Abstract
In contrast with urine formation, bile flow is not dependent on hydrostatic forces, but driven by osmotic pressure of solutes secreted across the apical membrane of hepatocytes and bile duct epithelial cells. This secretory process is mediated by a set of primary active transporters that use ATP hydrolysis to pump solutes against the concentration gradient. The most important solutes in bile are bile salts, lipids, electrolytes, and organic anions. The direct consequence of the osmotic mechanism of bile formation is that impaired function of these pumps leads to impaired bile flow—that is, cholestasis. The function of these pumps is highlighted by a number of inherited cholestatic diseases, which are caused by mutations in these genes. Identification of the molecular defect in these diseases was not only important for diagnostic reasons but also emphasised that impaired transporter function has pathological consequences. Indeed, it is now becoming clear that impaired or downregulated transporter function is also involved in the pathogenesis of acquired cholestatic syndromes.
Full Text
The Full Text of this article is available as a PDF (141.4 KB).
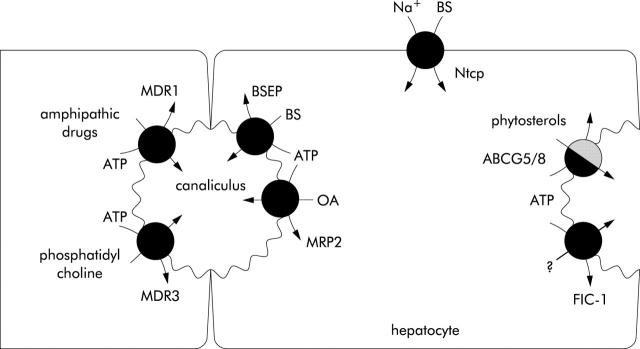
Figure 1 .
Transporters involved in canalicular bile formation. In the left canalicular membrane the ABC transporters are indicated, of which the function has been established. In the right canalicular membrane the heterodimer of ABCG5 and ABCG8 has been drawn, but this is speculative because the presence of these two half transporters in the canalicular membrane has not been demonstrated yet. It has also not yet been proved that phytosterols are transported by this transporter pair.
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Alonso E. M., Snover D. C., Montag A., Freese D. K., Whitington P. F. Histologic pathology of the liver in progressive familial intrahepatic cholestasis. J Pediatr Gastroenterol Nutr. 1994 Feb;18(2):128–133. doi: 10.1097/00005176-199402000-00002. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ananthanarayanan M., Balasubramanian N., Makishima M., Mangelsdorf D. J., Suchy F. J. Human bile salt export pump promoter is transactivated by the farnesoid X receptor/bile acid receptor. J Biol Chem. 2001 May 31;276(31):28857–28865. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M011610200. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bacq Y., Myara A., Brechot M. C., Hamon C., Studer E., Trivin F., Metman E. H. Serum conjugated bile acid profile during intrahepatic cholestasis of pregnancy. J Hepatol. 1995 Jan;22(1):66–70. doi: 10.1016/0168-8278(95)80261-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bacq Y., Sapey T., Bréchot M. C., Pierre F., Fignon A., Dubois F. Intrahepatic cholestasis of pregnancy: a French prospective study. Hepatology. 1997 Aug;26(2):358–364. doi: 10.1002/hep.510260216. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Beigneux A. P., Moser A. H., Shigenaga J. K., Grunfeld C., Feingold K. R. The acute phase response is associated with retinoid X receptor repression in rodent liver. J Biol Chem. 2000 May 26;275(21):16390–16399. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M000953200. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Berge K. E., Tian H., Graf G. A., Yu L., Grishin N. V., Schultz J., Kwiterovich P., Shan B., Barnes R., Hobbs H. H. Accumulation of dietary cholesterol in sitosterolemia caused by mutations in adjacent ABC transporters. Science. 2000 Dec 1;290(5497):1771–1775. doi: 10.1126/science.290.5497.1771. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bramlett K. S., Yao S., Burris T. P. Correlation of farnesoid X receptor coactivator recruitment and cholesterol 7alpha-hydroxylase gene repression by bile acids. Mol Genet Metab. 2000 Dec;71(4):609–615. doi: 10.1006/mgme.2000.3106. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bull L. N., van Eijk M. J., Pawlikowska L., DeYoung J. A., Juijn J. A., Liao M., Klomp L. W., Lomri N., Berger R., Scharschmidt B. F. A gene encoding a P-type ATPase mutated in two forms of hereditary cholestasis. Nat Genet. 1998 Mar;18(3):219–224. doi: 10.1038/ng0398-219. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carlton V. E., Knisely A. S., Freimer N. B. Mapping of a locus for progressive familial intrahepatic cholestasis (Byler disease) to 18q21-q22, the benign recurrent intrahepatic cholestasis region. Hum Mol Genet. 1995 Jun;4(6):1049–1053. doi: 10.1093/hmg/4.6.1049. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cascorbi I., Gerloff T., Johne A., Meisel C., Hoffmeyer S., Schwab M., Schaeffeler E., Eichelbaum M., Brinkmann U., Roots I. Frequency of single nucleotide polymorphisms in the P-glycoprotein drug transporter MDR1 gene in white subjects. Clin Pharmacol Ther. 2001 Mar;69(3):169–174. doi: 10.1067/mcp.2001.114164. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chiang J. Y., Kimmel R., Stroup D. Regulation of cholesterol 7alpha-hydroxylase gene (CYP7A1) transcription by the liver orphan receptor (LXRalpha). Gene. 2001 Jan 10;262(1-2):257–265. doi: 10.1016/s0378-1119(00)00518-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chiang J. Y., Kimmel R., Weinberger C., Stroup D. Farnesoid X receptor responds to bile acids and represses cholesterol 7alpha-hydroxylase gene (CYP7A1) transcription. J Biol Chem. 2000 Apr 14;275(15):10918–10924. doi: 10.1074/jbc.275.15.10918. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clayton R. J., Iber F. L., Ruebner B. H., McKusick V. A. Byler disease. Fatal familial intrahepatic cholestasis in an Amish kindred. Am J Dis Child. 1969 Jan;117(1):112–124. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cohen L., Lewis C., Arias I. M. Pregnancy, oral contraceptives, and chronic familial jaundice with predominantly conjugated hyperbilirubinemia (Dubin-Johnson syndrome). Gastroenterology. 1972 Jun;62(6):1182–1190. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Craddock A. L., Love M. W., Daniel R. W., Kirby L. C., Walters H. C., Wong M. H., Dawson P. A. Expression and transport properties of the human ileal and renal sodium-dependent bile acid transporter. Am J Physiol. 1998 Jan;274(1 Pt 1):G157–G169. doi: 10.1152/ajpgi.1998.274.1.G157. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Crawford J. M. Role of vesicle-mediated transport pathways in hepatocellular bile secretion. Semin Liver Dis. 1996 May;16(2):169–189. doi: 10.1055/s-2007-1007230. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Deleuze J. F., Jacquemin E., Dubuisson C., Cresteil D., Dumont M., Erlinger S., Bernard O., Hadchouel M. Defect of multidrug-resistance 3 gene expression in a subtype of progressive familial intrahepatic cholestasis. Hepatology. 1996 Apr;23(4):904–908. doi: 10.1002/hep.510230435. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Denson L. A., Auld K. L., Schiek D. S., McClure M. H., Mangelsdorf D. J., Karpen S. J. Interleukin-1beta suppresses retinoid transactivation of two hepatic transporter genes involved in bile formation. J Biol Chem. 2000 Mar 24;275(12):8835–8843. doi: 10.1074/jbc.275.12.8835. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dietrich C. G., de Waart D. R., Ottenhoff R., Schoots I. G., Elferink R. P. Increased bioavailability of the food-derived carcinogen 2-amino-1-methyl-6-phenylimidazo[4,5-b]pyridine in MRP2-deficient rats. Mol Pharmacol. 2001 May;59(5):974–980. doi: 10.1124/mol.59.5.974. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Doyle L. A., Yang W., Abruzzo L. V., Krogmann T., Gao Y., Rishi A. K., Ross D. D. A multidrug resistance transporter from human MCF-7 breast cancer cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1998 Dec 22;95(26):15665–15670. doi: 10.1073/pnas.95.26.15665. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Elferink R. P., Ottenhoff R., van Marle J., Frijters C. M., Smith A. J., Groen A. K. Class III P-glycoproteins mediate the formation of lipoprotein X in the mouse. J Clin Invest. 1998 Nov 1;102(9):1749–1757. doi: 10.1172/JCI3597. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Elferink R. P., Tytgat G. N., Groen A. K. Hepatic canalicular membrane 1: The role of mdr2 P-glycoprotein in hepatobiliary lipid transport. FASEB J. 1997 Jan;11(1):19–28. doi: 10.1096/fasebj.11.1.9034162. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Emond J. C., Whitington P. F. Selective surgical management of progressive familial intrahepatic cholestasis (Byler's disease). J Pediatr Surg. 1995 Dec;30(12):1635–1641. doi: 10.1016/0022-3468(95)90440-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Faubion W. A., Gores G. J. Death receptors in liver biology and pathobiology. Hepatology. 1999 Jan;29(1):1–4. doi: 10.1002/hep.510290101. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Faubion W. A., Guicciardi M. E., Miyoshi H., Bronk S. F., Roberts P. J., Svingen P. A., Kaufmann S. H., Gores G. J. Toxic bile salts induce rodent hepatocyte apoptosis via direct activation of Fas. J Clin Invest. 1999 Jan;103(1):137–145. doi: 10.1172/JCI4765. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gerloff T., Stieger B., Hagenbuch B., Madon J., Landmann L., Roth J., Hofmann A. F., Meier P. J. The sister of P-glycoprotein represents the canalicular bile salt export pump of mammalian liver. J Biol Chem. 1998 Apr 17;273(16):10046–10050. doi: 10.1074/jbc.273.16.10046. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goodwin B., Jones S. A., Price R. R., Watson M. A., McKee D. D., Moore L. B., Galardi C., Wilson J. G., Lewis M. C., Roth M. E. A regulatory cascade of the nuclear receptors FXR, SHP-1, and LRH-1 represses bile acid biosynthesis. Mol Cell. 2000 Sep;6(3):517–526. doi: 10.1016/s1097-2765(00)00051-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Green R. M., Hoda F., Ward K. L. Molecular cloning and characterization of the murine bile salt export pump. Gene. 2000 Jan 4;241(1):117–123. doi: 10.1016/s0378-1119(99)00460-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gregorio G. V., Ball C. S., Mowat A. P., Mieli-Vergani G. Effect of rifampicin in the treatment of pruritus in hepatic cholestasis. Arch Dis Child. 1993 Jul;69(1):141–143. doi: 10.1136/adc.69.1.141. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hamilton R. L., Havel R. J., Kane J. P., Blaurock A. E., Sata T. Cholestasis: lamellar structure of the abnormal human serum lipoprotein. Science. 1971 Apr 30;172(3982):475–478. doi: 10.1126/science.172.3982.475. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hinoshita E., Taguchi K., Inokuchi A., Uchiumi T., Kinukawa N., Shimada M., Tsuneyoshi M., Sugimachi K., Kuwano M. Decreased expression of an ATP-binding cassette transporter, MRP2, in human livers with hepatitis C virus infection. J Hepatol. 2001 Dec;35(6):765–773. doi: 10.1016/s0168-8278(01)00216-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hirohashi T., Suzuki H., Sugiyama Y. Characterization of the transport properties of cloned rat multidrug resistance-associated protein 3 (MRP3). J Biol Chem. 1999 May 21;274(21):15181–15185. doi: 10.1074/jbc.274.21.15181. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hoffmeyer S., Burk O., von Richter O., Arnold H. P., Brockmöller J., Johne A., Cascorbi I., Gerloff T., Roots I., Eichelbaum M. Functional polymorphisms of the human multidrug-resistance gene: multiple sequence variations and correlation of one allele with P-glycoprotein expression and activity in vivo. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2000 Mar 28;97(7):3473–3478. doi: 10.1073/pnas.050585397. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hofmann A. F. Bile acid secretion, bile flow and biliary lipid secretion in humans. Hepatology. 1990 Sep;12(3 Pt 2):17S–25S. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ismail H., Kaliciński P., Markiewicz M., Jankowska I., Pawłowska J., Kluge P., Eliadou E., Kamiński A., Szymczak M., Drewniak T. Treatment of progressive familial intrahepatic cholestasis: liver transplantation or partial external biliary diversion. Pediatr Transplant. 1999 Aug;3(3):219–224. doi: 10.1034/j.1399-3046.1999.00046.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jacquemin E., Cresteil D., Manouvrier S., Boute O., Hadchouel M. Heterozygous non-sense mutation of the MDR3 gene in familial intrahepatic cholestasis of pregnancy. Lancet. 1999 Jan 16;353(9148):210–211. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(05)77221-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jacquemin E., De Vree J. M., Cresteil D., Sokal E. M., Sturm E., Dumont M., Scheffer G. L., Paul M., Burdelski M., Bosma P. J. The wide spectrum of multidrug resistance 3 deficiency: from neonatal cholestasis to cirrhosis of adulthood. Gastroenterology. 2001 May;120(6):1448–1458. doi: 10.1053/gast.2001.23984. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jones E. A., Bergasa N. V. The pruritus of cholestasis and the opioid system. JAMA. 1992 Dec 16;268(23):3359–3362. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jones E. A., Bergasa N. V. The pruritus of cholestasis. Hepatology. 1999 Apr;29(4):1003–1006. doi: 10.1002/hep.510290450. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jonker J. W., Smit J. W., Brinkhuis R. F., Maliepaard M., Beijnen J. H., Schellens J. H., Schinkel A. H. Role of breast cancer resistance protein in the bioavailability and fetal penetration of topotecan. J Natl Cancer Inst. 2000 Oct 18;92(20):1651–1656. doi: 10.1093/jnci/92.20.1651. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kast Heidi R., Goodwin Bryan, Tarr Paul T., Jones Stacey A., Anisfeld Andrew M., Stoltz Catherine M., Tontonoz Peter, Kliewer Steve, Willson Timothy M., Edwards Peter A. Regulation of multidrug resistance-associated protein 2 (ABCC2) by the nuclear receptors pregnane X receptor, farnesoid X-activated receptor, and constitutive androstane receptor. J Biol Chem. 2001 Nov 12;277(4):2908–2915. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M109326200. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kiuchi Y., Suzuki H., Hirohashi T., Tyson C. A., Sugiyama Y. cDNA cloning and inducible expression of human multidrug resistance associated protein 3 (MRP3). FEBS Lett. 1998 Aug 14;433(1-2):149–152. doi: 10.1016/s0014-5793(98)00899-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kool M., de Haas M., Scheffer G. L., Scheper R. J., van Eijk M. J., Juijn J. A., Baas F., Borst P. Analysis of expression of cMOAT (MRP2), MRP3, MRP4, and MRP5, homologues of the multidrug resistance-associated protein gene (MRP1), in human cancer cell lines. Cancer Res. 1997 Aug 15;57(16):3537–3547. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kool M., van der Linden M., de Haas M., Scheffer G. L., de Vree J. M., Smith A. J., Jansen G., Peters G. J., Ponne N., Scheper R. J. MRP3, an organic anion transporter able to transport anti-cancer drugs. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1999 Jun 8;96(12):6914–6919. doi: 10.1073/pnas.96.12.6914. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kouzuki H., Suzuki H., Ito K., Ohashi R., Sugiyama Y. Contribution of sodium taurocholate co-transporting polypeptide to the uptake of its possible substrates into rat hepatocytes. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1998 Aug;286(2):1043–1050. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kouzuki H., Suzuki H., Stieger B., Meier P. J., Sugiyama Y. Characterization of the transport properties of organic anion transporting polypeptide 1 (oatp1) and Na(+)/taurocholate cotransporting polypeptide (Ntcp): comparative studies on the inhibitory effect of their possible substrates in hepatocytes and cDNA-transfected COS-7 cells. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 2000 Feb;292(2):505–511. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- König J., Rost D., Cui Y., Keppler D. Characterization of the human multidrug resistance protein isoform MRP3 localized to the basolateral hepatocyte membrane. Hepatology. 1999 Apr;29(4):1156–1163. doi: 10.1002/hep.510290404. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laatikainen T., Tulenheimo A. Maternal serum bile acid levels and fetal distress in cholestasis of pregnancy. Int J Gynaecol Obstet. 1984 Apr;22(2):91–94. doi: 10.1016/0020-7292(84)90019-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lammert F., Marschall H. U., Glantz A., Matern S. Intrahepatic cholestasis of pregnancy: molecular pathogenesis, diagnosis and management. J Hepatol. 2000 Dec;33(6):1012–1021. doi: 10.1016/s0168-8278(00)80139-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lecureur V., Sun D., Hargrove P., Schuetz E. G., Kim R. B., Lan L. B., Schuetz J. D. Cloning and expression of murine sister of P-glycoprotein reveals a more discriminating transporter than MDR1/P-glycoprotein. Mol Pharmacol. 2000 Jan;57(1):24–35. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lee M. H., Lu K., Hazard S., Yu H., Shulenin S., Hidaka H., Kojima H., Allikmets R., Sakuma N., Pegoraro R. Identification of a gene, ABCG5, important in the regulation of dietary cholesterol absorption. Nat Genet. 2001 Jan;27(1):79–83. doi: 10.1038/83799. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lindberg M. C. Hepatobiliary complications of oral contraceptives. J Gen Intern Med. 1992 Mar-Apr;7(2):199–209. doi: 10.1007/BF02598014. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Loe D. W., Deeley R. G., Cole S. P. Characterization of vincristine transport by the M(r) 190,000 multidrug resistance protein (MRP): evidence for cotransport with reduced glutathione. Cancer Res. 1998 Nov 15;58(22):5130–5136. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lown K. S., Mayo R. R., Leichtman A. B., Hsiao H. L., Turgeon D. K., Schmiedlin-Ren P., Brown M. B., Guo W., Rossi S. J., Benet L. Z. Role of intestinal P-glycoprotein (mdr1) in interpatient variation in the oral bioavailability of cyclosporine. Clin Pharmacol Ther. 1997 Sep;62(3):248–260. doi: 10.1016/S0009-9236(97)90027-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maggiore G., Bernard O., Hadchouel M., Lemonnier A., Alagille D. Diagnostic value of serum gamma-glutamyl transpeptidase activity in liver diseases in children. J Pediatr Gastroenterol Nutr. 1991 Jan;12(1):21–26. doi: 10.1097/00005176-199101000-00005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maggiore G., Bernard O., Riely C. A., Hadchouel M., Lemonnier A., Alagille D. Normal serum gamma-glutamyl-transpeptidase activity identifies groups of infants with idiopathic cholestasis with poor prognosis. J Pediatr. 1987 Aug;111(2):251–252. doi: 10.1016/s0022-3476(87)80079-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Makishima M., Okamoto A. Y., Repa J. J., Tu H., Learned R. M., Luk A., Hull M. V., Lustig K. D., Mangelsdorf D. J., Shan B. Identification of a nuclear receptor for bile acids. Science. 1999 May 21;284(5418):1362–1365. doi: 10.1126/science.284.5418.1362. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maliepaard M., Scheffer G. L., Faneyte I. F., van Gastelen M. A., Pijnenborg A. C., Schinkel A. H., van De Vijver M. J., Scheper R. J., Schellens J. H. Subcellular localization and distribution of the breast cancer resistance protein transporter in normal human tissues. Cancer Res. 2001 Apr 15;61(8):3458–3464. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marinelli R. A., LaRusso N. F. Aquaporin water channels in liver: their significance in bile formation. Hepatology. 1997 Nov;26(5):1081–1084. doi: 10.1002/hep.510260539. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meier P. J. Molecular mechanisms of hepatic bile salt transport from sinusoidal blood into bile. Am J Physiol. 1995 Dec;269(6 Pt 1):G801–G812. doi: 10.1152/ajpgi.1995.269.6.G801. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Milkiewicz P., Roma M. G., Cardenas R., Mills C. O., Elias E., Coleman R. Effect of tauroursodeoxycholate and S-adenosyl-L-methionine on 17beta-estradiol glucuronide-induced cholestasis. J Hepatol. 2001 Feb;34(2):184–191. doi: 10.1016/s0168-8278(00)00066-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ng V. L., Ryckman F. C., Porta G., Miura I. K., de Carvalho E., Servidoni M. F., Bezerra J. A., Balistreri W. F. Long-term outcome after partial external biliary diversion for intractable pruritus in patients with intrahepatic cholestasis. J Pediatr Gastroenterol Nutr. 2000 Feb;30(2):152–156. doi: 10.1097/00005176-200002000-00011. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nishida T., Gatmaitan Z., Che M., Arias I. M. Rat liver canalicular membrane vesicles contain an ATP-dependent bile acid transport system. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Aug 1;88(15):6590–6594. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.15.6590. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Noe J., Hagenbuch B., Meier P. J., St-Pierre M. V. Characterization of the mouse bile salt export pump overexpressed in the baculovirus system. Hepatology. 2001 May;33(5):1223–1231. doi: 10.1053/jhep.2001.24171. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Olefsky J. M. Nuclear receptor minireview series. J Biol Chem. 2001 Jul 17;276(40):36863–36864. doi: 10.1074/jbc.R100047200. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Panwala C. M., Jones J. C., Viney J. L. A novel model of inflammatory bowel disease: mice deficient for the multiple drug resistance gene, mdr1a, spontaneously develop colitis. J Immunol. 1998 Nov 15;161(10):5733–5744. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Parks D. J., Blanchard S. G., Bledsoe R. K., Chandra G., Consler T. G., Kliewer S. A., Stimmel J. B., Willson T. M., Zavacki A. M., Moore D. D. Bile acids: natural ligands for an orphan nuclear receptor. Science. 1999 May 21;284(5418):1365–1368. doi: 10.1126/science.284.5418.1365. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Paulusma C. C., van Geer M. A., Evers R., Heijn M., Ottenhoff R., Borst P., Oude Elferink R. P. Canalicular multispecific organic anion transporter/multidrug resistance protein 2 mediates low-affinity transport of reduced glutathione. Biochem J. 1999 Mar 1;338(Pt 2):393–401. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Plass Jacqueline R. M., Mol Olaf, Heegsma Janette, Geuken Mariska, Faber Klaas Nico, Jansen Peter L. M., Müller Michael. Farnesoid X receptor and bile salts are involved in transcriptional regulation of the gene encoding the human bile salt export pump. Hepatology. 2002 Mar;35(3):589–596. doi: 10.1053/jhep.2002.31724. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reyes H., Gonzalez M. C., Ribalta J., Aburto H., Matus C., Schramm G., Katz R., Medina E. Prevalence of intrahepatic cholestasis of pregnancy in Chile. Ann Intern Med. 1978 Apr;88(4):487–493. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-88-4-487. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roelofsen H., van der Veere C. N., Ottenhoff R., Schoemaker B., Jansen P. L., Oude Elferink R. P. Decreased bilirubin transport in the perfused liver of endotoxemic rats. Gastroenterology. 1994 Oct;107(4):1075–1084. doi: 10.1016/0016-5085(94)90232-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rosmorduc O., Hermelin B., Poupon R. MDR3 gene defect in adults with symptomatic intrahepatic and gallbladder cholesterol cholelithiasis. Gastroenterology. 2001 May;120(6):1459–1467. doi: 10.1053/gast.2001.23947. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ruetz S., Gros P. Phosphatidylcholine translocase: a physiological role for the mdr2 gene. Cell. 1994 Jul 1;77(7):1071–1081. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(94)90446-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scheffer G. L., Kool M., Heijn M., de Haas M., Pijnenborg A. C., Wijnholds J., van Helvoort A., de Jong M. C., Hooijberg J. H., Mol C. A. Specific detection of multidrug resistance proteins MRP1, MRP2, MRP3, MRP5, and MDR3 P-glycoprotein with a panel of monoclonal antibodies. Cancer Res. 2000 Sep 15;60(18):5269–5277. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schinkel A. H., Mayer U., Wagenaar E., Mol C. A., van Deemter L., Smit J. J., van der Valk M. A., Voordouw A. C., Spits H., van Tellingen O. Normal viability and altered pharmacokinetics in mice lacking mdr1-type (drug-transporting) P-glycoproteins. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1997 Apr 15;94(8):4028–4033. doi: 10.1073/pnas.94.8.4028. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schinkel A. H., Wagenaar E., Mol C. A., van Deemter L. P-glycoprotein in the blood-brain barrier of mice influences the brain penetration and pharmacological activity of many drugs. J Clin Invest. 1996 Jun 1;97(11):2517–2524. doi: 10.1172/JCI118699. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schroeder A., Eckhardt U., Stieger B., Tynes R., Schteingart C. D., Hofmann A. F., Meier P. J., Hagenbuch B. Substrate specificity of the rat liver Na(+)-bile salt cotransporter in Xenopus laevis oocytes and in CHO cells. Am J Physiol. 1998 Feb;274(2 Pt 1):G370–G375. doi: 10.1152/ajpgi.1998.274.2.G370. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Seligsohn U., Shani M. The Dubin Johnson syndrome and pregnancy. Acta Hepatogastroenterol (Stuttg) 1977 Jun;24(3):167–169. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shneider B. L., Dawson P. A., Christie D. M., Hardikar W., Wong M. H., Suchy F. J. Cloning and molecular characterization of the ontogeny of a rat ileal sodium-dependent bile acid transporter. J Clin Invest. 1995 Feb;95(2):745–754. doi: 10.1172/JCI117722. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sinal C. J., Tohkin M., Miyata M., Ward J. M., Lambert G., Gonzalez F. J. Targeted disruption of the nuclear receptor FXR/BAR impairs bile acid and lipid homeostasis. Cell. 2000 Sep 15;102(6):731–744. doi: 10.1016/s0092-8674(00)00062-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sjövall K., Sjövall J. Serum bile acid levels in pregnancy with pruritus (bile acids and steroids 158). Clin Chim Acta. 1966 Feb;13(2):207–211. doi: 10.1016/0009-8981(66)90294-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smit J. J., Schinkel A. H., Oude Elferink R. P., Groen A. K., Wagenaar E., van Deemter L., Mol C. A., Ottenhoff R., van der Lugt N. M., van Roon M. A. Homozygous disruption of the murine mdr2 P-glycoprotein gene leads to a complete absence of phospholipid from bile and to liver disease. Cell. 1993 Nov 5;75(3):451–462. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(93)90380-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith A. J., Timmermans-Hereijgers J. L., Roelofsen B., Wirtz K. W., van Blitterswijk W. J., Smit J. J., Schinkel A. H., Borst P. The human MDR3 P-glycoprotein promotes translocation of phosphatidylcholine through the plasma membrane of fibroblasts from transgenic mice. FEBS Lett. 1994 Nov 14;354(3):263–266. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(94)01135-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Staudinger J. L., Goodwin B., Jones S. A., Hawkins-Brown D., MacKenzie K. I., LaTour A., Liu Y., Klaassen C. D., Brown K. K., Reinhard J. The nuclear receptor PXR is a lithocholic acid sensor that protects against liver toxicity. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2001 Mar 13;98(6):3369–3374. doi: 10.1073/pnas.051551698. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stieger B., O'Neill B., Meier P. J. ATP-dependent bile-salt transport in canalicular rat liver plasma-membrane vesicles. Biochem J. 1992 May 15;284(Pt 1):67–74. doi: 10.1042/bj2840067. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stolz A., Takikawa H., Sugiyama Y., Kuhlenkamp J., Kaplowitz N. 3 alpha-hydroxysteroid dehydrogenase activity of the Y' bile acid binders in rat liver cytosol. Identification, kinetics, and physiologic significance. J Clin Invest. 1987 Feb;79(2):427–434. doi: 10.1172/JCI112829. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Strautnieks S. S., Bull L. N., Knisely A. S., Kocoshis S. A., Dahl N., Arnell H., Sokal E., Dahan K., Childs S., Ling V. A gene encoding a liver-specific ABC transporter is mutated in progressive familial intrahepatic cholestasis. Nat Genet. 1998 Nov;20(3):233–238. doi: 10.1038/3034. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Strautnieks S. S., Kagalwalla A. F., Tanner M. S., Knisely A. S., Bull L., Freimer N., Kocoshis S. A., Gardiner R. M., Thompson R. J. Identification of a locus for progressive familial intrahepatic cholestasis PFIC2 on chromosome 2q24. Am J Hum Genet. 1997 Sep;61(3):630–633. doi: 10.1086/515501. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Trauner M., Arrese M., Lee H., Boyer J. L., Karpen S. J. Endotoxin downregulates rat hepatic ntcp gene expression via decreased activity of critical transcription factors. J Clin Invest. 1998 May 15;101(10):2092–2100. doi: 10.1172/JCI1680. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Trauner M., Meier P. J., Boyer J. L. Molecular pathogenesis of cholestasis. N Engl J Med. 1998 Oct 22;339(17):1217–1227. doi: 10.1056/NEJM199810223391707. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ueda K., Yoshida A., Amachi T. Recent progress in P-glycoprotein research. Anticancer Drug Des. 1999 Apr;14(2):115–121. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Van Nieuwkerk C. M., Elferink R. P., Groen A. K., Ottenhoff R., Tytgat G. N., Dingemans K. P., Van Den Bergh Weerman M. A., Offerhaus G. J. Effects of Ursodeoxycholate and cholate feeding on liver disease in FVB mice with a disrupted mdr2 P-glycoprotein gene. Gastroenterology. 1996 Jul;111(1):165–171. doi: 10.1053/gast.1996.v111.pm8698195. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vos T. A., Hooiveld G. J., Koning H., Childs S., Meijer D. K., Moshage H., Jansen P. L., Müller M. Up-regulation of the multidrug resistance genes, Mrp1 and Mdr1b, and down-regulation of the organic anion transporter, Mrp2, and the bile salt transporter, Spgp, in endotoxemic rat liver. Hepatology. 1998 Dec;28(6):1637–1644. doi: 10.1002/hep.510280625. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wheeler H. O. Secretion of bile acids by the liver and their role in the formation of hepatic bile. Arch Intern Med. 1972 Oct;130(4):533–541. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Whitington P. F., Freese D. K., Alonso E. M., Schwarzenberg S. J., Sharp H. L. Clinical and biochemical findings in progressive familial intrahepatic cholestasis. J Pediatr Gastroenterol Nutr. 1994 Feb;18(2):134–141. doi: 10.1097/00005176-199402000-00003. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Whitington P. F., Freese D. K., Alonso E. M., Schwarzenberg S. J., Sharp H. L. Clinical and biochemical findings in progressive familial intrahepatic cholestasis. J Pediatr Gastroenterol Nutr. 1994 Feb;18(2):134–141. doi: 10.1097/00005176-199402000-00003. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Whitington P. F., Whitington G. L. Partial external diversion of bile for the treatment of intractable pruritus associated with intrahepatic cholestasis. Gastroenterology. 1988 Jul;95(1):130–136. doi: 10.1016/0016-5085(88)90301-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wong M. H., Oelkers P., Craddock A. L., Dawson P. A. Expression cloning and characterization of the hamster ileal sodium-dependent bile acid transporter. J Biol Chem. 1994 Jan 14;269(2):1340–1347. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Xie W., Radominska-Pandya A., Shi Y., Simon C. M., Nelson M. C., Ong E. S., Waxman D. J., Evans R. M. An essential role for nuclear receptors SXR/PXR in detoxification of cholestatic bile acids. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2001 Mar 13;98(6):3375–3380. doi: 10.1073/pnas.051014398. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zeng H., Liu G., Rea P. A., Kruh G. D. Transport of amphipathic anions by human multidrug resistance protein 3. Cancer Res. 2000 Sep 1;60(17):4779–4784. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zollner G., Fickert P., Zenz R., Fuchsbichler A., Stumptner C., Kenner L., Ferenci P., Stauber R. E., Krejs G. J., Denk H. Hepatobiliary transporter expression in percutaneous liver biopsies of patients with cholestatic liver diseases. Hepatology. 2001 Mar;33(3):633–646. doi: 10.1053/jhep.2001.22646. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- de Pagter A. G., van Berge Henegouwen G. P., ten Bokkel Huinink J. A., Brandt K. H. Familial benign recurrent intrahepatic cholestasis. Interrelation with intrahepatic cholestasis of pregnancy and from oral contraceptives? Gastroenterology. 1976 Aug;71(2):202–207. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- de Vree J. M., Jacquemin E., Sturm E., Cresteil D., Bosma P. J., Aten J., Deleuze J. F., Desrochers M., Burdelski M., Bernard O. Mutations in the MDR3 gene cause progressive familial intrahepatic cholestasis. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1998 Jan 6;95(1):282–287. doi: 10.1073/pnas.95.1.282. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- del Castillo-Olivares A., Gil G. Role of FXR and FTF in bile acid-mediated suppression of cholesterol 7alpha-hydroxylase transcription. Nucleic Acids Res. 2000 Sep 15;28(18):3587–3593. doi: 10.1093/nar/28.18.3587. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van Helvoort A., Smith A. J., Sprong H., Fritzsche I., Schinkel A. H., Borst P., van Meer G. MDR1 P-glycoprotein is a lipid translocase of broad specificity, while MDR3 P-glycoprotein specifically translocates phosphatidylcholine. Cell. 1996 Nov 1;87(3):507–517. doi: 10.1016/s0092-8674(00)81370-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van Nieuwerk C. M., Groen A. K., Ottenhoff R., van Wijland M., van den Bergh Weerman M. A., Tytgat G. N., Offerhaus J. J., Oude Elferink R. P. The role of bile salt composition in liver pathology of mdr2 (-/-) mice: differences between males and females. J Hepatol. 1997 Jan;26(1):138–145. doi: 10.1016/s0168-8278(97)80020-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- von Ahsen N., Richter M., Grupp C., Ringe B., Oellerich M., Armstrong V. W. No influence of the MDR-1 C3435T polymorphism or a CYP3A4 promoter polymorphism (CYP3A4-V allele) on dose-adjusted cyclosporin A trough concentrations or rejection incidence in stable renal transplant recipients. Clin Chem. 2001 Jun;47(6):1048–1052. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]