Full Text
The Full Text of this article is available as a PDF (278.5 KB).
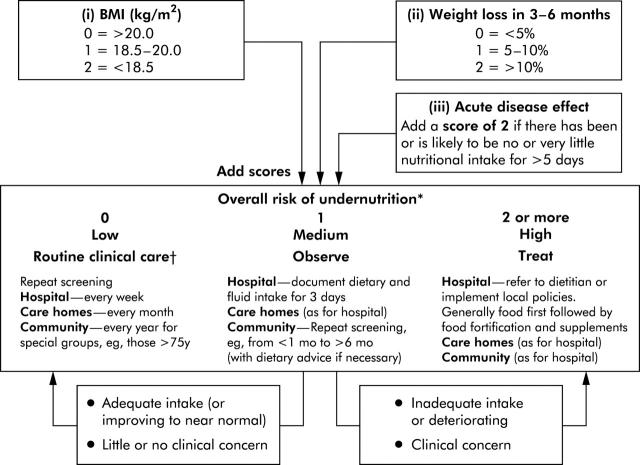
Figure A1 .
Malnutrition universal screening tool (MUST). *If height, weight, or weight loss cannot be established, use documented or recalled values (if considered reliable). When measured or recalled height cannot be obtained, use knee height as a surrogate measure. If neither can be calculated, obtain an overall impression of malnutrition risk (low, medium, high) using the following: (i) clinical impression (very thin, thin, average, overweight);(iia) clothes and/or jewellery have become loose fitting;(iib) history of decreased food intake, loss of appetite, or dysphagia up to 3–6 months; and (iiic) disease (underlying cause) and psychosocial/physical disabilities likely to cause weight loss. Involves treatment of underlying condition, and help with food choice and eating when necessary (also applies to other categories).
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Anderson K. R., Norris D. J., Godfrey L. B., Avent C. K., Butterworth C. E., Jr Bacterial contamination of tube-feeding formulas. JPEN J Parenter Enteral Nutr. 1984 Nov-Dec;8(6):673–678. doi: 10.1177/0148607184008006673. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Anderton A., Aidoo K. E. The effect of handling procedures on microbial contamination of enteral feeds. J Hosp Infect. 1988 May;11(4):364–372. doi: 10.1016/0195-6701(88)90090-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bengmark S. Progress in perioperative enteral tube feeding. Clin Nutr. 1998 Aug;17(4):145–152. doi: 10.1016/s0261-5614(98)80050-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Benya R., Layden T. J., Mobarhan S. Diarrhea associated with tube feeding: the importance of using objective criteria. J Clin Gastroenterol. 1991 Apr;13(2):167–172. doi: 10.1097/00004836-199104000-00010. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Braunschweig C. L., Levy P., Sheean P. M., Wang X. Enteral compared with parenteral nutrition: a meta-analysis. Am J Clin Nutr. 2001 Oct;74(4):534–542. doi: 10.1093/ajcn/74.4.534. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Buchman A. L., Moukarzel A. A., Bhuta S., Belle M., Ament M. E., Eckhert C. D., Hollander D., Gornbein J., Kopple J. D., Vijayaroghavan S. R. Parenteral nutrition is associated with intestinal morphologic and functional changes in humans. JPEN J Parenter Enteral Nutr. 1995 Nov-Dec;19(6):453–460. doi: 10.1177/0148607195019006453. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bury K. D., Jambunathan G. Effects of elemental diets on gastric emptying and gastric secretion in man. Am J Surg. 1974 Jan;127(1):59–64. doi: 10.1016/0002-9610(74)90012-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bussy V., Marechal F., Nasca S. Microbial contamination of enteral feeding tubes occurring during nutritional treatment. JPEN J Parenter Enteral Nutr. 1992 Nov-Dec;16(6):552–557. doi: 10.1177/0148607192016006552. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carr C. S., Ling K. D., Boulos P., Singer M. Randomised trial of safety and efficacy of immediate postoperative enteral feeding in patients undergoing gastrointestinal resection. BMJ. 1996 Apr 6;312(7035):869–871. doi: 10.1136/bmj.312.7035.869. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cummings J. H. Short chain fatty acids in the human colon. Gut. 1981 Sep;22(9):763–779. doi: 10.1136/gut.22.9.763. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dejong C. H., Greve J. W., Soeters P. B. Nutrition in patients with acute pancreatitis. Curr Opin Crit Care. 2001 Aug;7(4):251–256. doi: 10.1097/00075198-200108000-00007. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Delany H. M., Carnevale N. J., Garvey J. W. Jejunostomy by a needle catheter technique. Surgery. 1973 May;73(5):786–790. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DiSario J. A., Foutch P. G., Sanowski R. A. Poor results with percutaneous endoscopic jejunostomy. Gastrointest Endosc. 1990 May-Jun;36(3):257–260. doi: 10.1016/s0016-5107(90)71018-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dobb G. J., Towler S. C. Diarrhoea during enteral feeding in the critically ill: a comparison of feeds with and without fibre. Intensive Care Med. 1990;16(4):252–255. doi: 10.1007/BF01705161. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Driks M. R., Craven D. E., Celli B. R., Manning M., Burke R. A., Garvin G. M., Kunches L. M., Farber H. W., Wedel S. A., McCabe W. R. Nosocomial pneumonia in intubated patients given sucralfate as compared with antacids or histamine type 2 blockers. The role of gastric colonization. N Engl J Med. 1987 Nov 26;317(22):1376–1382. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198711263172204. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Duh Q. Y., Way L. W. Laparoscopic jejunostomy using T-fasteners as retractors and anchors. Arch Surg. 1993 Jan;128(1):105–108. doi: 10.1001/archsurg.1993.01420130117018. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eccles M., Clapp Z., Grimshaw J., Adams P. C., Higgins B., Purves I., Russell I. North of England evidence based guidelines development project: methods of guideline development. BMJ. 1996 Mar 23;312(7033):760–762. doi: 10.1136/bmj.312.7033.760. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Edes T. E., Walk B. E., Austin J. L. Diarrhea in tube-fed patients: feeding formula not necessarily the cause. Am J Med. 1990 Feb;88(2):91–93. doi: 10.1016/0002-9343(90)90454-l. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Edington J., Kon P., Martyn C. N. Prevalence of malnutrition in patients in general practice. Clin Nutr. 1996 Apr;15(2):60–63. doi: 10.1016/s0261-5614(96)80020-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Elia M. Changing concepts of nutrient requirements in disease: implications for artificial nutritional support. Lancet. 1995 May 20;345(8960):1279–1284. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(95)90929-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Flatt J. P., Blackburn G. L. The matabolic fuel regulatory system: implications for protein-sparing therapies during caloric deprivation and disease. Am J Clin Nutr. 1974 Feb;27(2):175–187. doi: 10.1093/ajcn/27.2.175. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gallagher M. W., Tyson K. R., Ashcraft K. W. Gastrostomy in pediatric patients: an analysis of complications and techniques. Surgery. 1973 Oct;74(4):536–539. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gauderer M. W., Picha G. J., Izant R. J., Jr The gastrostomy "button"--a simple, skin-level, nonrefluxing device for long-term enteral feedings. J Pediatr Surg. 1984 Dec;19(6):803–805. doi: 10.1016/s0022-3468(84)80373-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gault M. H., Dixon M. E., Doyle M., Cohen W. M. Hypernatremia, azotemia, and dehydration ue to high-protein tube feeding. Ann Intern Med. 1968 Apr;68(4):778–791. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-68-4-778. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Guenter P. A., Settle R. G., Perlmutter S., Marino P. L., DeSimone G. A., Rolandelli R. H. Tube feeding-related diarrhea in acutely Ill patients. JPEN J Parenter Enteral Nutr. 1991 May-Jun;15(3):277–280. doi: 10.1177/0148607191015003277. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Havala T., Shronts E. Managing the complications associated with refeeding. Nutr Clin Pract. 1990 Feb;5(1):23–29. doi: 10.1177/011542659000500123. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ho C. S., Yee A. C., McPherson R. Complications of surgical and percutaneous nonendoscopic gastrostomy: review of 233 patients. Gastroenterology. 1988 Nov;95(5):1206–1210. doi: 10.1016/0016-5085(88)90351-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hull M. A., Rawlings J., Murray F. E., Field J., McIntyre A. S., Mahida Y. R., Hawkey C. J., Allison S. P. Audit of outcome of long-term enteral nutrition by percutaneous endoscopic gastrostomy. Lancet. 1993 Apr 3;341(8849):869–872. doi: 10.1016/0140-6736(93)93072-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Iyer V. S., Reichel J. Perforation of the esophagus by a fine feeding tube. N Y State J Med. 1984 Feb;84(2):63–64. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jacobs S., Chang R. W., Lee B., Bartlett F. W. Continuous enteral feeding: a major cause of pneumonia among ventilated intensive care unit patients. JPEN J Parenter Enteral Nutr. 1990 Jul-Aug;14(4):353–356. doi: 10.1177/0148607190014004353. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jeejeebhoy K. N. Rhoads lecture--1988. Bulk or bounce--the object of nutritional support. JPEN J Parenter Enteral Nutr. 1988 Nov-Dec;12(6):539–549. doi: 10.1177/0148607188012006539. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jones B. J., Lees R., Andrews J., Frost P., Silk D. B. Comparison of an elemental and polymeric enteral diet in patients with normal gastrointestinal function. Gut. 1983 Jan;24(1):78–84. doi: 10.1136/gut.24.1.78. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kelly T. W., Patrick M. R., Hillman K. M. Study of diarrhea in critically ill patients. Crit Care Med. 1983 Jan;11(1):7–9. doi: 10.1097/00003246-198301000-00003. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Keohane P. P., Attrill H., Grimble G., Spiller R., Frost P., Silk D. B. Enteral nutrition in malnourished patients with hepatic cirrhosis and acute encephalopathy. JPEN J Parenter Enteral Nutr. 1983 Jul-Aug;7(4):346–350. doi: 10.1177/0148607183007004346. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Keohane P. P., Attrill H., Love M., Frost P., Silk D. B. Relation between osmolality of diet and gastrointestinal side effects in enteral nutrition. Br Med J (Clin Res Ed) 1984 Mar 3;288(6418):678–680. doi: 10.1136/bmj.288.6418.678. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kien G. L. Employment of a mobile infusion system for continuous ambulatory tube feeding. JPEN J Parenter Enteral Nutr. 1981 Nov-Dec;5(6):526–527. doi: 10.1177/0148607181005006526. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klein S., Heare B. R., Soloway R. D. The "buried bumper syndrome": a complication of percutaneous endoscopic gastrostomy. Am J Gastroenterol. 1990 Apr;85(4):448–451. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kocan M. J., Hickisch S. M. A comparison of continuous and intermittent enteral nutrition in NICU patients. J Neurosci Nurs. 1986 Dec;18(6):333–337. doi: 10.1097/01376517-198612000-00004. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Korula J., Harma C. A simple and inexpensive method of removal or replacement of gastrostomy tubes. JAMA. 1991 Mar 20;265(11):1426–1428. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Levy J., Van Laethem Y., Verhaegen G., Perpête C., Butzler J. P., Wenzel R. P. Contaminated enteral nutrition solutions as a cause of nosocomial bloodstream infection: a study using plasmid fingerprinting. JPEN J Parenter Enteral Nutr. 1989 May-Jun;13(3):228–234. doi: 10.1177/0148607189013003228. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lewis S. J., Egger M., Sylvester P. A., Thomas S. Early enteral feeding versus "nil by mouth" after gastrointestinal surgery: systematic review and meta-analysis of controlled trials. BMJ. 2001 Oct 6;323(7316):773–776. doi: 10.1136/bmj.323.7316.773. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lord L. M., Weiser-Maimone A., Pulhamus M., Sax H. C. Comparison of weighted vs unweighted enteral feeding tubes for efficacy of transpyloric intubation. JPEN J Parenter Enteral Nutr. 1993 May-Jun;17(3):271–273. doi: 10.1177/0148607193017003271. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MacFie J. Enteral versus parenteral nutrition: the significance of bacterial translocation and gut-barrier function. Nutrition. 2000 Jul-Aug;16(7-8):606–611. doi: 10.1016/s0899-9007(00)00249-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marcuard S. P., Stegall K. L., Trogdon S. Clearing obstructed feeding tubes. JPEN J Parenter Enteral Nutr. 1989 Jan-Feb;13(1):81–83. doi: 10.1177/014860718901300181. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McIntyre P. B., Fitchew M., Lennard-Jones J. E. Patients with a high jejunostomy do not need a special diet. Gastroenterology. 1986 Jul;91(1):25–33. doi: 10.1016/0016-5085(86)90434-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McWhirter J. P., Pennington C. R. Incidence and recognition of malnutrition in hospital. BMJ. 1994 Apr 9;308(6934):945–948. doi: 10.1136/bmj.308.6934.945. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Metheny N. A., Clouse R. E., Clark J. M., Reed L., Wehrle M. A., Wiersema L. pH testing of feeding-tube aspirates to determine placement. Nutr Clin Pract. 1994 Oct;9(5):185–190. doi: 10.1177/0115426594009005185. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Micklewright A. Nutritional status at submission for dietetic services and screening for malnutrition at admission to hospital. Clin Nutr. 1999 Feb;18(1):3–4. doi: 10.1016/s0261-5614(99)80042-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moore D. M., Calcaterra T. C. Inserting and securing the nasogastric tube. Laryngoscope. 1987 Dec;97(12):1460–1460. doi: 10.1288/00005537-198712000-00015. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moore F. A., Moore E. E., Poggetti R., McAnena O. J., Peterson V. M., Abernathy C. M., Parsons P. E. Gut bacterial translocation via the portal vein: a clinical perspective with major torso trauma. J Trauma. 1991 May;31(5):629–638. doi: 10.1097/00005373-199105000-00006. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moran B. J., Taylor M. B., Johnson C. D. Percutaneous endoscopic gastrostomy. Br J Surg. 1990 Aug;77(8):858–862. doi: 10.1002/bjs.1800770805. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- NAGLER R., SPIRO H. M. PERSISTENT GASTROESOPHAGEAL REFLUX INDUCED DURING PROLONGED GASTRIC INTUBATION. N Engl J Med. 1963 Sep 5;269:495–500. doi: 10.1056/NEJM196309052691003. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nightingale J. Gastrostomy placement in patients with Crohn's disease. Eur J Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2000 Oct;12(10):1073–1075. doi: 10.1097/00042737-200012100-00002. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Norton B., Homer-Ward M., Donnelly M. T., Long R. G., Holmes G. K. A randomised prospective comparison of percutaneous endoscopic gastrostomy and nasogastric tube feeding after acute dysphagic stroke. BMJ. 1996 Jan 6;312(7022):13–16. doi: 10.1136/bmj.312.7022.13. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Olivares L., Segovia A., Revuelta R. Tube feeding and lethal aspiration in neurological patients: a review of 720 autopsy cases. Stroke. 1974 Sep-Oct;5(5):654–657. doi: 10.1161/01.str.5.5.654. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- doi: 10.1136/gut.50.suppl_2.a86. [DOI] [PMC free article] [Google Scholar]
- Patil D. H., Grimble G. K., Keohane P., Attrill H., Love M., Silk D. B. Do fibre containing enteral diets have advantages over existing low residue diets? Clin Nutr. 1985 May;4(2):67–71. doi: 10.1016/0261-5614(85)90044-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Payne-James J. J., Rana S. K., Bray M. J., McSwiggan D. A., Silk D. B. Retrograde (ascending) bacterial contamination of enteral diet administration systems. JPEN J Parenter Enteral Nutr. 1992 Jul-Aug;16(4):369–373. doi: 10.1177/0148607192016004369. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Potter J., Langhorne P., Roberts M. Routine protein energy supplementation in adults: systematic review. BMJ. 1998 Aug 22;317(7157):495–501. doi: 10.1136/bmj.317.7157.495. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rees R. G., Attrill H., Quinn D., Silk D. B. Improved design of nasogastric feeding tubes. Clin Nutr. 1986 Nov;5(4):203–207. doi: 10.1016/0261-5614(86)90026-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rees R. G., Keohane P. P., Grimble G. K., Frost P. G., Attrill H., Silk D. B. Elemental diet administered nasogastrically without starter regimens to patients with inflammatory bowel disease. JPEN J Parenter Enteral Nutr. 1986 May-Jun;10(3):258–262. doi: 10.1177/0148607186010003258. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rees R. G., Keohane P. P., Grimble G. K., Frost P. G., Attrill H., Silk D. B. Elemental diet administered nasogastrically without starter regimens to patients with inflammatory bowel disease. JPEN J Parenter Enteral Nutr. 1986 May-Jun;10(3):258–262. doi: 10.1177/0148607186010003258. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reilly J. J., Jr, Hull S. F., Albert N., Waller A., Bringardener S. Economic impact of malnutrition: a model system for hospitalized patients. JPEN J Parenter Enteral Nutr. 1988 Jul-Aug;12(4):371–376. doi: 10.1177/0148607188012004371. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Robinson G., Goldstein M., Levine G. M. Impact of nutritional status on DRG length of stay. JPEN J Parenter Enteral Nutr. 1987 Jan-Feb;11(1):49–51. doi: 10.1177/014860718701100149. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schulz M. A., Santanello S. A., Monk J., Falcone R. E. An improved method for transpyloric placement of nasoenteric feeding tubes. Int Surg. 1993 Jan-Mar;78(1):79–82. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Silk D. B., Rees R. G., Keohane P. P., Attrill H. Clinical efficacy and design changes of "fine bore" nasogastric feeding tubes: a seven-year experience involving 809 intubations in 403 patients. JPEN J Parenter Enteral Nutr. 1987 Jul-Aug;11(4):378–383. doi: 10.1177/0148607187011004378. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Solomon S. M., Kirby D. F. The refeeding syndrome: a review. JPEN J Parenter Enteral Nutr. 1990 Jan-Feb;14(1):90–97. doi: 10.1177/014860719001400190. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sriram K., Jayanthi V., Lakshmi R. G., George V. S. Prophylactic locking of enteral feeding tubes with pancreatic enzymes. JPEN J Parenter Enteral Nutr. 1997 Nov-Dec;21(6):353–356. doi: 10.1177/0148607197021006353. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stephen A. M., Cummings J. H. Mechanism of action of dietary fibre in the human colon. Nature. 1980 Mar 20;284(5753):283–284. doi: 10.1038/284283a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thurn J., Crossley K., Gerdts A., Maki M., Johnson J. Enteral hyperalimentation as a source of nosocomial infection. J Hosp Infect. 1990 Apr;15(3):203–217. doi: 10.1016/0195-6701(90)90028-m. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wakefield S. E., Mansell N. J., Baigrie R. J., Dowling B. L. Use of a feeding jejunostomy after oesophagogastric surgery. Br J Surg. 1995 Jun;82(6):811–813. doi: 10.1002/bjs.1800820629. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Walike B. C., Walike J. W. Relative lactose intolerance. A clinical study of tube-fed patients. JAMA. 1977 Aug 29;238(9):948–951. doi: 10.1001/jama.238.9.948. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Winterbauer R. H., Durning R. B., Jr, Barron E., McFadden M. C. Aspirated nasogastric feeding solution detected by glucose strips. Ann Intern Med. 1981 Jul;95(1):67–68. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-95-1-67. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wolfsen H. C., Kozarek R. A., Ball T. J., Patterson D. J., Botoman V. A. Tube dysfunction following percutaneous endoscopic gastrostomy and jejunostomy. Gastrointest Endosc. 1990 May-Jun;36(3):261–263. doi: 10.1016/s0016-5107(90)71019-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wollman B., D'Agostino H. B., Walus-Wigle J. R., Easter D. W., Beale A. Radiologic, endoscopic, and surgical gastrostomy: an institutional evaluation and meta-analysis of the literature. Radiology. 1995 Dec;197(3):699–704. doi: 10.1148/radiology.197.3.7480742. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Woods J. H., Erickson L. W., Condon R. E., Schulte W. J., Sillin L. F. Postoperative ileus: a colonic problem? Surgery. 1978 Oct;84(4):527–533. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Woolfson A. M., Saour J. N., Ricketts C. R., Pollard B. J., Hardy S. M., Allison S. P. Prolonged nasogastric tube feeding in critically ill and surgical patients. Postgrad Med J. 1976 Nov;52(613):678–682. doi: 10.1136/pgmj.52.613.678. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wyler A. R., Reynolds A. F. An intracranial complication of nasogastric intubation. Case report. J Neurosurg. 1977 Aug;47(2):297–298. doi: 10.3171/jns.1977.47.2.0297. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zaloga G. P. Bedside method for placing small bowel feeding tubes in critically ill patients. A prospective study. Chest. 1991 Dec;100(6):1643–1646. doi: 10.1378/chest.100.6.1643. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]