien J. B., Gibson J. J. Quality control of BCG vaccine by WHO: a review of factors that may influence vaccine effectiveness and safety. Bull World Health Organ. 1990;68(1):93–108. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morrissey J. H. Silver stain for proteins in polyacrylamide gels: a modified procedure with enhanced uniform sensitivity. Anal Biochem. 1981 Nov 1;117(2):307–310. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(81)90783-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mosmann T. R., Cherwinski H., Bond M. W., Giedlin M. A., Coffman R. L. Two types of murine helper T cell clone. I. Definition according to profiles of lymphokine activities and secreted proteins. J Immunol. 1986 Apr 1;136(7):2348–2357. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mosmann T. R., Coffman R. L. Heterogeneity of cytokine secretion patterns and functions of helper T cells. Adv Immunol. 1989;46:111–147. doi: 10.1016/s0065-2776(08)60652-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Orme I. M., Andersen P., Boom W. H. T cell response to Mycobacterium tuberculosis. J Infect Dis. 1993 Jun;167(6):1481–1497. doi: 10.1093/infdis/167.6.1481. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Orme I. M., Collins F. M. Protection against Mycobacterium tuberculosis infection by adoptive immunotherapy. Requirement for T cell-deficient recipients. J Exp Med. 1983 Jul 1;158(1):74–83. doi: 10.1084/jem.158.1.74. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Orme I. M. Induction of nonspecific acquired resistance and delayed-type hypersensitivity, but not specific acquired resistance in mice inoculated with killed mycobacterial vaccines. Infect Immun. 1988 Dec;56(12):3310–3312. doi: 10.1128/iai.56.12.3310-3312.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Orme I. M., Stokes R. W., Collins F. M. Genetic control of natural resistance to nontuberculous mycobacterial infections in mice. Infect Immun. 1986 Oct;54(1):56–62. doi: 10.1128/iai.54.1.56-62.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pal P. G., Horwitz M. A. Immunization with extracellular proteins of Mycobacterium tuberculosis induces cell-mediated immune responses and substantial protective immunity in a guinea pig model of pulmonary tuberculosis. Infect Immun. 1992 Nov;60(11):4781–4792. doi: 10.1128/iai.60.11.4781-4792.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ribi E., Larson C., Wicht W., List R., Goode G. Effective nonliving vaccine against experimental tuberculosis in mice. J Bacteriol. 1966 Mar;91(3):975–983. doi: 10.1128/jb.91.3.975-983.1966. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scott P., Natovitz P., Coffman R. L., Pearce E., Sher A. Immunoregulation of cutaneous leishmaniasis. T cell lines that transfer protective immunity or exacerbation belong to different T helper subsets and respond to distinct parasite antigens. J Exp Med. 1988 Nov 1;168(5):1675–1684. doi: 10.1084/jem.168.5.1675. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Snapper S. B., Lugosi L., Jekkel A., Melton R. E., Kieser T., Bloom B. R., Jacobs W. R., Jr Lysogeny and transformation in mycobacteria: stable expression of foreign genes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Sep;85(18):6987–6991. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.18.6987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Snippe H., Belder M., Willers J. M. Dimethyl diotadecyl ammonium bromide as adjuvant for delayed hypersensitivity in mice. Immunology. 1977 Dec;33(6):931–936. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stanfield J. P., Gall D., Bracken P. M. Single-dose antenatal tetanus immunisation. Lancet. 1973 Feb 3;1(7797):215–219. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(73)90062-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- TOYOHARA M., KUDOH S., OBAYASHI Y. Studies on the effect of isoniazid upon the antituberculous immunity induced by BCG vaccination. Tubercle. 1959 Jun;40:184–191. doi: 10.1016/s0041-3879(59)80039-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WEISS D. W. Antituberculous vaccination in the guinea pig with non-living vaccines. Am Rev Tuberc. 1958 Apr;77(4):719–724. doi: 10.1164/artpd.1958.77.4.719. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wiegeshaus E. H., McMurray D. N., Grover A. A., Harding G. E., Smith D. W. Host-parasite relationships in experimental airborne tuberculosis. 3. Relevance of microbial enumeration to acquired resistance in guinea pigs. Am Rev Respir Dis. 1970 Sep;102(3):422–429. doi: 10.1164/arrd.1970.102.3.422. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Woodard L. F., Toone N. M., McLaughlin C. A. Comparison of muramyl dipeptide, trehalose dimycolate, and dimethyl dioctadecyl ammonium bromide as adjuvants in Brucella abortus 45/20 vaccines. Infect Immun. 1980 Nov;30(2):409–412. doi: 10.1128/iai.30.2.409-412.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Young D. B., Kaufmann S. H., Hermans P. W., Thole J. E. Mycobacterial protein antigens: a compilation. Mol Microbiol. 1992 Jan;6(2):133–145. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2958.1992.tb01994.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- von Koenig C. H., Finger H., Hof H. Failure of killed Listeria monocytogenes vaccine to produce protective immunity. Nature. 1982 May 20;297(5863):233–234. doi: 10.1038/297233a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]