Abstract
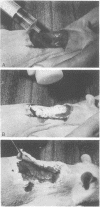
Allograft dressings to control Pseudomonas wound infections in rats were studied on surgical wounds and escharectomized burn wounds. The effects of allografts were compared with a collagen sheet (Aviderm) and a synthetic dressing, polyhydroxyethylmethacrylate (Hydron), formed on the wound by mixing the polymer and the solvent. The results indicated that infections in surgical wounds were more easily controlled by dressings than similar contaminations in burn wounds. A procedure was described for the formation of a synthetic dressing directly on the wound from a mixture of polymer and solvent. This type of preparation completely filled the wound area and sealed the edges, preventing further contamination, and gave excellent coverage of the wound. With 24 h of coverage of escharectomized burn wounds, allografts provided the best dressing for reduction of wound organisms. At 96 h of coverage, Hydron and Aviderm produce significant reductions in the Pseudomonas resident in the burn wound. The results support the thesis that suitable dressings promote local host defense processes which kill the contaminating bacteria.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Guldalian J., Jelenko C., 3rd, Callaway D., McKnight J. T. A comparative study of synthetic and biological materials for wound dressings. J Trauma. 1973 Jan;13(1):32–35. doi: 10.1097/00005373-197301000-00006. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nathan P., Holder I. A., MacMillan B. G. Burn wounds: microbiology, local host defenses, and current therapy. CRC Crit Rev Clin Lab Sci. 1973 Jul;4(1):61–100. doi: 10.3109/10408367309151684. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Robson M. C., Krizek T. J. The effect of human amniotic membranes on the bacteria population of infected rat burns. Ann Surg. 1973 Feb;177(2):144–149. doi: 10.1097/00000658-197302000-00003. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Saymen D. G., Nathan P., Holder I. A., Hill E. O., Macmillan B. G. Control of surface wound infection: skin versus synthetic grafts. Appl Microbiol. 1973 Jun;25(6):921–934. doi: 10.1128/am.25.6.921-934.1973. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Saymen D. G., Nathan P., Holder I. A., Hill E. O., Macmillan B. G. Infected surface wound: an experimental model and a method for the quantitation of bacteria in infected tissues. Appl Microbiol. 1972 Mar;23(3):509–514. doi: 10.1128/am.23.3.509-514.1972. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]