Abstract
Background
Pedigree, demographic, square-root transformed maximum alcohol (SRMAXAPD) and maximum cigarette (MAXCPD) consumption, and genome-wide scan data from the Framingham Heart Study (FHS) were used to investigate genetic factors that may affect alcohol and cigarette consumption in this population-based sample.
Results
A significant sister:sister correlation greater than spouse correlation was observed for MAXCPD only. Single-point sib-pair regression analysis provided nominal evidence for linkage of loci to both SRMAXAPD and MAXCPD consumption traits, with more significant evidence of linkage to SRMAXAPD than to MAXCPD. One genomic region, chr9q21.11, exhibits significant multi-point sib-pair regression to SRMAXAPD.
Conclusion
SRMAXAPD exhibits greater evidence for genetic linkage than does MAXCPD in the FHS sample. Four regions of the genome exhibiting nominal evidence for linkage to SRMAXAPD in the FHS sample correspond to regions of the genome previously identified as linked to alcoholism or related traits in the family data set ascertained on individuals affected with alcohol dependence known as COGA.
Background
Data from the ongoing NHLBI-supported Framingham Heart Study (FHS) on cardiovascular disease (CVD) was made available to Genetic Analysis Workshop 13 (GAW13). Two behaviors of general medical and psychiatric interest collected from this community-based sample were included in the data, i.e., alcohol consumption and cigarette consumption. Increased cigarette consumption in the FHS sample is associated with the development of CVD [1,2], but increased alcohol consumption in the FHS is not, except in those aged 60–69 [3,4], although meta-analyses of cohort and case-control samples, including the FHS [3], identify a protective effect of moderate (1–2 drinks/day) alcohol consumption [5]. The consumption of tobacco and alcohol confer significant risk for a variety of medical disorders other than CVD, e.g., oral and pharyngeal cancer [6] and for a common psychiatric comorbidity [7].
The consumption of these two substances varies significantly based on both sex and age and there has been a long-term decline in the consumption of cigarettes in the US in the latter half of the 20th century, due to health concerns and restrictions placed on this behavior [8]. The consumption of both substances is significantly correlated in the American population and the prevalence of consumption of alcohol and tobacco is increased by a factor of two in consumers of either substance [9]. The genetic influence on alcohol and tobacco dependence is significantly correlated in men [10]. Measures of consumption in multiple exams of the FHS provide an opportunity to study the genetic correlation of alcohol and tobacco consumption traits and search for susceptibility loci for these traits in a community-based sample.
Results
Descriptive analysis of MAXAPD and MAXCPD
There were a total of 4692 individuals in the GAW13 FHS sample, 2849 with a maximum alcohol consumption (MAXAPD) measure and 2881 with a maximum cigarette consumption (MAXCPD) measure. Descriptive statistics of the MAXAPD and MAXCPD traits and a square root transformation of MAXAPD, SRMAXAPD, are reported in Table 1. The maximum alcohol consumption traits are highly non-normal and the distribution remained highly non-normal whether or not individuals with APD = 0 (N = 346) were included. Individual outlier trait values > +4 standard deviations were changed to missing for analysis (without outliers); the individuals whose values were converted were predominantly male for all three traits but were mostly (≥80%) from Cohort 1 for APD traits (N = 28 for MAXAPD, N = 7 for SRMAXAPD) and from Cohort 2 for MAXCPD (N = 10). Removal of outliers brings SRMAXAPD and MAXCPD traits much closer to normality (Table 2). Because MAXAPD remains highly non-normal even after positive outlier removal (Table 2), correlation and linkage analysis results with MAXAPD are not reported.
Table 1.
Non-normality of MAXAPD, SRMAXAPD, and MAXCPD, with outliers.
| Trait | N | Min | Max | Mean | Median | SD | Kurtosis | SE | Skewness | SE |
| MAXAPD | 2849 | 0 | 624.00 | 23.34 | 11.00 | 35.80 | 57.88 | 0.09 | 5.39 | 0.05 |
| SRMAXAPD | 2849 | 0 | 24.98 | 3.86 | 3.32 | 2.91 | 2.82 | 0.09 | 1.14 | 0.05 |
| MAXCPD | 2881 | 0 | 95.00 | 13.93 | 10.00 | 15.61 | 0.96 | 0.09 | 1.06 | 0.05 |
Table 2.
Non-normality of MAXAPD, SRMAXAPD, and MAXCPD, without outliers.
| Trait | N | Min | Max | Mean | Median | SD | Kurtosis | SE | Skewness | SE |
| MAXAPD | 2821 | 0 | 166.00 | 21.15 | 11.00 | 26.25 | 5.64 | 0.09 | 2.14 | 0.05 |
| SRMAXAPD | 2842 | 0 | 15.43 | 3.82 | 3.32 | 2.80 | 0.77 | 0.09 | 0.84 | 0.05 |
| MAXCPD | 2871 | 0 | 70.00 | 13.69 | 10.00 | 15.08 | -0.03 | 0.09 | 0.88 | 0.05 |
Correlations of alcohol and cigarette consumption traits
Familial correlations of relative and parental pairs (sex-specific and non-sex-specific) without extreme positive outliers for MAXCPD and SRMAXAPD are reported in Table 3. For MAXCPD, only the correlation between sisters is greater than that between parents, with or without outliers. There are no familial correlations greater than the spousal correlation for SRMAXAPD, with or without outliers.
Table 3.
Significant familial correlations of SRMAXAPD and MAXCPD without outliers.
| Correlation | MAXCPD | ± SE | SRMAXAPD | ± SE |
| father:son | 0.058 | 0.041 | 0.133 | 0.041 |
| mother:son | 0.018 | 0.042 | 0.097 | 0.039 |
| father:daughter | 0.153 | 0.041 | 0.105 | 0.041 |
| mother:daughter | 0.141 | 0.041 | 0.163 | 0.039 |
| brother:brother | 0.179 | 0.045 | 0.150 | 0.046 |
| sister:brother | 0.130 | 0.034 | 0.164 | 0.032 |
| sister:sister | 0.268 | 0.046 | 0.186 | 0.045 |
| parent:offspring | 0.072 | 0.023 | 0.102 | 0.022 |
| sibling:sibling | 0.171 | 0.026 | 0.131 | 0.025 |
| mother:father | 0.199 | 0.044 | 0.310 | 0.042 |
Sib-pair linkage analyses
In the single-point analysis, SRMAXAPD shows nominal evidence for linkage at 17 markers on 10 chromosomes with a p-value < 0.01 (Table 4). Chromosomes 7 and 9 have 3 markers each significant at a p-value < 0.01. In addition, for this analysis treating sex as a covariate significantly predicted sib-pair trait covariance at p < 0.01, while the regression analysis of age at which the maximum amount of alcohol was consumed and cohort did not provide nominal evidence for linkage at the p < 0.05 level. Multi-point linkage analysis with SRMAXAPD identified chromosome 9 as the chromosome with the most significant multi-point linkage result in the 10 chromosomes evaluated. Thirteen consecutive markers on chromosome 9 showed evidence of linkage at p < 0.05, with five of them showing significance at p < 0.01. The most significant p-value observed on chromosome 9 was 3.77 × 10-4 at marker c9g8 (Figure 1).
Table 4.
Markers exhibiting evidence (p-value < 0.01) for linkage to SRMAXAPD.A
| Loci | Marker | Pairs | Regression Estimate | SE | p-Value |
| c1g27 | D1S549 | 1455 | 1.55 | 0.54 | 0.0023 |
| c4g3 | D4S2633 | 1373 | 1.54 | 0.55 | 0.0025 |
| c4g7 | D4S3248 | 1432 | 1.47 | 0.57 | 0.0051 |
| c6g10 | D6S1053 | 1478 | 1.37 | 0.54 | 0.0054 |
| c6g14 | D6S1021 | 1428 | 1.42 | 0.57 | 0.0061 |
| c7g10 | D7S2204 | 1448 | 1.43 | 0.51 | 0.0027 |
| c7g16 | D7S1804 | 1426 | 1.34 | 0.52 | 0.0049 |
| c7g22 | D7S559 | 1382 | 1.63 | 0.52 | 0.0010 |
| c9g8 | D9S301 | 1410 | 1.75 | 0.53 | 0.0005 |
| c9g9 | D9S1122 | 1458 | 1.50 | 0.59 | 0.0056 |
| c9g13 | D9S910 | 1499 | 1.57 | 0.60 | 0.0044 |
| c12g2 | Unknown | 1340 | 1.30 | 0.52 | 0.0061 |
| c12g11 | D12S1052 | 1458 | 1.35 | 0.56 | 0.0084 |
| c15g7 | D15S1507 | 1406 | 1.44 | 0.58 | 0.0064 |
| c16g13 | D16S539 | 1465 | 1.44 | 0.55 | 0.0046 |
| c17g12 | D17S1290 | 1485 | 1.63 | 0.50 | 0.0006 |
| c22g4 | D22S689 | 1470 | 1.39 | 0.55 | 0.0058 |
ALinkage analysis via regression of the mean corrected cross product of SRMAXAPD to allele IBD information with covariates sex, age at SRMAXAPD, and cohort.
Figure 1.
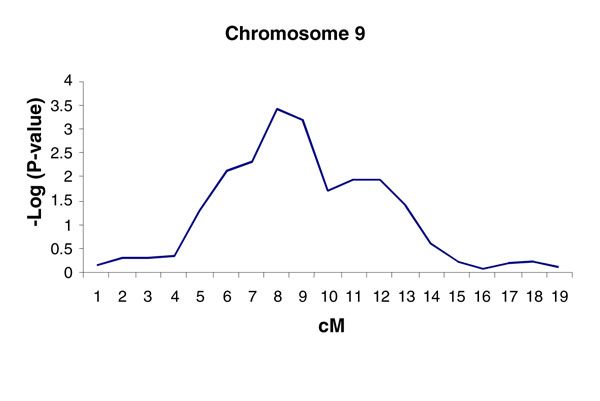
Multi-point linkage analysis of SRMAXAPD (outliers removed).
The single-point analysis for the trait for cigarette consumption, MAXCPD, found nominal evidence for linkage at nine markers on 7 chromosomes at p < 0.05 (Table 5). The effects of the covariates cohort, sex, and age at MAXCPD on sib-pair trait covariance were inconsistent. There was only one chromosome with more than one marker exhibiting nominal evidence for linkage. Multi-point results for MAXCPD were unremarkable.
Table 5.
Markers exhibiting evidence (p-value < 0.05) for linkage to MAXCPD.A
| Loci | Marker | Pairs | Regression Estimate | SE | p-Value |
| c5g14 | D5S1726 | 306 | 79.40 | 38.79 | 0.021 |
| c6g1 | Unknown | 1425 | 43.24 | 23.82 | 0.035 |
| c6g20 | 242zg51 | 1444 | 40.36 | 21.61 | 0.031 |
| c8g3 | D8S1130 | 1420 | 45.96 | 22.89 | 0.022 |
| c9g18 | 308vb11 | 313 | 94.17 | 55.44 | 0.045 |
| c15g9 | D15S818 | 1103 | 50.77 | 28.19 | 0.036 |
| c16g4 | 049xd21 | 1476 | 37.49 | 21.63 | 0.042 |
| c20g9 | 321xd11 | 300 | 84.67 | 43.70 | 0.027 |
| c20g10 | D20S480 | 1412 | 41.11 | 23.86 | 0.043 |
ALinkage analysis via regression of the mean corrected cross product of MAXCPD to allele IBD information with covariates sex, age at MAXCPD, and cohort.
Discussion
In the genome-wide search for linkage evidence to maximum alcohol consumption, we found a number (N = 17) of marker loci that were nominally linked (p < 0.01) with the maximum alcohol consumption traits, SRMAXAPD. A broad region on chromosome 9 exhibited the most significant evidence for linkage, with the maximum linkage evidence at ~66 cM (Table 4 and Figure 1). For the cigarette consumption trait, MAXCPD, we observed fewer loci (N = 9) with evidence for nominally significant (p < 0.05) linkage and no loci at p < 0.021. The low number of loci exhibiting nominal evidence for linkage to MAXCPD suggests that the MAXCPD trait, as investigated in this linkage analysis, lacks power to detect the influence of genetic susceptibility factors on maximum cigarette consumption.
Empirical p-values for the significance of linkage analysis results were not substantially different from asymptotic p-values for either trait, suggesting that assumptions of the SIBPAL regression model apply to the phenotypic and genotypic data analyzed in this study. Only the regions of maximum linkage to SRMAXAPD on chromosome 9 and the single-point linkage analysis result to SRMAXAPD on chromosome 17 at 89 cM provided statistical evidence for linkage at p < 0.0007, a level considered "significant" by Lander and Kruglyak [11]. Multiple testing corrections in investigations of alcohol and cigarette consumption phenotypes performed independently, as in this study, would need to consider the significant correlation between the two behaviors [9].
Linkage studies of alcohol- and cigarette-related traits have identified regions of the genome with more than nominal evidence for linkage [12]. Regions of the genome that have been identified as nominally linked to phenotypes related to alcohol consumption include chromosome 1 (~170 cM) and chromosome 7 (~80–100 cM) for alcohol dependence [13,14], chromosome 1 (~200–250 cM) and chromosome 15 (~70 cM) with a factor composed of later age of onset of drinking and increased harm avoidance [15], chromosome 4 (~120 cM) for alcohol consumption [16], chromosome 1 (~100–150 cM) for alcoholism or depression [17], chromosome 1 (~100–150 cM) and chromosome 21 (~80 cM) for alcohol sensitivity [18], all in the COGA sample [13], and chromosome 4 (~70 cM) and chromosome 11 (~0 cM) in the NIDDK/NIAAA American Indian sample [19]. Regions identified in this analysis of maximum alcohol consumption in the Framingham sample that correspond to the regions identified in the literature include chromosomes 1 [15], 4 [18], 7 [16], and 15 [15]. Regions of the genome that have been identified as nominally linked to phenotypes related to cigarette consumption in other samples include chromosome 1 (~0 cM), chromosome 2 (~90 cM), chromosome 14 (~95 cM) for ever-smoking in the COGA sample [20], and chromosome 2 (~145 cM) and chromosome 10 (~120 cM) in the Christchurch sample [21]. There were no regions of the genome in the Framingham sample with nominal evidence of linkage to cigarette consumption that overlapped regions identified in the COGA and Christchurch samples exhibiting linkage to cigarette related phenotypes. However, in the FHS sample, chromosome 15 contains markers that exhibit nominal evidence for linkage to SRMAXAPD (Table 4) and MAXCPD (Table 5) at 60 cM and 72 cM, close to a region of chromosome 15 in the COGA sample exhibiting suggestive linkage to a factor composed of later age of onset of drinking and increased harm avoidance [15].
Conclusions
We observed several marker loci with nominal evidence for linkage to the square-root transformed maximum alcohol consumption traits, SRMAXAPD, in the Framingham Heart Study sample. Some of the regions of the genome have been previously linked to alcoholism or related traits in Caucasian samples based on different ascertainment criteria.
Methods
Selection of consumption data
The traits of interest were defined as the maximum reported number of grams of alcohol per day (MAXAPD), and the maximum reported number of cigarettes smoked per day (MAXCPD). Exams 1, 2, 4, and 7 from FHS Cohort 1 and exams 1, 2, 3, and 4 from FHS Cohort 2 were chosen to assess MAXAPD and MAXCPD to utilize multiple exams at the earliest age possible to obtain measurements. Covariates of interest included cohort, age of maximum consumption measure, and sex.
Analysis of phenotypic, pedigree, and genotypic data
GAW13 FHS data were imported into a Microsoft Access database and exported in appropriate files for descriptive statistical analysis in SPSS Advanced Statistics or Microsoft Excel and familial correlation and linkage analysis in S.A.G.E. [22]. Familial correlations and the asymptotic standard errors were estimated using FCOR from S.A.G.E. 4.2. We used GENIBD from S.A.G.E. 4.2 to generate identity-by-descent (IBD) sharing distributions of the GAW13 data. Before running the GENIBD analysis, we used MEGA2 [23] to convert the GAW13 data to the column-delimited S.A.G.E. format.
SIBPAL from S.A.G.E. 4.2 was used to model the sib-pair covariance of traits reported as a function of marker allele identity-by-descent (IBD) sharing. Our analyses used estimated IBD information from the GENIBD procedure described above to perform single-point linkage analysis in which the mean corrected cross product of the trait was regressed onto the IBD information one trait at a time. The single-point linkage analysis was carried out separately for traits MAXAPD, SRMAXAPD, and MAXCPD, treated as continuous variables. The covariates sex, age of trait report, and cohort were included in the regression models. SRMAXAPD single-point linkage analysis was only performed without outliers. Empirical p-values were obtained for single-point linkage analysis of MAXCPD and SRMAXAPD to evaluate possible deviation from asymptotic p-values. Multi-point linkage analysis was performed using IBD distributions at multiple markers for MAXCPD and SRMAXAPD on those chromosomes showing nominal evidence (p < 0.05 and p < 0.01, respectively) for linkage at two or more consecutive loci.
Authors' contributions
AB nominated the traits, performed the descriptive and FCOR analyses, and wrote the manuscript, XY performed the linkage analysis of the alcohol consumption traits, YB performed the linkage analysis of the cigarette consumption trait, MB performed the GAW13 FHS databasing, selection, reduction, transformation, and export, and AG and LG provided analysis direction and recommendations at each phase of the analysis.
Acknowledgments
Acknowledgments
Some of the analyses described in this paper were carried out using S.A.G.E., which is supported by a U.S. Public Health Service Resource Grant (1 P41 RR03655) from the National Center for Research Resources.
Contributor Information
Andrew W Bergen, Email: bergena@mail.nih.gov.
Xiaohong Rose Yang, Email: royang@mail.nih.gov.
Yan Bai, Email: baiy@mail.nih.gov.
Michael B Beerman, Email: beermanm@mail.nih.gov.
Alisa M Goldstein, Email: goldstea@mail.nih.gov.
Lynn R Goldin, Email: goldinl@mail.nih.gov.
References
- Dawber T. Summary of recent literature regarding cigarette smoking and coronary heart disease. Circulation. 1960;22:164–166. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Freund KM, Belanger AJ, D'Agostino RB, Kannel WB. The health risks of smoking. The Framingham Study: 34 years of follow-up. Ann Epidemiol. 1993;3:417–424. doi: 10.1016/1047-2797(93)90070-k. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Djousse L, Ellison RC, Beiser A, Scaramucci A, D'Agostino RB, Wolf PA. Alcohol consumption and risk of ischemic stroke: the Framingham Study. Stroke. 2002;33:907–912. doi: 10.1161/hs0402.105245. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Walsh CR, Larson MG, Evans JC, Djousse L, Ellison RC, Vasan RS, Levy D. Alcohol consumption and risk for congestive heart failure in the Framingham Heart Study. Ann Intern Med. 2002;136:181–191. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-136-3-200202050-00005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reynolds K, Lewis LB, Nolen JD, Kinney GL, Sathya B, He J. Alcohol consumption and risk of stroke: a meta-analysis. JAMA. 2003;289:579–588. doi: 10.1001/jama.289.5.579. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Day GL, Blot WJ, Austin DF, Bernstein L, Greenberg RS, Preston-Martin S, Schoenberg JB, Winn DM, McLaughlin JK, Fraumeni JF., Jr Racial differences in risk of oral and pharyngeal cancer: alcohol, tobacco, and other determinants. J Natl Cancer Inst. 1993;85:465–473. doi: 10.1093/jnci/85.6.465. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goldman D, Bergen A. General and specific inheritance of substance abuse and alcoholism. Arch Gen Psychiatry. 1998;11:964–965. doi: 10.1001/archpsyc.55.11.964. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Giovino GA, Henningfield JE, Tomar SL, Escobedo LG, Slade J. Epidemiology of tobacco use and dependence. Epidemiol Rev. 1995;17:48–65. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.epirev.a036185. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schiffman S, Balabanis BA. Associations between alcohol and tobacco. In: Fertig JB, Allen JP, editor. Alcohol and Tobacco: From Basic Science to Clinical Practice. Bethesda, MD, National Institutes of Health; 1995. pp. 17–36. [Google Scholar]
- True WR, Xian H, Scherrer JF, Madden PA, Bucholz KK, Heath AC, Eisen SA, Lyons MJ, Goldberg J, Tsuang M. Common genetic vulnerability for nicotine and alcohol dependence in men. Arch Gen Psychiatry. 1999;56:655–661. doi: 10.1001/archpsyc.56.7.655. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lander E, Kruglyak L. Genetic dissection of complex traits: guidelines for interpreting and reporting linkage results. Nat Genet. 1995;11:241–247. doi: 10.1038/ng1195-241. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Uhl GR, Liu QR, Naiman D. Substance abuse vulnerability loci: converging genome scanning data. Trends Genet. 2002;18:420–425. doi: 10.1016/S0168-9525(02)02719-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reich T, Edenberg HJ, Goate A, Williams JT, Rice JP, Van Eerdewegh P, Foroud T, Hesselbrock V, Schuckit MA, Bucholz K, Porjesz B, Li TK, Conneally PM, Nurnberger JI, Jr, Tischfield JA, Crowe RR, Cloninger CR, Wu W, Shears S, Carr K, Crose C, Willig C, Begleiter H. Genome-wide search for genes affecting the risk for alcohol dependence. Am J Med Genet. 1998;81:207–215. doi: 10.1002/(SICI)1096-8628(19980508)81:3<207::AID-AJMG1>3.3.CO;2-X. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Foroud T, Edenberg HJ, Goate A, Rice J, Flury L, Koller DL, Bierut LJ, Conneally PM, Nurnberger JI, Bucholz KK, Li TK, Hesselbrock V, Crowe R, Schuckit M, Porjesz B, Begleiter H, Reich T. Alcoholism susceptibility loci: confirmation studies in a replicate sample and further mapping. Alcohol Clin Exp Res. 2000;24:933–945. doi: 10.1097/00000374-200007000-00001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dick DM, Nurnberger J, Jr, Edenberg HJ, Goate A, Crowe R, Rice J, Bucholz KK, Kramer J, Schuckit MA, Smith TL, Porjesz B, Begleiter H, Hesselbrock V, Foroud T. Suggestive linkage on chromosome 1 for a quantitative alcohol-related phenotype. Alcohol Clin Exp Res. 2002;10:1453–1460. doi: 10.1097/00000374-200210000-00001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Saccone NL, Kwon JM, Corbett J, Goate A, Rochberg N, Edenberg HJ, Foroud T, Li TK, Begleiter H, Reich T, Rice JP. A genome screen of maximum number of drinks as an alcoholism phenotype. Am J Med Genet. 2000;96:632–637. doi: 10.1002/1096-8628(20001009)96:5<632::AID-AJMG8>3.0.CO;2-#. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nurnberger JI, Jr, Foroud T, Flury L, Su J, Meyer ET, Hu K, Crowe R, Edenberg H, Goate A, Bierut L, Reich T, Schuckit M, Reich W. Evidence for a locus on chromosome 1 that influences vulnerability to alcoholism and affective disorder. Am J Psychiatry. 2001;158:718–724. doi: 10.1176/appi.ajp.158.5.718. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schuckit MA, Edenberg HJ, Kalmijn J, Flury L, Smith TL, Reich T, Bierut L, Goate A, Foroud T. A genome-wide search for genes that relate to a low level of response to alcohol. Alcohol Clin Exp Res. 2001;25:323–329. doi: 10.1097/00000374-200103000-00002. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Long JC, Knowler WC, Hanson RL, Robin RW, Urbanek M, Moore E, Bennett PH, Goldman D. Evidence for genetic linkage to alcohol dependence on chromosomes 4 and 11 from an autosome-wide scan in an American Indian population. Am J Med Genet. 1998;81:216–221. doi: 10.1002/(SICI)1096-8628(19980508)81:3<216::AID-AJMG2>3.0.CO;2-U. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bergen AW, Korczak JF, Weissbecker KA, Goldstein AM. A genome-wide search for loci contributing to smoking and alcoholism. Genet Epidemiol. 1999;17:S55–S60. doi: 10.1002/gepi.1370170710. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Straub RE, Sullivan PF, Ma Y, Myakishev MV, Harris-Kerr C, Wormley B, Kadambi B, Sadek H, Silverman MA, Webb BT, Neale MC, Bulik CM, Joyce PR, Kendler KS. Susceptibility genes for nicotine dependence: a genome scan and followup in an independent sample suggest that regions on chromosomes 2, 4, 10, 16, 17 and 18 merit further study. Mol Psychiatry. 1999;4:129–144. doi: 10.1038/sj.mp.4000518. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Department of Epidemiology and Biostatistics, Rammelkamp Center for Education and Research, MetroHealth Campus, Case Western Reserve University, Cleveland. Statistical Analysis for Genetic Epidemiology, Release 42. 2001.
- Mukhopadhyay N, Almasy L, Schroeder M, Mulvihill WP, Weeks DE. Mega2, a data-handling program for facilitating genetic linkage and association analyses. Am J Hum Genet. 1999;65:A436. doi: 10.1093/bioinformatics/bti364. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


