Full Text
The Full Text of this article is available as a PDF (133.8 KB).
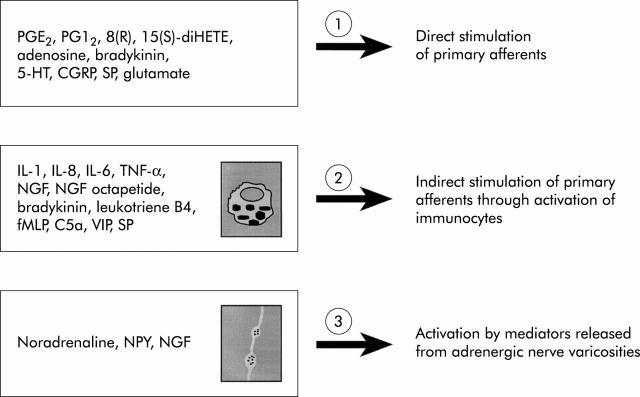
Figure 1 .
Substances and major local pathways involved in triggering hyperalgesia to distension within the gut. Note that several mediators such as substance P (SP) may directly and indirectly influence the threshold of response of afferent fibres to a mechanical stimulus. CGRP, calcitonin gene related peptide; C5a, complement 5a; fMLP, formyl-methionyl-leucyl-phenylanine; IL, interleukin; NGF, nerve growth factor; NPY, neuropeptide Y; PGI2, prostacyclin I2; PGE 2, prostaglandin E2; TNF, tumour necrosis factor; VIP, vasoactive intestinal peptide; 5-HT, serotonin; 8(R),15(S)-diHETE, 8(R),15(S)-dihydroxyeicosatetraenoic acid. Modified from Coelho and colleagues.34
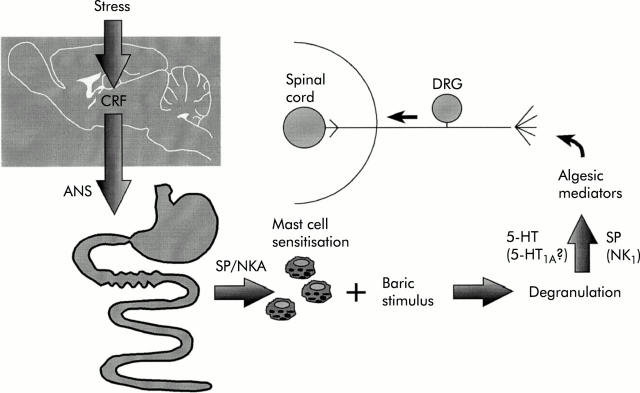
Figure 2 .
Pathways, structures, and mediators involved in stress induced hyperalgesia to visceral (rectal) mechanical stimulus. ANS, autonomic nervous system; CRF, corticotrophin releasing factor; DRG, dorsal root ganglia; NKA, neurokinin A; SP, substance P; 5-HT, serotonin.
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Anton P. M., Theodorou V., Fioramonti J., Bueno L. Chronic low-level administration of diquat increases the nociceptive response to gastric distension in rats: role of mast cells and tachykinin receptor activation. Pain. 2001 May;92(1-2):219–227. doi: 10.1016/s0304-3959(01)00257-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bathon J. M., Proud D. Bradykinin antagonists. Annu Rev Pharmacol Toxicol. 1991;31:129–162. doi: 10.1146/annurev.pa.31.040191.001021. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Birch P. J., Harrison S. M., Hayes A. G., Rogers H., Tyers M. B. The non-peptide NK1 receptor antagonist, (+/-)-CP-96,345, produces antinociceptive and anti-oedema effects in the rat. Br J Pharmacol. 1992 Mar;105(3):508–510. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1992.tb09008.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Botella A., Fioramonti J., Eeckhout C., Bueno L. Intracolonic glycerol induces abdominal contractions in rats: role of 5-HT3 receptors. Fundam Clin Pharmacol. 1998;12(6):619–623. doi: 10.1111/j.1472-8206.1998.tb00995.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bradesi S., Eutamene H., Theodorou V., Fioramonti J., Bueno L. Effect of ovarian hormones on intestinal mast cell reactivity to substance P. Life Sci. 2001 Jan 19;68(9):1047–1056. doi: 10.1016/s0024-3205(00)01008-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Buéno L., Fioramonti J., Garcia-Villar R. Pathobiology of visceral pain: molecular mechanisms and therapeutic implications. III. Visceral afferent pathways: a source of new therapeutic targets for abdominal pain. Am J Physiol Gastrointest Liver Physiol. 2000 May;278(5):G670–G676. doi: 10.1152/ajpgi.2000.278.5.G670. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Coelho A. M., Fioramonti J., Bueno L. Mast cell degranulation induces delayed rectal allodynia in rats: role of histamine and 5-HT. Dig Dis Sci. 1998 Apr;43(4):727–737. doi: 10.1023/a:1018853728251. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Coelho A. M., Fioramonti J., Buéno L. Systemic lipopolysaccharide influences rectal sensitivity in rats: role of mast cells, cytokines, and vagus nerve. Am J Physiol Gastrointest Liver Physiol. 2000 Oct;279(4):G781–G790. doi: 10.1152/ajpgi.2000.279.4.G781. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Costello A. H., Hargreaves K. M. Suppression of carrageenan-induced hyperalgesia, hyperthermia and edema by a bradykinin antagonist. Eur J Pharmacol. 1989 Nov 21;171(2-3):259–263. doi: 10.1016/0014-2999(89)90118-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Delree P., Martin D., Sadzot-Delvaux C., Rogister B., Leprince P., Robe P., Rigo J. M., Lefebvre P. P., Malgrange B., Schoenen J. In vitro and in vivo modulation of 5-hydroxytryptamine-, thyrotropin-releasing hormone- and calcitonin-gene related peptide-like immunoreactivities in adult rat sensory neurons. Neuroscience. 1992 Nov;51(2):401–410. doi: 10.1016/0306-4522(92)90324-u. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gué M., Del Rio-Lacheze C., Eutamene H., Théodorou V., Fioramonti J., Buéno L. Stress-induced visceral hypersensitivity to rectal distension in rats: role of CRF and mast cells. Neurogastroenterol Motil. 1997 Dec;9(4):271–279. doi: 10.1046/j.1365-2982.1997.d01-63.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Julia V., Buéno L. Tachykininergic mediation of viscerosensitive responses to acute inflammation in rats: role of CGRP. Am J Physiol. 1997 Jan;272(1 Pt 1):G141–G146. doi: 10.1152/ajpgi.1997.272.1.G141. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Julia V., Morteau O., Buéno L. Involvement of neurokinin 1 and 2 receptors in viscerosensitive response to rectal distension in rats. Gastroenterology. 1994 Jul;107(1):94–102. doi: 10.1016/0016-5085(94)90065-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kennedy C., Leff P. Painful connection for ATP. Nature. 1995 Oct 5;377(6548):385–386. doi: 10.1038/377385a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mayer E. A., Gebhart G. F. Basic and clinical aspects of visceral hyperalgesia. Gastroenterology. 1994 Jul;107(1):271–293. doi: 10.1016/0016-5085(94)90086-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McLean P. G., Picard C., Garcia-Villar R., Ducos de Lahitte R., Moré J., Fioramonti J., Buéno L. Role of kinin B1 and B2 receptors and mast cells in post intestinal infection-induced hypersensitivity to distension. Neurogastroenterol Motil. 1998 Dec;10(6):499–508. doi: 10.1046/j.1365-2982.1998.00123.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McLean P. G., Picard C., Garcia-Villar R., Moré J., Fioramonti J., Buéno L. Effects of nematode infection on sensitivity to intestinal distension: role of tachykinin NK2 receptors. Eur J Pharmacol. 1997 Oct 22;337(2-3):279–282. doi: 10.1016/s0014-2999(97)01275-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McMahon S. B. Mechanisms of sympathetic pain. Br Med Bull. 1991 Jul;47(3):584–600. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.bmb.a072494. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moss H. E., Sanger G. J. The effects of granisetron, ICS 205-930 and ondansetron on the visceral pain reflex induced by duodenal distension. Br J Pharmacol. 1990 Jul;100(3):497–501. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1990.tb15836.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Murphy A. Z., Murphy R. M., Zemlan F. P. Role of spinal serotonin1 receptor subtypes in thermally and mechanically elicited nociceptive reflexes. Psychopharmacology (Berl) 1992;108(1-2):123–130. doi: 10.1007/BF02245296. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Purcell W. M., Atterwill C. K. Mast cells in neuroimmune function: neurotoxicological and neuropharmacological perspectives. Neurochem Res. 1995 May;20(5):521–532. doi: 10.1007/BF01694534. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ricciardolo F. L., Steinhoff M., Amadesi S., Guerrini R., Tognetto M., Trevisani M., Creminon C., Bertrand C., Bunnett N. W., Fabbri L. M. Presence and bronchomotor activity of protease-activated receptor-2 in guinea pig airways. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 2000 May;161(5):1672–1680. doi: 10.1164/ajrccm.161.5.9907133. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sharkey K. A., Coggins P. J., Tetzlaff W., Zwiers H., Bisby M. A., Davision J. S. Distribution of growth-associated protein, B-50 (GAP-43) in the mammalian enteric nervous system. Neuroscience. 1990;38(1):13–20. doi: 10.1016/0306-4522(90)90370-j. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stead R. H., Kosecka-Janiszewska U., Oestreicher A. B., Dixon M. F., Bienenstock J. Remodeling of B-50 (GAP-43)- and NSE-immunoreactive mucosal nerves in the intestines of rats infected with Nippostrongylus brasiliensis. J Neurosci. 1991 Dec;11(12):3809–3821. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.11-12-03809.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Steranka L. R., Manning D. C., DeHaas C. J., Ferkany J. W., Borosky S. A., Connor J. R., Vavrek R. J., Stewart J. M., Snyder S. H. Bradykinin as a pain mediator: receptors are localized to sensory neurons, and antagonists have analgesic actions. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 May;85(9):3245–3249. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.9.3245. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sternini C. Enteric and visceral afferent CGRP neurons. Targets of innervation and differential expression patterns. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1992 Jun 30;657:170–186. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1992.tb22766.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tracey D. J., Walker J. S. Pain due to nerve damage: are inflammatory mediators involved? Inflamm Res. 1995 Oct;44(10):407–411. doi: 10.1007/BF01757696. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zemlan F. P., Murphy A. Z., Behbehani M. M. 5-HT1A receptors mediate the effect of the bulbospinal serotonin system on spinal dorsal horn nociceptive neurons. Pharmacology. 1994 Jan;48(1):1–10. doi: 10.1159/000139156. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]