Full Text
The Full Text of this article is available as a PDF (111.4 KB).
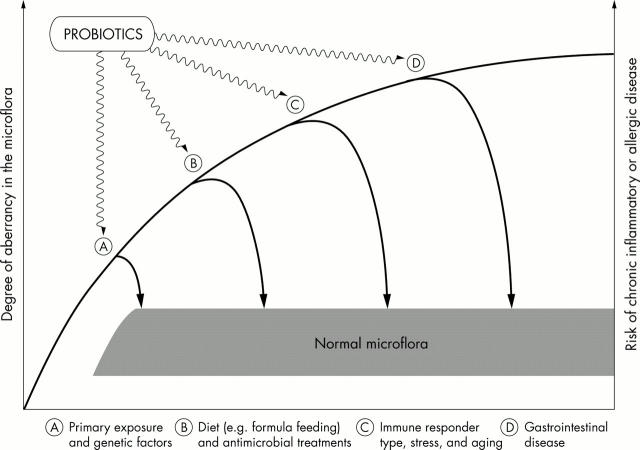
Figure 1 .
Evolution of the gut microflora and the rationale of probiotic therapy. Different internal and external challenges interfere with the normal balance of the healthy gut microflora. Their effects can be reversed by specific strains of the healthy gut microflora. Normalisation of the properties of unbalanced indigenous microflora by specific strains of the healthy gut microflora forms the rationale of probiotic therapy.
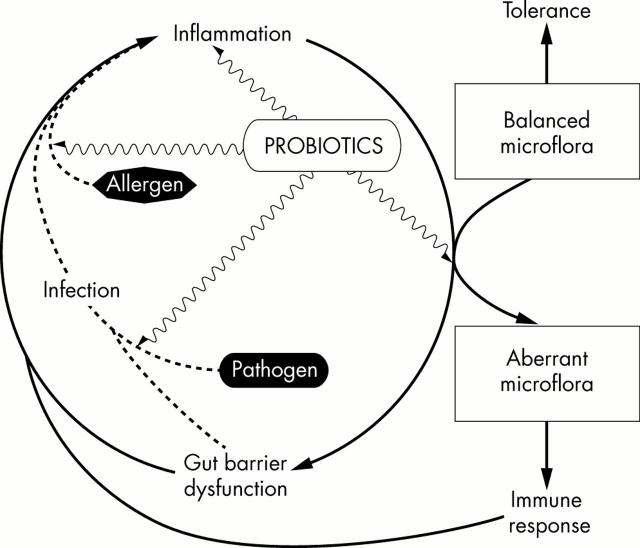
Figure 2 .
Gut microflora in inflammation. Inflammation may direct the composition and function of a balanced normal microflora to become aberrant and immunogenic, leading to perpetuation of the inflammation and gut barrier dysfunction. Probiotic bacteria may counteract the inflammatory process by enhancing the degradation of enteral antigens, reducing the secretion of inflammatory mediators, and promoting the normalisation of indigenous flora and the exclusion of pathogens.
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Apostolou E., Pelto L., Kirjavainen P. V., Isolauri E., Salminen S. J., Gibson G. R. Differences in the gut bacterial flora of healthy and milk-hypersensitive adults, as measured by fluorescence in situ hybridization. FEMS Immunol Med Microbiol. 2001 Apr;30(3):217–221. doi: 10.1111/j.1574-695X.2001.tb01573.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Berg R. D. The indigenous gastrointestinal microflora. Trends Microbiol. 1996 Nov;4(11):430–435. doi: 10.1016/0966-842x(96)10057-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Björkstén B., Naaber P., Sepp E., Mikelsaar M. The intestinal microflora in allergic Estonian and Swedish 2-year-old children. Clin Exp Allergy. 1999 Mar;29(3):342–346. doi: 10.1046/j.1365-2222.1999.00560.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Duchmann R., Kaiser I., Hermann E., Mayet W., Ewe K., Meyer zum Büschenfelde K. H. Tolerance exists towards resident intestinal flora but is broken in active inflammatory bowel disease (IBD) Clin Exp Immunol. 1995 Dec;102(3):448–455. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2249.1995.tb03836.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Groux H., Powrie F. Regulatory T cells and inflammatory bowel disease. Immunol Today. 1999 Oct;20(10):442–445. doi: 10.1016/s0167-5699(99)01510-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grönlund M. M., Arvilommi H., Kero P., Lehtonen O. P., Isolauri E. Importance of intestinal colonisation in the maturation of humoral immunity in early infancy: a prospective follow up study of healthy infants aged 0-6 months. Arch Dis Child Fetal Neonatal Ed. 2000 Nov;83(3):F186–F192. doi: 10.1136/fn.83.3.F186. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grönlund M. M., Lehtonen O. P., Eerola E., Kero P. Fecal microflora in healthy infants born by different methods of delivery: permanent changes in intestinal flora after cesarean delivery. J Pediatr Gastroenterol Nutr. 1999 Jan;28(1):19–25. doi: 10.1097/00005176-199901000-00007. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Guandalini S., Pensabene L., Zikri M. A., Dias J. A., Casali L. G., Hoekstra H., Kolacek S., Massar K., Micetic-Turk D., Papadopoulou A. Lactobacillus GG administered in oral rehydration solution to children with acute diarrhea: a multicenter European trial. J Pediatr Gastroenterol Nutr. 2000 Jan;30(1):54–60. doi: 10.1097/00005176-200001000-00018. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Guarino A., Canani R. B., Spagnuolo M. I., Albano F., Di Benedetto L. Oral bacterial therapy reduces the duration of symptoms and of viral excretion in children with mild diarrhea. J Pediatr Gastroenterol Nutr. 1997 Nov;25(5):516–519. doi: 10.1097/00005176-199711000-00005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harmsen H. J., Wildeboer-Veloo A. C., Raangs G. C., Wagendorp A. A., Klijn N., Bindels J. G., Welling G. W. Analysis of intestinal flora development in breast-fed and formula-fed infants by using molecular identification and detection methods. J Pediatr Gastroenterol Nutr. 2000 Jan;30(1):61–67. doi: 10.1097/00005176-200001000-00019. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hartke A., Bouche S., Gansel X., Boutibonnes P., Auffray Y. Starvation-Induced Stress Resistance in Lactococcus lactis subsp. lactis IL1403. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1994 Sep;60(9):3474–3478. doi: 10.1128/aem.60.9.3474-3478.1994. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hartke A, Bouche S, Giard JC, Benachour A, Boutibonnes P, Auffray Y. The Lactic Acid Stress Response of Lactococcus lactis subsp. lactis. Curr Microbiol. 1996 Sep;33(3):194–199. doi: 10.1007/s002849900099. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hooper L. V., Wong M. H., Thelin A., Hansson L., Falk P. G., Gordon J. I. Molecular analysis of commensal host-microbial relationships in the intestine. Science. 2001 Feb 2;291(5505):881–884. doi: 10.1126/science.291.5505.881. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Isolauri E., Juntunen M., Rautanen T., Sillanaukee P., Koivula T. A human Lactobacillus strain (Lactobacillus casei sp strain GG) promotes recovery from acute diarrhea in children. Pediatrics. 1991 Jul;88(1):90–97. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Isolauri E., Kaila M., Arvola T., Majamaa H., Rantala I., Virtanen E., Arvilommi H. Diet during rotavirus enteritis affects jejunal permeability to macromolecules in suckling rats. Pediatr Res. 1993 Jun;33(6):548–553. doi: 10.1203/00006450-199306000-00002. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Isolauri E., Kaila M., Mykkänen H., Ling W. H., Salminen S. Oral bacteriotherapy for viral gastroenteritis. Dig Dis Sci. 1994 Dec;39(12):2595–2600. doi: 10.1007/BF02087695. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jin L. Z., Marquardt R. R., Zhao X. A strain of Enterococcus faecium (18C23) inhibits adhesion of enterotoxigenic Escherichia coli K88 to porcine small intestine mucus. Appl Environ Microbiol. 2000 Oct;66(10):4200–4204. doi: 10.1128/aem.66.10.4200-4204.2000. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaila M., Isolauri E., Soppi E., Virtanen E., Laine S., Arvilommi H. Enhancement of the circulating antibody secreting cell response in human diarrhea by a human Lactobacillus strain. Pediatr Res. 1992 Aug;32(2):141–144. doi: 10.1203/00006450-199208000-00002. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kalliomäki M., Kirjavainen P., Eerola E., Kero P., Salminen S., Isolauri E. Distinct patterns of neonatal gut microflora in infants in whom atopy was and was not developing. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2001 Jan;107(1):129–134. doi: 10.1067/mai.2001.111237. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kalliomäki M., Salminen S., Arvilommi H., Kero P., Koskinen P., Isolauri E. Probiotics in primary prevention of atopic disease: a randomised placebo-controlled trial. Lancet. 2001 Apr 7;357(9262):1076–1079. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(00)04259-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kets E., Teunissen P., de Bont J. Effect of compatible solutes on survival of lactic Acid bacteria subjected to drying. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1996 Jan;62(1):259–261. doi: 10.1128/aem.62.1.259-261.1996. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lee Y. K., Lim C. Y., Teng W. L., Ouwehand A. C., Tuomola E. M., Salminen S. Quantitative approach in the study of adhesion of lactic acid bacteria to intestinal cells and their competition with enterobacteria. Appl Environ Microbiol. 2000 Sep;66(9):3692–3697. doi: 10.1128/aem.66.9.3692-3697.2000. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MacFie J., O'Boyle C., Mitchell C. J., Buckley P. M., Johnstone D., Sudworth P. Gut origin of sepsis: a prospective study investigating associations between bacterial translocation, gastric microflora, and septic morbidity. Gut. 1999 Aug;45(2):223–228. doi: 10.1136/gut.45.2.223. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Majamaa H., Isolauri E. Probiotics: a novel approach in the management of food allergy. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 1997 Feb;99(2):179–185. doi: 10.1016/s0091-6749(97)70093-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Majamaa H., Isolauri E., Saxelin M., Vesikari T. Lactic acid bacteria in the treatment of acute rotavirus gastroenteritis. J Pediatr Gastroenterol Nutr. 1995 Apr;20(3):333–338. doi: 10.1097/00005176-199504000-00012. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Malin M., Suomalainen H., Saxelin M., Isolauri E. Promotion of IgA immune response in patients with Crohn's disease by oral bacteriotherapy with Lactobacillus GG. Ann Nutr Metab. 1996;40(3):137–145. doi: 10.1159/000177907. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Malin M., Verronen P., Mykkänen H., Salminen S., Isolauri E. Increased bacterial urease activity in faeces in juvenile chronic arthritis: evidence of altered intestinal microflora? Br J Rheumatol. 1996 Jul;35(7):689–694. doi: 10.1093/rheumatology/35.7.689. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mao Y., Nobaek S., Kasravi B., Adawi D., Stenram U., Molin G., Jeppsson B. The effects of Lactobacillus strains and oat fiber on methotrexate-induced enterocolitis in rats. Gastroenterology. 1996 Aug;111(2):334–344. doi: 10.1053/gast.1996.v111.pm8690198. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oberhelman R. A., Gilman R. H., Sheen P., Taylor D. N., Black R. E., Cabrera L., Lescano A. G., Meza R., Madico G. A placebo-controlled trial of Lactobacillus GG to prevent diarrhea in undernourished Peruvian children. J Pediatr. 1999 Jan;134(1):15–20. doi: 10.1016/s0022-3476(99)70366-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pant A. R., Graham S. M., Allen S. J., Harikul S., Sabchareon A., Cuevas L., Hart C. A. Lactobacillus GG and acute diarrhoea in young children in the tropics. J Trop Pediatr. 1996 Jun;42(3):162–165. doi: 10.1093/tropej/42.3.162. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pelto L., Isolauri E., Lilius E. M., Nuutila J., Salminen S. Probiotic bacteria down-regulate the milk-induced inflammatory response in milk-hypersensitive subjects but have an immunostimulatory effect in healthy subjects. Clin Exp Allergy. 1998 Dec;28(12):1474–1479. doi: 10.1046/j.1365-2222.1998.00449.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pessi T., Sütas Y., Hurme M., Isolauri E. Interleukin-10 generation in atopic children following oral Lactobacillus rhamnosus GG. Clin Exp Allergy. 2000 Dec;30(12):1804–1808. doi: 10.1046/j.1365-2222.2000.00948.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Saavedra J. M., Bauman N. A., Oung I., Perman J. A., Yolken R. H. Feeding of Bifidobacterium bifidum and Streptococcus thermophilus to infants in hospital for prevention of diarrhoea and shedding of rotavirus. Lancet. 1994 Oct 15;344(8929):1046–1049. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(94)91708-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Salminen S., von Wright A., Morelli L., Marteau P., Brassart D., de Vos W. M., Fondén R., Saxelin M., Collins K., Mogensen G. Demonstration of safety of probiotics -- a review. Int J Food Microbiol. 1998 Oct 20;44(1-2):93–106. doi: 10.1016/s0168-1605(98)00128-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanderson I. R., Walker W. A. Uptake and transport of macromolecules by the intestine: possible role in clinical disorders (an update). Gastroenterology. 1993 Feb;104(2):622–639. doi: 10.1016/0016-5085(93)90436-g. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Steidler L., Hans W., Schotte L., Neirynck S., Obermeier F., Falk W., Fiers W., Remaut E. Treatment of murine colitis by Lactococcus lactis secreting interleukin-10. Science. 2000 Aug 25;289(5483):1352–1355. doi: 10.1126/science.289.5483.1352. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Strachan D. P. Hay fever, hygiene, and household size. BMJ. 1989 Nov 18;299(6710):1259–1260. doi: 10.1136/bmj.299.6710.1259. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sudo N., Sawamura S., Tanaka K., Aiba Y., Kubo C., Koga Y. The requirement of intestinal bacterial flora for the development of an IgE production system fully susceptible to oral tolerance induction. J Immunol. 1997 Aug 15;159(4):1739–1745. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Szajewska H., Kotowska M., Mrukowicz J. Z., Armańska M., Mikołajczyk W. Efficacy of Lactobacillus GG in prevention of nosocomial diarrhea in infants. J Pediatr. 2001 Mar;138(3):361–365. doi: 10.1067/mpd.2001.111321. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sütas Y., Hurme M., Isolauri E. Down-regulation of anti-CD3 antibody-induced IL-4 production by bovine caseins hydrolysed with Lactobacillus GG-derived enzymes. Scand J Immunol. 1996 Jun;43(6):687–689. doi: 10.1046/j.1365-3083.1996.d01-258.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sütas Y., Soppi E., Korhonen H., Syväoja E. L., Saxelin M., Rokka T., Isolauri E. Suppression of lymphocyte proliferation in vitro by bovine caseins hydrolyzed with Lactobacillus casei GG-derived enzymes. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 1996 Jul;98(1):216–224. doi: 10.1016/s0091-6749(96)70245-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weiner H. L., van Rees E. P. Mucosal tolerance. Immunol Lett. 1999 Jun 15;69(1):3–4. doi: 10.1016/s0165-2478(99)00092-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- el-Nezami H., Kankaanpä P., Salminen S., Ahokas J. Physicochemical alterations enhance the ability of dairy strains of lactic acid bacteria to remove aflatoxin from contaminated media. J Food Prot. 1998 Apr;61(4):466–468. doi: 10.4315/0362-028x-61.4.466. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]