Abstract
Most afferent signals from the viscera do not give rise to conscious experience and yet they participate in the complex neural control of visceral functions. Surprisingly little information is available on the origin, morphology, and receptor functional characteristics of the nerve endings of most primary afferent neurones to the digestive tract. This review deals with the morphological nature of the afferent neurones that supply the gastrointestinal tract specifically.
Full Text
The Full Text of this article is available as a PDF (157.5 KB).
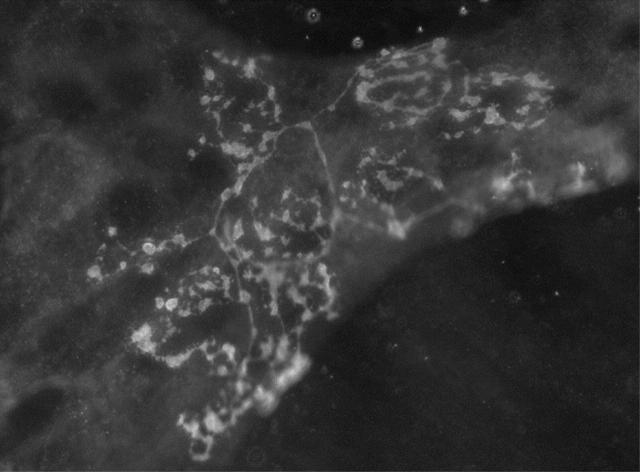
Figure 1 .
Whole mount preparation of mouse stomach with an intraganglionic laminar ending showing P2X2 receptor immunoreactivity.
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Aldskogius H., Elfvin L. G., Forsman C. A. Primary sensory afferents in the inferior mesenteric ganglion and related nerves of the guinea pig. An experimental study with anterogradely transported wheat germ agglutinin-horseradish peroxidase conjugate. J Auton Nerv Syst. 1986 Feb;15(2):179–190. doi: 10.1016/0165-1838(86)90013-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Berthoud H. R., Kressel M., Raybould H. E., Neuhuber W. L. Vagal sensors in the rat duodenal mucosa: distribution and structure as revealed by in vivo DiI-tracing. Anat Embryol (Berl) 1995 Mar;191(3):203–212. doi: 10.1007/BF00187819. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Berthoud H. R., Neuhuber W. L. Functional and chemical anatomy of the afferent vagal system. Auton Neurosci. 2000 Dec 20;85(1-3):1–17. doi: 10.1016/S1566-0702(00)00215-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Berthoud H. R., Powley T. L. Vagal afferent innervation of the rat fundic stomach: morphological characterization of the gastric tension receptor. J Comp Neurol. 1992 May 8;319(2):261–276. doi: 10.1002/cne.903190206. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Castelucci Patricia, Robbins Heather L., Furness John B. P2X(2) purine receptor immunoreactivity of intraganglionic laminar endings in the mouse gastrointestinal tract. Cell Tissue Res. 2003 Apr 11;312(2):167–174. doi: 10.1007/s00441-003-0715-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cervero F., Sharkey K. A. An electrophysiological and anatomical study of intestinal afferent fibres in the rat. J Physiol. 1988 Jul;401:381–397. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1988.sp017168. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Costa M., Furness J. B., Gibbins I. L. Chemical coding of enteric neurons. Prog Brain Res. 1986;68:217–239. doi: 10.1016/s0079-6123(08)60241-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DUTHIE H. L., GAIRNS F. W. Sensory nerve-endings and sensation in the anal region of man. Br J Surg. 1960 May;47:585–595. doi: 10.1002/bjs.18004720602. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dockray G. J., Sharkey K. A. Neurochemistry of visceral afferent neurones. Prog Brain Res. 1986;67:133–148. doi: 10.1016/s0079-6123(08)62760-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Doerffler-Melly J., Neuhuber W. L. Rectospinal neurons: evidence for a direct projection from the enteric to the central nervous system in the rat. Neurosci Lett. 1988 Oct 5;92(2):121–125. doi: 10.1016/0304-3940(88)90046-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dütsch M., Eichhorn U., Wörl J., Wank M., Berthoud H. R., Neuhuber W. L. Vagal and spinal afferent innervation of the rat esophagus: a combined retrograde tracing and immunocytochemical study with special emphasis on calcium-binding proteins. J Comp Neurol. 1998 Aug 24;398(2):289–307. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fjell J., Hjelmström P., Hormuzdiar W., Milenkovic M., Aglieco F., Tyrrell L., Dib-Hajj S., Waxman S. G., Black J. A. Localization of the tetrodotoxin-resistant sodium channel NaN in nociceptors. Neuroreport. 2000 Jan 17;11(1):199–202. doi: 10.1097/00001756-200001170-00039. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fox E. A., Phillips R. J., Baronowsky E. A., Byerly M. S., Jones S., Powley T. L. Neurotrophin-4 deficient mice have a loss of vagal intraganglionic mechanoreceptors from the small intestine and a disruption of short-term satiety. J Neurosci. 2001 Nov 1;21(21):8602–8615. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.21-21-08602.2001. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fox E. A., Phillips R. J., Martinson F. A., Baronowsky E. A., Powley T. L. Vagal afferent innervation of smooth muscle in the stomach and duodenum of the mouse: morphology and topography. J Comp Neurol. 2000 Dec 18;428(3):558–576. doi: 10.1002/1096-9861(20001218)428:3<558::aid-cne11>3.0.co;2-m. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gibbins I. L., Furness J. B., Costa M., MacIntyre I., Hillyard C. J., Girgis S. Co-localization of calcitonin gene-related peptide-like immunoreactivity with substance P in cutaneous, vascular and visceral sensory neurons of guinea pigs. Neurosci Lett. 1985 Jun 12;57(2):125–130. doi: 10.1016/0304-3940(85)90050-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gibbins I. L., Furness J. B., Costa M. Pathway-specific patterns of the co-existence of substance P, calcitonin gene-related peptide, cholecystokinin and dynorphin in neurons of the dorsal root ganglia of the guinea-pig. Cell Tissue Res. 1987 May;248(2):417–437. doi: 10.1007/BF00218210. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Green T., Dockray G. J. Calcitonin gene-related peptide and substance P in afferents to the upper gastrointestinal tract in the rat. Neurosci Lett. 1987 May 6;76(2):151–156. doi: 10.1016/0304-3940(87)90707-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Green T., Dockray G. J. Characterization of the peptidergic afferent innervation of the stomach in the rat, mouse and guinea-pig. Neuroscience. 1988 Apr;25(1):181–193. doi: 10.1016/0306-4522(88)90017-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Iino S., Kato M., Hidaka H., Kobayashi S. Neurocalcin-like immunoreactivity in the rat esophageal nervous system. Cell Tissue Res. 1998 Oct;294(1):57–68. doi: 10.1007/s004410051156. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jänig W., Koltzenburg M. On the function of spinal primary afferent fibres supplying colon and urinary bladder. J Auton Nerv Syst. 1990 Jul;30 (Suppl):S89–S96. doi: 10.1016/0165-1838(90)90108-u. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jänig W., McLachlan E. M. Organization of lumbar spinal outflow to distal colon and pelvic organs. Physiol Rev. 1987 Oct;67(4):1332–1404. doi: 10.1152/physrev.1987.67.4.1332. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kawatani M., Nagel J., de Groat W. C. Identification of neuropeptides in pelvic and pudendal nerve afferent pathways to the sacral spinal cord of the cat. J Comp Neurol. 1986 Jul 1;249(1):117–132. doi: 10.1002/cne.902490109. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kern Mark K., Shaker Reza. Cerebral cortical registration of subliminal visceral stimulation. Gastroenterology. 2002 Feb;122(2):290–298. doi: 10.1053/gast.2002.30989. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kuramoto H., Kuwano R. Immunohistochemical demonstration of calbindin-containing nerve endings in the rat esophagus. Cell Tissue Res. 1994 Oct;278(1):57–64. doi: 10.1007/BF00305778. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Luckensmeyer G. B., Keast J. R. Immunohistochemical characterisation of viscerofugal neurons projecting to the inferior mesenteric and major pelvic ganglia in the male rat. J Auton Nerv Syst. 1996 Oct 7;61(1):6–16. doi: 10.1016/0165-1838(96)00056-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lynn P. A., Blackshaw L. A. In vitro recordings of afferent fibres with receptive fields in the serosa, muscle and mucosa of rat colon. J Physiol. 1999 Jul 1;518(Pt 1):271–282. doi: 10.1111/j.1469-7793.1999.0271r.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lynn Penny A., Olsson Catharina, Zagorodnyuk Vladimir, Costa Marcello, Brookes Simon J. H. Rectal intraganglionic laminar endings are transduction sites of extrinsic mechanoreceptors in the guinea pig rectum. Gastroenterology. 2003 Sep;125(3):786–794. doi: 10.1016/s0016-5085(03)01050-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McRoberts J. A., Coutinho S. V., Marvizón J. C., Grady E. F., Tognetto M., Sengupta J. N., Ennes H. S., Chaban V. V., Amadesi S., Creminon C. Role of peripheral N-methyl-D-aspartate (NMDA) receptors in visceral nociception in rats. Gastroenterology. 2001 Jun;120(7):1737–1748. doi: 10.1053/gast.2001.24848. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Neuhuber W. L. Sensory vagal innervation of the rat esophagus and cardia: a light and electron microscopic anterograde tracing study. J Auton Nerv Syst. 1987 Oct;20(3):243–255. doi: 10.1016/0165-1838(87)90153-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Phillips R. J., Powley T. L. Tension and stretch receptors in gastrointestinal smooth muscle: re-evaluating vagal mechanoreceptor electrophysiology. Brain Res Brain Res Rev. 2000 Nov;34(1-2):1–26. doi: 10.1016/s0165-0173(00)00036-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Raybould H. E. Nutrient tasting and signaling mechanisms in the gut. I. Sensing of lipid by the intestinal mucosa. Am J Physiol. 1999 Oct;277(4 Pt 1):G751–G755. doi: 10.1152/ajpgi.1999.277.4.G751. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SCHOFIELD G. C. Experimental studies on the innervation of the mucous membrane of the gut. Brain. 1960 Sep;83:490–514. doi: 10.1093/brain/83.3.490. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sharkey K. A., Lomax A. E., Bertrand P. P., Furness J. B. Electrophysiology, shape, and chemistry of neurons that project from guinea pig colon to inferior mesenteric ganglia. Gastroenterology. 1998 Oct;115(4):909–918. doi: 10.1016/s0016-5085(98)70263-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sharkey K. A., Williams R. G., Dockray G. J. Sensory substance P innervation of the stomach and pancreas. Demonstration of capsaicin-sensitive sensory neurons in the rat by combined immunohistochemistry and retrograde tracing. Gastroenterology. 1984 Oct;87(4):914–921. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sheehan D. The Afferent Nerve Supply of the Mesentery and its Significance in the Causation of Abdominal Pain. J Anat. 1933 Jan;67(Pt 2):233–249. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stucky C. L., Lewin G. R. Isolectin B(4)-positive and -negative nociceptors are functionally distinct. J Neurosci. 1999 Aug 1;19(15):6497–6505. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.19-15-06497.1999. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tassicker B. C., Hennig G. W., Costa M., Brookes S. J. Rapid anterograde and retrograde tracing from mesenteric nerve trunks to the guinea-pig small intestine in vitro. Cell Tissue Res. 1999 Mar;295(3):437–452. doi: 10.1007/s004410051250. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thor K. B., Morgan C., Nadelhaft I., Houston M., De Groat W. C. Organization of afferent and efferent pathways in the pudendal nerve of the female cat. J Comp Neurol. 1989 Oct 8;288(2):263–279. doi: 10.1002/cne.902880206. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wang F. B., Powley T. L. Topographic inventories of vagal afferents in gastrointestinal muscle. J Comp Neurol. 2000 Jun 5;421(3):302–324. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zagorodnyuk V. P., Brookes S. J. Transduction sites of vagal mechanoreceptors in the guinea pig esophagus. J Neurosci. 2000 Aug 15;20(16):6249–6255. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.20-16-06249.2000. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zagorodnyuk V. P., Chen B. N., Brookes S. J. Intraganglionic laminar endings are mechano-transduction sites of vagal tension receptors in the guinea-pig stomach. J Physiol. 2001 Jul 1;534(Pt 1):255–268. doi: 10.1111/j.1469-7793.2001.00255.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zhu J. X., Zhu X. Y., Owyang C., Li Y. Intestinal serotonin acts as a paracrine substance to mediate vagal signal transmission evoked by luminal factors in the rat. J Physiol. 2001 Feb 1;530(Pt 3):431–442. doi: 10.1111/j.1469-7793.2001.0431k.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]