Full Text
The Full Text of this article is available as a PDF (154.4 KB).
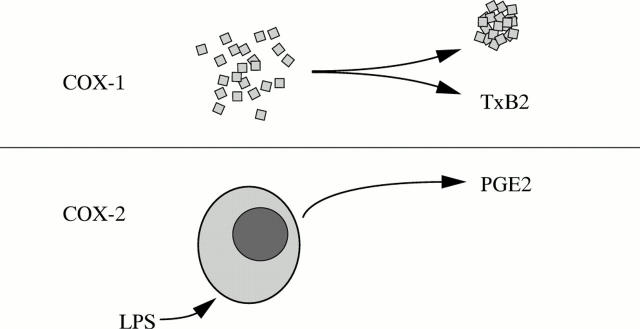
Figure 1 .
Schematic representation of COX selectivity assay.
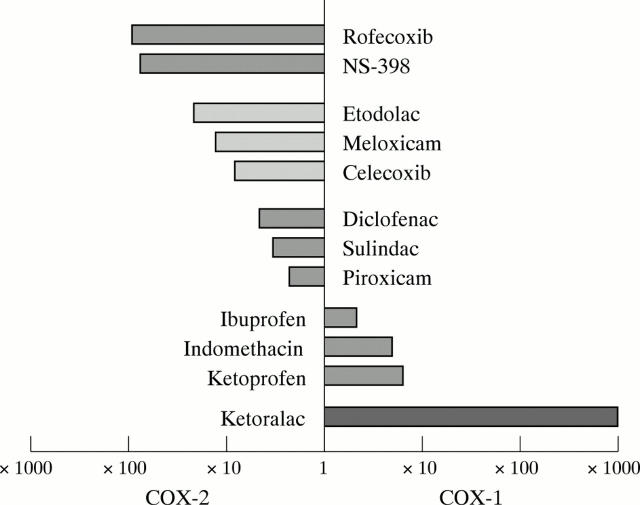
Figure 2 .
Selectivity ratios of selected drugs. Derived from IC80 data.31
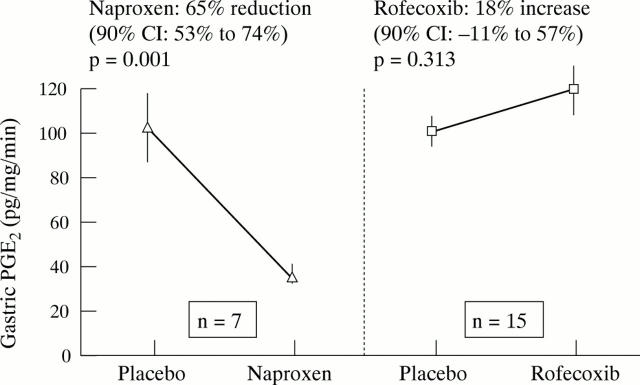
Figure 3 .
Effect of naproxen 1 g daily and rofecoxib 50 mg daily on ex vivo gastric mucosal prostaglandin synthesis. Volunteers received placebo, naproxen, or rofecoxib for seven days. Twelve standardised gastric mucosal biopsy samples were taken and prostaglandin synthesis stimulated by vortex mixing. Reproduced from Gastroenterology with permission.33
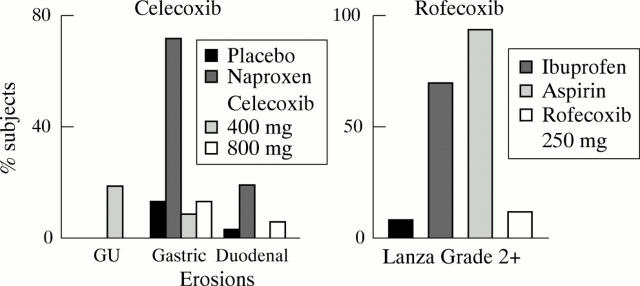
Figure 4 .
Acute volunteer studies. Lanza grade 2 = one or more erosions. Data derived from Lanza.35, 43
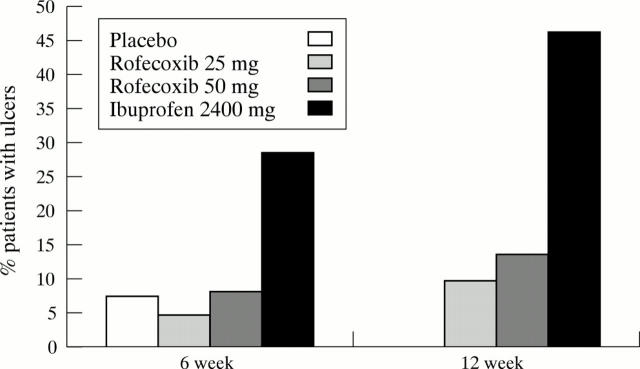
Figure 5 .
Ulcer development over 12 weeks in patients receiving placebo, rofecoxib 25 mg, rofecoxib 50 mg, or ibuprofen 2.4 g daily. Combined data from two studies covering 1516 patients. Reproduced by permission from Arthritis & Rheumatism.39
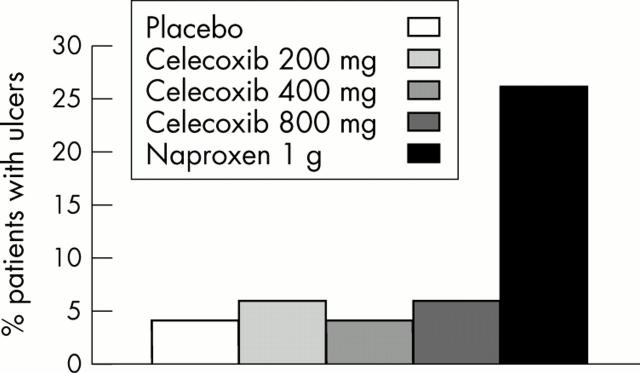
Figure 6 .
Ulcer development in patients receiving celecoxib in endoscopic studies. Reproduced with kind permission of the Journal of the American Medical Association.44
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bjorkman D. Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drug-associated toxicity of the liver, lower gastrointestinal tract, and esophagus. Am J Med. 1998 Nov 2;105(5A):17S–21S. doi: 10.1016/s0002-9343(98)00276-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bombardier C., Laine L., Reicin A., Shapiro D., Burgos-Vargas R., Davis B., Day R., Ferraz M. B., Hawkey C. J., Hochberg M. C. Comparison of upper gastrointestinal toxicity of rofecoxib and naproxen in patients with rheumatoid arthritis. VIGOR Study Group. N Engl J Med. 2000 Nov 23;343(21):1520-8, 2 p following 1528. doi: 10.1056/NEJM200011233432103. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brater D. C. Effects of nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs on renal function: focus on cyclooxygenase-2-selective inhibition. Am J Med. 1999 Dec 13;107(6A):65S–71S. doi: 10.1016/s0002-9343(99)00369-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brooks P., Emery P., Evans J. F., Fenner H., Hawkey C. J., Patrono C., Smolen J., Breedveld F., Day R., Dougados M. Interpreting the clinical significance of the differential inhibition of cyclooxygenase-1 and cyclooxygenase-2. Rheumatology (Oxford) 1999 Aug;38(8):779–788. doi: 10.1093/rheumatology/38.8.779. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ciompi M. L., Puccetti L., Bazzichi L., Remorini E., Marotta G. Etodolac versus diclofenac: double-blind cross-over study in rheumatoid arthritis. Int J Clin Pharmacol Res. 1989;9(3):217–222. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Degner F., Sigmund R., Zeidler H. Efficacy and tolerability of meloxicam in an observational, controlled cohort study in patients with rheumatic disease. Clin Ther. 2000 Apr;22(4):400–410. doi: 10.1016/S0149-2918(00)89009-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dequeker J., Hawkey C., Kahan A., Steinbrück K., Alegre C., Baumelou E., Bégaud B., Isomäki H., Littlejohn G., Mau J. Improvement in gastrointestinal tolerability of the selective cyclooxygenase (COX)-2 inhibitor, meloxicam, compared with piroxicam: results of the Safety and Efficacy Large-scale Evaluation of COX-inhibiting Therapies (SELECT) trial in osteoarthritis. Br J Rheumatol. 1998 Sep;37(9):946–951. doi: 10.1093/rheumatology/37.9.946. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Distel M., Mueller C., Bluhmki E., Fries J. Safety of meloxicam: a global analysis of clinical trials. Br J Rheumatol. 1996 Apr;35 (Suppl 1):68–77. doi: 10.1093/rheumatology/35.suppl_1.68. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fu J. Y., Masferrer J. L., Seibert K., Raz A., Needleman P. The induction and suppression of prostaglandin H2 synthase (cyclooxygenase) in human monocytes. J Biol Chem. 1990 Oct 5;265(28):16737–16740. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gabriel S. E., Jaakkimainen L., Bombardier C. Risk for serious gastrointestinal complications related to use of nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs. A meta-analysis. Ann Intern Med. 1991 Nov 15;115(10):787–796. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-115-10-787. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- García Rodríguez L. A., Jick H. Risk of upper gastrointestinal bleeding and perforation associated with individual non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs. Lancet. 1994 Mar 26;343(8900):769–772. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(94)91843-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gurwitz J. H., Avorn J., Bohn R. L., Glynn R. J., Monane M., Mogun H. Initiation of antihypertensive treatment during nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drug therapy. JAMA. 1994 Sep 14;272(10):781–786. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harris R. C. Macula densa signalling--a potential role of cyclooxygenase-2 (COX-2)? Nephrol Dial Transplant. 2000 Oct;15(10):1504–1506. doi: 10.1093/ndt/15.10.1504. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harris R. C., McKanna J. A., Akai Y., Jacobson H. R., Dubois R. N., Breyer M. D. Cyclooxygenase-2 is associated with the macula densa of rat kidney and increases with salt restriction. J Clin Invest. 1994 Dec;94(6):2504–2510. doi: 10.1172/JCI117620. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hawkey C. J. COX-2 inhibitors. Lancet. 1999 Jan 23;353(9149):307–314. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(98)12154-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hawkey C. J. Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drug gastropathy. Gastroenterology. 2000 Aug;119(2):521–535. doi: 10.1053/gast.2000.9561. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hawkey C., Kahan A., Steinbrück K., Alegre C., Baumelou E., Bégaud B., Dequeker J., Isomäki H., Littlejohn G., Mau J. Gastrointestinal tolerability of meloxicam compared to diclofenac in osteoarthritis patients. International MELISSA Study Group. Meloxicam Large-scale International Study Safety Assessment. Br J Rheumatol. 1998 Sep;37(9):937–945. doi: 10.1093/rheumatology/37.9.937. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hawkey C., Laine L., Simon T., Beaulieu A., Maldonado-Cocco J., Acevedo E., Shahane A., Quan H., Bolognese J., Mortensen E. Comparison of the effect of rofecoxib (a cyclooxygenase 2 inhibitor), ibuprofen, and placebo on the gastroduodenal mucosa of patients with osteoarthritis: a randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled trial. The Rofecoxib Osteoarthritis Endoscopy Multinational Study Group. Arthritis Rheum. 2000 Feb;43(2):370–377. doi: 10.1002/1529-0131(200002)43:2<370::AID-ANR17>3.0.CO;2-D. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Henry D., Lim L. L., Garcia Rodriguez L. A., Perez Gutthann S., Carson J. L., Griffin M., Savage R., Logan R., Moride Y., Hawkey C. Variability in risk of gastrointestinal complications with individual non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs: results of a collaborative meta-analysis. BMJ. 1996 Jun 22;312(7046):1563–1566. doi: 10.1136/bmj.312.7046.1563. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Henry D., Page J., Whyte I., Nanra R., Hall C. Consumption of non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs and the development of functional renal impairment in elderly subjects. Results of a case-control study. Br J Clin Pharmacol. 1997 Jul;44(1):85–90. doi: 10.1046/j.1365-2125.1997.00631.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hunt R. H., Bowen B., Mortensen E. R., Simon T. J., James C., Cagliola A., Quan H., Bolognese J. A. A randomized trial measuring fecal blood loss after treatment with rofecoxib, ibuprofen, or placebo in healthy subjects. Am J Med. 2000 Aug 15;109(3):201–206. doi: 10.1016/s0002-9343(00)00470-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jick S. S. The risk of gastrointestinal bleed, myocardial infarction, and newly diagnosed hypertension in users of meloxicam, diclofenac, naproxen, and piroxicam. Pharmacotherapy. 2000 Jul;20(7):741–744. doi: 10.1592/phco.20.9.741.35209. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johnson A. G., Nguyen T. V., Day R. O. Do nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs affect blood pressure? A meta-analysis. Ann Intern Med. 1994 Aug 15;121(4):289–300. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-121-4-199408150-00011. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laine L., Cominelli F., Sloane R., Casini-Raggi V., Marin-Sorensen M., Weinstein W. M. Interaction of NSAIDs and Helicobacter pylori on gastrointestinal injury and prostaglandin production: a controlled double-blind trial. Aliment Pharmacol Ther. 1995 Apr;9(2):127–135. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2036.1995.tb00361.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laine L., Harper S., Simon T., Bath R., Johanson J., Schwartz H., Stern S., Quan H., Bolognese J. A randomized trial comparing the effect of rofecoxib, a cyclooxygenase 2-specific inhibitor, with that of ibuprofen on the gastroduodenal mucosa of patients with osteoarthritis. Rofecoxib Osteoarthritis Endoscopy Study Group. Gastroenterology. 1999 Oct;117(4):776–783. doi: 10.1016/s0016-5085(99)70334-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Langman M. J., Weil J., Wainwright P., Lawson D. H., Rawlins M. D., Logan R. F., Murphy M., Vessey M. P., Colin-Jones D. G. Risks of bleeding peptic ulcer associated with individual non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs. Lancet. 1994 Apr 30;343(8905):1075–1078. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(94)90185-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lanza F. L., Rack M. F., Simon T. J., Quan H., Bolognese J. A., Hoover M. E., Wilson F. R., Harper S. E. Specific inhibition of cyclooxygenase-2 with MK-0966 is associated with less gastroduodenal damage than either aspirin or ibuprofen. Aliment Pharmacol Ther. 1999 Jun;13(6):761–767. doi: 10.1046/j.1365-2036.1999.00529.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lightfoot R. Comparison of the efficacy and safety of etodolac and piroxicam in patients with rheumatoid arthritis. Etodolac Study 326 Rheumatoid Arthritis Investigators Group. J Rheumatol Suppl. 1997 Feb;47:10–16. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lipscomb G. R., Wallis N., Armstrong G., Rees W. D. Gastrointestinal tolerability of meloxicam and piroxicam: a double-blind placebo-controlled study. Br J Clin Pharmacol. 1998 Aug;46(2):133–137. doi: 10.1046/j.1365-2125.1998.00761.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McGiff J. C., Quilley J. 20-HETE and the kidney: resolution of old problems and new beginnings. Am J Physiol. 1999 Sep;277(3 Pt 2):R607–R623. doi: 10.1152/ajpregu.1999.277.3.R607. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nantel F., Meadows E., Denis D., Connolly B., Metters K. M., Giaid A. Immunolocalization of cyclooxygenase-2 in the macula densa of human elderly. FEBS Lett. 1999 Sep 3;457(3):475–477. doi: 10.1016/s0014-5793(99)01088-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Page J., Henry D. Consumption of NSAIDs and the development of congestive heart failure in elderly patients: an underrecognized public health problem. Arch Intern Med. 2000 Mar 27;160(6):777–784. doi: 10.1001/archinte.160.6.777. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Panara M. R., Renda G., Sciulli M. G., Santini G., Di Giamberardino M., Rotondo M. T., Tacconelli S., Seta F., Patrono C., Patrignani P. Dose-dependent inhibition of platelet cyclooxygenase-1 and monocyte cyclooxygenase-2 by meloxicam in healthy subjects. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1999 Jul;290(1):276–280. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Patoia L., Santucci L., Furno P., Dionisi M. S., Dell'Orso S., Romagnoli M., Sattarinia A., Marini M. G. A 4-week, double-blind, parallel-group study to compare the gastrointestinal effects of meloxicam 7.5 mg, meloxicam 15 mg, piroxicam 20 mg and placebo by means of faecal blood loss, endoscopy and symptom evaluation in healthy volunteers. Br J Rheumatol. 1996 Apr;35 (Suppl 1):61–67. doi: 10.1093/rheumatology/35.suppl_1.61. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Patrignani P., Panara M. R., Greco A., Fusco O., Natoli C., Iacobelli S., Cipollone F., Ganci A., Créminon C., Maclouf J. Biochemical and pharmacological characterization of the cyclooxygenase activity of human blood prostaglandin endoperoxide synthases. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1994 Dec;271(3):1705–1712. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Patrignani P., Panara M. R., Sciulli M. G., Santini G., Renda G., Patrono C. Differential inhibition of human prostaglandin endoperoxide synthase-1 and -2 by nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs. J Physiol Pharmacol. 1997 Dec;48(4):623–631. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Perpignano G., Bogliolo A., Puccetti L. Double-blind comparison of the efficacy and safety of etodolac SR 600 mg u.i.d. and of tenoxicam 20 mg u.i.d. in elderly patients with osteoarthritis of the hip and of the knee. Int J Clin Pharmacol Res. 1994;14(5-6):203–216. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Piper J. M., Ray W. A., Daugherty J. R., Griffin M. R. Corticosteroid use and peptic ulcer disease: role of nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs. Ann Intern Med. 1991 May 1;114(9):735–740. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-114-9-735. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schnermann J. Juxtaglomerular cell complex in the regulation of renal salt excretion. Am J Physiol. 1998 Feb;274(2 Pt 2):R263–R279. doi: 10.1152/ajpregu.1998.274.2.R263. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schoenfeld P., Kimmey M. B., Scheiman J., Bjorkman D., Laine L. Review article: nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drug-associated gastrointestinal complications--guidelines for prevention and treatment. Aliment Pharmacol Ther. 1999 Oct;13(10):1273–1285. doi: 10.1046/j.1365-2036.1999.00617.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shorr R. I., Ray W. A., Daugherty J. R., Griffin M. R. Concurrent use of nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs and oral anticoagulants places elderly persons at high risk for hemorrhagic peptic ulcer disease. Arch Intern Med. 1993 Jul 26;153(14):1665–1670. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sigthorsson G., Crane R., Simon T., Hoover M., Quan H., Bolognese J., Bjarnason I. COX-2 inhibition with rofecoxib does not increase intestinal permeability in healthy subjects: a double blind crossover study comparing rofecoxib with placebo and indomethacin. Gut. 2000 Oct;47(4):527–532. doi: 10.1136/gut.47.4.527. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Silverstein F. E., Faich G., Goldstein J. L., Simon L. S., Pincus T., Whelton A., Makuch R., Eisen G., Agrawal N. M., Stenson W. F. Gastrointestinal toxicity with celecoxib vs nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs for osteoarthritis and rheumatoid arthritis: the CLASS study: A randomized controlled trial. Celecoxib Long-term Arthritis Safety Study. JAMA. 2000 Sep 13;284(10):1247–1255. doi: 10.1001/jama.284.10.1247. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Silverstein F. E., Faich G., Goldstein J. L., Simon L. S., Pincus T., Whelton A., Makuch R., Eisen G., Agrawal N. M., Stenson W. F. Gastrointestinal toxicity with celecoxib vs nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs for osteoarthritis and rheumatoid arthritis: the CLASS study: A randomized controlled trial. Celecoxib Long-term Arthritis Safety Study. JAMA. 2000 Sep 13;284(10):1247–1255. doi: 10.1001/jama.284.10.1247. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Simmons D. L., Botting R. M., Robertson P. M., Madsen M. L., Vane J. R. Induction of an acetaminophen-sensitive cyclooxygenase with reduced sensitivity to nonsteroid antiinflammatory drugs. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1999 Mar 16;96(6):3275–3280. doi: 10.1073/pnas.96.6.3275. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Simmons D. L., Levy D. B., Yannoni Y., Erikson R. L. Identification of a phorbol ester-repressible v-src-inducible gene. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Feb;86(4):1178–1182. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.4.1178. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Simon L. S., Lanza F. L., Lipsky P. E., Hubbard R. C., Talwalker S., Schwartz B. D., Isakson P. C., Geis G. S. Preliminary study of the safety and efficacy of SC-58635, a novel cyclooxygenase 2 inhibitor: efficacy and safety in two placebo-controlled trials in osteoarthritis and rheumatoid arthritis, and studies of gastrointestinal and platelet effects. Arthritis Rheum. 1998 Sep;41(9):1591–1602. doi: 10.1002/1529-0131(199809)41:9<1591::AID-ART9>3.0.CO;2-J. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Simon L. S., Weaver A. L., Graham D. Y., Kivitz A. J., Lipsky P. E., Hubbard R. C., Isakson P. C., Verburg K. M., Yu S. S., Zhao W. W. Anti-inflammatory and upper gastrointestinal effects of celecoxib in rheumatoid arthritis: a randomized controlled trial. JAMA. 1999 Nov 24;282(20):1921–1928. doi: 10.1001/jama.282.20.1921. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Swan S. K., Rudy D. W., Lasseter K. C., Ryan C. F., Buechel K. L., Lambrecht L. J., Pinto M. B., Dilzer S. C., Obrda O., Sundblad K. J. Effect of cyclooxygenase-2 inhibition on renal function in elderly persons receiving a low-salt diet. A randomized, controlled trial. Ann Intern Med. 2000 Jul 4;133(1):1–9. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-133-1-200007040-00002. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Taha A. S., McLaughlin S., Holland P. J., Kelly R. W., Sturrock R. D., Russell R. I. Effect on gastric and duodenal mucosal prostaglandins of repeated intake of therapeutic doses of naproxen and etodolac in rheumatoid arthritis. Ann Rheum Dis. 1990 Jun;49(6):354–358. doi: 10.1136/ard.49.6.354. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tramèr M. R., Moore R. A., Reynolds D. J., McQuay H. J. Quantitative estimation of rare adverse events which follow a biological progression: a new model applied to chronic NSAID use. Pain. 2000 Mar;85(1-2):169–182. doi: 10.1016/s0304-3959(99)00267-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vane J. R. Inhibition of prostaglandin synthesis as a mechanism of action for aspirin-like drugs. Nat New Biol. 1971 Jun 23;231(25):232–235. doi: 10.1038/newbio231232a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wallace J. L., McKnight W., Reuter B. K., Vergnolle N. NSAID-induced gastric damage in rats: requirement for inhibition of both cyclooxygenase 1 and 2. Gastroenterology. 2000 Sep;119(3):706–714. doi: 10.1053/gast.2000.16510. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Warner T. D., Giuliano F., Vojnovic I., Bukasa A., Mitchell J. A., Vane J. R. Nonsteroid drug selectivities for cyclo-oxygenase-1 rather than cyclo-oxygenase-2 are associated with human gastrointestinal toxicity: a full in vitro analysis. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1999 Jun 22;96(13):7563–7568. doi: 10.1073/pnas.96.13.7563. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weil J., Langman M. J., Wainwright P., Lawson D. H., Rawlins M., Logan R. F., Brown T. P., Vessey M. P., Murphy M., Colin-Jones D. G. Peptic ulcer bleeding: accessory risk factors and interactions with non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs. Gut. 2000 Jan;46(1):27–31. doi: 10.1136/gut.46.1.27. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Whelton A., Fort J. G., Puma J. A., Normandin D., Bello A. E., Verburg K. M., SUCCESS VI Study Group Cyclooxygenase-2--specific inhibitors and cardiorenal function: a randomized, controlled trial of celecoxib and rofecoxib in older hypertensive osteoarthritis patients. Am J Ther. 2001 Mar-Apr;8(2):85–95. doi: 10.1097/00045391-200103000-00003. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wight N. J., Gottesdiener K., Garlick N. M., Atherton C. T., Novak S., Gertz B. J., Calder N. A., Cote J., Wong P., Dallob A. Rofecoxib, a COX-2 inhibitor, does not inhibit human gastric mucosal prostaglandin production. Gastroenterology. 2001 Mar;120(4):867–873. doi: 10.1053/gast.2001.22432. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Willoughby D. A., Moore A. R., Colville-Nash P. R. COX-1, COX-2, and COX-3 and the future treatment of chronic inflammatory disease. Lancet. 2000 Feb 19;355(9204):646–648. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(99)12031-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wolf K., Castrop H., Hartner A., Goppelt-Strübe M., Hilgers K. F., Kurtz A. Inhibition of the renin-angiotensin system upregulates cyclooxygenase-2 expression in the macula densa. Hypertension. 1999 Sep;34(3):503–507. doi: 10.1161/01.hyp.34.3.503. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Xie W. L., Chipman J. G., Robertson D. L., Erikson R. L., Simmons D. L. Expression of a mitogen-responsive gene encoding prostaglandin synthase is regulated by mRNA splicing. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Apr 1;88(7):2692–2696. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.7.2692. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yang T., Schnermann J. B., Briggs J. P. Regulation of cyclooxygenase-2 expression in renal medulla by tonicity in vivo and in vitro. Am J Physiol. 1999 Jul;277(1 Pt 2):F1–F9. doi: 10.1152/ajprenal.1999.277.1.F1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yang T., Singh I., Pham H., Sun D., Smart A., Schnermann J. B., Briggs J. P. Regulation of cyclooxygenase expression in the kidney by dietary salt intake. Am J Physiol. 1998 Mar;274(3 Pt 2):F481–F489. doi: 10.1152/ajprenal.1998.274.3.F481. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]